
Computational Physics An Introduction Weihua Gu Department of Physics Shanghai Jiao Tong University 14/09/2015 1口“4元,4元↑重QC Weihua Gu (SJTU) Computational Physics An Introduction 14/09/20151120
Computational Physics An Introduction Weihua Gu Department of Physics Shanghai Jiao Tong University 14/09/2015 Weihua Gu (SJTU) Computational Physics An Introduction 14/09/2015 1 / 20
Info Instructor: Weihua Gu E-mail: whgu@sjtu.edu.cn QQ: 27241705730 Office: Room 1106,Physics Department Building Course Webite: http://cc.sjtu.edu.cn/G2S/site/Comp Ftp site: ftp://whgu:cp2011@public.sjtu.edu.c (updated regularly. ¥口“1元4元↑至QC Weihua Gu (SJTU) Computational Physics An Introduction 14/0920152120
Info Instructor: Weihua Gu E-mail: whgu@sjtu.edu.cn QQ: 2724 1705 73O Office: Room 1106, Physics Department Building Course Webite: http://cc.sjtu.edu.cn/G2S/site/ComputationalPhysic.html Ftp site: ftp://whgu:cp2011@public.sjtu.edu.cn (updated regularly.) Weihua Gu (SJTU) Computational Physics An Introduction 14/09/2015 2 / 20
What is CP? What Is CP? o A interdisciplinary subject of natural science overlapping physics,applied mathematics,and computer science; a fast developing field; o focus on solving physical problems; o a powerful tool to explore new fields. Physics application C cs Math hard/software techniques 1口“4元,4元↑重QC Weihua Gu (SJTU) Computational Physics An Introduction 14/0920153120
What is CP? What Is CP? A interdisciplinary subject of natural science overlapping physics, applied mathematics, and computer science; a fast developing field; focus on solving physical problems; a powerful tool to explore new fields. Weihua Gu (SJTU) Computational Physics An Introduction 14/09/2015 3 / 20
What is CP? What Is CP? o A interdisciplinary subject of natural science overlapping physics,applied mathematics,and computer science; a fast developing field; o focus on solving physical problems; o a powerful tool to explore new fields. Physics application P cs Math uoneinw!S Truth hard/software techniques Fxneriment Weihua Gu (SJTU) Computational Physics An Introduction 14/0920153120
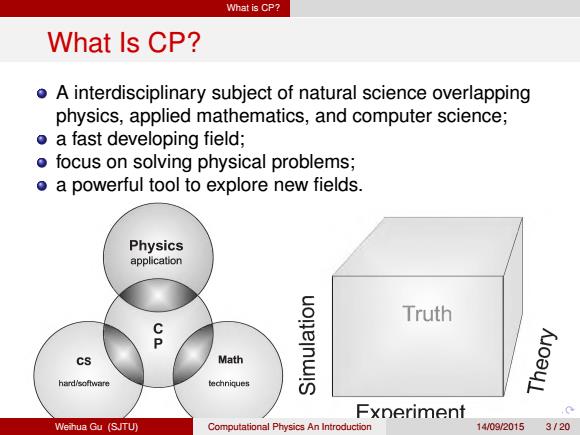
What is CP? What Is CP? A interdisciplinary subject of natural science overlapping physics, applied mathematics, and computer science; a fast developing field; focus on solving physical problems; a powerful tool to explore new fields. Weihua Gu (SJTU) Computational Physics An Introduction 14/09/2015 3 / 20

Objectives of CP Course Objectives of CP Course After you learn the course,you should be able to o understand basic numerical techniques,apply them to solve physical problems and explore new interesting topics, enhance programming skill, enhance problem-solving skill. enhance English skill. o enhance team-working skill. 1口回1元4元1至0QC Weihua Gu (SJTU) Computational Physics An Introduction 14/09/20154120
Objectives of CP Course Objectives of CP Course After you learn the course, you should be able to understand basic numerical techniques, apply them to solve physical problems and explore new interesting topics, enhance programming skill, enhance problem-solving skill. enhance English skill. enhance team-working skill. Weihua Gu (SJTU) Computational Physics An Introduction 14/09/2015 4 / 20
Objectives of CP Course Focus on Physics-The Problem-Solving Paradigm A practical problem Laws of physics Model Numerical methods Nonlinear->linear Continuous->discrete Multidimensional->1D Simplified Model Variable coe.->constant coe. Results Programming,visualization Convergence,stability, Evaluation error analysis,time consuming 重00C Weihua Gu (SJTU) Computational Physics An Introduction 14/09/2015 5120
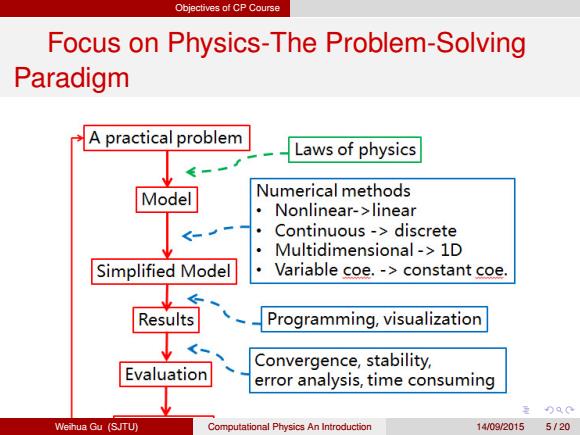
Objectives of CP Course Focus on Physics-The Problem-Solving Paradigm Weihua Gu (SJTU) Computational Physics An Introduction 14/09/2015 5 / 20
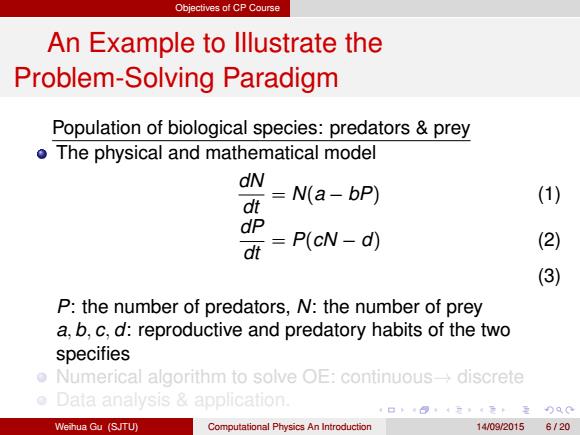
Objectives of CP Course An Example to lllustrate the Problem-Solving Paradigm Population of biological species:predators prey o The physical and mathematical model dN dt N(a-bP) (1) dP dt =P(cN-d) (2) (3) P:the number of predators,N:the number of prey a,b,c,d:reproductive and predatory habits of the two specifies Numerical algorithm to solve OE:continuousdiscrete Data analysis application. ¥口,4元4元卡重)90 Weihua Gu (SJTU) Computational Physics An Introduction 14/09/2015 6120
Objectives of CP Course An Example to Illustrate the Problem-Solving Paradigm Population of biological species: predators & prey The physical and mathematical model dN dt = N(a − bP) (1) dP dt = P(cN − d) (2) (3) P: the number of predators, N: the number of prey a, b, c, d: reproductive and predatory habits of the two specifies Numerical algorithm to solve OE: continuous→ discrete Data analysis & application. Weihua Gu (SJTU) Computational Physics An Introduction 14/09/2015 6 / 20
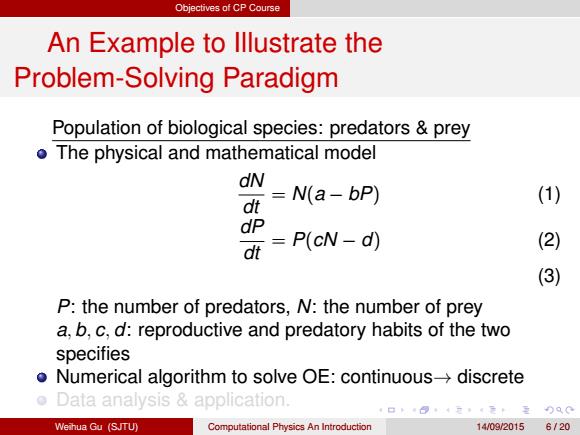
Objectives of CP Course An Example to lllustrate the Problem-Solving Paradigm Population of biological species:predators prey o The physical and mathematical model dN N(a-bP) (1) dt dP dt P(cN-d) (2) (3) P:the number of predators,N:the number of prey a,b,c,d:reproductive and predatory habits of the two specifies Numerical algorithm to solve OE:continuous->discrete o Data analysis application. Weihua Gu (SJTU) Computational Physics An Introduction 14/092015 6120
Objectives of CP Course An Example to Illustrate the Problem-Solving Paradigm Population of biological species: predators & prey The physical and mathematical model dN dt = N(a − bP) (1) dP dt = P(cN − d) (2) (3) P: the number of predators, N: the number of prey a, b, c, d: reproductive and predatory habits of the two specifies Numerical algorithm to solve OE: continuous→ discrete Data analysis & application. Weihua Gu (SJTU) Computational Physics An Introduction 14/09/2015 6 / 20
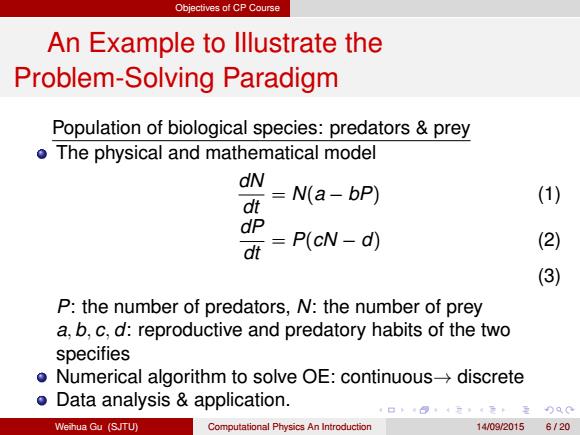
Objectives of CP Course An Example to lllustrate the Problem-Solving Paradigm Population of biological species:predators prey o The physical and mathematical model dN N(a-bP) (1) dt dP dt =P(cN-d) (2) (3) P:the number of predators,N:the number of prey a,b,c,d:reproductive and predatory habits of the two specifies o Numerical algorithm to solve OE:continuous->discrete o Data analysis application. Weihua Gu (SJTU) Computational Physics An Introduction 14/09/20156120
Objectives of CP Course An Example to Illustrate the Problem-Solving Paradigm Population of biological species: predators & prey The physical and mathematical model dN dt = N(a − bP) (1) dP dt = P(cN − d) (2) (3) P: the number of predators, N: the number of prey a, b, c, d: reproductive and predatory habits of the two specifies Numerical algorithm to solve OE: continuous→ discrete Data analysis & application. Weihua Gu (SJTU) Computational Physics An Introduction 14/09/2015 6 / 20
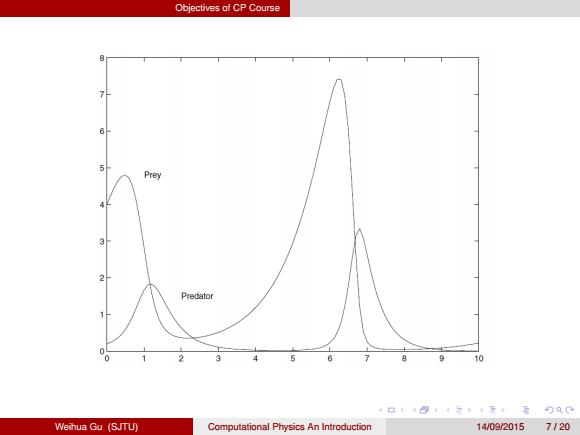
Objectives of CP Course Pre倒 3 2 Predator 0 10 4口404元,4无:至分Q0 Weihua Gu (SJTU) Computational Physics An Introduction 14/09/20157120
Objectives of CP Course Weihua Gu (SJTU) Computational Physics An Introduction 14/09/2015 7 / 20