
先进材料疑固实验室 Laboratory of Advanced Materials Solidification 1896 1920 1987 2006 uai过a metal with the atomie strocture Structure and properties of liquid metals(2) Dr.Mingxu Xia 上浒充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
1896 1920 1987 2006 Structure and properties of liquid metals (2) Dr. Mingxu Xia

先进材料疑固实验室 Outline Laboratory of Advanced Materials Solidification State of matter Brief introduction to liquid metal The structure of liquid metal Viscosity of liquid metal Surface and interface of liquid metal Fluidity of liquid metal Other properties of liquid metal anced Materials Solid 上浒充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
Outline State of matter Brief introduction to liquid metal The structure of liquid metal Viscosity of liquid metal Surface and interface of liquid metal Fluidity of liquid metal Other properties of liquid metal

先进材料疑固实验室 Viscosity of liquid metal Laboratory of Advanced Materials Solidification The viscosity of a liquid is a measure of its resistance to gradual deformation by shear stress or tensile stress.For liquids,it corresponds to the informal concept of "thickness". 上浒充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
Viscosity of liquid metal The viscosity of a liquid is a measure of its resistance to gradual deformation by shear stress or tensile stress. For liquids, it corresponds to the informal concept of “thickness
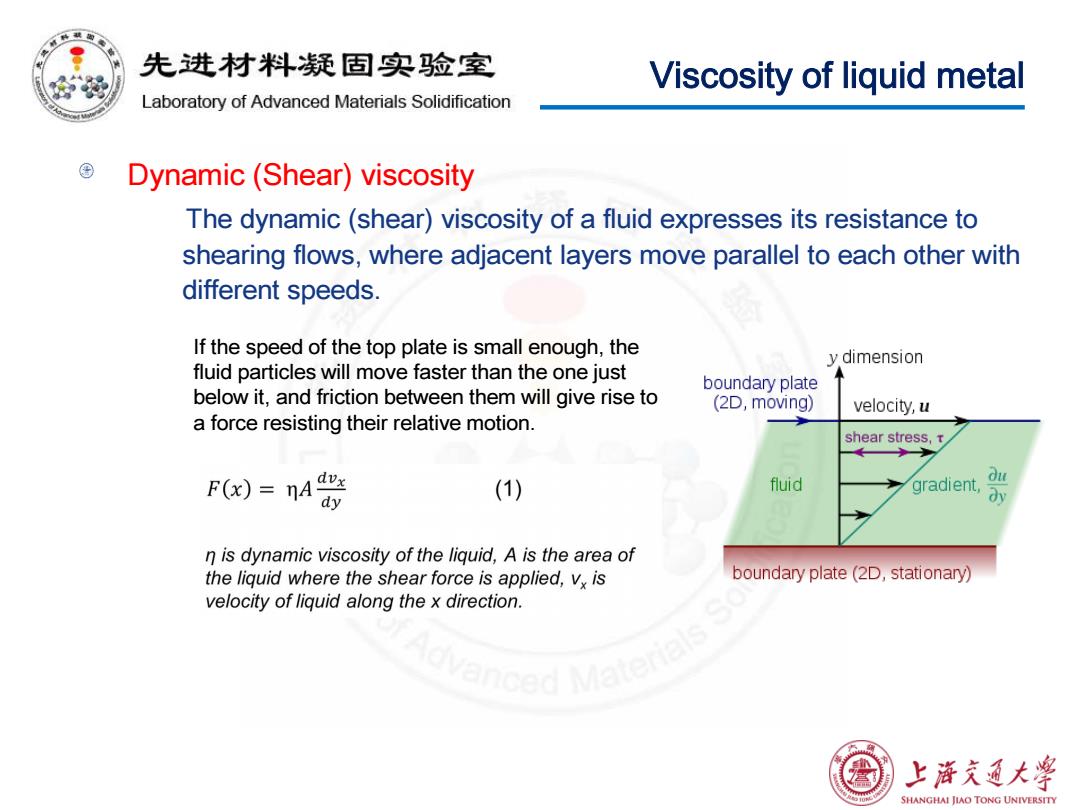
先进材料疑固实验室 Viscosity of liquid metal Laboratory of Advanced Materials Solidification Dynamic(Shear)viscosity The dynamic(shear)viscosity of a fluid expresses its resistance to shearing flows,where adjacent layers move parallel to each other with different speeds. If the speed of the top plate is small enough,the y dimension fluid particles will move faster than the one just boundary plate below it,and friction between them will give rise to (2D,moving) velocity,u a force resisting their relative motion. shear stress,t F()=nA警 (1) fluid gradient, n is dynamic viscosity of the liquid,A is the area of the liquid where the shear force is applied,vx is boundary plate(2D,stationary) velocity of liquid along the x direction. 上浒充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
Viscosity of liquid metal Dynamic (Shear) viscosity The dynamic (shear) viscosity of a fluid expresses its resistance to shearing flows, where adjacent layers move parallel to each other with different speeds. If the speed of the top plate is small enough, the fluid particles will move faster than the one just below it, and friction between them will give rise to a force resisting their relative motion
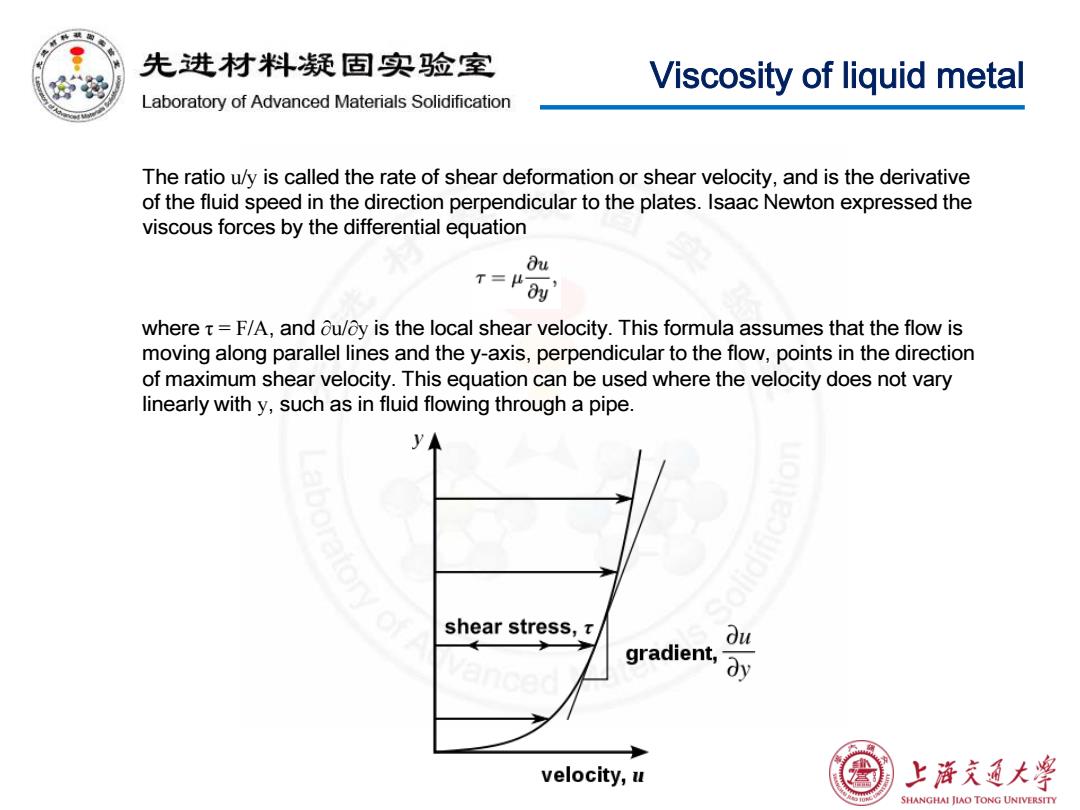
先进材料疑固实验室 Viscosity of liquid metal Laboratory of Advanced Materials Solidification The ratio u/y is called the rate of shear deformation or shear velocity,and is the derivative of the fluid speed in the direction perpendicular to the plates.Isaac Newton expressed the viscous forces by the differential equation Bu T=μ0y where t=F/A,and ou/oy is the local shear velocity.This formula assumes that the flow is moving along parallel lines and the y-axis,perpendicular to the flow,points in the direction of maximum shear velocity.This equation can be used where the velocity does not vary linearly with y,such as in fluid flowing through a pipe. shear stress,r gradient, velocity,u 上浒充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
Viscosity of liquid metal The ratio u/y is called the rate of shear deformation or shear velocity, and is the derivative of the fluid speed in the direction perpendicular to the plates. Isaac Newton expressed the viscous forces by the differential equation where τ = F/A, and ∂u/∂y is the local shear velocity. This formula assumes that the flow is moving along parallel lines and the y-axis, perpendicular to the flow, points in the direction of maximum shear velocity. This equation can be used where the velocity does not vary linearly with y, such as in fluid flowing through a pipe

先进材料疑固实验室 Viscosity of liquid metal Laboratory of Advanced Materials Solidification Kinematic viscosity Also called "momentum diffusivity",is the ratio of the dynamic viscosity n to the density of the fluid p. anced Materials 上浒充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
Viscosity of liquid metal Kinematic viscosity Also called “momentum diffusivity”, is the ratio of the dynamic viscosity η to the density of the fluid ρ

先进材料疑固实验室 Viscosity of liquid metal Laboratory of Advanced Materials Solidification Newtonian fluids:A fluid that behaves according to Newton's law,with a viscosity that is independent of the stress,is said to be Newtonian.Gases, water and many common liquids can be considered Newtonian in ordinary conditions and contexts. Non-Newtonian fluids,a fluid significantly deviate from that law in some way or other.For example: Shear-thickening liquids,whose viscosity increases with the rate of shear strain. 。 Shear-thinning liquids,whose viscosity decreases with the rate of shear strain. ● Thixotropic liquids,that become less viscous over time when shaken,agitated, or otherwise stressed. Rheopectic liquids,that become more viscous over time when shaken, agitated,or otherwise stressed. Bingham plastics that behave as a solid at low stresses but flow as a viscous fluid at high stresses. 上海充通大¥ SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
Newtonian fluids: A fluid that behaves according to Newton’s law, with a viscosity that is independent of the stress, is said to be Newtonian. Gases, water and many common liquids can be considered Newtonian in ordinary conditions and contexts. Non-Newtonian fluids, a fluid significantly deviate from that law in some way or other. For example: • Shear-thickening liquids, whose viscosity increases with the rate of shear strain. • Shear-thinning liquids, whose viscosity decreases with the rate of shear strain. • Thixotropic liquids, that become less viscous over time when shaken, agitated, or otherwise stressed. • Rheopectic liquids, that become more viscous over time when shaken, agitated, or otherwise stressed. • Bingham plastics that behave as a solid at low stresses but flow as a viscous fluid at high stresses. Viscosity of liquid metal

先进材料疑固实验室 Viscosity of liquid metal Laboratory of Advanced Materials Solidification Physically,viscosity can be expressed as: 2tokeT./k 3 where kg is Boltzmann constant, U is the internal bonding energy without external force. to is the vibration period of the atoms at equilibrium position 10-13s for liquid metal. 6 is the distance between atomic layers in liquid. nced Ma 上浒充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
Viscosity of liquid metal Physically, viscosity can be expressed as: where kB is Boltzmann constant, U is the internal bonding energy without external force. τ0 is the vibration period of the atoms at equilibrium position 10-13s for liquid metal. δ is the distance between atomic layers in liquid. U / k T 3 B 0 B e 2 k T = ⋅ δ τ η
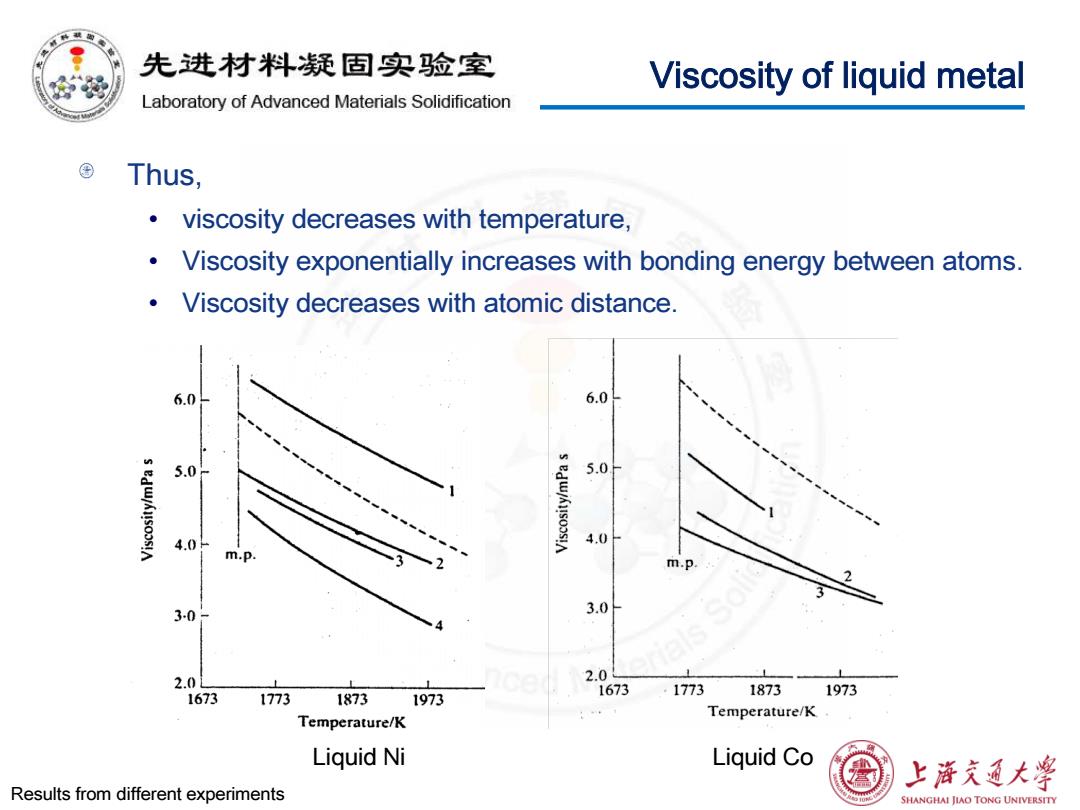
先进材料疑固实验室 Viscosity of liquid metal Laboratory of Advanced Materials Solidification Thus, viscosity decreases with temperature, Viscosity exponentially increases with bonding energy between atoms. Viscosity decreases with atomic distance. 6.0 6.0 5.0 5.0 4.0- 4.0 m.p m.p. 3-0 3.0 2.0L 2. 1673 1773 1873 1673 1773 1873 1973 1973 Temperature/K Temperature/K Liquid Ni Liquid Co 上游文通大学 Results from different experiments SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
Viscosity of liquid metal Thus, • viscosity decreases with temperature, • Viscosity exponentially increases with bonding energy between atoms. • Viscosity decreases with atomic distance. Liquid Ni Liquid Co Results from different experiments

先进材料疑固实验室 Viscosity of liquid metal Laboratory of Advanced Materials Solidification Alloy composition effect on viscosity of alloys(Moelwyn-Hughes model,M-H model) 9=0xn+xm- Where y,and u,are the viscosity of pure element,x,and x2 are the mole fraction of the elements.R is the gas constant and /is the mixing enthalpy of two elements. vanced Mater 上浒充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
Viscosity of liquid metal Alloy composition effect on viscosity of alloys (Moelwyn-Hughes model, M-H model) Where μ1 and μ2 are the viscosity of pure element, x1 and x2 are the mole fraction of the elements. R is the gas constant and Hm is the mixing enthalpy of two elements. = + − RT H X X m η ( 1 η1 2 η2 ) 1 2