
先进材料疑固实验室 Laboratory of Advanced Materials Solidification 1896 1920 1987 2006 Crystal growth of single element solids(2) Dr.Mingxu Xia anced Mat 上浒充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
1896 1920 1987 2006 Crystal growth of single element solids (2) Dr. Mingxu Xia

先进材料疑固实验室 References Laboratory of Advanced Materials Solidification 闵乃本晶体生长的物理基础 W.Kurz擬固原理Fundamentals of Solidification 胡汉起金属凝固原理 M.C.Flemings凝固过程Solidification Processing 张克从,晶体生长科学与技术 y of vanced Materials Soll 上浒充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
References 闵乃本 晶体生长的物理基础 W. Kurz 凝固原理 Fundamentals of Solidification 胡汉起 金属凝固原理 M.C.Flemings 凝固过程 Solidification Processing 张克从,晶体生长科学与技术

先进材料疑固实验室 OUTLINE Laboratory of Advanced Materials Solidification Liquid/solid interface Crystal growth of single element solids Types of crystal growth Kinetics of growth(growth speed) Morphology control of crystal Crystal growth methods(technology) ory of vanced Materials Solid 上浒充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
OUTLINE Liquid/solid interface Crystal growth of single element solids • Types of crystal growth • Kinetics of growth (growth speed) • Morphology control of crystal Crystal growth methods (technology)

先进材料疑固实验室 Types of crystal growth Laboratory of Advanced Materials Solidification Continuous growth:the solid crystal grows by continuously and randomly transferring atoms from liquid to solid. Lateral growth:the crystal growth process involves ledges which are required for adding atoms from liquid to the solid crystal. vanced Materd 上浒充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
Types of crystal growth Continuous growth: the solid crystal grows by continuously and randomly transferring atoms from liquid to solid. Lateral growth: the crystal growth process involves ledges which are required for adding atoms from liquid to the solid crystal
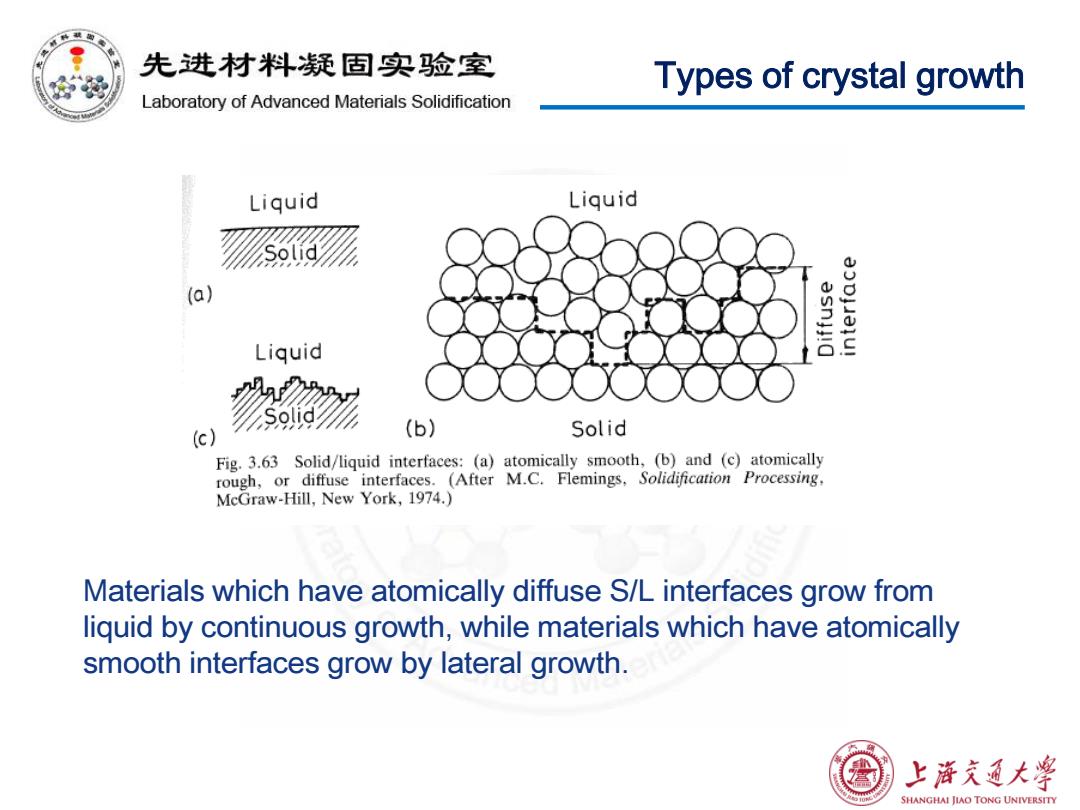
先进材料疑固实验室 Types of crystal growth Laboratory of Advanced Materials Solidification Liquid Liquid Solid (a) asnjJ!O Liquid % (c) (b) Solid Fig.3.63 Solid/liquid interfaces:(a)atomically smooth,(b)and (c)atomically rough,or diffuse interfaces.(After M.C.Flemings,. Solidification Processing, McGraw-Hill,New York,1974.) Materials which have atomically diffuse S/L interfaces grow from liquid by continuous growth,while materials which have atomically smooth interfaces grow by lateral growth. 上游文通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
Types of crystal growth Materials which have atomically diffuse S/L interfaces grow from liquid by continuous growth, while materials which have atomically smooth interfaces grow by lateral growth

先进材料疑固实验室 Types of crystal growth Laboratory of Advanced Materials Solidification Continuous growth Liquid R:Growth speed Deposited↓ Rebound个 Interface Solid >Continuous growth occurs on a rough interface,where more than 50%lattice points are void. >Rough surface is normally more than one atomic layer. >Deposited atoms are more stable at the new position due to the bonding from the neighbor atoms. 上游文通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
Types of crystal growth Continuous growth Deposited Rebound Liquid Solid Interface R: Growth speed Continuous growth occurs on a rough interface, where more than 50% lattice points are void. Rough surface is normally more than one atomic layer. Deposited atoms are more stable at the new position due to the bonding from the neighbor atoms

先进材料疑固实验室 Types of crystal growth Laboratory of Advanced Materials Solidification Lateral growth >Sharp interface(smooth surface)only has less than 10%void lattice points.This Arriving atom void lattice points will form Ledges (steps). >The ledges forming from void lattice points are normally less than a few atomic layers. >The deposited atoms on this kind of surface are less bonded. broken bonds'by four.(b)Addition to a ledge (L)only increases the number of broken boods by two,whereas at a jog in a ledge (J)there is no increase. >But the energy barrier for deposition of atoms are different with the deposition position. 上浒充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
Types of crystal growth Lateral growth Sharp interface (smooth surface) only has less than 10% void lattice points. This void lattice points will form Ledges (steps). The ledges forming from void lattice points are normally less than a few atomic layers. The deposited atoms on this kind of surface are less bonded. But the energy barrier for deposition of atoms are different with the deposition position
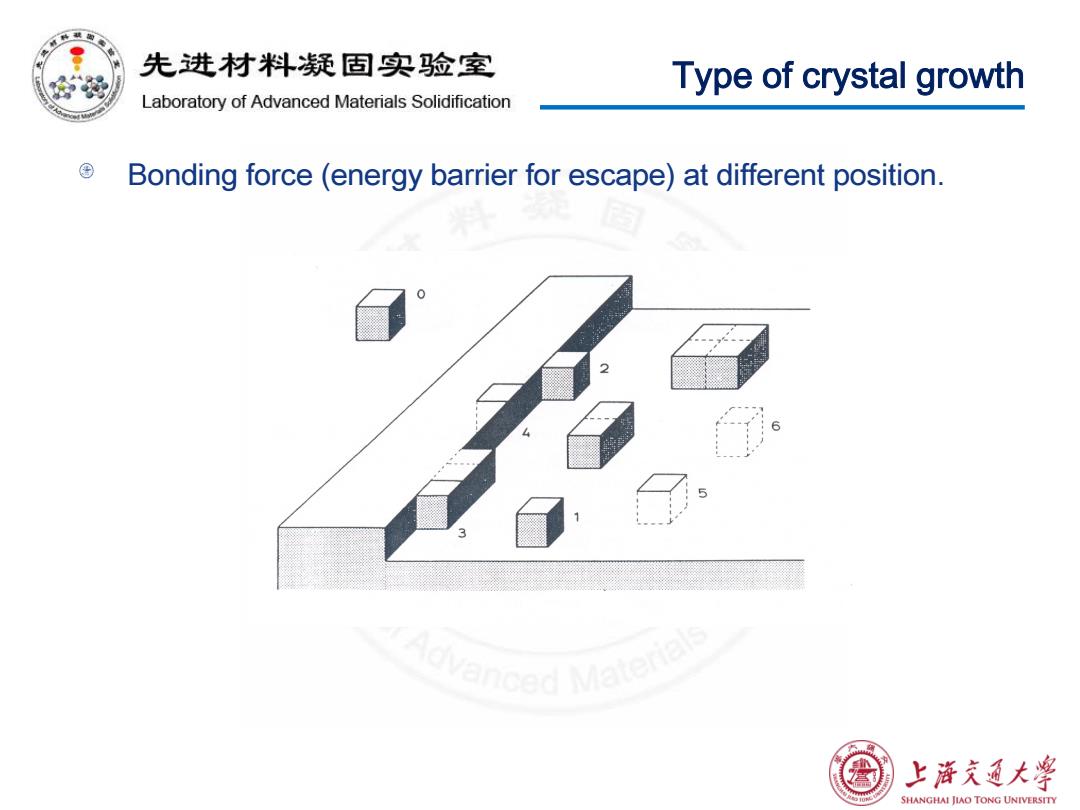
先进材料疑固实验室 Type of crystal growth Laboratory of Advanced Materials Solidification Bonding force (energy barrier for escape)at different position. 0 上浒充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
Type of crystal growth Bonding force (energy barrier for escape) at different position

先进材料疑固实验室 Types of crystal growth Laboratory of Advanced Materials Solidification Mechanism for lateral growth Surface nucleation:a ledge is created by nucleation of a piece of crystal on the S/L interface,and atoms from the liquid are added to the ledge to facilitate the crystal growth. Spiral growth around a screw dislocation:a ledge is created by having a screw dislocation in the solid which terminates at the S/L interface,and atoms from the liquid are added to the ledge to facilitate the crystal growth. Lateral growth utilizing the wedges and corners created by twins:the wedges created by mirror reflection twins and corners created by rotational twins are used to nucleate new solid layers. 熟 上海充通大¥ SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
Types of crystal growth Mechanism for lateral growth Surface nucleation: a ledge is created by nucleation of a piece of crystal on the S/L interface, and atoms from the liquid are added to the ledge to facilitate the crystal growth. Spiral growth around a screw dislocation: a ledge is created by having a screw dislocation in the solid which terminates at the S/L interface, and atoms from the liquid are added to the ledge to facilitate the crystal growth. Lateral growth utilizing the wedges and corners created by twins: the wedges created by mirror reflection twins and corners created by rotational twins are used to nucleate new solid layers
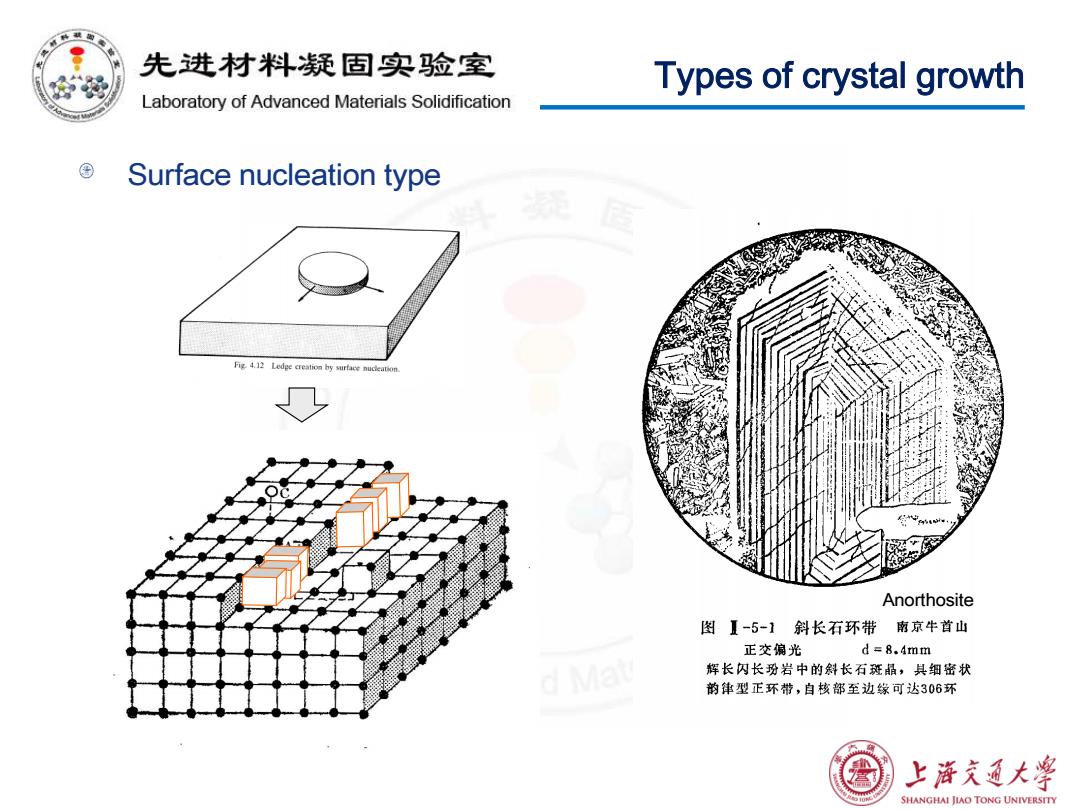
先进材料疑固实验室 Types of crystal growth Laboratory of Advanced Materials Solidification Surface nucleation type Fig 4.12 Ledge nuc Anorthosite 图I-5-1斜长石环带南京牛首山 正交偏光 d =8.4mm 辉长闪长玢岩中的斜长石斑晶,具细密状 韵律型正环带,自核部至边缘可达306环 熟 上浒充通大 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
Types of crystal growth Surface nucleation type Anorthosite