
Outline Introduction Processing maps Elements of plastic theory Plastic deformation mechanism Recovery recrystallization
Outline Processing maps Plastic deformation mechanism Elements of plastic theory Recovery & recrystallization Introduction
上清充通大¥ SANCEAI JUO TO阳UY Introduction Processing maps Introduction Stress Elements of plastic theory Equilibrium Equations Plastic deformation mechanism Strain Recovery recrystallization Yielding crietria Stress-strain relations Equivalent stress
Introduction Plastic deformation mechanism Recovery & recrystallization Elements of plastic theory Introduction Stress Equilibrium Equations Strain Yielding crietria Stress‐strain relations Equivalent stress 1 1 1 1 Processing maps 1

Reference books 上清文通大¥ SHEAMGHAI DUD TONO UHTVEREETTY .Mechanical Metallurgy* George E Dieter McGraw-Hill Book Company,London(1988) Metal Forming Mechanics and Metallurgy (further reading) William F.Hosford and Robert M.Caddell Cambridge University Press,3rd Edition(2007) Institute of Forming Technology Equipment 41
Institute of Forming Technology & Equipment Reference books 4 • Mechanical Metallurgy * George E Dieter McGraw‐Hill Book Company, London (1988) • Metal Forming Mechanics and Metallurgy (further reading) William F. Hosford and Robert M. Caddell Cambridge University Press,3rd Edition (2007)
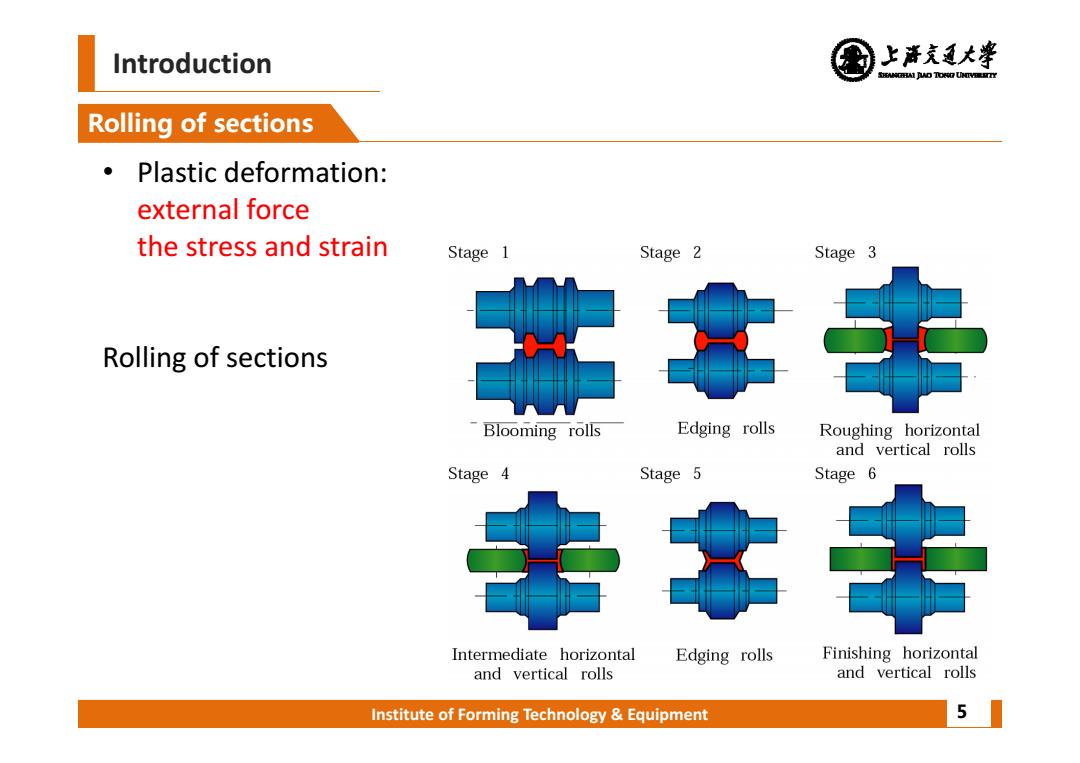
Introduction 上清充通大¥ SHEAMGHAI DUD TONO UHTVEREETTY Rolling of sections Plastic deformation: external force the stress and strain Stage 1 Stage 2 Stage 3 Rolling of sections Blooming rolls Edging rolls Roughing horizontal and vertical rolls Stage 4 Stage 5 Stage 6 Intermediate horizontal Edging rolls Finishing horizontal and vertical rolls and vertical rolls Institute of Forming Technology Equipment 5
Institute of Forming Technology & Equipment Introduction Rolling of sections 5 • Plastic deformation: external force the stress and strain Rolling of sections
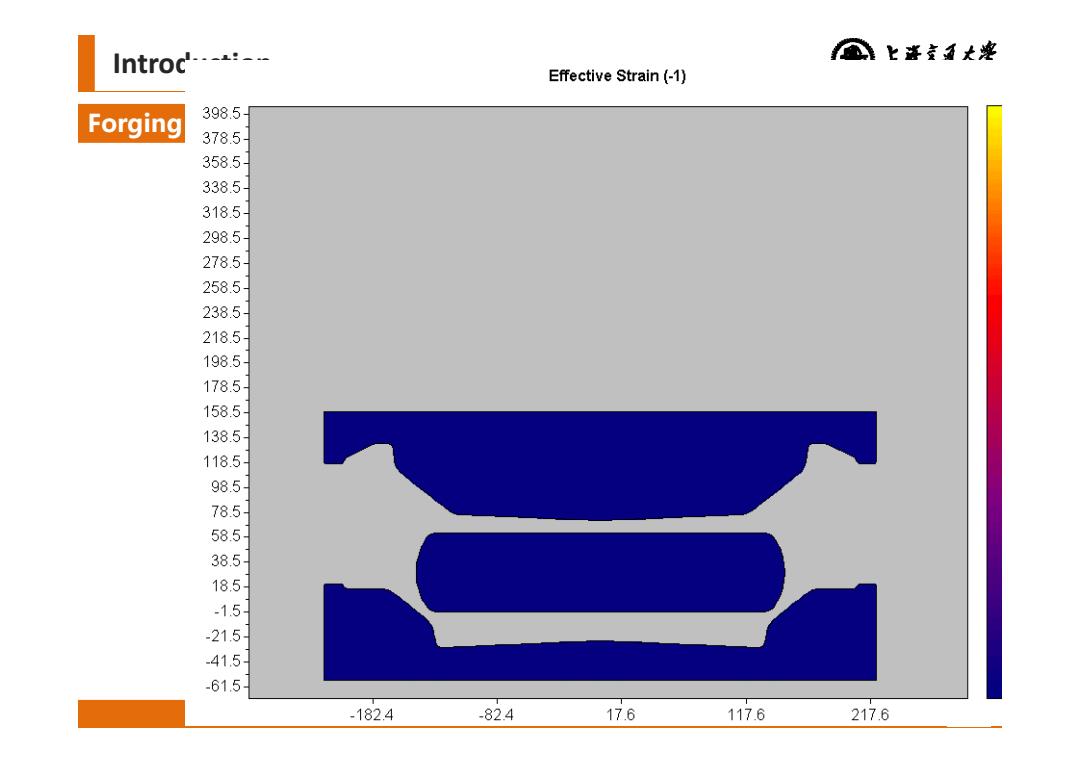
Introc'---*:-- 上善室五大滓 Effective Strain(-1) Forging 398.5 378.5- 358.5 338.5- 318.5- 298.5- 278.5- 258.5- 238.5- 218.5 198.5- 1785- 158.5- 138.5- 118.5 98.5 78.5- 58.5 38.5- 18.5- -15 -21.5- 41.5- 61.5- -182.4 -824 17.6 117.6 217.6
Institute of Forming Technology & Equipment Introduction Forging 6

Introduction 上清充通大¥ SHEAMGRAI DUAD TONO UNTVEEETTY Assumption Basic assumptions of material in plastic theory 1)Continuity 2)Homogenous 3)Isotropy 4)No initial stress 5)No body force 6)Volume constant Institute of Forming Technology Equipment
Institute of Forming Technology & Equipment Introduction Assumption 7 Basic assumptions of material in plastic theory 1) Continuity 2) Homogenous 3) Isotropy 4) No initial stress 5) No body force 6) Volume constant

Introduction 国上海克通大米 SANCEAI JUO TO阳UY External force Forces distributed over the Gravitational force volume of a body Bulk force Inertia force External force Magnetic force Hydrostatic pressure Surface force Normal pressure Pressure exerted by Forces distributed over the one body on another surface of the body Friction force centrifugal forces thermal stress Institute of Forming Technology Equipment 8
Institute of Forming Technology & Equipment Introduction External force 8 External force Gravitational force Inertia force Magnetic force Hydrostatic pressure Pressure exerted by one body on another Bulk force Surface force Forces distributed over the volume of a body Forces distributed over the surface of the body centrifugal forces thermal stress Normal pressure Friction force
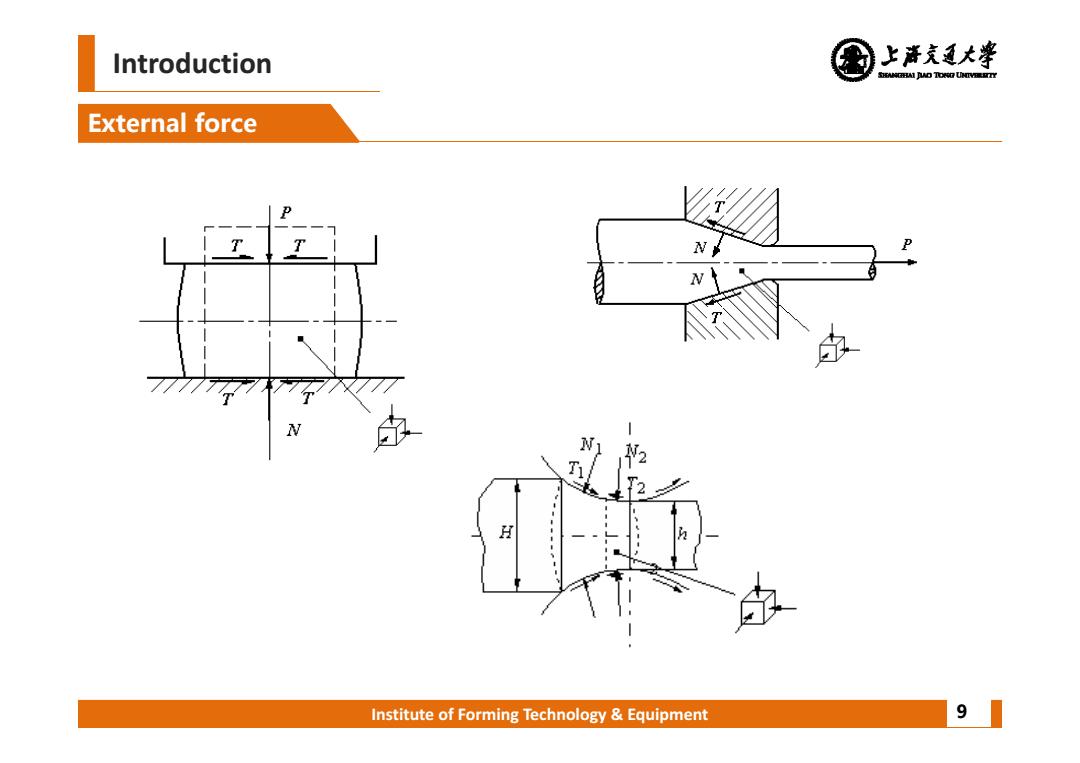
Introduction 上清充通大¥ SHEAMGRAI DUD TONO UHTVEREETTY External force N 2 H Institute of Forming Technology Equipment 9
Institute of Forming Technology & Equipment Introduction External force 9
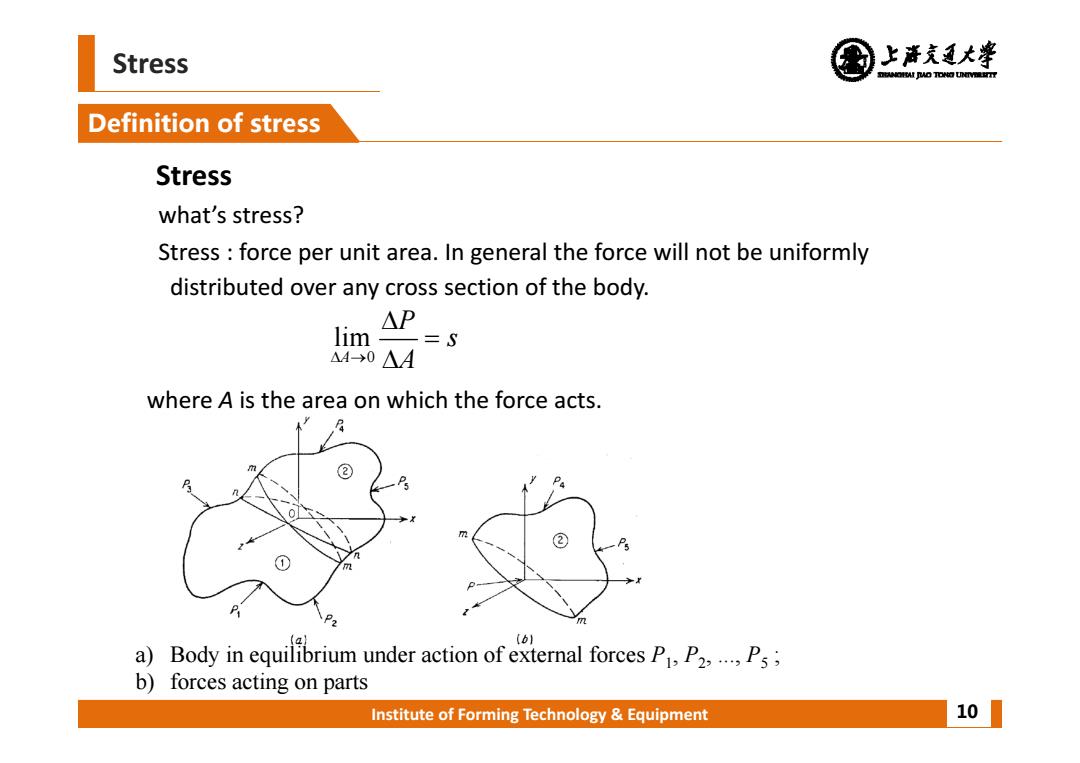
Stress 上清充通大婆 DREANOIAI AO TONG UNIVEREITT Definition of stress Stress what's stress? Stress force per unit area.In general the force will not be uniformly distributed over any cross section of the body. lim △P =S △4-→0△A where A is the area on which the force acts. ② ② 9% (b1 a) Body inequibrium under action of external forces PP b)forces acting on parts Institute of Forming Technology Equipment 10
Institute of Forming Technology & Equipment Stress Definition of stress 10 Stress what’s stress? Stress : force per unit area. In general the force will not be uniformly distributed over any cross section of the body. where A is the area on which the force acts. a) Body in equilibrium under action of external forces P1, P2, ..., P5 ; b) forces acting on parts 0 lim A P s A
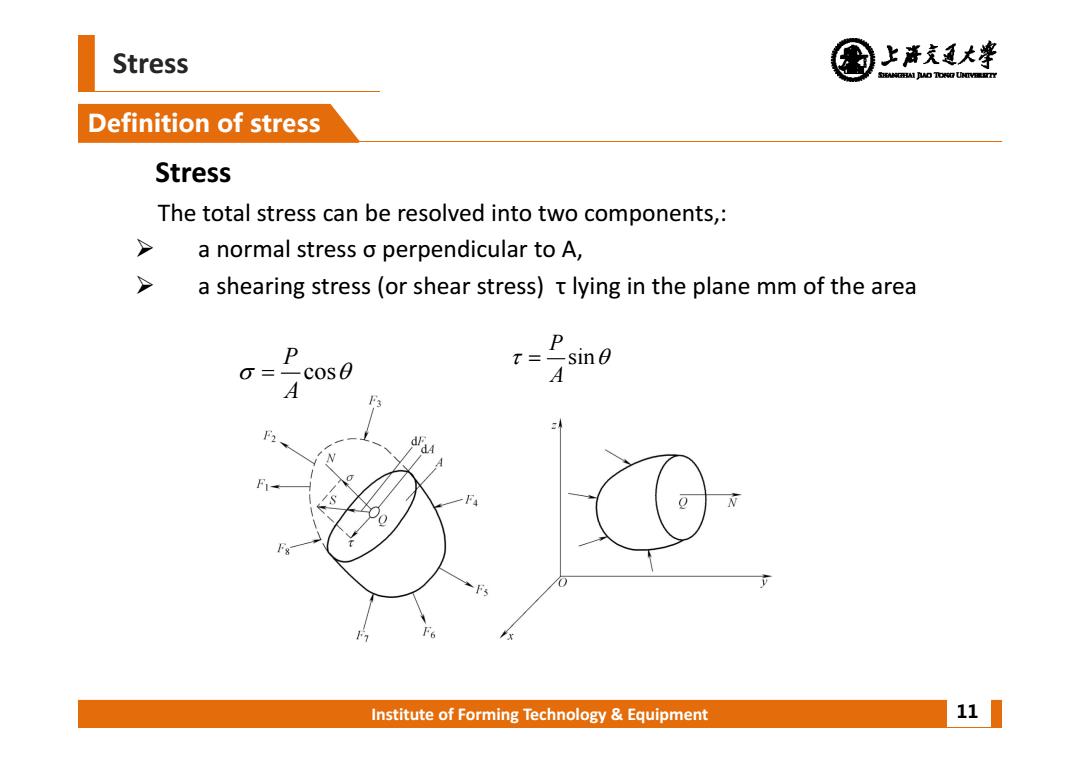
Stress 上清充通大¥ SHEAMGRAI DUD TONO UHTVEREETTY Definition of stress Stress The total stress can be resolved into two components,: > a normal stress o perpendicular to A, > a shearing stress(or shear stress)t lying in the plane mm of the area P P cos0 T=-sin0 A F A Institute of Forming Technology Equipment 11
Institute of Forming Technology & Equipment Stress Definition of stress 11 Stress The total stress can be resolved into two components,: a normal stress σ perpendicular to A, a shearing stress (or shear stress) τ lying in the plane mm of the area cos P A sin PA