
Contents of Today S.J.T.0. Phase Transformation and Applications Review previous Condition of equilibrium Phase equilibrium Clapeyron equation in vapor equilibria Variation of vapor pressure with particle size Second-order transition SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Spring2008©X.J.Jin Lecture 7 equilibrium I
Phase Transformation and Applications S. J. T. U. SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Spring 2008 © X. J. Jin Lecture 7 equilibrium I Contents of Today Review previous Condition of equilibrium Phase equilibrium Clapeyron equation in vapor equilibria Variation of vapor pressure with particle size Second-order transition

Property Relation S.J.T.0. Phase Transformation and Applications dU=TdS-PdV 〔器) -T =-P dF =-SdT-Pdv 〔) =-S =-P dG =-SdT +Vap =-S =V dH TaS +Vap =T ap a as aP)s as U av ap SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Spring2o08©X.J.Jin Lecture 7 equilibrium I
Phase Transformation and Applications S. J. T. U. SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Spring 2008 © X. J. Jin Lecture 7 equilibrium I Property Relation S S V P V T S S P V PT T T V P V S T T P V PS dU TdS PdV dF SdT PdV dG SdT VdP dH TdS VdP P V U T S U V S P V F S T F V T V P G S T G P T V P H T S H P S
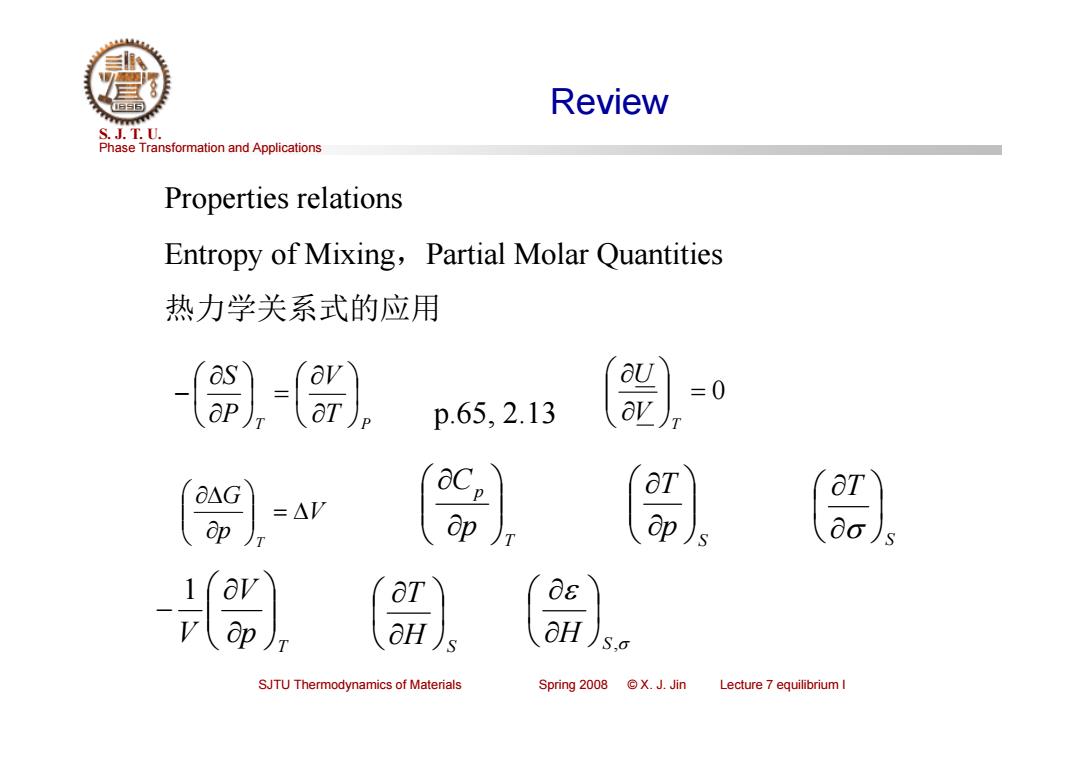
Review S.J.T.0. Phase Transformation and Applications Properties relations Entropy of Mixing,Partial Molar Quantities 热力学关系式的应用 as p65,213 =0 -AV OT ap ap)s 0o)s OT 0s OH aH S.o SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Spring 2008 @X.J.Jin Lecture 7 equilibrium I
Phase Transformation and Applications S. J. T. U. SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Spring 2008 © X. J. Jin Lecture 7 equilibrium I Review Properties relations Entropy of Mixing,Partial Molar Quantities 热力学关系式的应用 T T P V P S 0 T VU p.65, 2.13 V p G T T p pC S pT S T T p V V 1 H S T H S ,

Index of nomenclature S.J.T.0. Phase Transformation and Applications Equilibrium:平衡 Phase equilibrium:相平衡 First order transitions:一级相变 Second-order transition:二级相变 SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Spring2o08©X.J.Jin Lecture 7 equilibrium I
Phase Transformation and Applications S. J. T. U. SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Spring 2008 © X. J. Jin Lecture 7 equilibrium I Index of nomenclature Equilibrium: 平衡 Phase equilibrium: 相平衡 First order transitions: 一级相变 Second-order transition: 二级相变

Introduction to equilibrium S.J.T.0. Phase Transformation and Applications The concept of equilibrium is fundamental 。 Stable,unchanging with time and certain properties of the system are uniform throughout The system may not be homogeneous in form Co-existence of ice and water 。Phase -A portion of matter that is uniform throughout,not only in chemical composition,but also in physical state The usefulness of many metallic,polymeric,and ceramic systems depends on the presence,at equilibrium,of various different phases in the material 组织 SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Spring2008©X.J.Jin Lecture 7 equilibrium I
Phase Transformation and Applications S. J. T. U. SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Spring 2008 © X. J. Jin Lecture 7 equilibrium I Introduction to equilibrium • The concept of equilibrium is fundamental • Stable, unchanging with time and certain properties of the system are uniform throughout • The system may not be homogeneous in form – Co-existence of ice and water • Phase – A portion of matter that is uniform throughout, not only in chemical composition, but also in physical state – The usefulness of many metallic, polymeric, and ceramic systems depends on the presence, at equilibrium, of various different phases in the material 组织
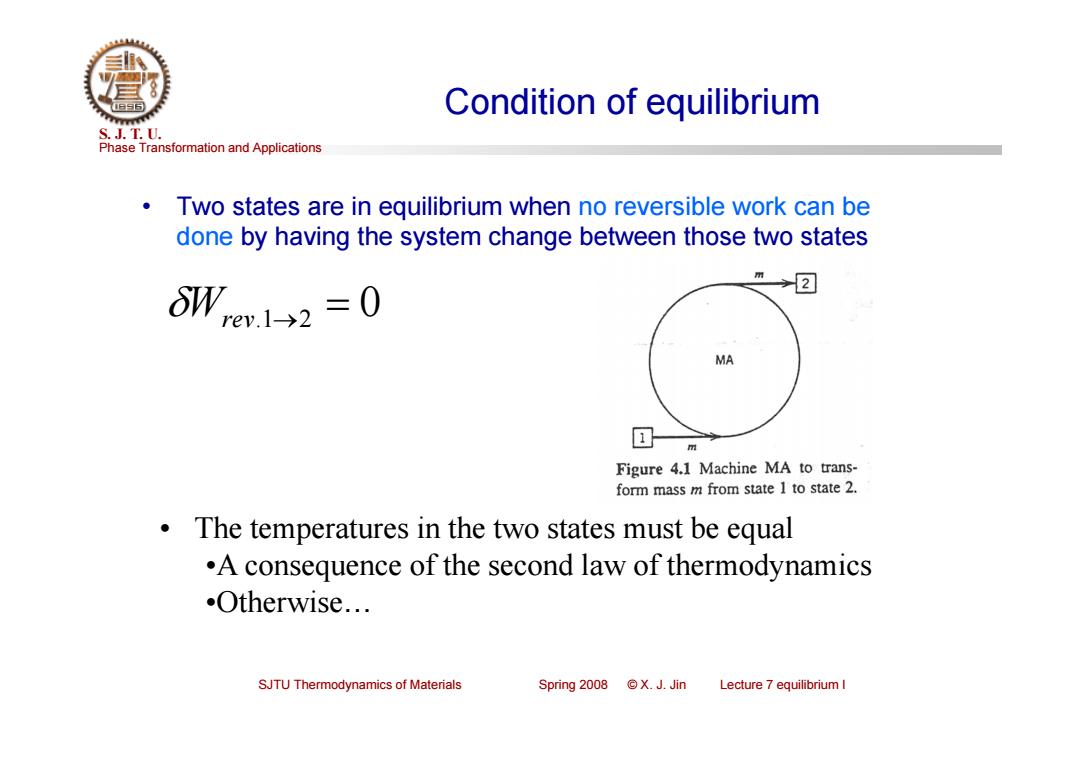
Condition of equilibrium S.J.T.0. Phase Transformation and Applications Two states are in equilibrium when no reversible work can be done by having the system change between those two states →2 oW,e1→2=0 MA 回 Figure 4.1 Machine MA to trans- form mass m from state 1 to state 2. The temperatures in the two states must be equal .A consequence of the second law of thermodynamics Otherwise... SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Spring2008©X.J.Jin Lecture 7 equilibrium I
Phase Transformation and Applications S. J. T. U. SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Spring 2008 © X. J. Jin Lecture 7 equilibrium I Condition of equilibrium • Two states are in equilibrium when no reversible work can be done by having the system change between those two states Wrev.12 0 • The temperatures in the two states must be equal •A consequence of the second law of thermodynamics •Otherwise…
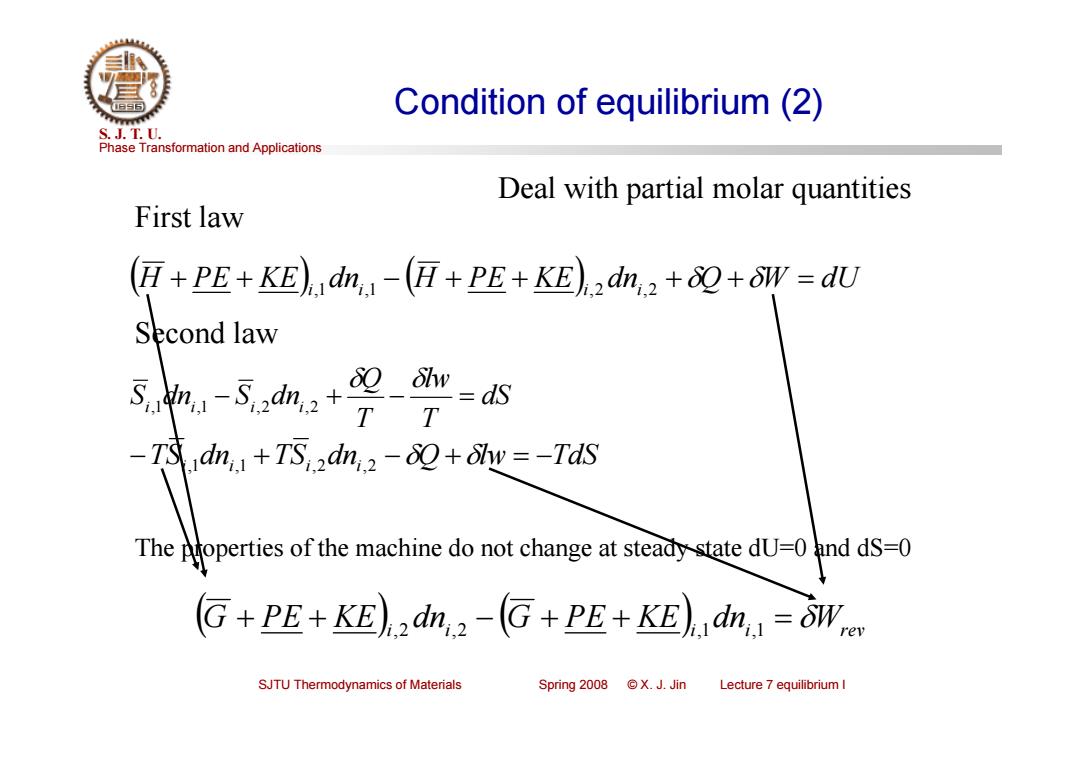
Condition of equilibrium(2) S.J.T.0. Phase Transformation and Applications Deal with partial molar quantities First law (▣+PE+KE)dmu-(匠+PE+KE)2dn,2+2+oW=dU Second law S女5血9的 -TS dn +TS,.dn.2-80+lw=-TdS The operties of the machine do not change at steady state dU-0and dS-0 G+PE+KE)2dn2-G+PE+KE)dn =5Wrc SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Spring2o08©X.J.Jin Lecture 7 equilibrium I
Phase Transformation and Applications S. J. T. U. SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Spring 2008 © X. J. Jin Lecture 7 equilibrium I Condition of equilibrium (2) dS T lw T Q Si dni Si dni ,1 ,1 ,2 ,2 H PE KE i,1 dni,1 H PE KEi,2 dni,2 Q W dU Deal with partial molar quantities TS dn TS dn Q lw TdS i,1 i,1 i,2 i,2 First law Second law The properties of the machine do not change at steady state dU=0 and dS=0 i i i i Wrev G PE KE ,2 dn ,2 G PE KE ,1 dn ,1
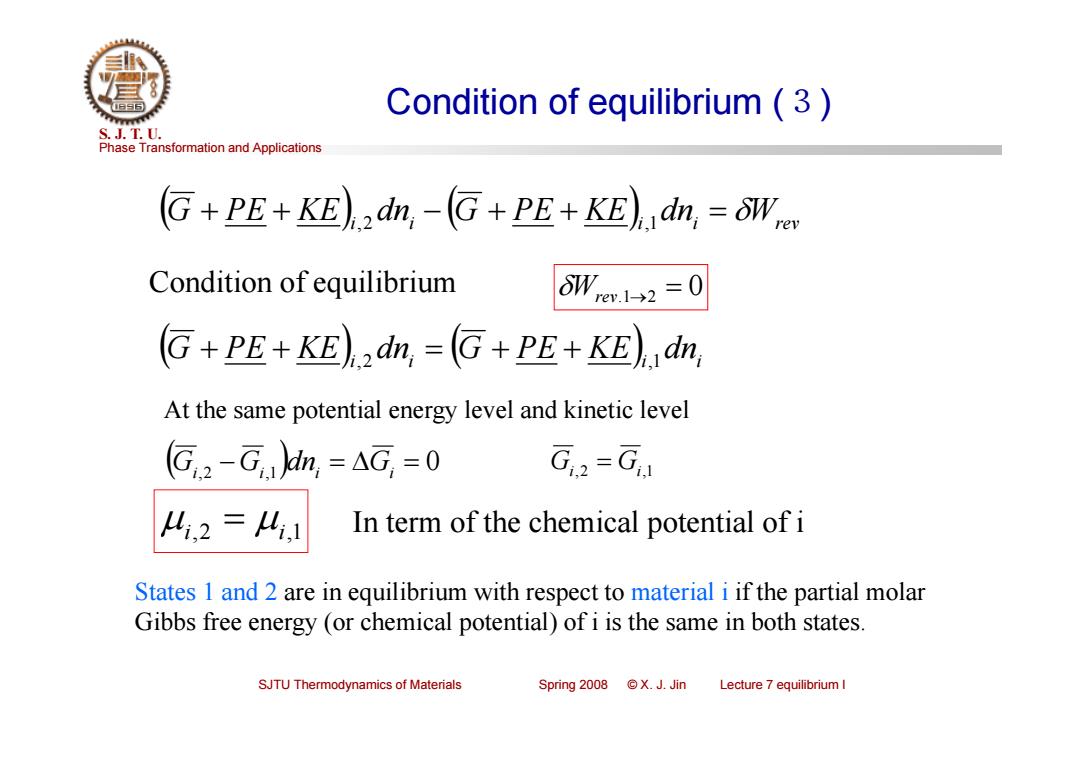
Condition of equilibrium (3 S.J.T.0. Phase Transformation and Applications G+PE+KE)2dn,-(G+PE+KE)dn,=oWc Condition of equilibrium 6Wem12=0 G+PE+KE)2dn,=(G+PE+KE)dn, At the same potential energy level and kinetic level (G,2-G.)din,=AG,=0 G,2=G 4,2=4,1 In term of the chemical potential of i States 1 and 2 are in equilibrium with respect to material i if the partial molar Gibbs free energy(or chemical potential)of i is the same in both states. SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Spring2008©X.J.Jin Lecture 7 equilibrium I
Phase Transformation and Applications S. J. T. U. SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Spring 2008 © X. J. Jin Lecture 7 equilibrium I Condition of equilibrium (3) G PE KE i,2 dni G PE KE i,1 dni Wrev Condition of equilibrium Wrev.12 0 i i i i G PE KE dn G PE KE dn ,2 ,1 Gi,2 Gi,1 dni Gi 0 Gi,2 Gi,1 At the same potential energy level and kinetic level i,2 i,1 In term of the chemical potential of i States 1 and 2 are in equilibrium with respect to material i if the partial molar Gibbs free energy (or chemical potential) of i is the same in both states

Condition of equilibrium(4) S.J.T.0. Phase Transformation and Applications 4,2=4,1 For single-component (G2-G)dn=AGdn=8W,e If the difference in Gibbs free energy between the two states 1 and 2 is negative,then the reversible work term is negative.That means that the material may change spontaneously from state 1 to state 2 because no work needs to be done to force the change;in fact,work can be generated by the change.The potential to do so might be dissipated as lost work,but the potential to do reversible work exists. SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Spring2008©X.J.Jin Lecture 7 equilibrium I
Phase Transformation and Applications S. J. T. U. SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Spring 2008 © X. J. Jin Lecture 7 equilibrium I Condition of equilibrium (4) i,2 i,1 G2 G1 dn Gdn Wrev For single-component If the difference in Gibbs free energy between the two states 1 and 2 is negative, then the reversible work term is negative. That means that the material may change spontaneously from state 1 to state 2 because no work needs to be done to force the change; in fact, work can be generated by the change. The potential to do so might be dissipated as lost work, but the potential to do reversible work exists
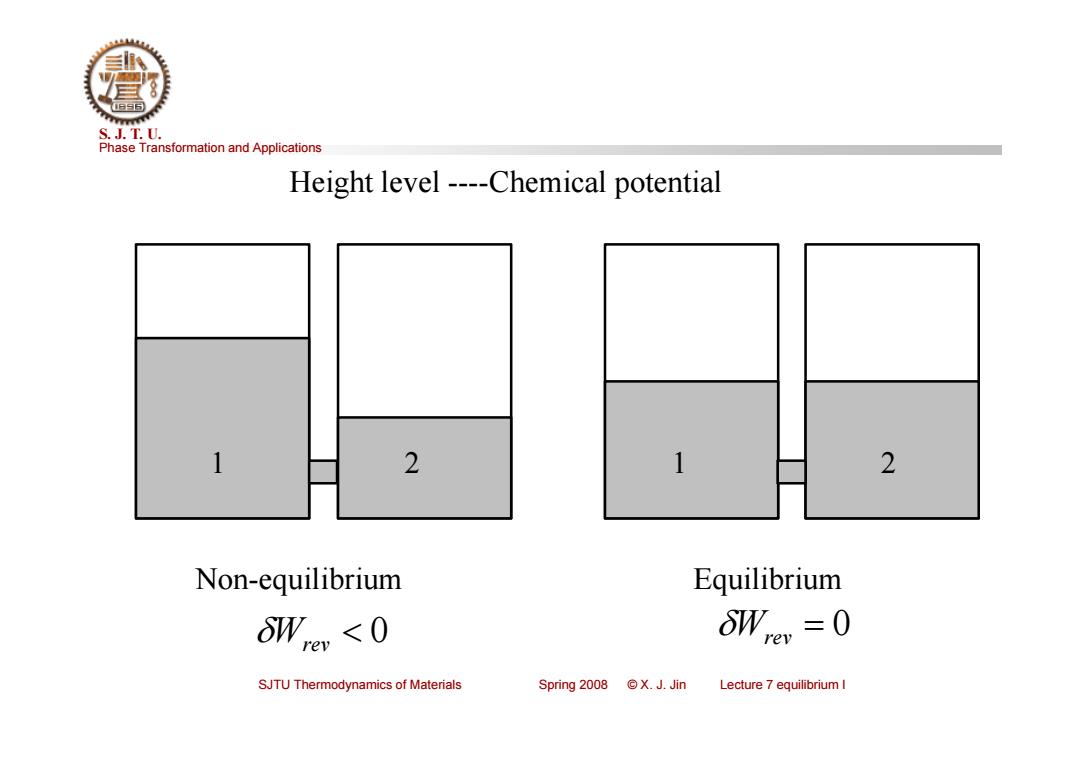
S.J.T.U. Phase Transformation and Applications Height level----Chemical potential 1 2 1 2 Non-equilibrium Equilibrium Wre Wre =0 SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Spring2008©X.J.Jin Lecture 7 equilibrium I
Phase Transformation and Applications S. J. T. U. SJTU Thermodynamics of Materials Spring 2008 © X. J. Jin Lecture 7 equilibrium I Non-equilibrium Equilibrium 1 2 Height level ----Chemical potential Wrev 0 0 Wrev 1 2