
上海交通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY Chapter 11.Surface and Interface Surface energy surface tension Effect of surface curvature ·Vapor pressure ·Solubility of small particles ·Wetting of surfaces 1
Chapter 11. Surface and Interface 1
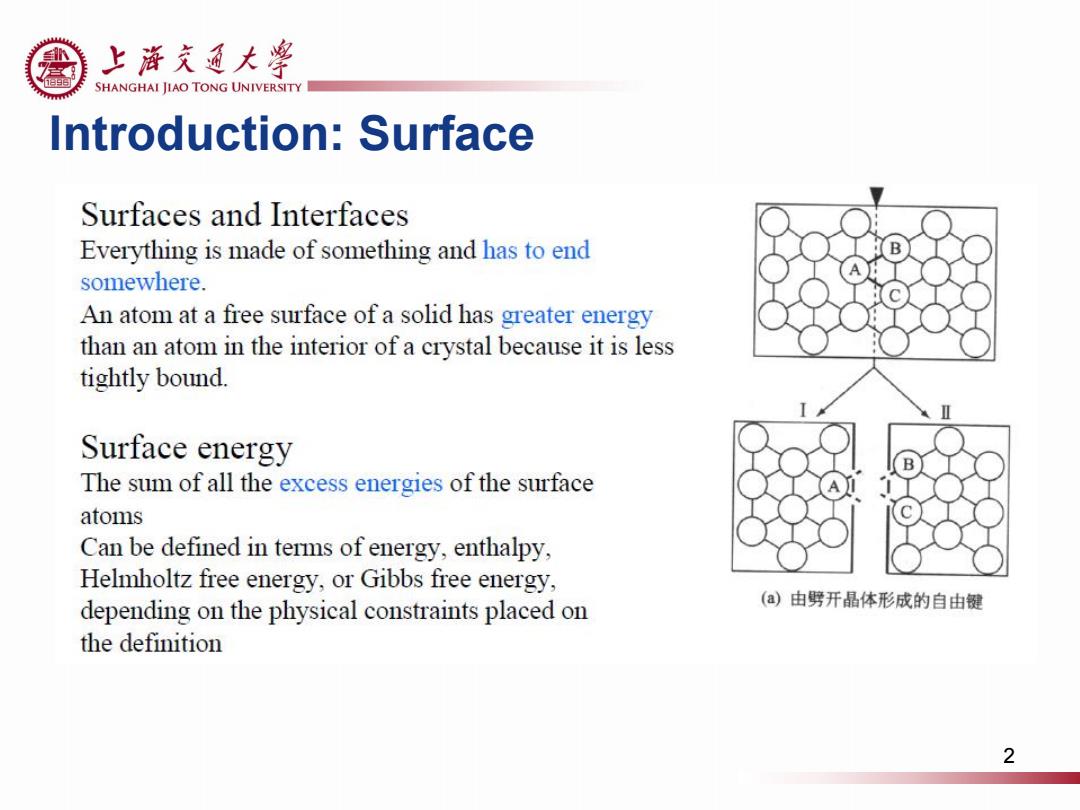
上游充通大粤 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY Introduction:Surface Surfaces and Interfaces Everything is made of something and has to end somewhere. An atom at a free surface of a solid has greater energy than an atom in the interior of a crystal because it is less tightly bound. Surface energy The sum of all the excess energies of the surface atoms Can be defined in terms of energy,enthalpy, Helmholtz free energy,or Gibbs free energy, depending on the physical constraints placed on (a)由劈开晶体形成的自由键 the definition 2
Introduction: Surface 2

上游充通大粤 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY Introduction:Surface energy Surface energy based on Gibbs free energy dG=-SdT+VaP+ydA OH OF 6A T.P Water droplets try to minimize its Small particles of metals will melt free energy by agglomerating into or sinter into spherical particles arger spherical particles. ro
Introduction: Surface energy 3 Water droplets try to minimize its free energy by agglomerating into larger spherical particles. Small particles of metals will melt or sinter into spherical particles
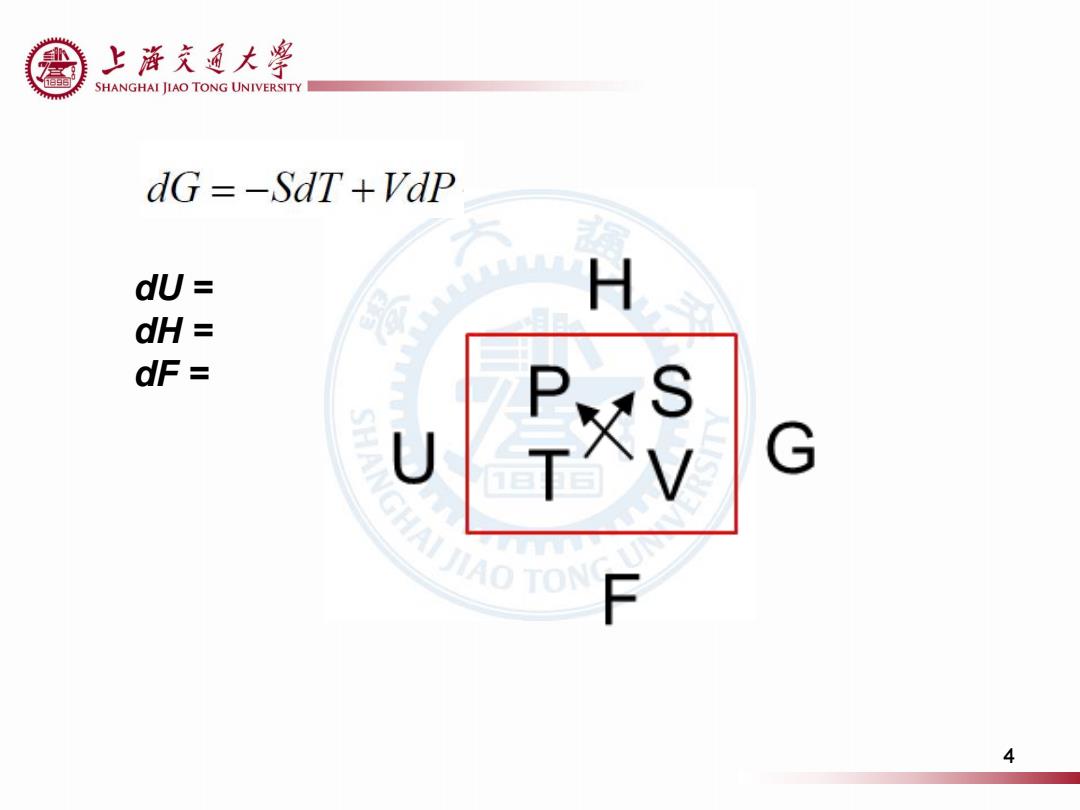
上浒充通大粤 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY dG =-SdT +VdP dU H dH 是 dF= P SHANGHAIAO TON U G F 4
4 dU = dH = dF =

上游充通大粤 SHANGHALILAO TONG UNIVERSITY Bareret Media
5
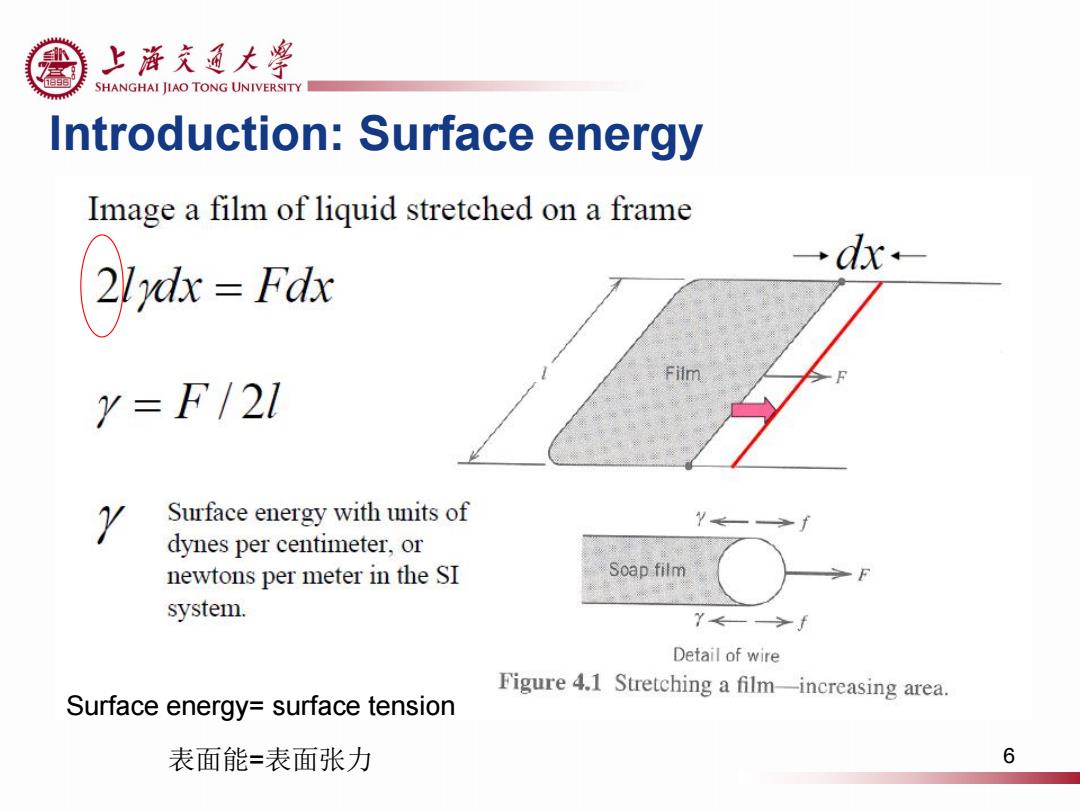
上游充通大粤 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY Introduction:Surface energy Image a film of liquid stretched on a frame 2dFd →dx- Y=F/21 Y Surface energy with units of dynes per centimeter,or newtons per meter in the SI Soap film system. Y←—>f Detail of wire Figure 4.1 Stretching a film-increasing area. Surface energy=surface tension 表面能=表面张力 6
Introduction: Surface energy 6 Surface energy= surface tension 表面能=表面张力

上游充通大粤 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY Surface energy surface tension Y Surface energy with units of dynes per centimeter,or newtons per meter in the SI system. [界面张力] [界面能] SI单位制 N(牛顿)·m1=J(焦耳)·m-2 cgs单位制 dyn(达因)·cm-1=erg(尔格)·cm-2 7
Surface energy / surface tension 7
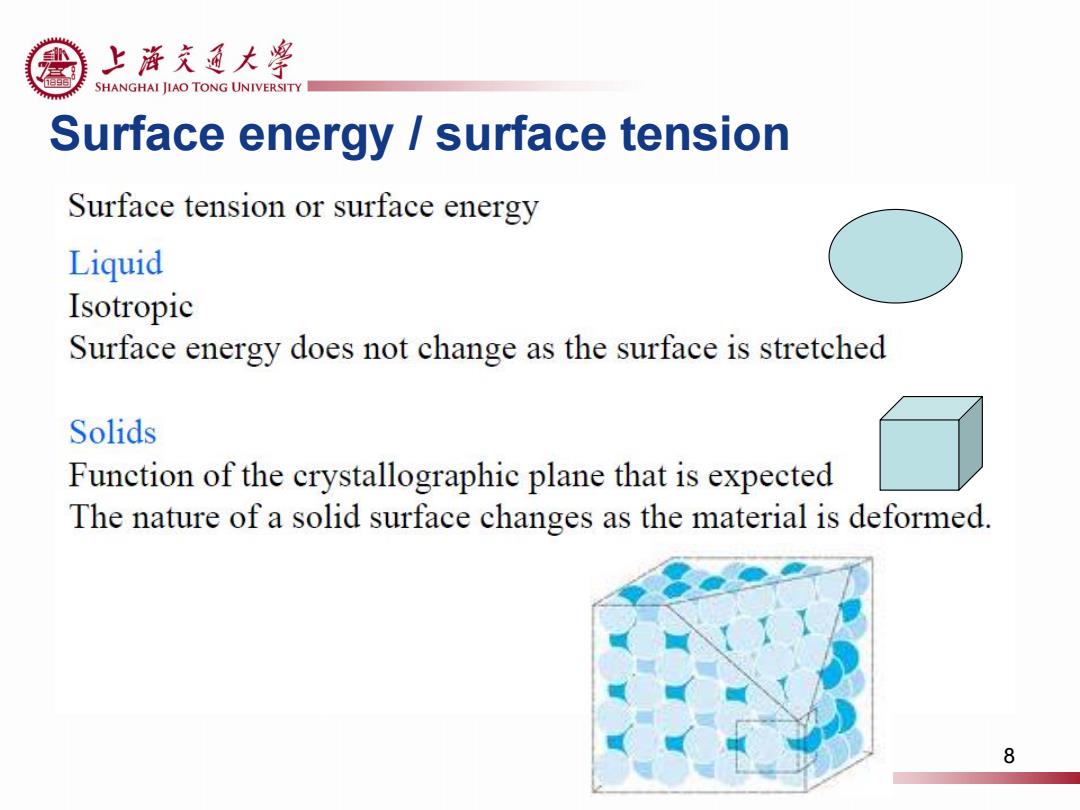
上浒充通大率 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY Surface energy surface tension Surface tension or surface energy Liquid Isotropic Surface energy does not change as the surface is stretched Solids Function of the crystallographic plane that is expected The nature of a solid surface changes as the material is deformed 8
Surface energy / surface tension 8
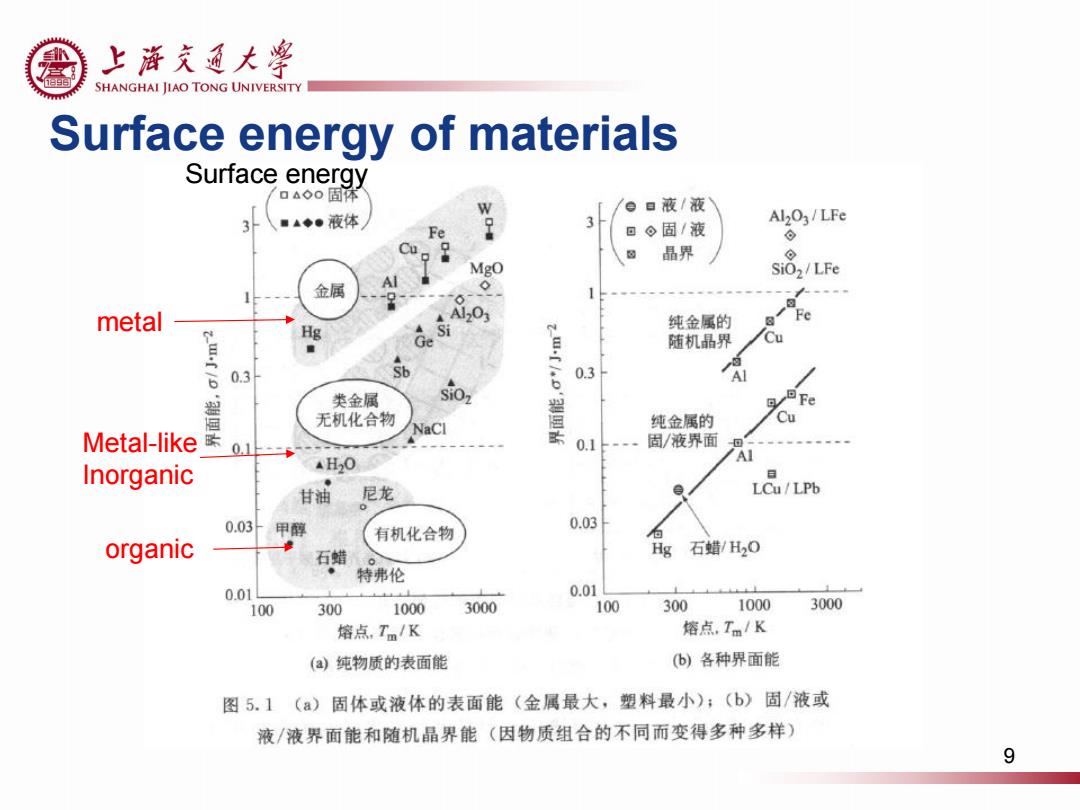
上游充通大¥ SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY Surface energy of materials Surface energy △0固体 a液/液 ■▲◆●液体 Al2O3/LFe Fe 。固/液 ⊙ Cu 晶界 ⊙ Mgo SiO,/LFe 金属 0 metal A120 HE Ge Si 纯金属的 Fe 随机晶界 Cu 6 0.3 Sb 0.3 类金属 SiOz 无机化合物 Cu NaCl 纯金属的 Metal-like 天0+ 0.1 固/液界面 Al Inorganic AH2O 甘油 尼龙 LCu/LPb 0.03甲醇 0.03 有机化合物 organic 石蜡 Hg石蜡/H20 特弗伦 0.01 0.0 100 300 1000 3000 100 300 1000 3000 熔点,Tm/K 熔点,Tm/K (a纯物质的表面能 (b)各种界面能 图5.1(a)固体或液体的表面能(金属最大,塑料最小);(b)固/液或 液/液界面能和随机晶界能(因物质组合的不同而变得多种多样) 9
Surface energy of materials 9 metal Metal-like Inorganic organic Surface energy
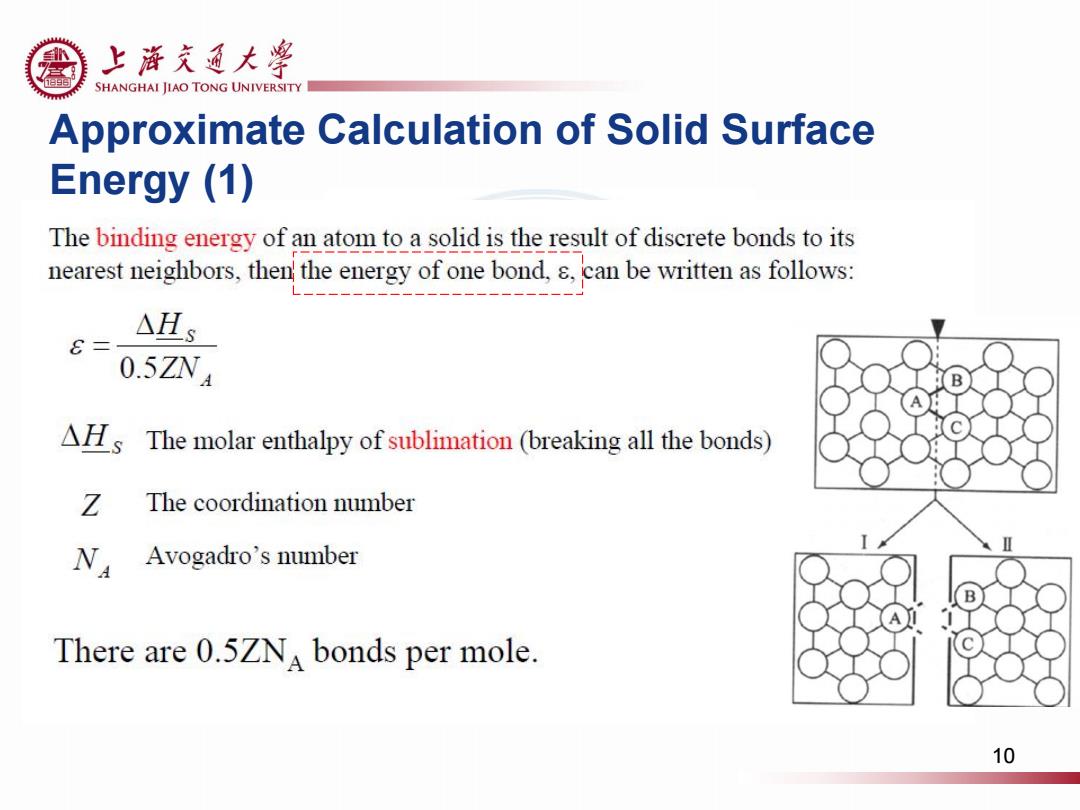
上游充通大粤 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY Approximate Calculation of Solid Surface Energy (1) The binding energy of an atom to a solid is the result of discrete bonds to its nearest neighbors,then the energy of one bond,.can be written as follows: △Hs 0.5ZN4 B AHs The molar enthalpy of sublimation (breaking all the bonds) Z The coordination number N Avogadro's number There are 0.5ZNA bonds per mole. 10
Approximate Calculation of Solid Surface Energy (1) 10