
Outline Introduction Processing maps Elements of plastic theory Plastic deformation mechanism Recovery recrystallization
Outline Processing maps Plastic deformation mechanism Elements of plastic theory Recovery & recrystallization Introduction

国上泽充大李 BRANCHAI JIAO TONQ UNTPERSTTY Introduction Processing maps Elements of plastic theory Plastic deformation of crystal Outline and terminology Recovery recrystallization Recovery Recrystallization DRV DRX
Introduction Elements of plastic theory 1 Recovery & recrystallization 1 1 Outline and terminology Recovery Recrystallization DRV & DRX 1 Plastic deformation of crystal Processing maps 1

上清充通大¥ Outline and terminology SHEAMGRAI DUD TONO UHTVEREETTY Main annealing processes -microstructure (a)Deformed state (b)Recovered state (c)Partially recrystallized state (d)Fully recrystallized state (e)Grain growth (f )Abnormal grain growth Schematic diagram of the main annealing processes Institute of Forming Technology Equipment 4
Outline and terminology Institute of Forming Technology & Equipment 4 Main annealing processes ‐ microstructure Schematic diagram of the main annealing processes (a) Deformed state (b) Recovered state (c) Partially recrystallized state (d) Fully recrystallized state (e) Grain growth (f ) Abnormal grain growth
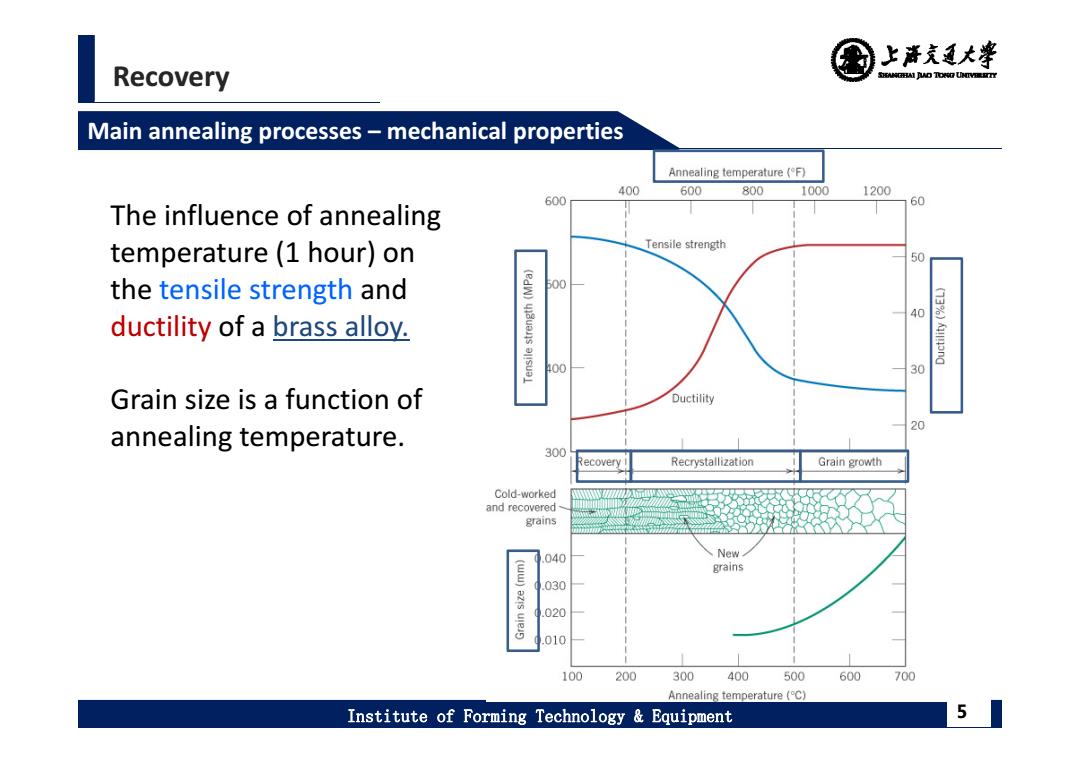
上清充通大¥ Recovery SHEAMGHAI DUD TONO UHTVEREETTY Main annealing processes-mechanical properties Annealing temperature(F) 400 600 800 1000 1200 600 60 The influence of annealing temperature(1 hour)on Tensile strength 50 the tensile strength and 500 40 ductility of a brass alloy. 00 30 Grain size is a function of Ductility 20 annealing temperature. 300 ecovery Recrystallization Grain growth Cold-worked and recovered grains 040 New grains 030 020 010 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 Annealing temperature(C) Institute of Forming Technology Equipment 5
Recovery Institute of Forming Technology & Equipment 5 Main annealing processes – mechanical properties The influence of annealing temperature (1 hour) on the tensile strength and ductility of a brass alloy. Grain size is a function of annealing temperature
Outline and terminology 上清充通大学 SHEAMGRAI DUD TONO UHTVEREETTY Terminology Why can discovery and recrystallization occur in deformed material? The increases in stored energy are a result of deformation. The dislocations provide the driving force for the annealing phenomena. Thermodynamically Lower energy unstable conditions conditions Temperature,time,the nature of material Institute of Forming Technology Equipment 6
Outline and terminology Institute of Forming Technology & Equipment 6 Terminology Why can discovery and recrystallization occur in deformed material? Temperature, time, the nature of material Thermodynamically unstable conditions Lower energy conditions • The increases in stored energy are a result of deformation. • The dislocations provide the driving force for the annealing phenomena
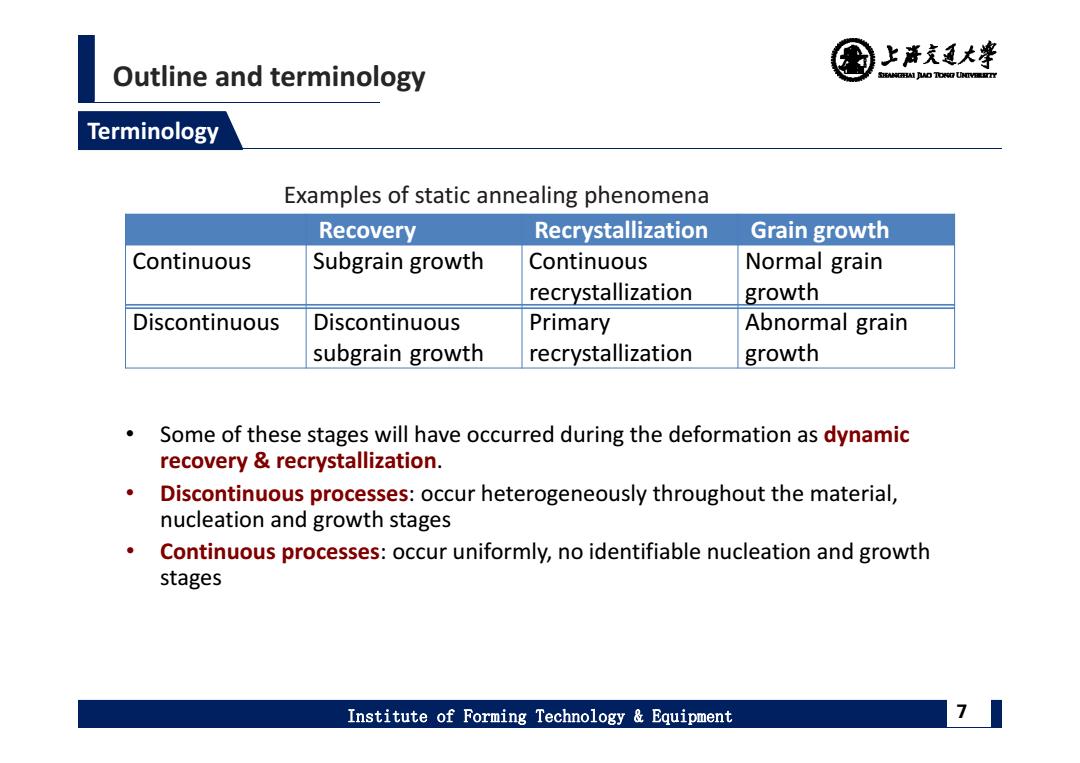
上清充通大¥ Outline and terminology SHEAMGRAI DUD TONO UHTVEREETTY Terminology Examples of static annealing phenomena Recovery Recrystallization Grain growth Continuous Subgrain growth Continuous Normal grain recrystallization growth Discontinuous Discontinuous Primary Abnormal grain subgrain growth recrystallization growth Some of these stages will have occurred during the deformation as dynamic recovery recrystallization. Discontinuous processes:occur heterogeneously throughout the material, nucleation and growth stages Continuous processes:occur uniformly,no identifiable nucleation and growth stages Institute of Forming Technology Equipment 7
Outline and terminology Institute of Forming Technology & Equipment 7 Terminology Examples of static annealing phenomena Recovery Recrystallization Grain growth Continuous Subgrain growth Continuous recrystallization Normal grain growth Discontinuous Discontinuous subgrain growth Primary recrystallization Abnormal grain growth • Some of these stages will have occurred during the deformation as dynamic recovery & recrystallization. • Discontinuous processes: occur heterogeneously throughout the material, nucleation and growth stages • Continuous processes: occur uniformly, no identifiable nucleation and growth stages
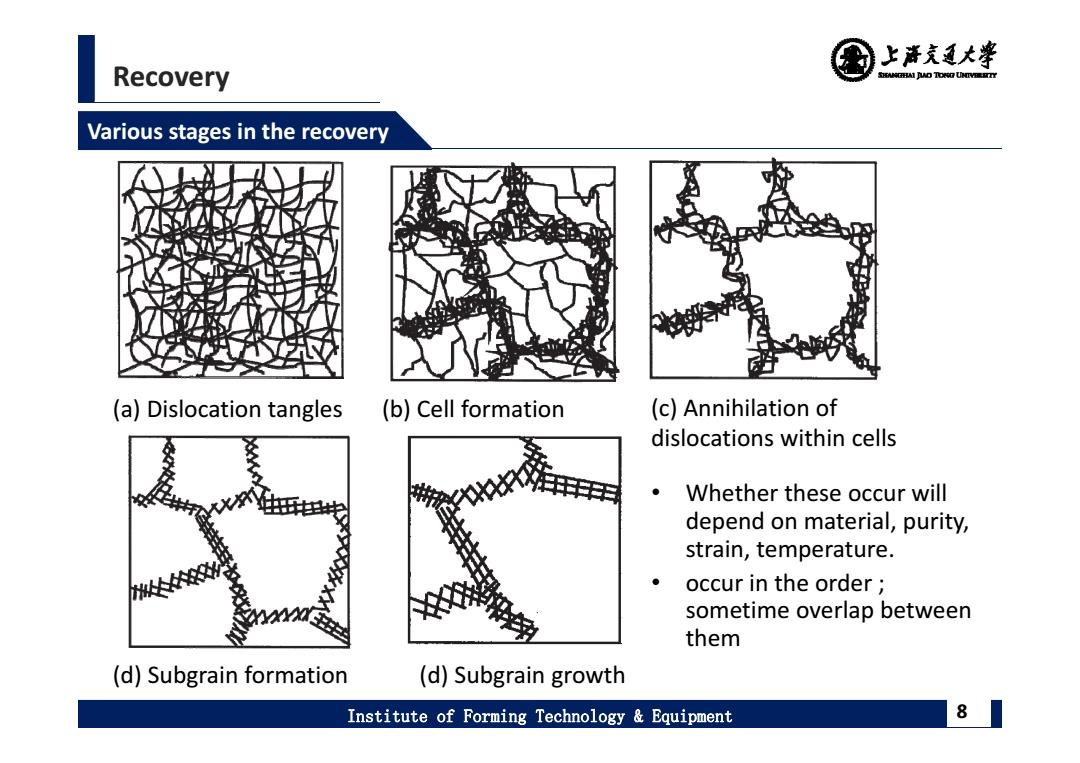
上清充通大¥ Recovery SHEAMGRAI DUD TONO UHTVEREETTY Various stages in the recovery a)Dislocation tangles (b)Cell formation (c)Annihilation of dislocations within cells Whether these occur will depend on material,purity, strain,temperature. occur in the order sometime overlap between them (d)Subgrain formation (d)Subgrain growth Institute of Forming Technology Equipment 8
Recovery Institute of Forming Technology & Equipment 8 Various stages in the recovery (a) Dislocation tangles (b) Cell formation (c) Annihilation of dislocations within cells (d) Subgrain formation (d) Subgrain growth • Whether these occur will depend on material, purity, strain, temperature. • occur in the order ; sometime overlap between them
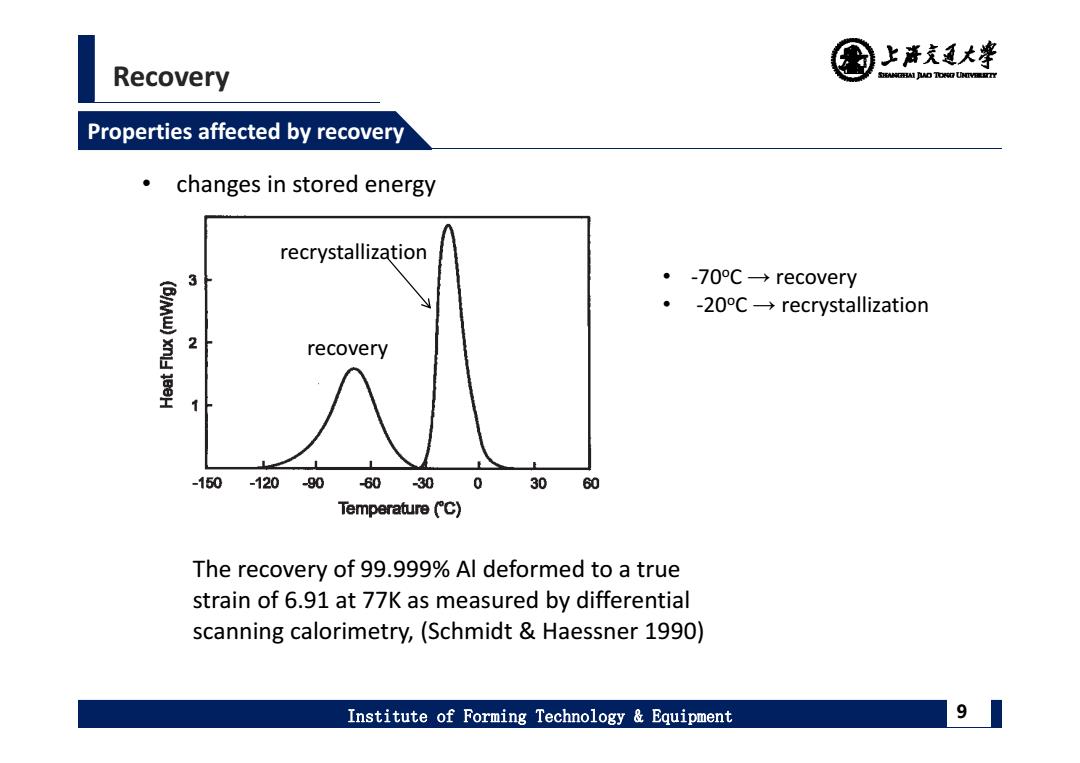
上清充通大¥ Recovery SHEAMGRAI DUD TONO UHTVEREETTY Properties affected by recovery changes in stored energy recrystallization 3 ·-70c→recovery ·-20c→recrystallization 2 recovery -150 -120-90 60 30 0 30 60 Temperature (C) The recovery of 99.999%Al deformed to a true strain of 6.91 at 77K as measured by differential scanning calorimetry,(Schmidt Haessner 1990) Institute of Forming Technology Equipment 9
Recovery Institute of Forming Technology & Equipment 9 Properties affected by recovery The recovery of 99.999% Al deformed to a true strain of 6.91 at 77K as measured by differential scanning calorimetry, (Schmidt & Haessner 1990) • changes in stored energy • ‐70oC → recovery • ‐20oC → recrystallization recrystallization recovery
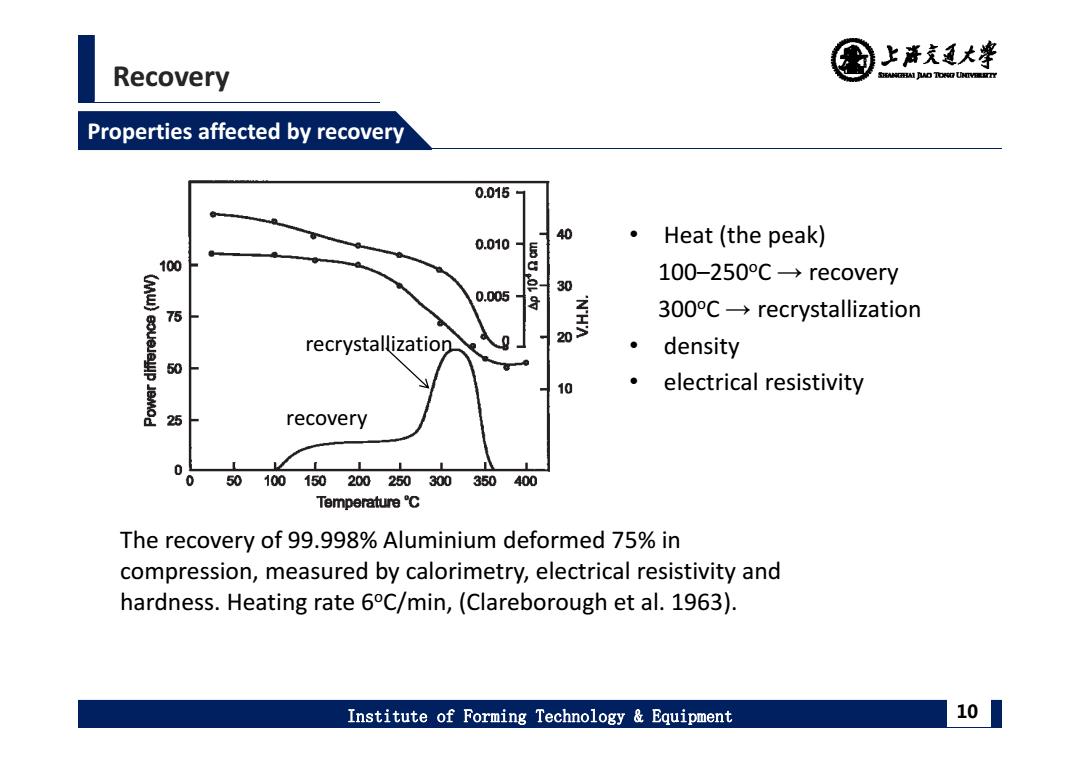
上清充通大¥ Recovery SHEAMGRAI DUD TONO UHTVEREETTY Properties affected by recovery 0.015 40 0.010 Heat(the peak) 100 54. 100-250C-recovery 30 0.005 仓 高以 300C-recrystallization recrystallization density 50 人 10 electrical resistivity 25 人 recovery 0 0 50100150200250300350400 Temperature℃ The recovery of 99.998%Aluminium deformed 75%in compression,measured by calorimetry,electrical resistivity and hardness.Heating rate 6C/min,(Clareborough et al.1963) Institute of Forming Technology Equipment 10
Recovery Institute of Forming Technology & Equipment 10 Properties affected by recovery The recovery of 99.998% Aluminium deformed 75% in compression, measured by calorimetry, electrical resistivity and hardness. Heating rate 6oC/min, (Clareborough et al. 1963). • Heat (the peak) 100–250oC → recovery 300oC → recrystallization • density • electrical resistivity recovery recrystallization
上产充毛大睾 Recovery SHEAMGHAI DUD TONO UHTVEREETTY Influencing factors The effect of strain For polycrystalline metals,complete recovery+lightly deformed. Single crystals of hexagonal close-packed metals such as zinc,deformed to large strains on only one slip system-completely recover. Single crystals of cubic metals if oriented for single slip and √ deformed in stage I of work hardening may recover almost. / deformed into stages ll or Ill of work hardening,then recrystallization may intervene before any significant amount of recovery has occurred. The recovered fraction of the property change increase with strain at a constant temperature. However,this trend may be reversed in more highly strained materials, because of the earlier onset of recrystallization. Institute of Forming Technology Equipment 11
Recovery Institute of Forming Technology & Equipment 11 Influencing factors The effect of strain For polycrystalline metals, complete recovery ← lightly deformed. Single crystals of hexagonal close‐packed metals such as zinc, deformed to large strains on only one slip system → completely recover. Single crystals of cubic metals if oriented for single slip and deformed in stage I of work hardening may recover almost. deformed into stages II or III of work hardening, then recrystallization may intervene before any significant amount of recovery has occurred. The recovered fraction of the property change increase with strain at a constant temperature. However, this trend may be reversed in more highly strained materials, because of the earlier onset of recrystallization