
Outline Introduction Processing maps Elements of plastic theory Plastic deformation mechanism Recovery recrystallization
Outline Processing maps Plastic deformation mechanism Elements of plastic theory Recovery & recrystallization Introduction
上清充通大学 SANCEAI JUO TO阳UY Introduction Processing maps 创 General Review Elements of plastic theory Basics for processing maps Computation of processing maps plastic deformation mechanism Recovery recrystallization
Introduction Processing maps 1 1 1 General Review Basics for processing maps Computation of processing maps 1 1 Elements of plastic theory Recovery & recrystallization plastic deformation mechanism

Reference books 上清充通大¥ SHEAMGRAI DUD TONO UHTVEREETTY Hot Working Guide:A Compendium of Processing Maps Y.V.R.K.Prasad and S.Sasidhara ASM International The Materials Information Society Handbook of Workability and Process Design George E.Dieter,S.L.Semiatin October 1st 2003 by ASM International(OH) Institute of Forming Technology Equipment 41
Reference books Institute of Forming Technology & Equipment 4 • Hot Working Guide: A Compendium of Processing Maps Y. V. R. K. Prasad and S. Sasidhara ASM International The Materials Information Society Handbook of Workability and Process Design George E. Dieter, S.L. Semiatin October 1st 2003 by ASM International(OH)

General Review 上产克大睾 SHEAMGRAI DUAD TONO UNTVEEETTY Techniques of mechanical processing Mechanical processing shaping materials into engineering components (dimensional accuracy,specified microstructures and mechanical properties). Techniques of mechanical processing > bulk metal working:using rolling,forging or extrusion (at elevated temperatures);large strains may be imposed in a single step of the operation without the onset of fracture. > cold working:good surface finish,high dimensional tolerance and better strength,smaller strains and require large number of steps with to restore the ductility (sheet metal working cold forging,intermediate annealing impact extrusion,coining,wire and tube drawing) Institute of Forming Technology Equipment
General Review Institute of Forming Technology & Equipment Techniques of mechanical processing 5 Mechanical processing : shaping materials into engineering components (dimensional accuracy, specified microstructures and mechanical properties). Techniques of mechanical processing bulk metal working: using rolling, forging or extrusion (at elevated temperatures) ; large strains may be imposed in a single step of the operation without the onset of fracture. cold working: good surface finish, high dimensional tolerance and better strength, smaller strains and require large number of steps with to restore the ductility (sheet metal working cold forging, intermediate annealing impact extrusion, coining, wire and tube drawing)

General Review 国上清充大半 SHANCBHAI JUAO TONO UNTVEEETTY Bulk metal working ●Bulk metal working: major microstructural changes occur >a influence on the subsequent processing steps large tonnage of material by bulk metal working The objective:manufacture components with controlled microstructure and properties,without macro or microstructural defects. Trial and error techniques expensive,time consuming,and may not always lead to a successful solution or optimization. In recent years,the trial and error techniques are replaced by modeling techniques. Institute of Forming Technology Equipment 6
General Review Institute of Forming Technology & Equipment Bulk metal working 6 Bulk metal working: major microstructural changes occur a influence on the subsequent processing steps large tonnage of material by bulk metal working The objective: manufacture components with controlled microstructure and properties, without macro or microstructural defects. Trial and error techniques : expensive, time consuming, and may not always lead to a successful solution or optimization. In recent years, the trial and error techniques are replaced by modeling techniques

General Review 上产克大睾 SHEAMGHAI DUD TONO UHTVEREETTY Techniques of mechanical processing Modelling techniques address the t following design and manufacturing issues. o The design requirements are: Arriving at optimum processing conditions Controlling the microstructure in the component Designing optimum die shapes or perform geometry without resorting to shop floor trials >Obtaining the process limits for the design of control systems The manufacturing issues revolve around: The reduction of lead time in manufacturing Increasing the productivity without sacrificing the product quality Reducing the rejects to improve yield Ensuring the repeatability in manufacturing Institute of Forming Technology Equipment
General Review Institute of Forming Technology & Equipment Techniques of mechanical processing 7 Modelling techniques address the following design and manufacturing issues. The design requirements are: Arriving at optimum processing conditions Controlling the microstructure in the component Designing optimum die shapes or perform geometry without resorting to shop floor trials Obtaining the process limits for the design of control systems The manufacturing issues revolve around: The reduction of lead time in manufacturing Increasing the productivity without sacrificing the product quality Reducing the rejects to improve yield Ensuring the repeatability in manufacturing

General Review 上产克大睾 SHEAMGHAI DUD TONO UHTVEREETTY Workability Formability Workability refers to the relative ease with which a metal can be shaped through plastic deformation. This general term includes all other terms like forgeability, rollability,extrudability and formability (sheet metal working). A complete description of the workability of a material its flow stress dependence on processing variables(for example, strain,strain rate,preheat temperature and die temperature), stress state in the deformation zone,its failure behavior,and the metallurgical transformations that characterize the alloy system to which is belongs. Institute of Forming Technology Equipment 8
General Review Institute of Forming Technology & Equipment Workability & Formability 8 Workability refers to the relative ease with which a metal can be shaped through plastic deformation. This general term includes all other terms like forgeability, rollability, extrudability and formability (sheet metal working). A complete description of the workability of a material : its flow stress dependence on processing variables (for example, strain, strain rate, preheat temperature and die temperature), stress state in the deformation zone, its failure behavior, and the metallurgical transformations that characterize the alloy system to which is belongs
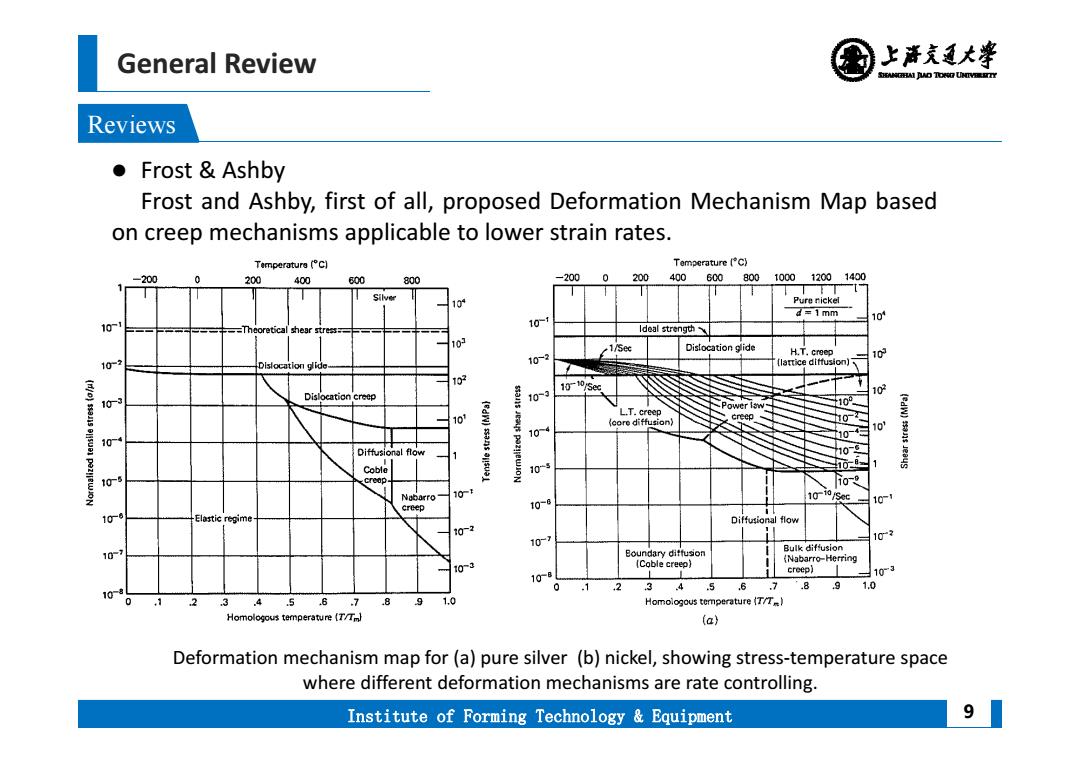
General Review 上清充通大¥ SHEAMGRAI DUD TONO UHTVEREETTY Reviews ● Frost Ashby Frost and Ashby,first of all,proposed Deformation Mechanism Map based on creep mechanisms applicable to lower strain rates. Temperature(°Cl Temperature [C) -200 200 400 00 800 -2000 200 400600.800 100012001400 104 Pure nickel d=1mm 10 10 10 Theoretical shear stress Ideal strength 10N 1/Sec Distocation glide H.T.creep 10 102 102 lattice ditfusion)、 101o5e Dislocation creep 102 10 10-3 D Power law- 102 10 (edw) L.T.creep core diffusion) eep、 104 10 10 10- Diffusional ftow 10 Coble 10 10T 10- 10 10 10- creep 108 10 Elastic regime Diffusional flow 107 10 10 Boundary diftusion Bulk diffusion 103 (Coble creep) (Nabarro-Herring 10a creep) 103 .4 .7 .89 1.0 10 .1 2 3 .3 4.5 .6.7 9 1.0 Homologous temperature (T/T) Homologous temperature(/Tm (a} Deformation mechanism map for(a)pure silver (b)nickel,showing stress-temperature space where different deformation mechanisms are rate controlling. Institute of Forming Technology Equipment 9
General Review Institute of Forming Technology & Equipment Reviews 9 Frost & Ashby Frost and Ashby, first of all, proposed Deformation Mechanism Map based on creep mechanisms applicable to lower strain rates. Deformation mechanism map for (a) pure silver (b) nickel, showing stress‐temperature space where different deformation mechanisms are rate controlling
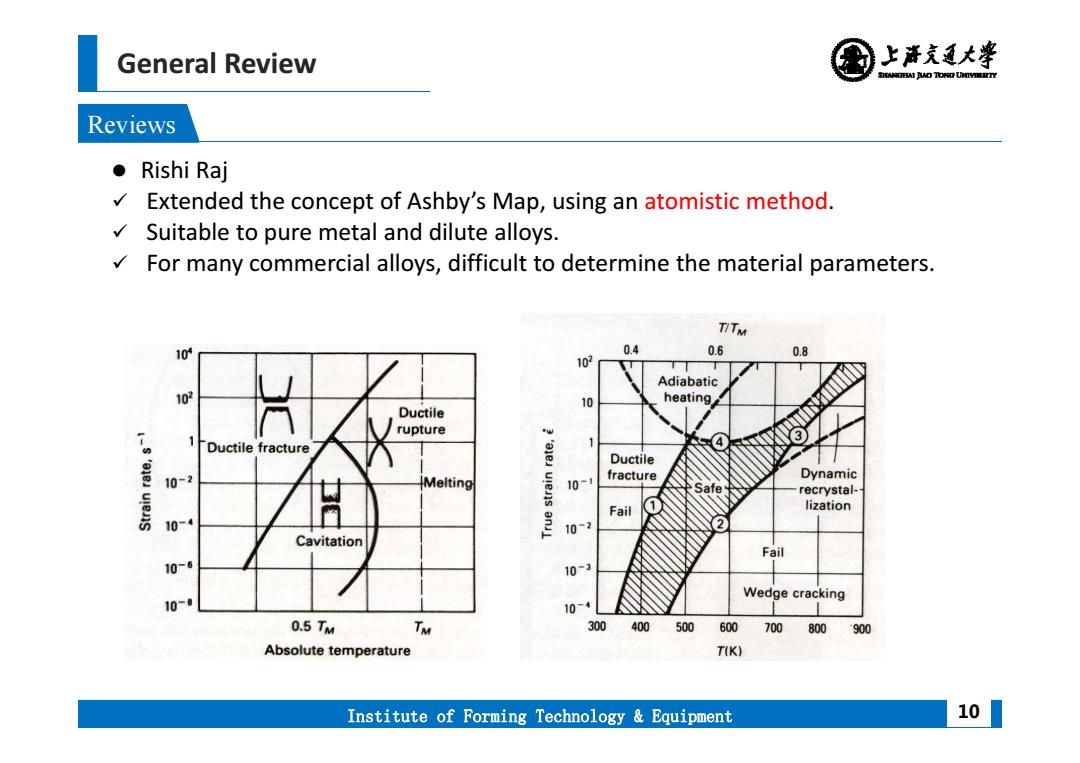
General Review 上清充通大¥ SHEAMGRAI DUD TONO UHTVEREETTY Reviews ●Rishi Raj Extended the concept of Ashby's Map,using an atomistic method. Suitable to pure metal and dilute alloys. For many commercial alloys,difficult to determine the material parameters. TTM 10 0.4 0.6 0.8 102 Adiabatic 102 10 heating Ductile rupture Ductile fracture 4 3 Ductile 10-2 Melting uiens fracture Dynamic 10-1 Safe recrystal- Fail lization 10-4 10-2 Cavitation Fail 10-6 10-3 Wedge cracking 10-8 10-4 0.5TM TM 300 400500 600 700 800 900 Absolute temperature T(K) Institute of Forming Technology Equipment 10
General Review Institute of Forming Technology & Equipment Reviews 10 Rishi Raj Extended the concept of Ashby’s Map, using an atomistic method. Suitable to pure metal and dilute alloys. For many commercial alloys, difficult to determine the material parameters

Basics for processing maps 上产克大睾 SHEAMGHAI DUD TONO UHTVEREETTY Dynamic materials model ●Prasad YVRK Prasad proposed processing map based on Dynamic materials model (DMM). ● A processing map consists of a superimposition of a power dissipation map and an instability map at different temperatures and strain rates.The basis of the processing maps is the dynamic materials model(DMM). The flow stress,when the strain and temperature are fixed,is given by: O=Kξm where K is a material constant,m is the strain rate sensitivity and can be expressed as follow: m=0(Ino)/(In) Institute of Forming Technology Equipment 11
Basics for processing maps Institute of Forming Technology & Equipment Dynamic materials model 11 Prasad Y V R K Prasad proposed processing map based on Dynamic materials model (DMM). A processing map consists of a superimposition of a power dissipation map and an instability map at different temperatures and strain rates. The basis of the processing maps is the dynamic materials model (DMM). The flow stress, when the strain and temperature are fixed, is given by: where K is a material constant, m is the strain rate sensitivity and can be expressed as follow: m ln ln m K