
先进材料疑固实验室 Laboratory of Advanced Materials Solidification 1896 1920 1987 2006 Solidification of single phase alloys(3) Dr.Mingxu Xia anced Mat 上浒充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
1896 1920 1987 2006 Solidification of single phase alloys (3) Dr. Mingxu Xia
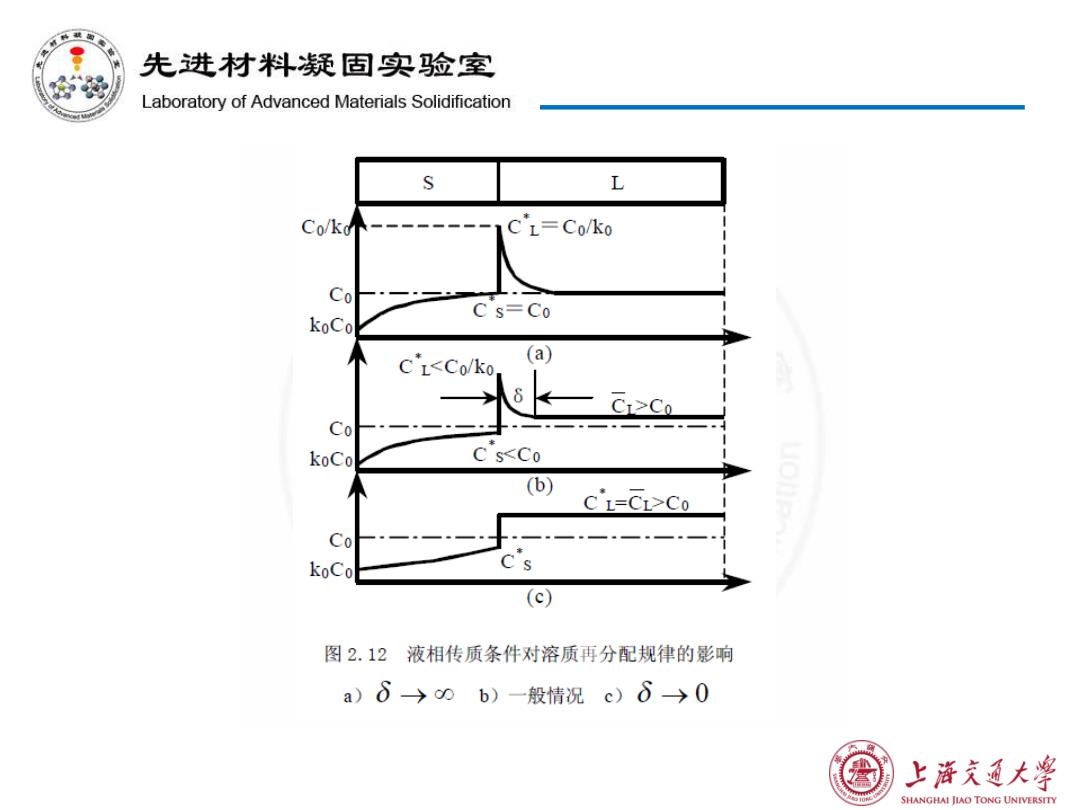
先进材料疑固实验室 Laboratory of Advanced Materials Solidification S L Co/k个 CL=Co/ko Co C s=Co koCo C'LCo C0一 koCo C sCo Co koCo (c) 图2.12液相传质条件对溶质再分配规律的影响 a)6→0b)一般情况c)8→0 上浒充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY

先进材料疑固实验室 Laboratory of Advanced Materials Solidification 5 =0.5 =0.5 ◆◆k=0.1 ◆◆k点=0.1 -而=0.01 ■点=0.01 △4=0.001 △4k=0.001 3 2 -△△△△ 44 0 200 400 600 800 1000 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 Vp/De 1+vp(E -L)/2De (a)Initial transients (b)Final transients Fig.5.6 The computed initial and final solid composition profiles for binary alloys with different values of ko,solidified at constant velocity.The data in this figure correspond to De/vp=1 mm. 上浒充通大 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY

先进材料疑固实验室 References Laboratory of Advanced Materials Solidification M.C.Flemings,凝固过程 © W.Kurz,凝固原理 ©介万奇,凝固技术 Aavalcer 上浒充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
References M.C.Flemings, 凝固过程 W.Kurz,凝固原理 介万奇,凝固技术

先进材料疑固实验室 OUTLINE Laboratory of Advanced Materials Solidification Solute Redistribution Solute distribution coefficient Solute redistribution in equilibrium state Solute redistribution in non-equilibrium state Solute distribution in front of S/L interface Application:Zone melting Morphology Instability of a S/L interface Constitutional undercooling Morphological instability of a S/L interface Solidification microstructure:Cells and dendrites 上浒充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
OUTLINE Solute Redistribution • Solute distribution coefficient • Solute redistribution in equilibrium state • Solute redistribution in non-equilibrium state • Solute distribution in front of S/L interface • Application: Zone melting Morphology Instability of a S/L interface • Constitutional undercooling • Morphological instability of a S/L interface • Solidification microstructure: Cells and dendrites

先进材料疑固实验室 Application:Zone melting Laboratory of Advanced Materials Solidification Process of zone melting: Start with a solid alloy bar with uniform cross-section. Place the bar horizontally. Only melt the bar within a short zone with a small heater. Move the heater along the bar from one end to the other end. Repeat the process for many times. y o vancedl Matera 上浒充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
Application: Zone melting Process of zone melting: • Start with a solid alloy bar with uniform cross-section. • Place the bar horizontally. • Only melt the bar within a short zone with a small heater. • Move the heater along the bar from one end to the other end. • Repeat the process for many times
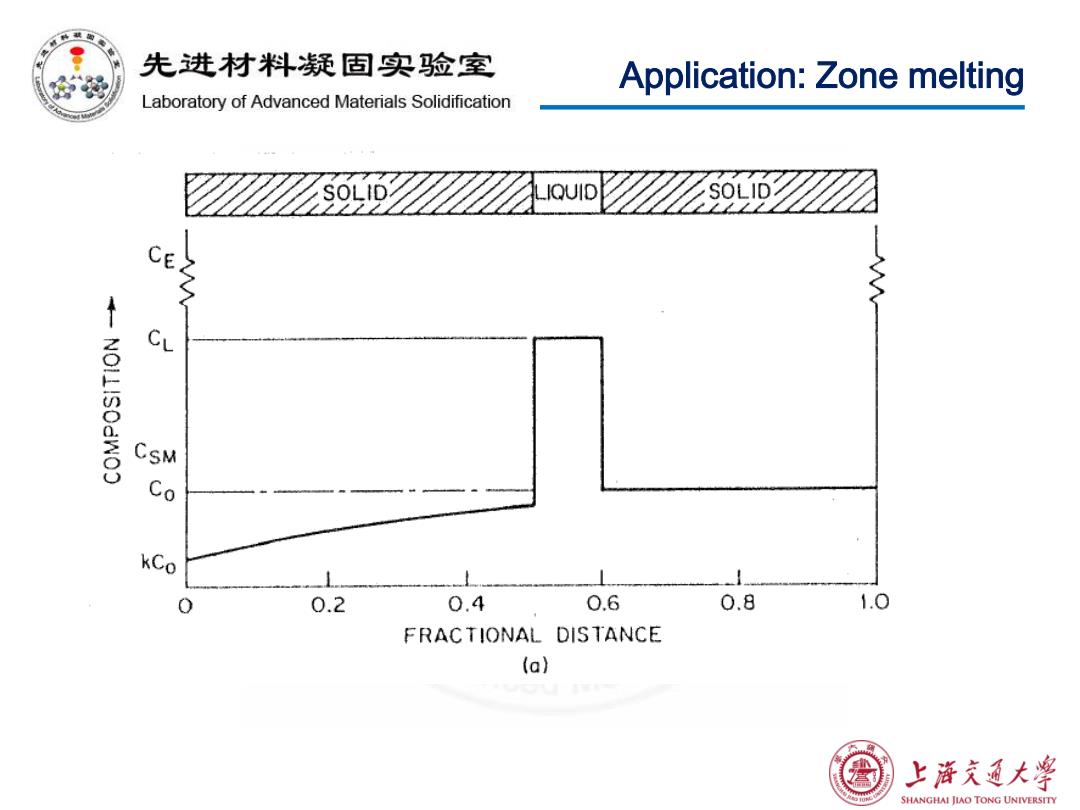
先进材料疑固实验室 Application:Zone melting Laboratory of Advanced Materials Solidification IQUID CE CL CSM kCo 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0 FRACTIONAL DISTANCE (a) 上游文通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
Application: Zone melting

先进材料疑固实验室 Application:Zone melting Laboratory of Advanced Materials Solidification Zone melting is a widely used technique for purifying metals. We can derive the equation used to calculate the solute concentration distribution in the solid after the first pass. ©Assumptions: No solute diffusion in the solid Complete solute diffusion and mixing in the liquid zone. 上浒充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
Application: Zone melting Zone melting is a widely used technique for purifying metals. We can derive the equation used to calculate the solute concentration distribution in the solid after the first pass. Assumptions: • No solute diffusion in the solid • Complete solute diffusion and mixing in the liquid zone

先进材料疑固实验室 Application:Zone melting Laboratory of Advanced Materials Solidification From the mass balance,we have: (CL*-Cs*)Adx+(Co-CL*)Adx ALdCL* (1) L is the length of the liquid zone,A is the cross-section area of the bar. Equation(1)can be simplified to get: (Co-Cs*)dx LdCL* (2) We know Cs*=kCL*,so we can change equation(2)into: k(Co-Cs*)dx LdCs* anced M (3) 上海充通大¥ SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
Application: Zone melting From the mass balance, we have: (CL* - CS*)Adx + (C0 – CL*) Adx = ALdCL * (1) L is the length of the liquid zone, A is the cross-section area of the bar. Equation (1) can be simplified to get: (C0 – CS*) dx = LdCL * (2) We know CS*=kCL*, so we can change equation (2) into: k(C0 – CS*) dx = LdCS * (3)
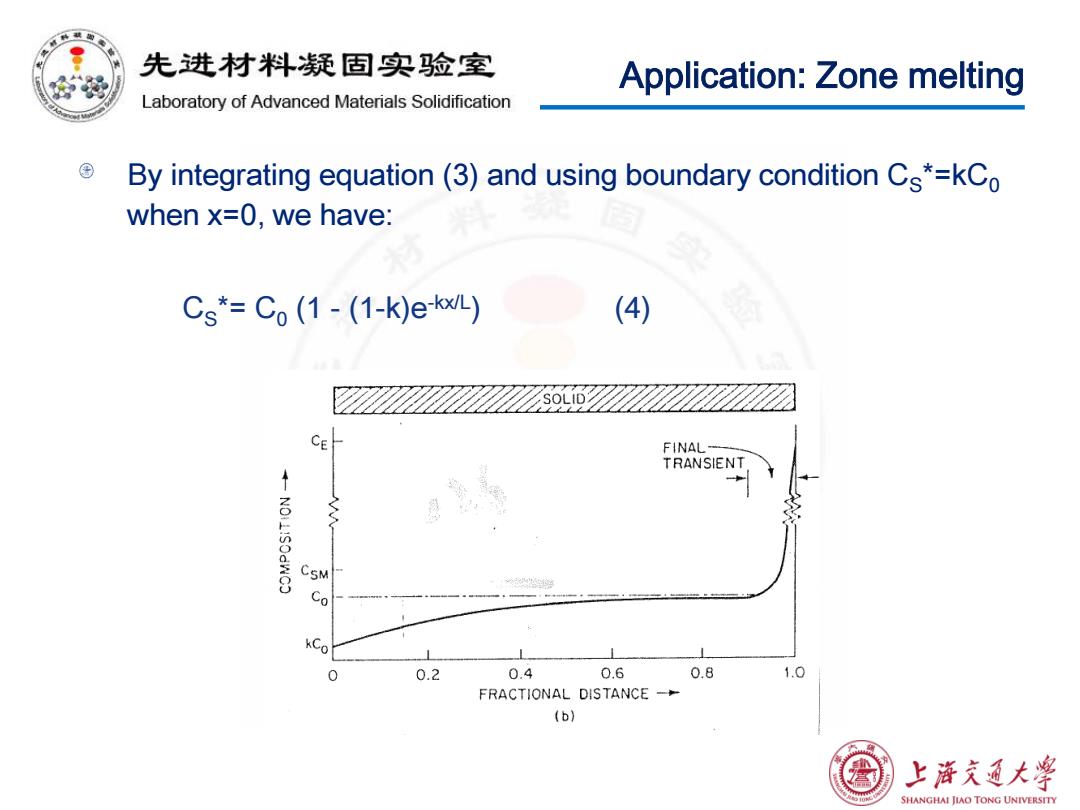
先进材料疑固实验室 Application:Zone melting Laboratory of Advanced Materials Solidification By integrating equation(3)and using boundary condition Cs*=kCo when x=0,we have: Cs*=Co(1-(1-k)e-kx/L) (4) CE FINAL- TRANSIENT CSM Co L 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0 FRACTIONAL DISTANCE- (b) 上浒充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
Application: Zone melting By integrating equation (3) and using boundary condition CS*=kC0 when x=0, we have: CS*= C0 (1 - (1-k)e-kx/L) (4)