
先进材料疑固实验室 Laboratory of Advanced Materials Solidification 1896 1920 1987 2006 ciquidmeta metal with the atomle structure oraliquld Nucleation in solidification(2) Dr.Mingxu Xia anced Mate 周 上浒充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
1896 1920 1987 2006 Nucleation in solidification (2) Dr. Mingxu Xia
先进材料疑固实验室 Outline Laboratory of Advanced Materials Solidification Solidification Concepts: >Definition >Nucleation free energy Thermo performance >Nucleation barrier Conventional Nucleation Theory >Critical nucleus >Homogeneous nucleation Heterogeneous nucleation >Nucleation rate Nucleation rate and its control Nucleation rate >Grain refining >Metallic glass Further Nucleation in atomic level Non-Conventional Nucleation Theory nced 上浒充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
Outline Solidification Definition Thermo performance Conventional Nucleation Theory Homogeneous nucleation Heterogeneous nucleation Nucleation rate and its control Nucleation rate Grain refining Metallic glass Further Nucleation in atomic level Non-Conventional Nucleation Theory Concepts: Nucleation free energy Nucleation barrier Critical nucleus Nucleation rate

先进材料疑固实验室 Nucleation rate and its control Laboratory of Advanced Materials Solidification Nucleation rate is the number of nucleation events per unit volume per unit time. For the nucleation of a solid crystal to occur,one of the fluctuating solid embryos needs to reach a radius being equal or greater than Rc. The rate for this event to occur is the nucleation rate,1. 上降充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
Nucleation rate and its control • Nucleation rate is the number of nucleation events per unit volume per unit time. • For the nucleation of a solid crystal to occur, one of the fluctuating solid embryos needs to reach a radius being equal or greater than Rc. • The rate for this event to occur is the nucleation rate, I
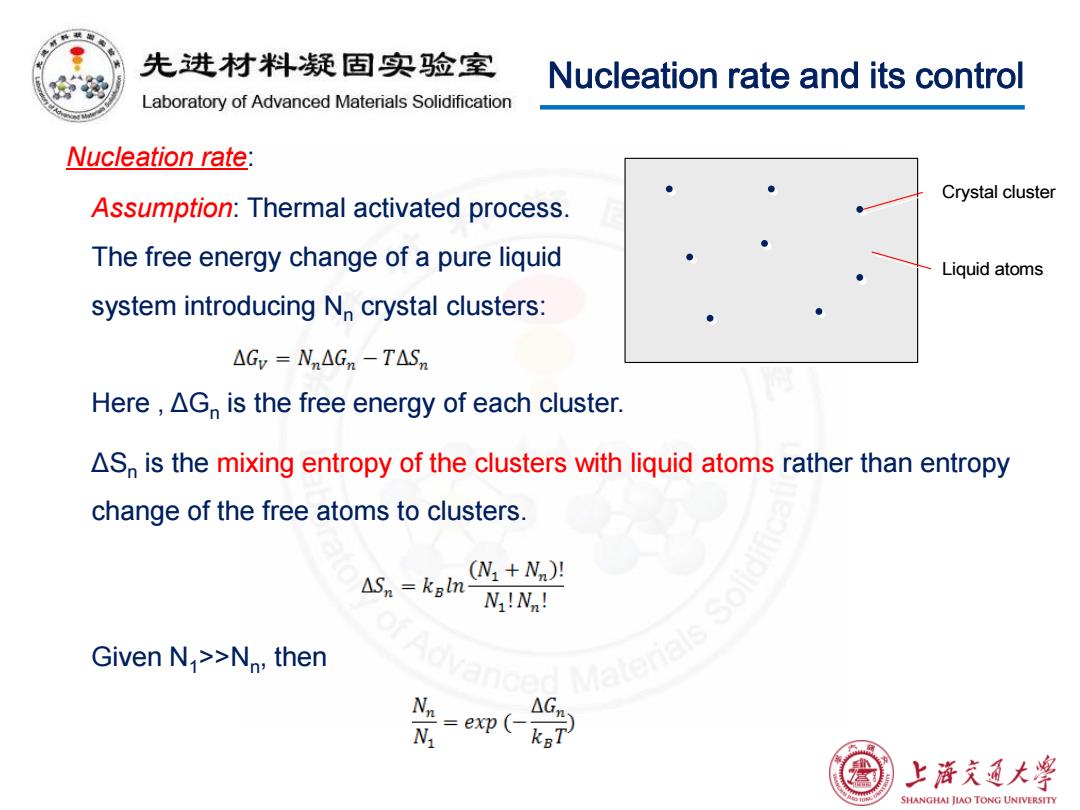
先进材料疑固实验室 Nucleation rate and its control Laboratory of Advanced Materials Solidification Nucleation rate: Crystal cluster Assumption:Thermal activated process. The free energy change of a pure liquid Liquid atoms system introducing N crystal clusters: △Gv-Nn△Gn-T△Sm Here,AG is the free energy of each cluster. AS is the mixing entropy of the clusters with liquid atoms rather than entropy change of the free atoms to clusters. △Sn=kal (N1+Nn)! N!N! Given N >>Nn,then G =ep( 上降充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
Nucleation rate and its control Nucleation rate: Assumption: Thermal activated process. The free energy change of a pure liquid system introducing Nn crystal clusters: Here , ΔGn is the free energy of each cluster. Crystal cluster Liquid atoms ΔSn is the mixing entropy of the clusters with liquid atoms rather than entropy change of the free atoms to clusters. Given N1>>Nn , then
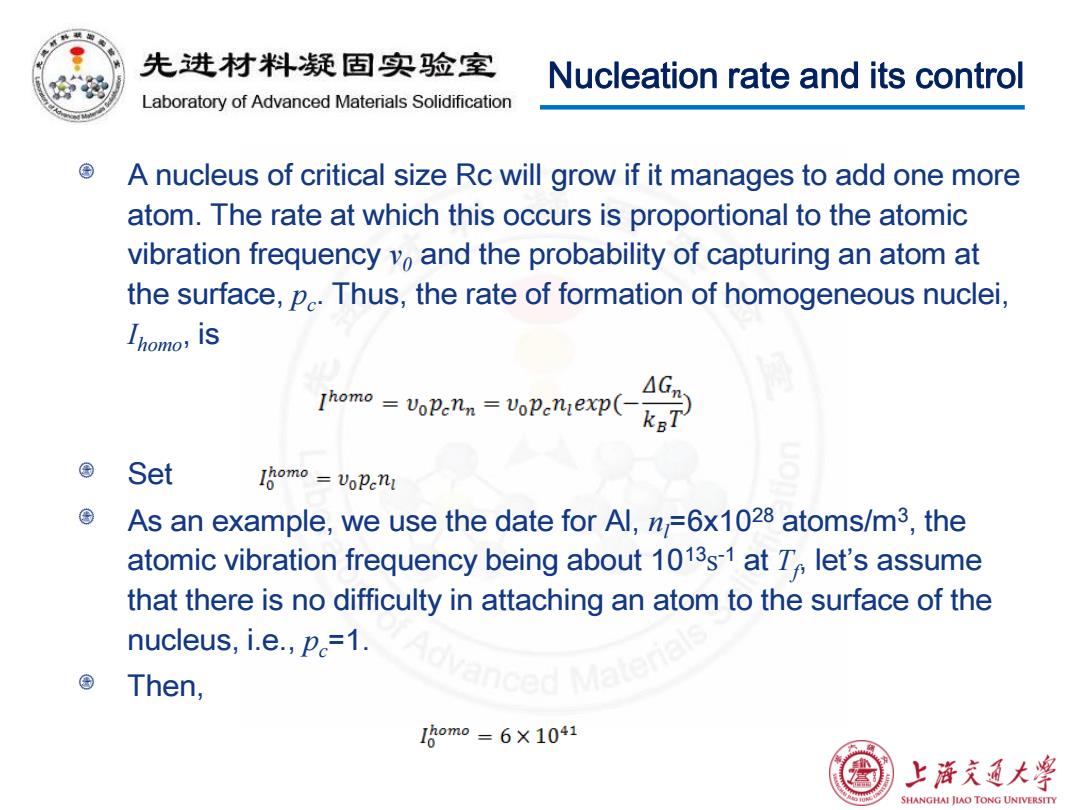
积 先进材料疑固实验室 Nucleation rate and its control Laboratory of Advanced Materials Solidification A nucleus of critical size Rc will grow if it manages to add one more atom.The rate at which this occurs is proportional to the atomic vibration frequency vo and the probability of capturing an atom at the surface,p.Thus,the rate of formation of homogeneous nuclei, Ihomo,iS Thomo =VoPenn VoPeniexp( △G Set Iomo=voPenI As an example,we use the date for Al,n=6x1028 atoms/m3,the atomic vibration frequency being about 1013s-1 at T let's assume that there is no difficulty in attaching an atom to the surface of the nucleus,i.e.,p=1. Then, I8om0=6×1041 上浒充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
Nucleation rate and its control A nucleus of critical size Rc will grow if it manages to add one more atom. The rate at which this occurs is proportional to the atomic vibration frequency ν0 and the probability of capturing an atom at the surface, pc . Thus, the rate of formation of homogeneous nuclei, Ihomo, is Set As an example, we use the date for Al, nl=6x1028 atoms/m3 , the atomic vibration frequency being about 1013s -1 at Tf , let’s assume that there is no difficulty in attaching an atom to the surface of the nucleus, i.e., pc=1. Then
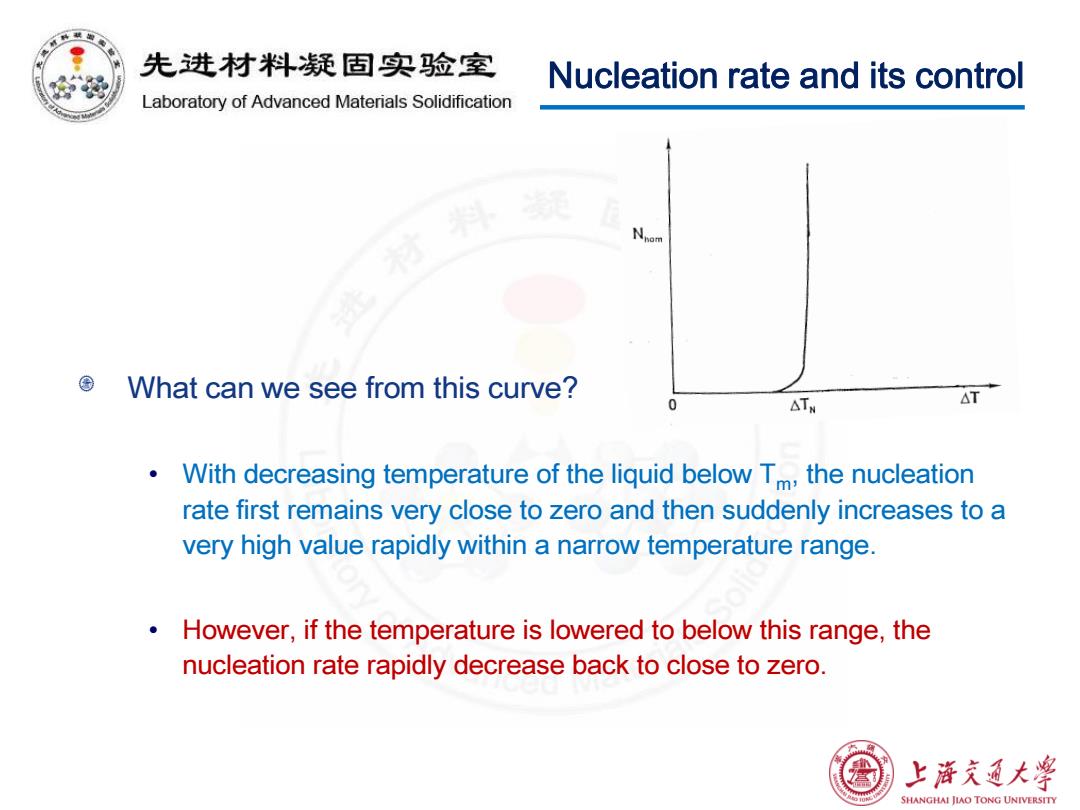
先进材料疑固实验室 Nucleation rate and its control Laboratory of Advanced Materials Solidification What can we see from this curve? △TW △T o With decreasing temperature of the liquid below Tm,the nucleation rate first remains very close to zero and then suddenly increases to a very high value rapidly within a narrow temperature range. However,if the temperature is lowered to below this range,the nucleation rate rapidly decrease back to close to zero. 上游文通大¥ SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
What can we see from this curve? • With decreasing temperature of the liquid below Tm, the nucleation rate first remains very close to zero and then suddenly increases to a very high value rapidly within a narrow temperature range. • However, if the temperature is lowered to below this range, the nucleation rate rapidly decrease back to close to zero. Nucleation rate and its control
先进材料疑固实验室 Nucleation rate and its control Laboratory of Advanced Materials Solidification The reasons for this phenomenon: With decreasing temperature of the liquid,the magnitude of the nucleation barrier decreases>a higher nucleation rate,but atom diffusivity also decreases >a lower nucleation rate. These two opposite effects of decreasing temperature lead to a temperature at which the nucleation rate reaches its maximum. vanced Materd 上游充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
Nucleation rate and its control The reasons for this phenomenon: • With decreasing temperature of the liquid, the magnitude of the nucleation barrier decreases a higher nucleation rate, but atom diffusivity also decreases a lower nucleation rate. • These two opposite effects of decreasing temperature lead to a temperature at which the nucleation rate reaches its maximum

先进材料疑固实验室 Nucleation rate and its control Laboratory of Advanced Materials Solidification When the cooling rate is very high,the nucleation of solid crystal may be avoided in the process of rapid cooling of the liquid metal or alloy until the liquid turns into a solid through glass transition.This solid is called metallic glass. vanced Materials S 上游充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
Nucleation rate and its control • When the cooling rate is very high, the nucleation of solid crystal may be avoided in the process of rapid cooling of the liquid metal or alloy until the liquid turns into a solid through glass transition. This solid is called metallic glass
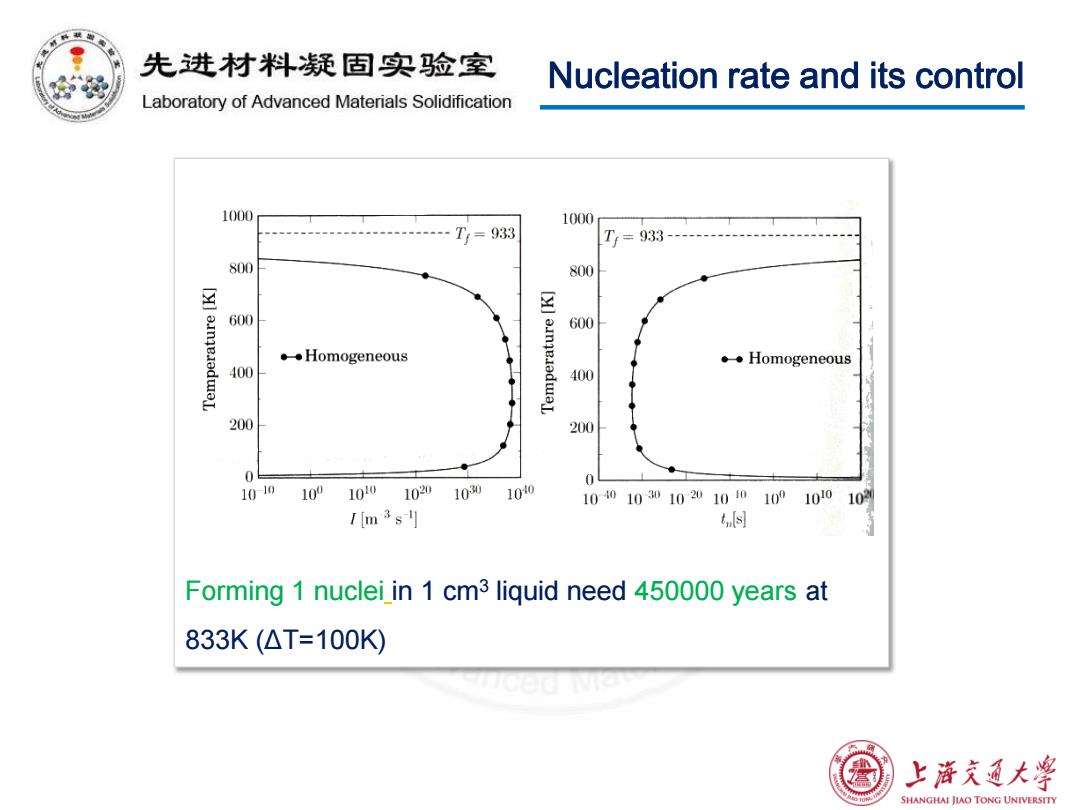
先进材料疑固实验室 Nucleation rate and its control Laboratory of Advanced Materials Solidification 1(000 1000 T=933 Tr=933 800 800 600 [y]ainqeiadwaL 600 ◆◆Homogeneous 。◆Homogeneous 400 400 200 200 0 1010 109 100 1020 1030 100 10401030102010101001010 102 1m3s1 n母 Forming 1 nuclei in 1 cm3 liquid need 450000 years at 833K(△T=100K 上游文通大¥ SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
Nucleation rate and its control Forming 1 nuclei in 1 cm3 liquid need 450000 years at 833K (ΔT=100K)
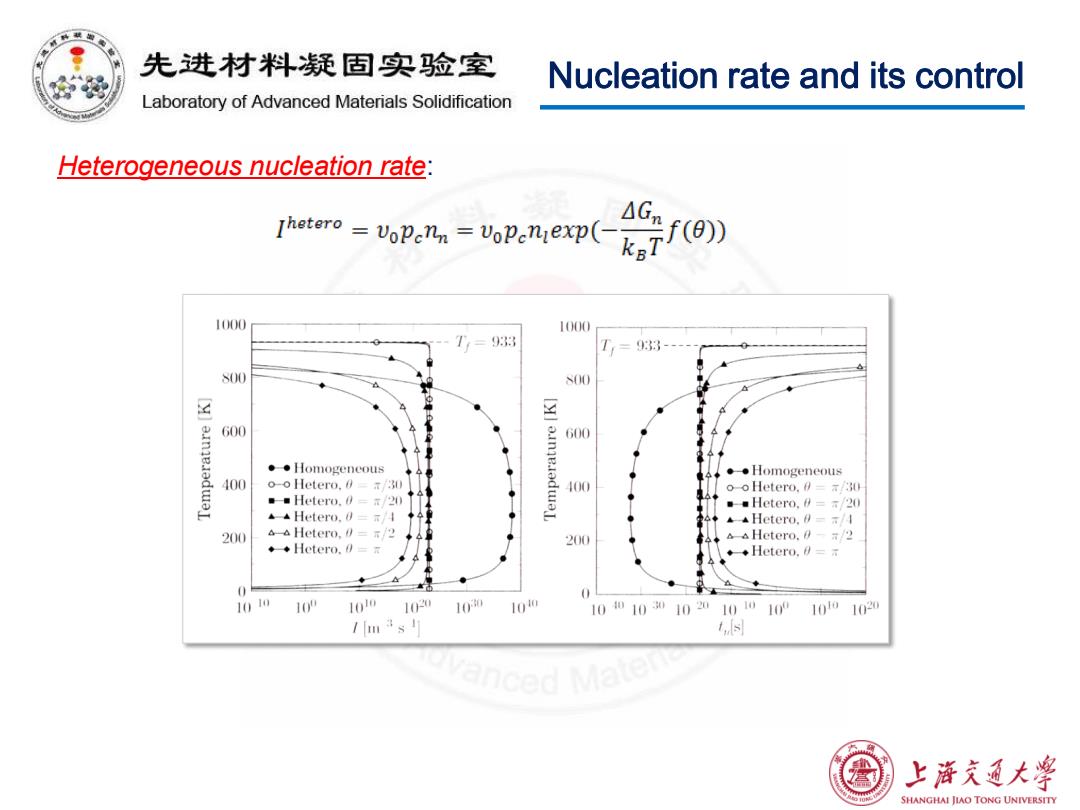
先进材料疑固实验室 Nucleation rate and its control Laboratory of Advanced Materials Solidification Heterogeneous nucleation rate: Thotero vopenn=VoPeniexp( 1000 1000 T,=933 T= 33- S00 S00 三 600 00 。◆Homogeneous ◆◆Homogeneous 400 o-o Hetero.030 o-o Hetero.30 。■Hetero.0=r/20) 。Hetero.∥=T/20 Hetero,0=π/A ▲Hetero.∥=a/I 200 Hetero,∥=r/2 Hetero.0/2 ◆◆Hetero.0=r 200 ◆Hetero,a=r 直 1010 1 10o 10 10 10 10010010201010100 1010 102 /3s Ls ced 上游文通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
Nucleation rate and its control Heterogeneous nucleation rate: