
先进材料疑固实验室 Laboratory of Advanced Materials Solidification 1896 1920 1987 2006 ciquidmeta metal with the atomle structure oraliquld Nucleation in solidification(1) Dr.Mingxu Xia anced Mate 周 上浒充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
1896 1920 1987 2006 Nucleation in solidification (1) Dr. Mingxu Xia
先进材料疑固实验室 LOGO of LAMS Laboratory of Advanced Materials Solidification 进材料凝固实验宝 Advanced Material Amorphous Crystal What controls nucleation? How does it control? When nucleation initiates? How does nucleation initiate? Why growth is oriented? How is it decided? 上游文通大¥ SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
LOGO of LAMS Amorphous Crystal What controls nucleation? When nucleation initiates? Why growth is oriented? How does it control? How does nucleation initiate? How is it decided?
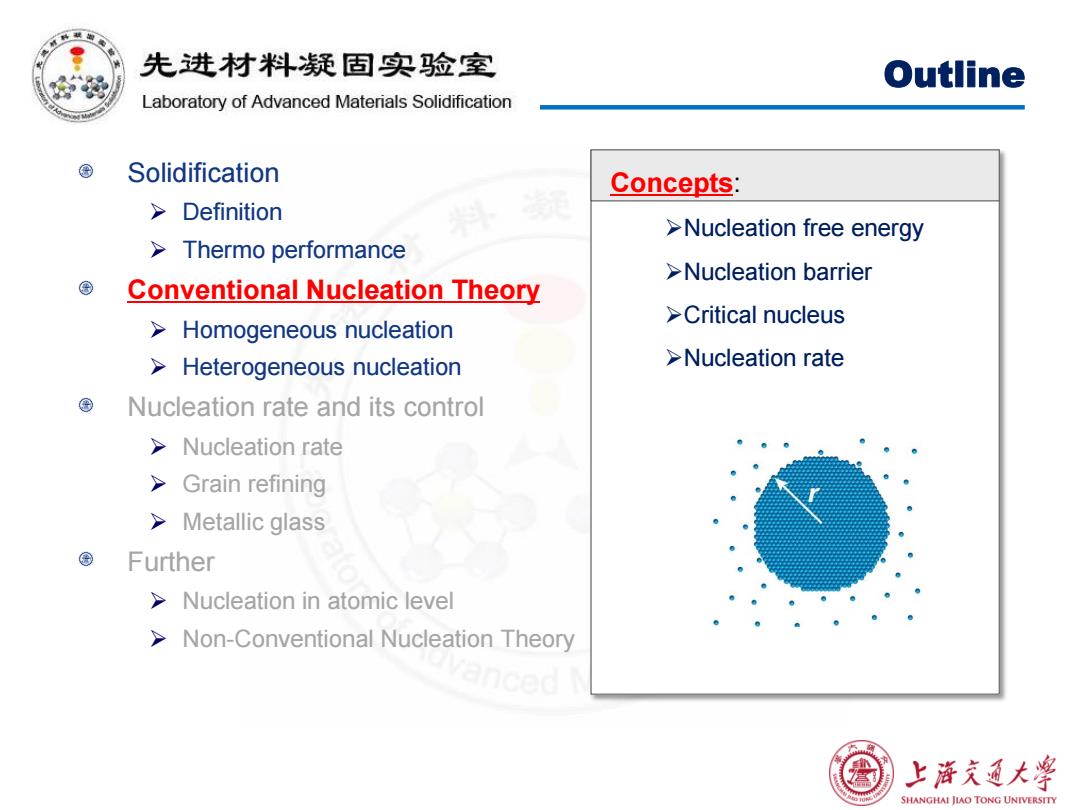
先进材料疑固实验室 Outline Laboratory of Advanced Materials Solidification Solidification Concepts: >Definition >Nucleation free energy Thermo performance >Nucleation barrier Conventional Nucleation Theory >Critical nucleus Homogeneous nucleation Heterogeneous nucleation >Nucleation rate Nucleation rate and its control >Nucleation rate >Grain refining >Metallic glass Further >Nucleation in atomic level Non-Conventional Nucleation Theory anced 上浒充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
Outline Solidification Definition Thermo performance Conventional Nucleation Theory Homogeneous nucleation Heterogeneous nucleation Nucleation rate and its control Nucleation rate Grain refining Metallic glass Further Nucleation in atomic level Non-Conventional Nucleation Theory Concepts: Nucleation free energy Nucleation barrier Critical nucleus Nucleation rate
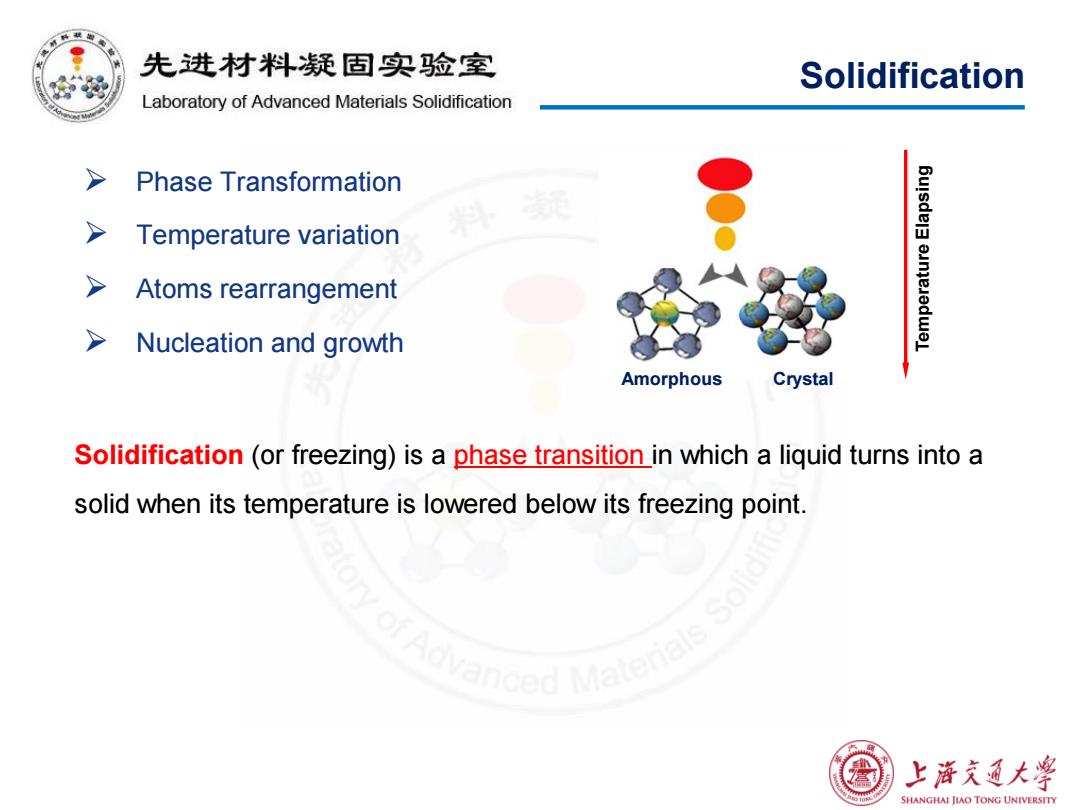
先进材料疑固实验室 路 Solidification Laboratory of Advanced Materials Solidification > Phase Transformation > Temperature variation Atoms rearrangement Nucleation and growth Amorphous Crystal Solidification (or freezing)is a phase transition in which a liquid turns into a solid when its temperature is lowered below its freezing point. nced Ma 上降充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
Solidification Phase Transformation Temperature variation Atoms rearrangement Nucleation and growth Solidification (or freezing) is a phase transition in which a liquid turns into a solid when its temperature is lowered below its freezing point. Temperature Elapsing Amorphous Crystal

先进材料疑固实验室 Solidfiication Laboratory of Advanced Materials Solidification Nucleation is the very initial stage of phase transformation during which small embryos of the new phase (or phases)become large enough to grow by themselves. Nucleation has both a thermodynamic driving force and a thermodynamic barrier. vanced Materials Solic 上降充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
Solidfiication Nucleation is the very initial stage of phase transformation during which small embryos of the new phase (or phases) become large enough to grow by themselves. Nucleation has both a thermodynamic driving force and a thermodynamic barrier
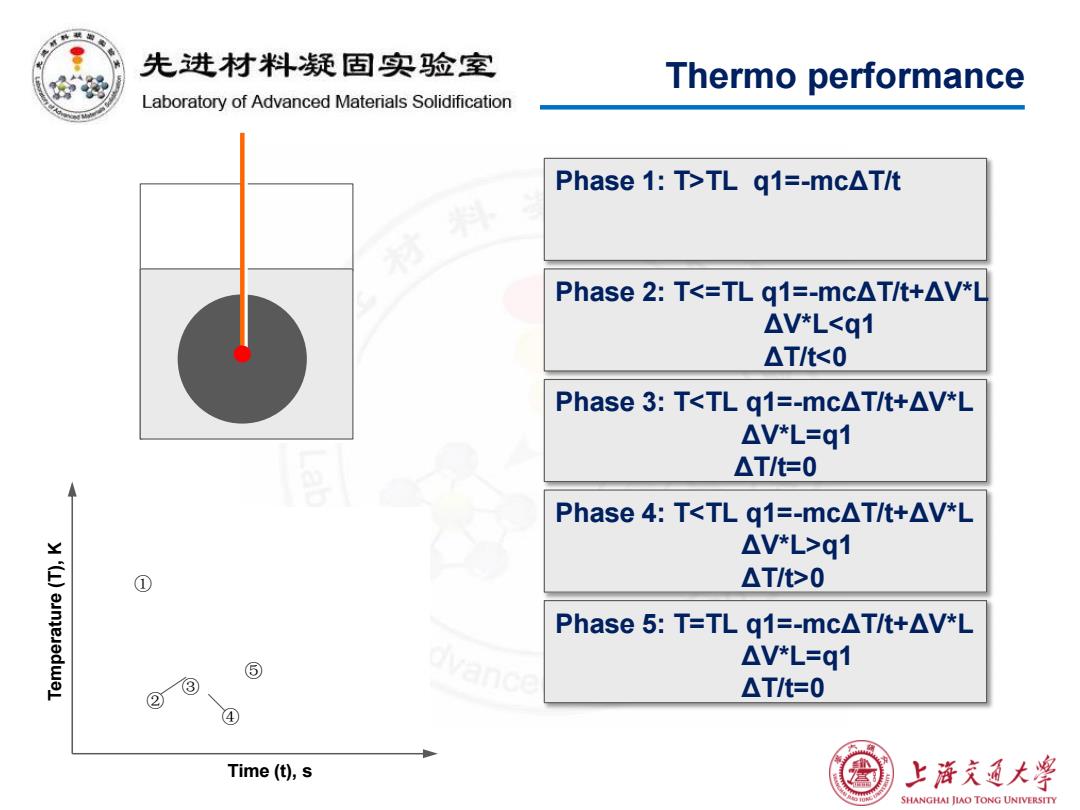
先进材料疑固实验室 Thermo performance Laboratory of Advanced Materials Solidification Phase 1:T>TL g1=-mcAT/t Phase2:Tq1 ① △T/t>0 unjeJedwel Phase5:T=TLq1=-mc△T/t+△V*L ⑤ △V*L=q1 ③ ② △T/t=0 ④ Time(t),s 上游充通大¥ SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
Thermo performance Temperature (T), K Time (t), s Phase 1: T>TL q1=-mcΔT/t ① Phase 3: Tq1 ΔT/t>0 ④

Conventional Nucleation 先进材料疑固实验室 Laboratory of Advanced Materials Solidification Theory(CNT) When T=Tm,Gs GL,both the liquid and the solid are stable phases,and there is no thermodynamic driving force for solidification of the liquid or melting of the solid. (Tm is the melting point of the solid,and Gs and GL are the free energies of the solid and the liquid respectively.) www.shutterstock.com 94316782 上浒充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
Conventional Nucleation Theory(CNT) When T= Tm, GS = GL , both the liquid and the solid are stable phases, and there is no thermodynamic driving force for solidification of the liquid or melting of the solid. (Tm is the melting point of the solid, and GS and GL are the free energies of the solid and the liquid respectively.)
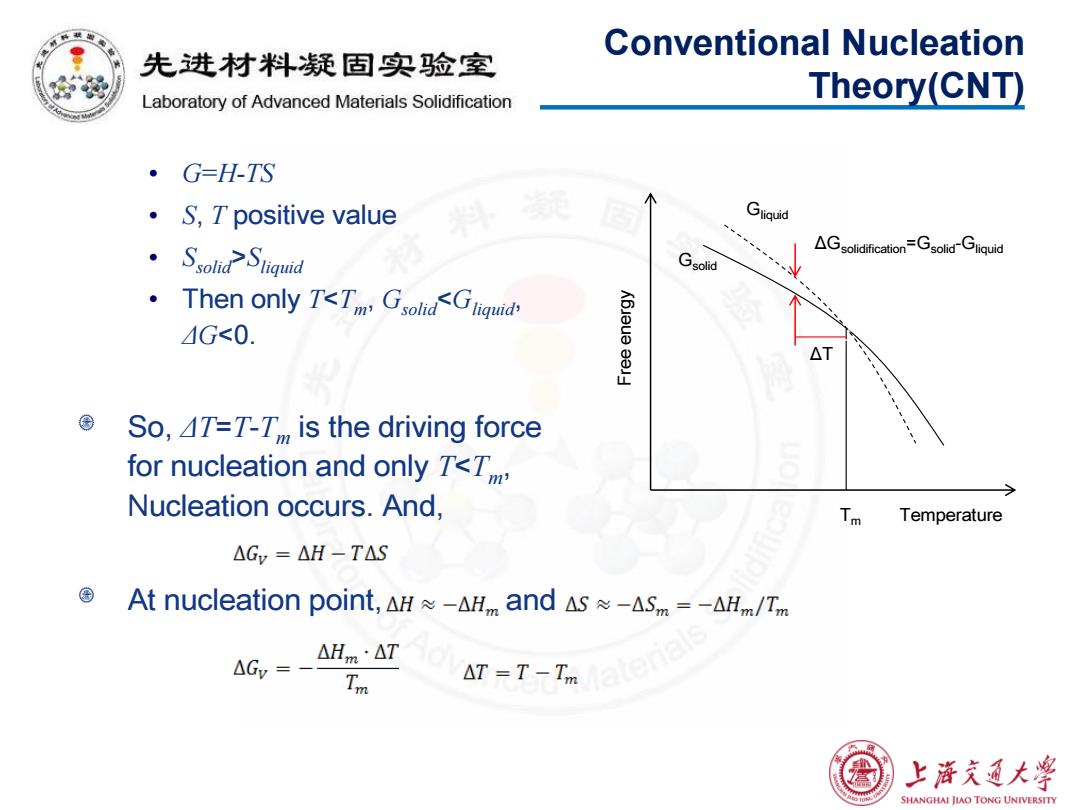
Conventional Nucleation 先进材料疑固实验室 Laboratory of Advanced Materials Solidification Theory(CNT) ·G=H-TS ·S,T positive value Gliquid ·Ssolid2 Siqud AGsolidification=Gsolid Gliquid Gsolid Then only T<T Gsolid<Gliquid G<0. △ So,4T=T-T,,is the driving force for nucleation and only T<T, Nucleation occurs.And, Tm Temperature △GY=△H-TAS At nucleation point,.△H≈-△and△s≈-ASm=-AHm/Tm △Hm·△T Tm △T=T-Taeri8 上游充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
Conventional Nucleation Theory(CNT) • G=H-TS • S, T positive value • Ssolid>Sliquid • Then only T<Tm , Gsolid<Gliquid, ΔG<0. So, ΔT=T-Tm is the driving force for nucleation and only T<Tm, Nucleation occurs. And, At nucleation point, and Gsolid Gliquid ΔGsolidification=Gsolid-Gliquid Tm Free energy Temperature ΔT
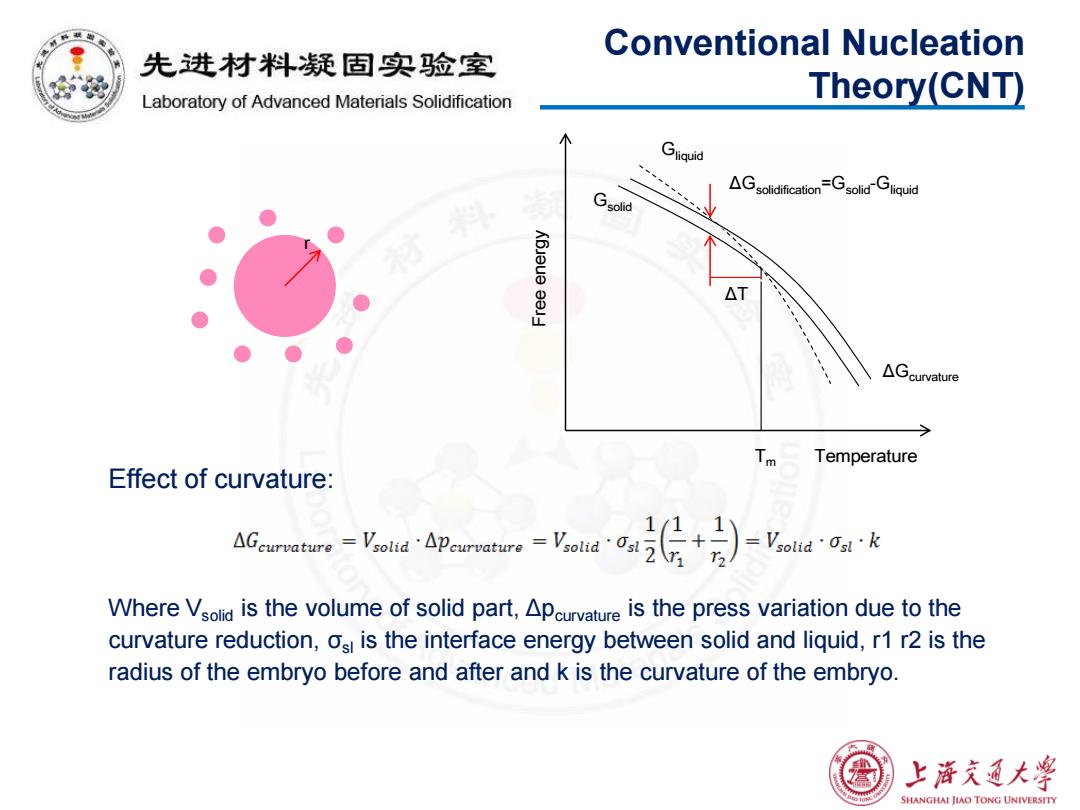
Conventional Nucleation 先进材料疑固实验室 Laboratory of Advanced Materials Solidification Theory(CNT) Gliquid AGsolidificationGsolidGliquid Gsolid △ △Gcurvature 人 Temperature Effect of curvature: AGeurvature=VsoldApeurvatureVsold Where Vsolid is the volume of solid part,Apcurvature is the press variation due to the curvature reduction,osi is the interface energy between solid and liquid,r1 r2 is the radius of the embryo before and after and k is the curvature of the embryo. 上游文通大¥ SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
Effect of curvature: Where Vsolid is the volume of solid part, Δpcurvature is the press variation due to the curvature reduction, σsl is the interface energy between solid and liquid, r1 r2 is the radius of the embryo before and after and k is the curvature of the embryo. Conventional Nucleation Theory(CNT) r Gsolid Gliquid ΔGsolidification=Gsolid-Gliquid Tm Free energy Temperature ΔT ΔGcurvature
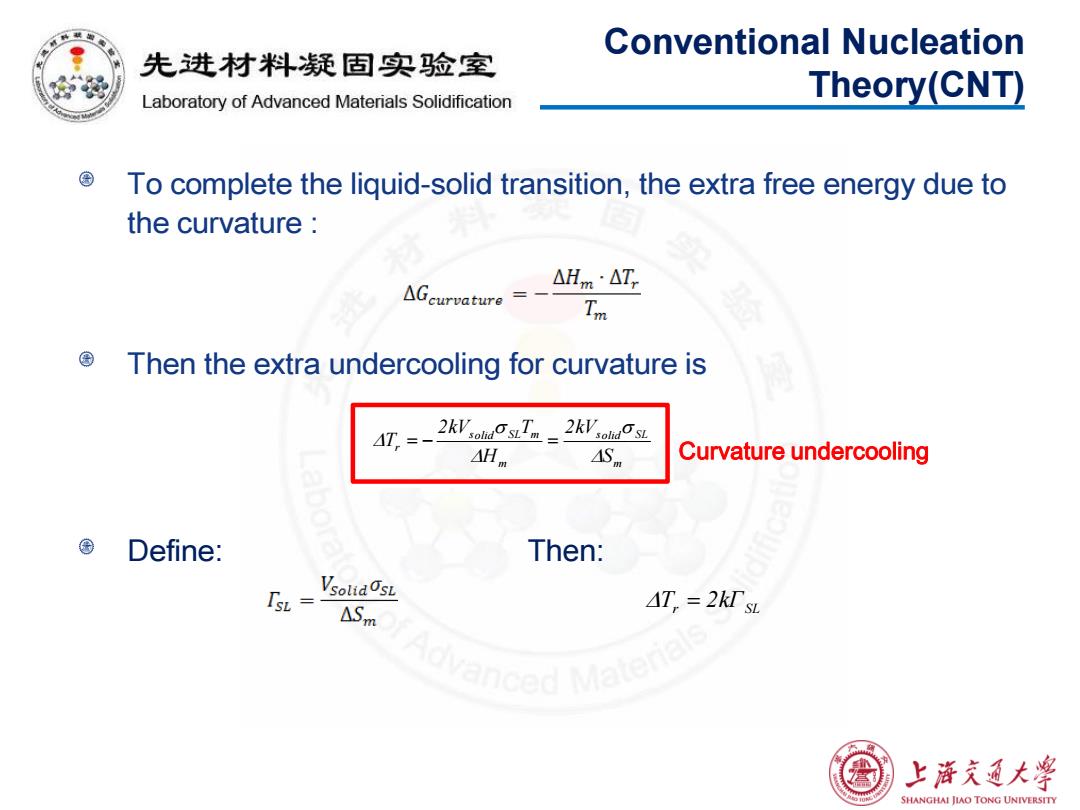
Conventional Nucleation 先进材料疑固实验室 Laboratory of Advanced Materials Solidification Theory(CNT) To complete the liquid-solid transition,the extra free energy due to the curvature △Hm·△T, △Gcurvature= Im Then the extra undercooling for curvature is 2 kV OsT。_2 kVuOs AH AS Curvature undercooling Define: Then: VsoudOsL ASm AT,=2kl'sL 上游充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
To complete the liquid-solid transition, the extra free energy due to the curvature : Then the extra undercooling for curvature is Define: Then: Conventional Nucleation Theory(CNT) m solid SL m solid SL m r S 2kV H 2kV T T Curvature undercooling r ΓSL T 2k