
上充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY Principles of Materials Processing -Technology of plasticity 漏 员是 LIU Juan (liujuan@situ.edu.cn,62933955,13818928215) Institute of Forming Technology Equipment SMSE SJTU
Principles of Materials Processing ──Technology of plasƟcity LIU Juan (liujuan@sjtu.edu.cn, 62933955, 13818928215) Institute of Forming Technology & Equipment SMSE SJTU

Outline Introduction Processing maps Elements of plastic theory Plastic deformation mechanism Recovery recrystallization
Outline Processing maps Plastic deformation mechanism Elements of plastic theory Recovery & recrystallization Introduction
上清充通大学 SHEAMGRAI DUD TONO UHTVEREETTY Introduction General Review Tensile Response of Materials Processing maps Effect of temperature strain rate Elements of plastic theory plastic deformation mechanism Recovery recrystallization
Processing maps Introduction 1 Elements of plastic theory Recovery & recrystallization 1 1 General Review Tensile Response of Materials Effect of temperature & strain rate 1 plastic deformation mechanism 1

Reference books 上清充通大¥ SHEAMGRAI DUD TONO UHTVEREETTY Mechanical Metallurgy* George E Dieter McGraw-Hill Book Company,London(1988) Institute of Forming Technology Equipment 41
Reference books Institute of Forming Technology & Equipment 4 • Mechanical Metallurgy * George E Dieter McGraw‐Hill Book Company, London (1988)
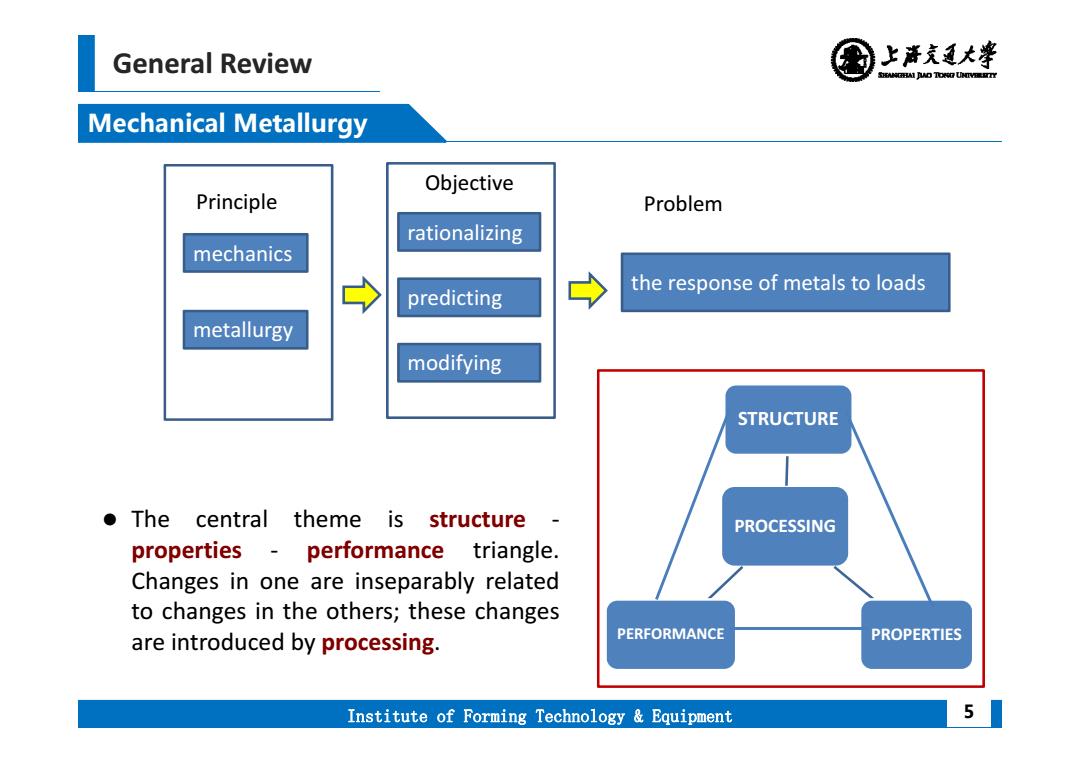
General Review 上清充通大¥ SHEAMGRAI DUD TONO UHTVEREETTY Mechanical Metallurgy Objective Principle Problem rationalizing mechanics → predicting 白 the response of metals to loads metallurgy modifying STRUCTURE The central theme is structure - PROCESSING properties performance triangle. Changes in one are inseparably related to changes in the others;these changes are introduced by processing PERFORMANCE PROPERTIES Institute of Forming Technology Equipment 5
General Review Institute of Forming Technology & Equipment Mechanical Metallurgy 5 The central theme is structure ‐ properties ‐ performance triangle. Changes in one are inseparably related to changes in the others; these changes are introduced by processing. PROCESSING STRUCTURE PERFORMANCE PROPERTIES mechanics metallurgy rationalizing predicting modifying the response of metals to loads Principle Objective Problem

General Review 4 上清充通大学 SHEAMGRAI DUD TONO UHTVEREETTY Overview of processes Solidification processes Particulate processes Shaping processes Deformation processes Material removal Processing Property enhancing Heat treatment operations processes Cleaning surface treatments Surface processing Manufacturing operations Coating deposition processes processes Welding Permanent joining processes Brazing soldering Assembly operations Adhesive bonding Threaded fasteners Mechanical fastening Permanent fastening methods Institute of Forming Technology Equipment 6
General Review Institute of Forming Technology & Equipment Overview of processes 6 Solidification processes Particulate processes Deformation processes Material removal Heat treatment Cleaning & surface treatments Coating & deposition processes Welding Brazing & soldering Adhesive bonding Threaded fasteners Permanent fastening methods Manufacturing processes Shaping processes Property enhancing processes Surface processing operations Permanent joining processes Mechanical fastening Processing operations Assembly operations

General Review 上产克大睾 SHEAMGHAI DUD TONO UHTVEREETTY Overview of metal forming Metal forming:to change the shape of metal workpieces. Plastic deformation:a permanent change of shape,i.e.,the stress in materials is larger than its yield strength. Usually a die-to force deformed metal into the shape of the die. Metal forming is divided into: (1)Bulk forming:large strain,small displacement,surface area to volume of the work is small. (2)Sheet forming:small strain,large displacement;Surface area to volume of the work is large. Institute of Forming Technology Equipment 7
General Review Institute of Forming Technology & Equipment Overview of metal forming 7 Metal forming: to change the shape of metal workpieces. Plastic deformation: a permanent change of shape, i.e., the stress in materials is larger than its yield strength. Usually a die → to force deformed metal into the shape of the die. Metal forming is divided into: (1) Bulk forming: large strain, small displacement, surface area to volume of the work is small. (2) Sheet forming: small strain, large displacement; Surface area to volume of the work is large
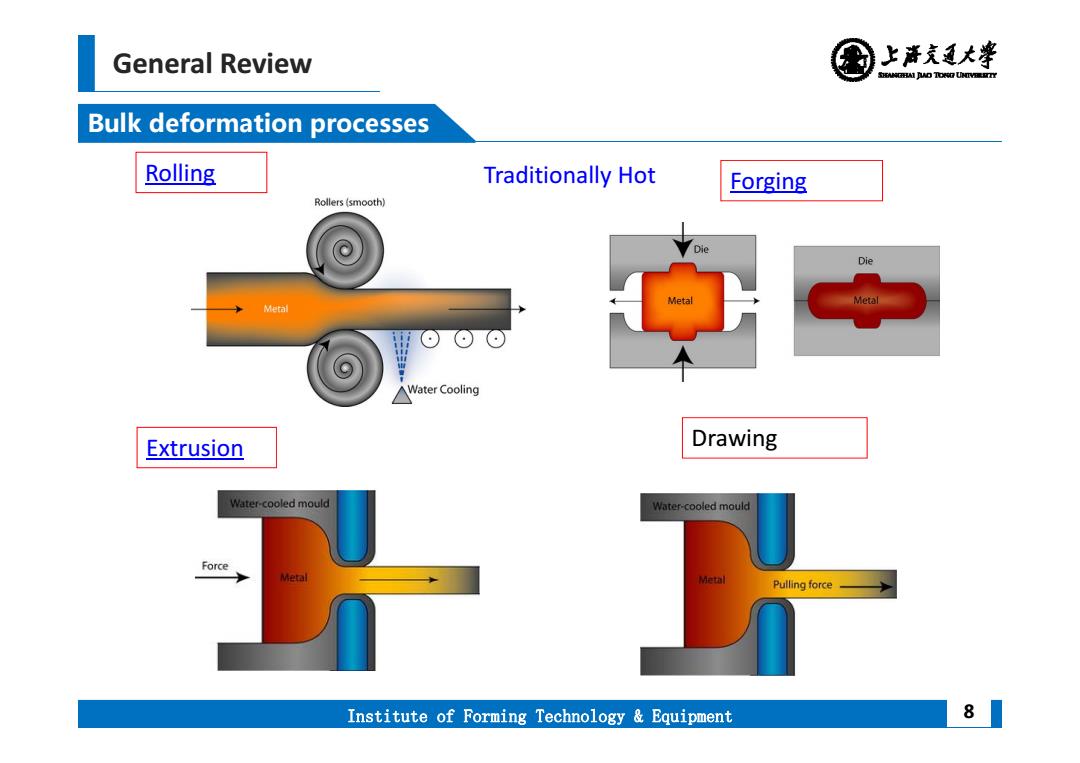
General Review 上清充通大学 SHEAMGRAI DUD TONO UHTVEREETTY Bulk deformation processes Rolling Traditionally Hot Forging Rollers(smooth) Die Metal Metal Metal △Water Cooling Extrusion Drawing Water-cooled mould Water-cooled mould Force Meta Metal Pulling force Institute of Forming Technology Equipment 8
General Review Institute of Forming Technology & Equipment Bulk deformation processes 8 Rolling Forging Extrusion Drawing Traditionally Hot
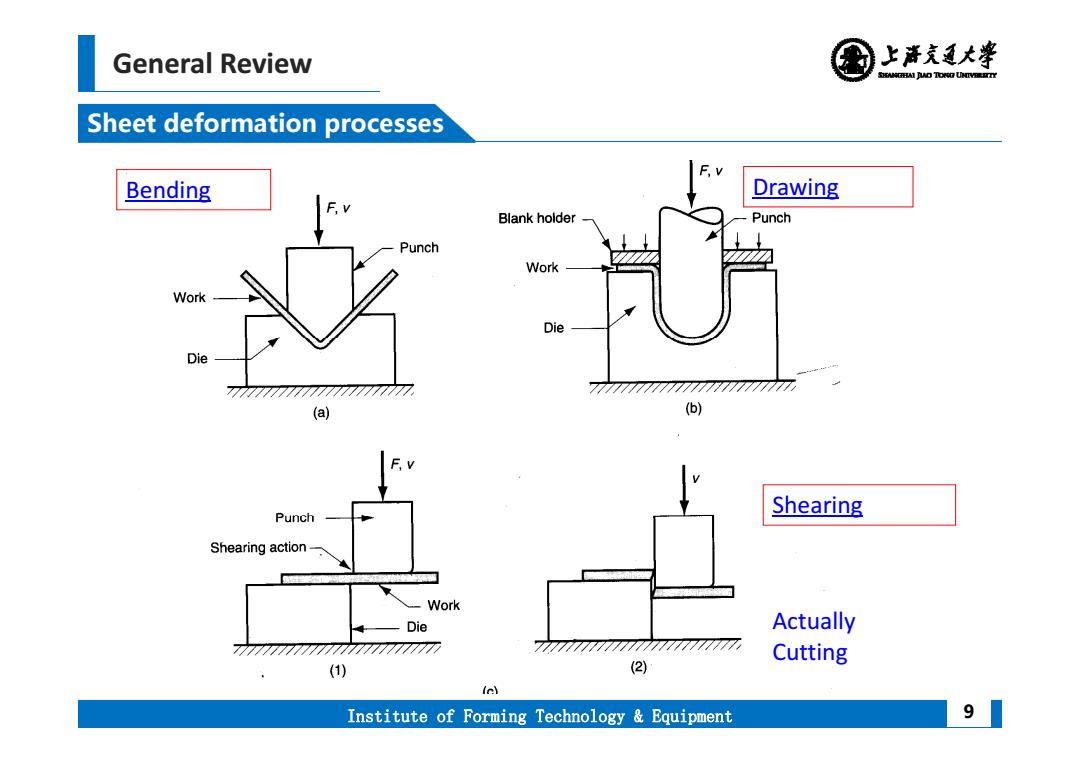
General Review 上清充通大学 SHEAMGRAI DUD TONO UHTVEREETTY Sheet deformation processes Bending Drawing Blank holder Punch Punch Work Work Die Die 777777777777777777777 7777777777777777777 (a) (b) Punch Shearing Shearing action- Work Die Actually 7777777777777777元 7777 Cutting (1) (2) (e) Institute of Forming Technology Equipment 9
General Review Institute of Forming Technology & Equipment Sheet deformation processes 9 Bending Drawing Shearing Actually Cutting

General Review 上产克大睾 SHEAMGHAI DUD TONO UHTVEREETTY Methodology Two methods to study the strength,deformation and failure of materials (a)Engineering Mechanics or Continuum approach Assuming that materials are isotropic and homogeneous Applying mathematical methods,using global parameters to determine stress state and material's response to external forces. (b)Materials Science or Microscopic approach Understanding of the mechanical properties based on the atomic/mesoscopic scale. Institute of Forming Technology Equipment 10
General Review Institute of Forming Technology & Equipment Methodology 10 Two methods to study the strength, deformation and failure of materials : (a) Engineering Mechanics or Continuum approach ‐ Assuming that materials are isotropic and homogeneous ‐ Applying mathematical methods, using global parameters to determine stress state and material’s response to external forces. (b) Materials Science or Microscopic approach ‐ Understanding of the mechanical properties based on the atomic/mesoscopic scale