
By Lin Yuan-Shao Cao Wen-Qing Guo Dong-Hui Wu Li-Sheng (Dept. of Oceanography, XMU) Chapter 15
By Lin Yuan-Shao Cao Wen-Qing Guo Dong-Hui Wu Li-Sheng (Dept. of Oceanography, XMU) Chapter 15

Some terms and definition 1. Dominant species(优势种):生态系或群落中,数量多、出现频率高的 物种。 2. Common species(习见种):群落中分布广、但数量不是很多的种类。 3. Locally abundant species(局限种):局限分布于某一海域或地区的种 类。 4. Uncommon species(少见种):群落中少见的种类。 5. Rare species(稀有种):海域或群落中数量稀少,分布窄的种类 根据海域或群落中生物的数量等级和出现频率划分5级,如上
Some terms and definition 1. Dominant species(优势种):生态系或群落中,数量多、出现频率高的 物种。 2. Common species(习见种):群落中分布广、但数量不是很多的种类。 3. Locally abundant species(局限种):局限分布于某一海域或地区的种 类。 4. Uncommon species(少见种):群落中少见的种类。 5. Rare species(稀有种):海域或群落中数量稀少,分布窄的种类 根据海域或群落中生物的数量等级和出现频率划分5级,如上

6. Cold water species(冷水种):生殖、生长最适温度低于4℃,自然分布区月平均水温 20℃,自然分布区月平均水温>15 ℃的 种类;包括亚热带种(适温20-25℃)和热带种(适温>25℃) • Subtropical species(亚热带种) • Tropical species(热带种)
6. Cold water species(冷水种):生殖、生长最适温度低于4℃,自然分布区月平均水温 20℃,自然分布区月平均水温>15 ℃的 种类;包括亚热带种(适温20-25℃)和热带种(适温>25℃) • Subtropical species(亚热带种) • Tropical species(热带种)

• Native species(本地种) • Immigrant species(迁入种) • Exotic species(外地种) • Cosmopolitan species(世界种):广温广盐性生物, 能分布于世界各海域。 • Littoral organisms(沿岸生物) • Indicate organisms (bio-indicator)
• Native species(本地种) • Immigrant species(迁入种) • Exotic species(外地种) • Cosmopolitan species(世界种):广温广盐性生物, 能分布于世界各海域。 • Littoral organisms(沿岸生物) • Indicate organisms (bio-indicator)

• Eurybathic organisms • Euryhaline • Eurytherm • Reproductive eurythermy • Vegetative eurythermy • Stenobathic organisms • Stenohaline • Stenotherm • Reproductive stenothermy • Vegetative stenothermy
• Eurybathic organisms • Euryhaline • Eurytherm • Reproductive eurythermy • Vegetative eurythermy • Stenobathic organisms • Stenohaline • Stenotherm • Reproductive stenothermy • Vegetative stenothermy

• Tropical submergence(热带深潜):某些广深性冷水种生物,能分布在南、 北两半球冷水水域,同时也能通过赤道深层水域,而呈现南、北两半球的连续分布。 • Bipolarity(两极同源):也称两极分布(bipolar distribution). 海洋生物的一种分布隔 离现象。一个动物的种或类群同时分布在南北两半球海洋的某一区域内,而不分布在中间 的热带海洋。如Calanus helgolandicus〕同时分布在北大西洋和新西兰的海洋中。 • Discontinuous distribution(隔离分布):一个物种或类群的分布区不是连续 的,它们的分布区有2个或几个相距很远的地区或水域所组成,中间地区没有该种或该类 群生物的存在。这种分布状态称为隔离分布。导致隔离分布往往是由于环境的温度、盐度 所引起的;此外,海底地貌的也是导致隔离分布的原因之一。 • Geographic isolation(地理隔离):由地理障碍,入开阔海洋、河口或其它因 子所产生的对生物分布的隔离。 • Vegetative distribution(营养分布):某些生物的分布区超过其适于生殖 的分布区,在不宜生殖的分布区的种群,必须不断地从外界移入成体或幼体。生物在这种 分布区的分布称为营养分布,也称不妊分布(sterile distribution)
• Tropical submergence(热带深潜):某些广深性冷水种生物,能分布在南、 北两半球冷水水域,同时也能通过赤道深层水域,而呈现南、北两半球的连续分布。 • Bipolarity(两极同源):也称两极分布(bipolar distribution). 海洋生物的一种分布隔 离现象。一个动物的种或类群同时分布在南北两半球海洋的某一区域内,而不分布在中间 的热带海洋。如Calanus helgolandicus〕同时分布在北大西洋和新西兰的海洋中。 • Discontinuous distribution(隔离分布):一个物种或类群的分布区不是连续 的,它们的分布区有2个或几个相距很远的地区或水域所组成,中间地区没有该种或该类 群生物的存在。这种分布状态称为隔离分布。导致隔离分布往往是由于环境的温度、盐度 所引起的;此外,海底地貌的也是导致隔离分布的原因之一。 • Geographic isolation(地理隔离):由地理障碍,入开阔海洋、河口或其它因 子所产生的对生物分布的隔离。 • Vegetative distribution(营养分布):某些生物的分布区超过其适于生殖 的分布区,在不宜生殖的分布区的种群,必须不断地从外界移入成体或幼体。生物在这种 分布区的分布称为营养分布,也称不妊分布(sterile distribution)

§15.1 Some concepts: • Fertilregion • Sterilregion sterile distribution
§15.1 Some concepts: • Fertilregion • Sterilregion sterile distribution
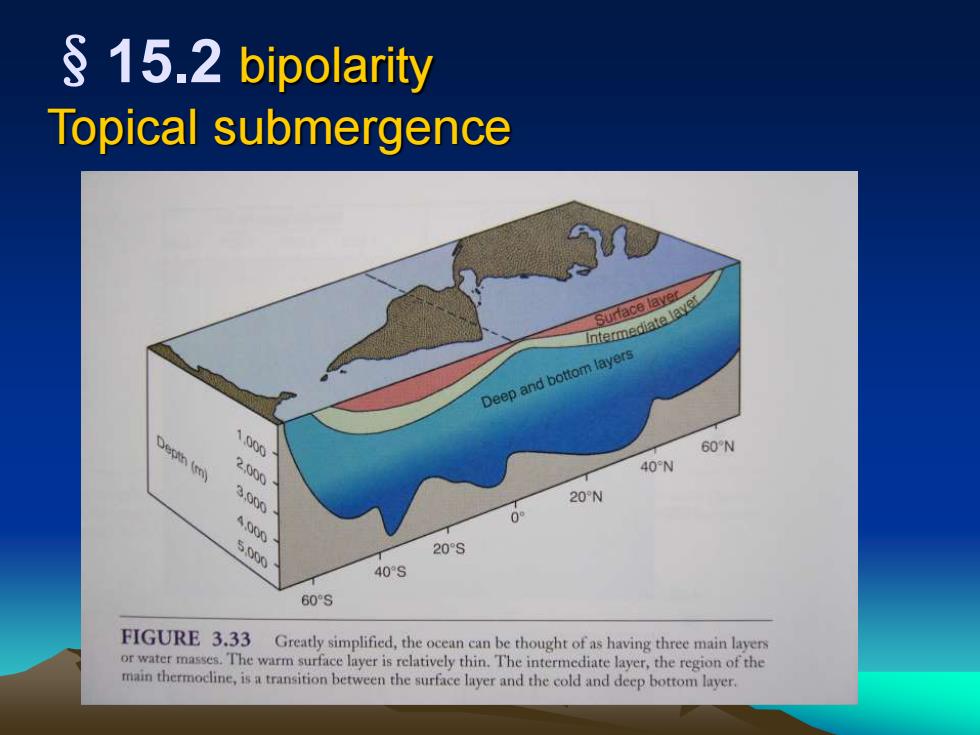
§15.2 bipolarity Topical submergence
§15.2 bipolarity Topical submergence
RUSSIA CHINA Tropic of Cance PACIFIC OCEAN QTA MICRONESIA INDIAN AUSTRALLA OCEAN AUSTRALIA 13 ?1988-2000 Microsoft and/or its suppliers.All rights reserved
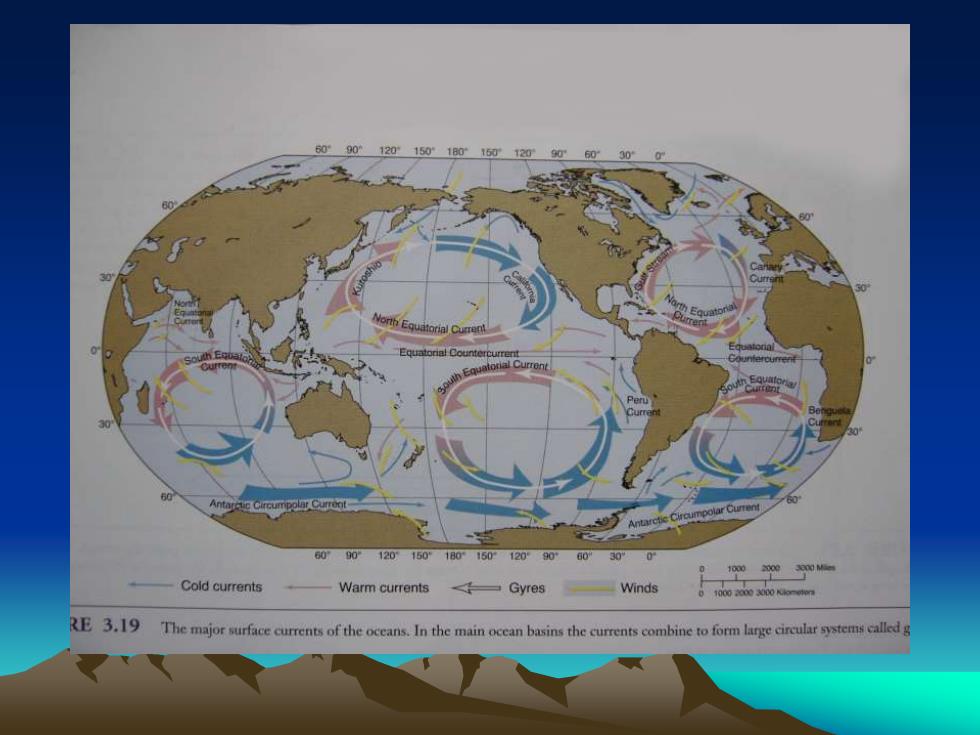
60 901201501B01612090 0 60901201501801601209060”30°0 Cold currents Warm currents Gyres Winds RE3.19 The major surface currents of the oceans.In the main ocean basins the currents combine to form large circular systemcalledg