
NGG430Protaistics fonr Chapter 2:Discrete Random Variables Instructor:Shengyu Zhang
Instructor: Shengyu Zhang

Content 0 Basic Concepts Probability Mass Function Functions of Random variables Expectation,Mean,and Variance Joint PMFs of Multiple Random Variables ■ Conditioning Independence
Content Basic Concepts Probability Mass Function Functions of Random Variables Expectation, Mean, and Variance Joint PMFs of Multiple Random Variables Conditioning Independence
Basic Concepts In some experiments,the outcomes are numerical. E.g.stock price. In some other experiments,the outcomes are not numerical,but they may be associated with some numerical values of interest. Example.Selection of students from a given population,we may wish to consider their grade point average. The students are not numerical,but their GPA scores are
Basic Concepts In some experiments, the outcomes are numerical. E.g. stock price. In some other experiments, the outcomes are not numerical, but they may be associated with some numerical values of interest. Example. Selection of students from a given population, we may wish to consider their grade point average. The students are not numerical, but their GPA scores are

Basic Concepts When dealing with these numerical values,it is useful to assign probabilities to them. This is done through the notion of a random variable. Random Variable X Sample Space 2 X Real Number Line
Basic Concepts When dealing with these numerical values, it is useful to assign probabilities to them. This is done through the notion of a random variable. Sample Space Ω Random Variable 𝑋 𝑥 Real Number Line

Main Concepts Related to Random Variables Starting with a probabilistic model of an experiment: A random variable is a real-valued function of the outcome of the experiment. A function of a random variable defines another random variable
Main Concepts Related to Random Variables Starting with a probabilistic model of an experiment: A random variable is a real-valued function of the outcome of the experiment. A function of a random variable defines another random variable

Examples 5 tosses of a coin. This is a random variable: The number of heads This is not: 三 CA 2005 2009 2005
Examples 5 tosses of a coin. This is a random variable: The number of heads This is not:

Main Concepts Related to Random Variables We can associate with each random variable certain“averages”of interest,such as the mean and the variance. A random variable can be conditioned on an event or on another random variable. Notion of independence of a random variable from an event or from another random variable. We'll talk about all these in this lecture
Main Concepts Related to Random Variables We can associate with each random variable certain “averages” of interest, such as the mean and the variance. A random variable can be conditioned on an event or on another random variable. Notion of independence of a random variable from an event or from another random variable. We’ll talk about all these in this lecture

Discrete Random Variable A random variable is called discrete if its range is either finite or countably infinite. Example.Two rolls of a die. The sum of the two rolls. o The number of sixes in the two rolls. The second roll raised to the fifth power
Discrete Random Variable A random variable is called discrete if its range is either finite or countably infinite. Example. Two rolls of a die. The sum of the two rolls. The number of sixes in the two rolls. The second roll raised to the fifth power
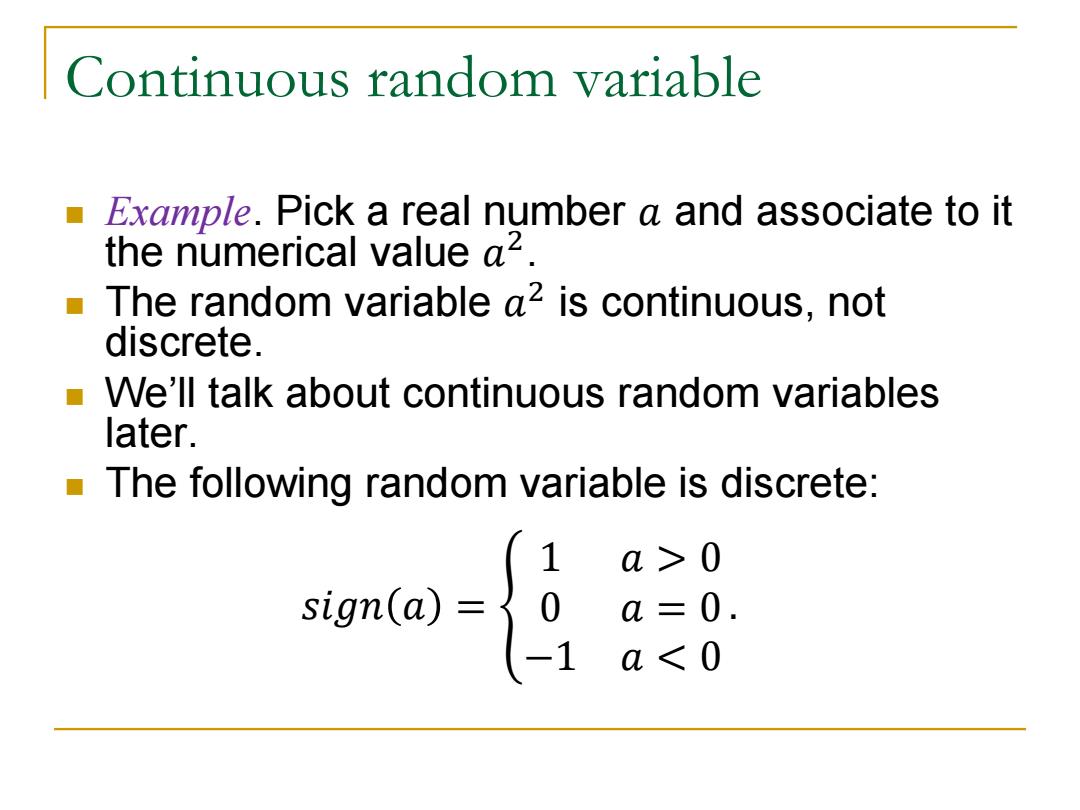
Continuous random variable Example.Pick a real number a and associate to it the numerical value a2. The random variable a2 is continuous,not discrete. We'll talk about continuous random variables later. The following random variable is discrete: 1 a>0 a=0. a<0
Continuous random variable Example. Pick a real number 𝑎 and associate to it the numerical value 𝑎 2 . The random variable 𝑎 2 is continuous, not discrete. We’ll talk about continuous random variables later. The following random variable is discrete: 𝑠𝑖𝑔𝑛 𝑎 = ቐ 1 𝑎 > 0 0 𝑎 = 0 −1 𝑎 < 0
Discrete Random Variables:Concepts A discrete random variable is a real-valued function of the outcome of a discrete experiment A discrete random variable has an associated probability mass function(PMF),which gives the probability of each numerical value that the random variable can take. A function of a discrete random variable defines another discrete random variable,whose PMF can be obtained from the PMF of the original random variable
Discrete Random Variables: Concepts A discrete random variable is a real-valued function of the outcome of a discrete experiment. A discrete random variable has an associated probability mass function (PMF), which gives the probability of each numerical value that the random variable can take. A function of a discrete random variable defines another discrete random variable, whose PMF can be obtained from the PMF of the original random variable