1907 Ch02 Supply and Demand Economics ECONOMICS MANAGEMENT SCHOOL,TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Economics ECONOMICS & MANAGEMENT SCHOOL, TONGJI UNIVERSITY Ch02 Supply and Demand

02-2 10 Volatile Markets Markets are skin to the weather.They are always changing,dynamic,unpredictable, subject to frequent periods of storm and calm, complex,and fascinating. The essential tool for understanding the movement of prices and outputs in individual markets is called the analysis of supply and demand. Economics ECONOMICS MANAGEMENT SCHOOL,TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Economics ECONOMICS & MANAGEMENT SCHOOL, TONGJI UNIVERSITY 02-2 Volatile Markets • Markets are skin to the weather. They are always changing, dynamic, unpredictable, subject to frequent periods of storm and calm, complex, and fascinating. • The essential tool for understanding the movement of prices and outputs in individual markets is called the analysis of supply and demand
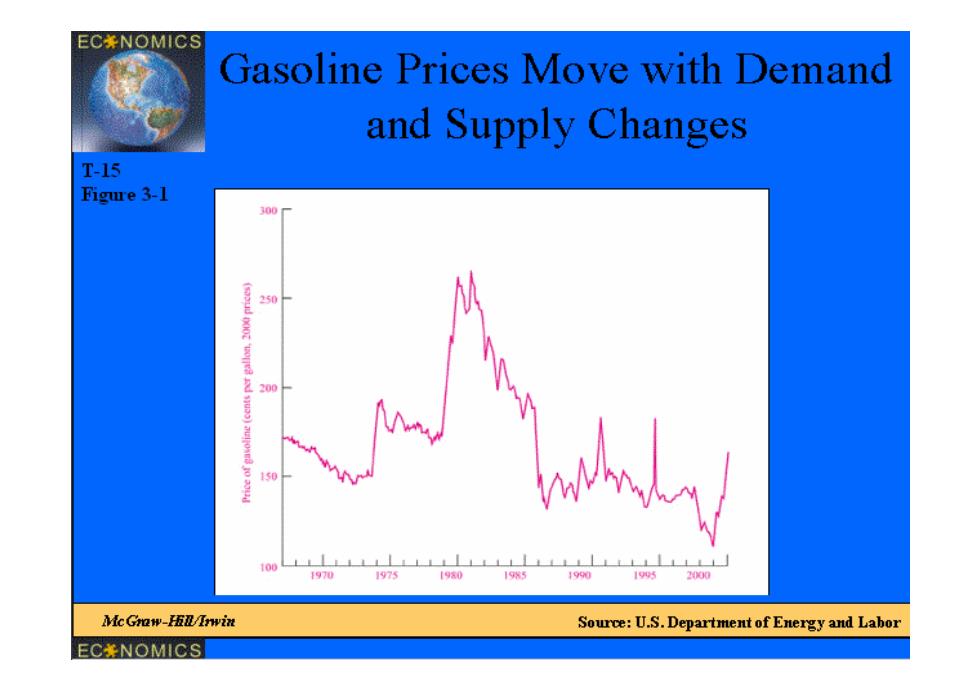
EC年NOMICS Gasoline Prices Move with Demand and Supply Changes T-15 Figure 3-1 300 250 200 g70 19w5 1990 19952000 c Graw-五0wi Source:U.S.Department of Energy and Labor EC米NOMICS|
Economics ECONOMICS & MANAGEMENT SCHOOL, TONGJI UNIVERSITY 02-3 Gasoline Prices Move with Demand and Supply Changes

02-4 0 砂 Topics to Be Discussed ·Supply and Demand ·The Market Mechanism Changes in Market Equilibrium Economics ECONOMICS MANAGEMENT SCHOOL,TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Economics ECONOMICS & MANAGEMENT SCHOOL, TONGJI UNIVERSITY 02-4 Topics to Be Discussed • Supply and Demand • The Market Mechanism • Changes in Market Equilibrium

1907 2.1 Demand ·Demand Schedule The demand schedule is a table that shows the relationship between the price of the good and the quantity demanded. Economics ECONOMICS MANAGEMENT SCHOOL,TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Economics ECONOMICS & MANAGEMENT SCHOOL, TONGJI UNIVERSITY • Demand Schedule – The demand schedule is a table that shows the relationship between the price of the good and the quantity demanded. 2.1 Demand
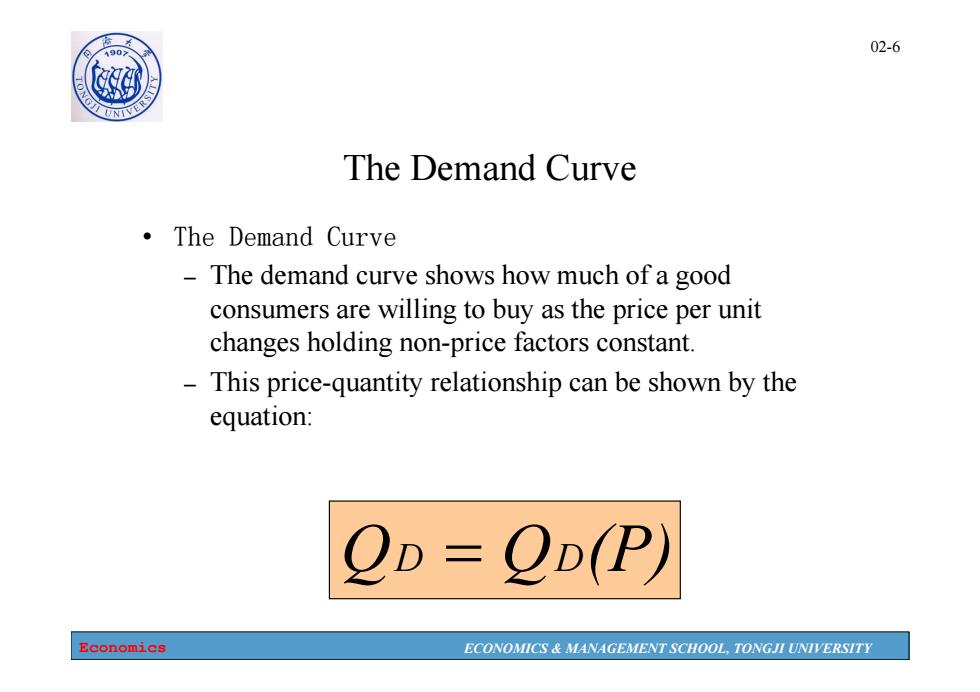
02-6 0 The Demand Curve ·The Demand Curve The demand curve shows how much of a good consumers are willing to buy as the price per unit changes holding non-price factors constant. This price-quantity relationship can be shown by the equation: 2D=QD(P Economics ECONOMICS MANAGEMENT SCHOOL,TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Economics ECONOMICS & MANAGEMENT SCHOOL, TONGJI UNIVERSITY 02-6 The Demand Curve • The Demand Curve – The demand curve shows how much of a good consumers are willing to buy as the price per unit changes holding non-price factors constant. – This price-quantity relationship can be shown by the equation: QD QD(P)
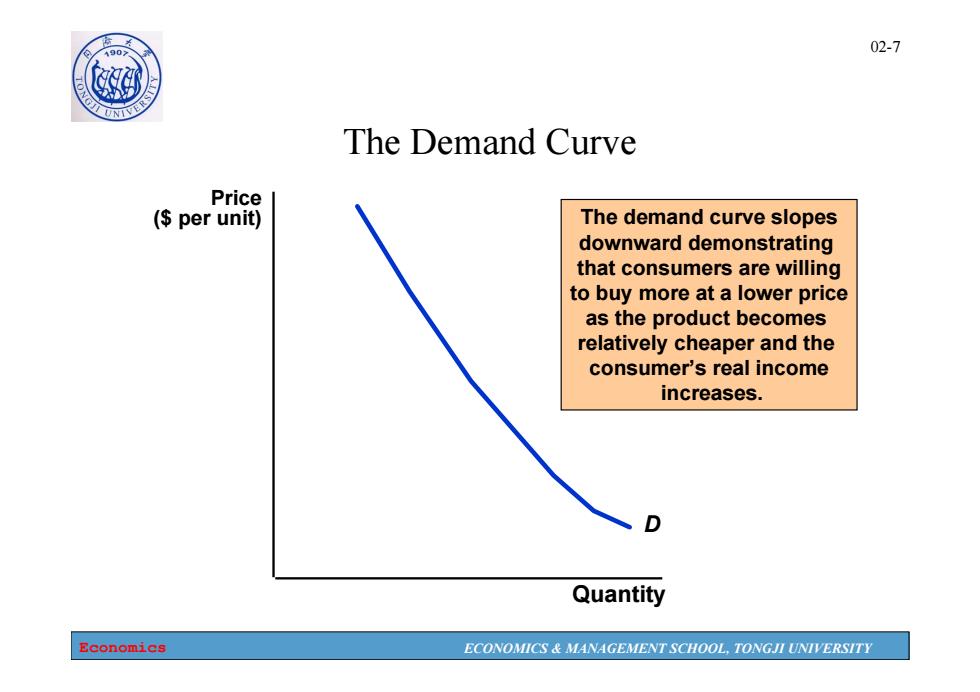
1907 02-7 The Demand Curve Price (per unit) The demand curve slopes downward demonstrating that consumers are willing to buy more at a lower price as the product becomes relatively cheaper and the consumer's real income increases. Quantity Economics ECONOMICS MANAGEMENT SCHOOL,TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Economics ECONOMICS & MANAGEMENT SCHOOL, TONGJI UNIVERSITY 02-7 D The demand curve slopes downward demonstrating that consumers are willing to buy more at a lower price as the product becomes relatively cheaper and the consumer’s real income increases. Quantity Price ($ per unit) The Demand Curve

0 Law of Demand Quantity demanded is the amount of a good that buyers are willing and able to purchase. ·Law of Demand -The law of demand (the law of downward-sloping demandstates that,other things equal,the quantity demanded of a good falls when the price of the good rises. Economics ECONOMICS MANAGEMENT SCHOOL,TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Economics ECONOMICS & MANAGEMENT SCHOOL, TONGJI UNIVERSITY Law of Demand • Quantity demanded is the amount of a good that buyers are willing and able to purchase. • Law of Demand – The law of demand (the law of downward-sloping demand)states that, other things equal, the quantity demanded of a good falls when the price of the good rises

190 02-9 砂 Market Demand versus Individual Demand Market demand refers to the sum of all individual demands for a particular good or service. Graphically,individual demand curves are summed horizontally to obtain the market demand curve. Economics ECONOMICS MANAGEMENT SCHOOL,TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Economics ECONOMICS & MANAGEMENT SCHOOL, TONGJI UNIVERSITY 02-9 Market Demand versus Individual Demand • Market demand refers to the sum of all individual demands for a particular good or service. • Graphically, individual demand curves are summed horizontally to obtain the market demand curve

10 Movement along the demand curve Change in Quantity Demanded -Movement along the demand curve -Caused by a change in the price of the product. Economics ECONOMICS MANAGEMENT SCHOOL,TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Economics ECONOMICS & MANAGEMENT SCHOOL, TONGJI UNIVERSITY Movement along the demand curve • Change in Quantity Demanded – Movement along the demand curve. – Caused by a change in the price of the product