
1907 Ch04 Producer Behavior Economics ECONOMICS MANAGEMENT SCHOOL,TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Economics ECONOMICS & MANAGEMENT SCHOOL, TONGJI UNIVERSITY Ch04 Producer Behavior

05-2 0 ④ Topics to be Discussed The Technology of Production ·Isoquants Production with One Variable Input (Labor) Production with Two Variable Inputs ·Returns to Scale Economics ECONOMICS MANAGEMENT SCHOOL,TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Economics ECONOMICS & MANAGEMENT SCHOOL, TONGJI UNIVERSITY 05-2 Topics to be Discussed • The Technology of Production • Isoquants • Production with One Variable Input (Labor) • Production with Two Variable Inputs • Returns to Scale
1907 05-3 4.1 Production Function Production Function: The relationship between the quantity of output (such as wheat,steel,or automobiles)and the quantities of inputs(of labor,land,and capital)is called the production function Indicates the highest output that a firm can produce for every specified combination of inputs given the state of technology. Shows what is technically feasible when the firm operates efficiently. Economics ECONOMICS MANAGEMENT SCHOOL,TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Economics ECONOMICS & MANAGEMENT SCHOOL, TONGJI UNIVERSITY 05-3 4.1 Production Function • Production Function: – The relationship between the quantity of output (such as wheat, steel, or automobiles) and the quantities of inputs (of labor, land, and capital) is called the production function – Indicates the highest output that a firm can produce for every specified combination of inputs given the state of technology. – Shows what is technically feasible when the firm operates efficiently
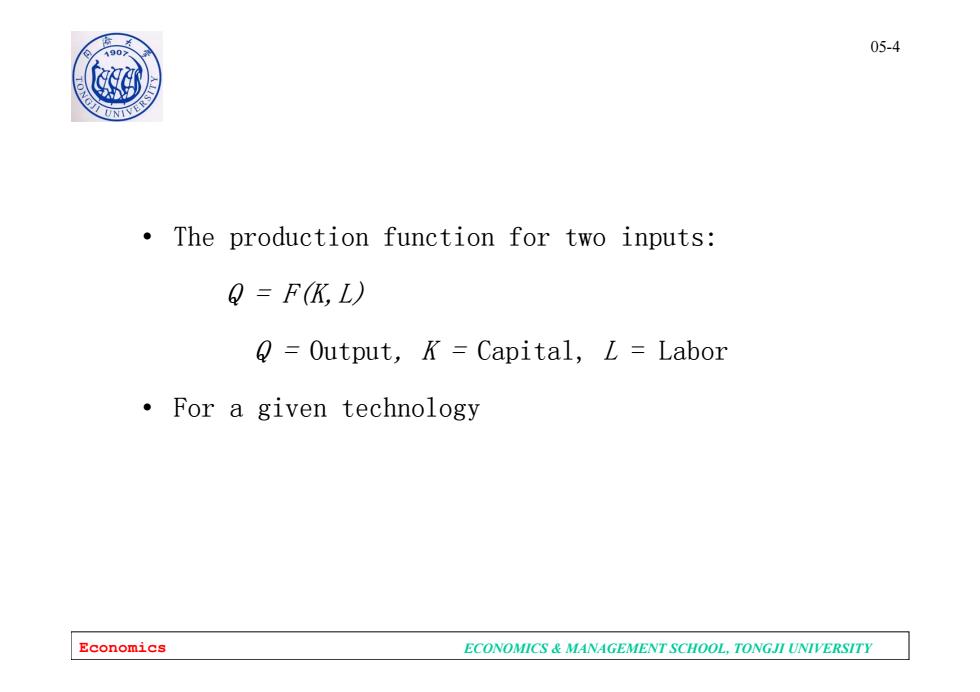
05-4 0 The production function for two inputs: Q=FK,L) Output,K=Capital,L Labor For a given technology Economics ECONOMICS MANAGEMENT SCHOOL,TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Economics ECONOMICS & MANAGEMENT SCHOOL, TONGJI UNIVERSITY 05-4 • The production function for two inputs: Q = F(K,L) Q = Output, K = Capital, L = Labor • For a given technology

1907 05-5 TP,AP and MP Total product is the total output produced. Average product equals total output divided by the total quantity of inputs. We can calculate the marginal product of a factor as the extra output added for each additional unit of input while holding all other inputs constant. Economics ECONOMICS MANAGEMENT SCHOOL,TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Economics ECONOMICS & MANAGEMENT SCHOOL, TONGJI UNIVERSITY 05-5 TP,AP and MP • Total product is the total output produced. • Average product equals total output divided by the total quantity of inputs. • We can calculate the marginal product of a factor as the extra output added for each additional unit of input while holding all other inputs constant

05-6 0 Short Run and Long Run 。Short-run: -Period of time in which quantities of one or more production factors cannot be changed. These inputs are called fixed inputs. ·Long-run Amount of time needed to make all production inputs variable. Economics ECONOMICS MANAGEMENT SCHOOL,TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Economics ECONOMICS & MANAGEMENT SCHOOL, TONGJI UNIVERSITY 05-6 Short Run and Long Run • Short-run: – Period of time in which quantities of one or more production factors cannot be changed. – These inputs are called fixed inputs. • Long-run – Amount of time needed to make all production inputs variable
1907 05-7 4.4 Production Function in Short Run Economics ECONOMICS MANAGEMENT SCHOOL.TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Economics ECONOMICS & MANAGEMENT SCHOOL, TONGJI UNIVERSITY 05-7 4.4 Production Function in Short Run
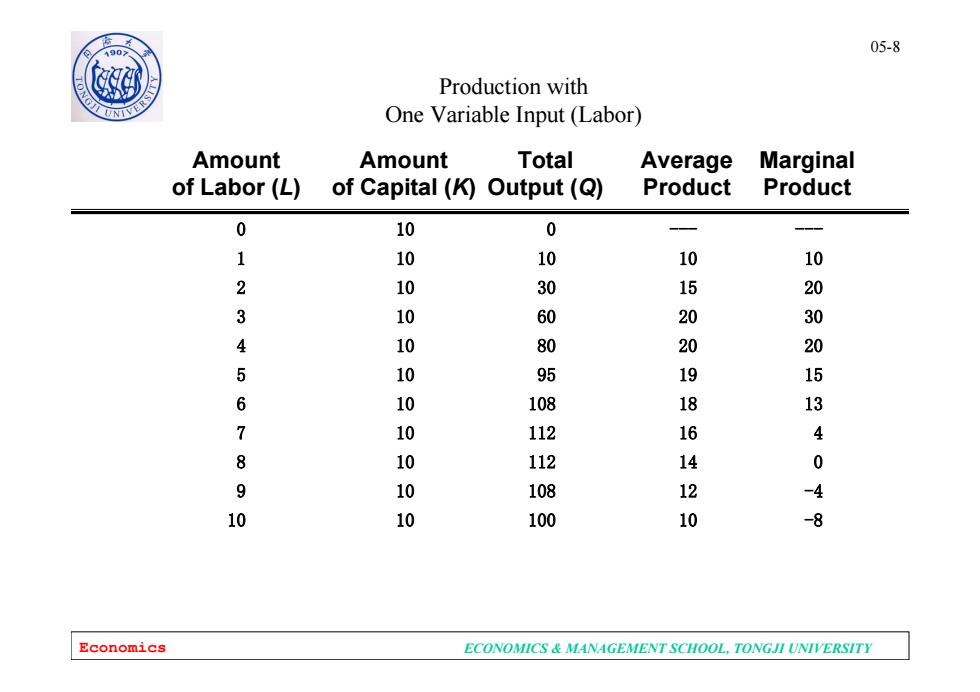
05-8 0 Production with One Variable Input (Labor) Amount Amount Total Average Marginal of Labor (L) of Capital(K)Output(Q) Product I Product 0 10 0 1 10 10 10 10 2 10 30 15 20 3 10 60 20 30 4 10 80 20 20 5 10 95 19 15 6 10 108 18 13 7 10 112 16 8 1 112 14 0 9 10 108 12 -4 10 0 100 10 -8 Economics ECONOMICS MANAGEMENT SCHOOL,TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Economics ECONOMICS & MANAGEMENT SCHOOL, TONGJI UNIVERSITY 05-8 Amount Amount Total Average Marginal of Labor (L) of Capital (K) Output (Q) Product Product Production with One Variable Input (Labor) 0 10 0 --- --- 1 10 10 10 10 2 10 30 15 20 3 10 60 20 30 4 10 80 20 20 5 10 95 19 15 6 10 108 18 13 7 10 112 16 4 8 10 112 14 0 9 10 108 12 -4 10 10 100 10 -8
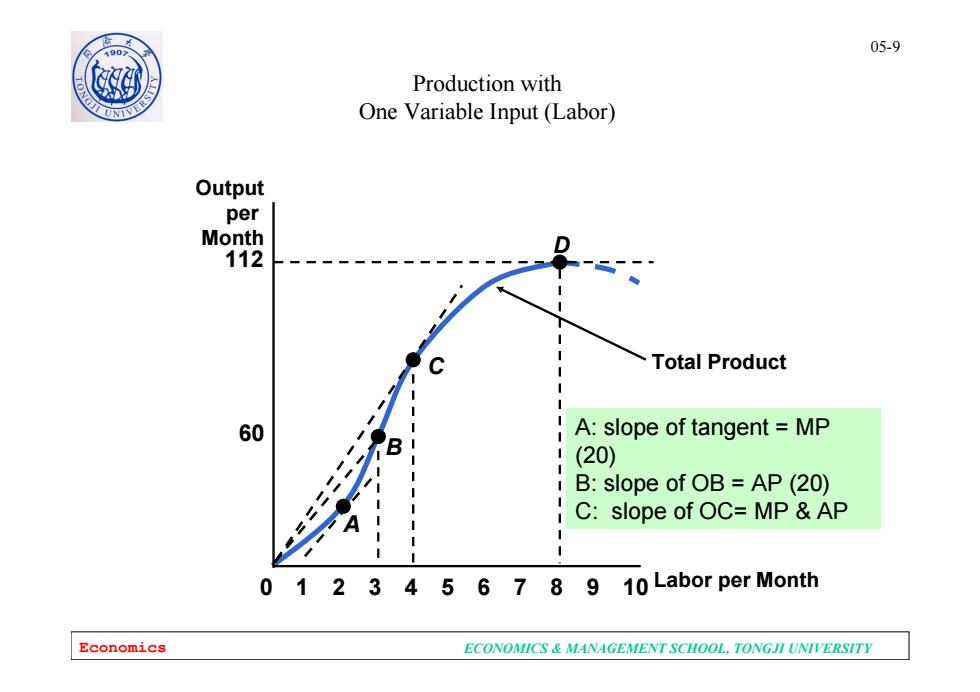
05-9 190 Production with One Variable Input (Labor) Output per Month 112 Total Product 60 A:slope of tangent MP (20) 1 B:slope of OB=AP(20) C:slope of OC=MP AP 0 1 23 4 56789 10 Labor per Month Economics ECONOMICS MANAGEMENT SCHOOL.TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Economics ECONOMICS & MANAGEMENT SCHOOL, TONGJI UNIVERSITY 05-9 Total Product Labor per Month Output per Month 60 112 0 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 1 A B C D Production with One Variable Input (Labor) A: slope of tangent = MP (20) B: slope of OB = AP (20) C: slope of OC= MP & AP
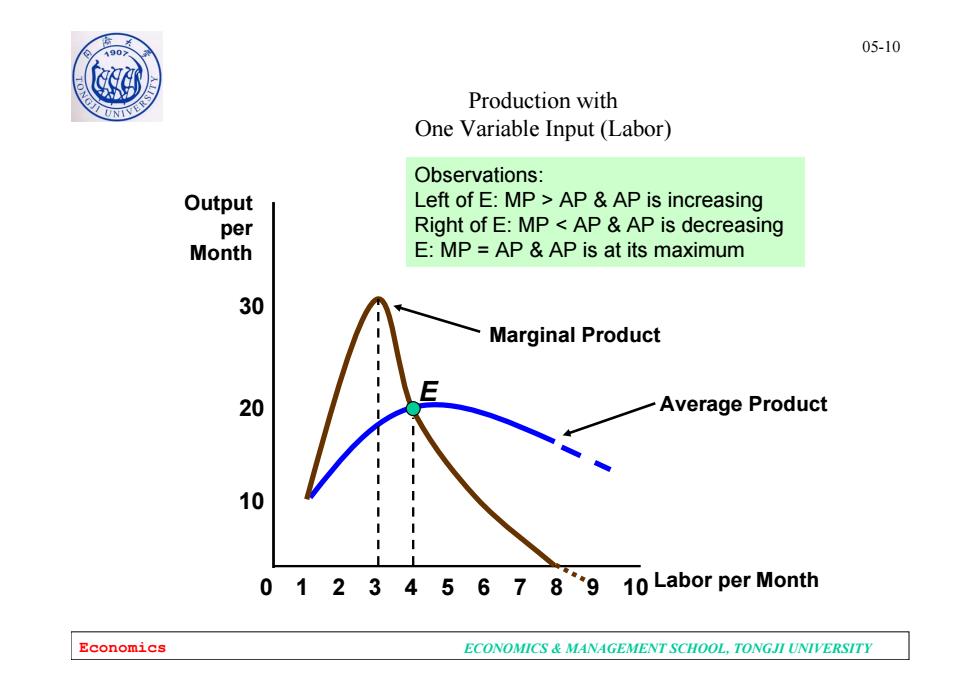
05-10 0 Production with One Variable Input (Labor) Observations: Output Left of E:MP>APAP is increasing per Right of E:MP AP AP is decreasing Month E:MP APAP is at its maximum 30 Marginal Product 20 Average Product 10 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8"9 10Labor per Month Economics ECONOMICS MANAGEMENT SCHOOL,TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Economics ECONOMICS & MANAGEMENT SCHOOL, TONGJI UNIVERSITY 05-10 Average Product Production with One Variable Input (Labor) 8 10 20 Output per Month 0 2 3 4 5 6 7 9 10 1 Labor per Month 30 E Marginal Product Observations: Left of E: MP > AP & AP is increasing Right of E: MP < AP & AP is decreasing E: MP = AP & AP is at its maximum