
1907 Ch06-2 Imperfect Competition Economics ECONOMICS MANAGEMENT SCHOOL,TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Economics ECONOMICS & MANAGEMENT SCHOOL, TONGJI UNIVERSITY Ch06-2 Imperfect Competition

08-2 0 砂 Topics to be Discussed ·Monopoly Price Discrimination Monopolistic Competition ·0 ligopoly Economics ECONOMICS MANAGEMENT SCHOOL,TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Economics ECONOMICS & MANAGEMENT SCHOOL, TONGJI UNIVERSITY 08-2 Topics to be Discussed • Monopoly • Price Discrimination • Monopolistic Competition • Oligopoly

1907 08-3 8.1 Monopoly Monopoly 1)One seller -many buyers 2) One product (no good substitutes) 3) Barriers to entry 4)Price Maker Economics ECONOMICS MANAGEMENT SCHOOL,TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Economics ECONOMICS & MANAGEMENT SCHOOL, TONGJI UNIVERSITY 08-3 8.1 Monopoly • Monopoly 1) One seller - many buyers 2) One product (no good substitutes) 3) Barriers to entry 4) Price Maker

08-4 0 Monopoly Barriers to entry have three sources: -Ownership of a key resource. -The government gives a single firm the exclusive right to produce some good. Costs of production make a single producer more efficient than a large number of producers. Economics ECONOMICS MANAGEMENT SCHOOL,TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Economics ECONOMICS & MANAGEMENT SCHOOL, TONGJI UNIVERSITY 08-4 • Barriers to entry have three sources: – Ownership of a key resource. – The government gives a single firm the exclusive right to produce some good. – Costs of production make a single producer more efficient than a large number of producers. Monopoly
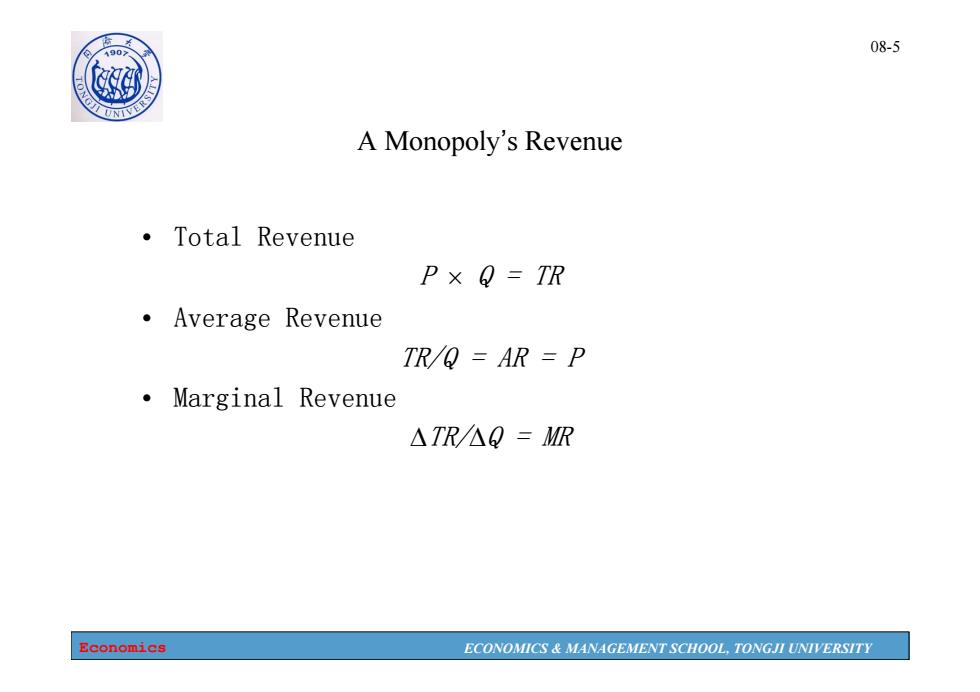
1907 08-5 A Monopoly's Revenue ·Total Revenue P×Q=TR ·Average revenue TR/Q=AR =P ·Marginal Revenue △TR△Q=MR Economics ECONOMICS MANAGEMENT SCHOOL,TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Economics ECONOMICS & MANAGEMENT SCHOOL, TONGJI UNIVERSITY 08-5 A Monopoly’s Revenue • Total Revenue P Q = TR • Average Revenue TR/Q = AR = P • Marginal Revenue TR/Q = MR
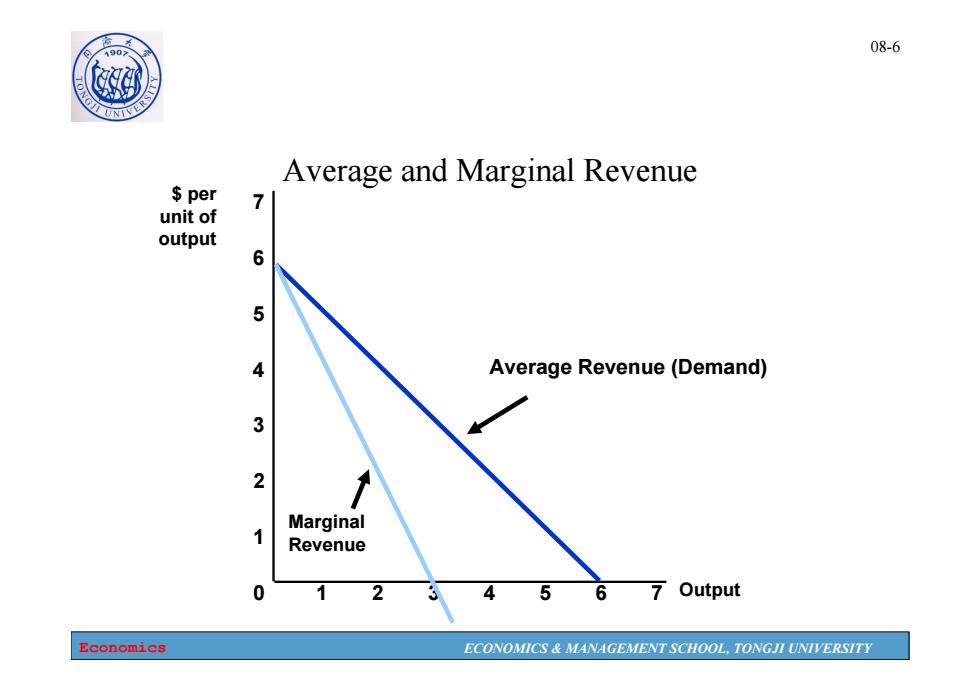
08-6 0 Average and Marginal Revenue $per unit of output 6 5 Average Revenue(Demand) 3 2 Marginal Revenue 0 2 A 6 7 Output Economics ECONOMICS MANAGEMENT SCHOOL,TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Economics ECONOMICS & MANAGEMENT SCHOOL, TONGJI UNIVERSITY 08-6 Average and Marginal Revenue 0 Output 1 2 3 $ per unit of output 1234567 4 5 6 7 Average Revenue (Demand) Marginal Revenue

1907 08-7 Monopoly Observations 1)To increase sales the price must fall 2)MR<P 3) Compared to perfect competition No change in price to change sales ·MR=P Economics ECONOMICS MANAGEMENT SCHOOL,TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Economics ECONOMICS & MANAGEMENT SCHOOL, TONGJI UNIVERSITY 08-7 Monopoly • Observations 1) To increase sales the price must fall 2) MR < P 3) Compared to perfect competition • No change in price to change sales • MR = P
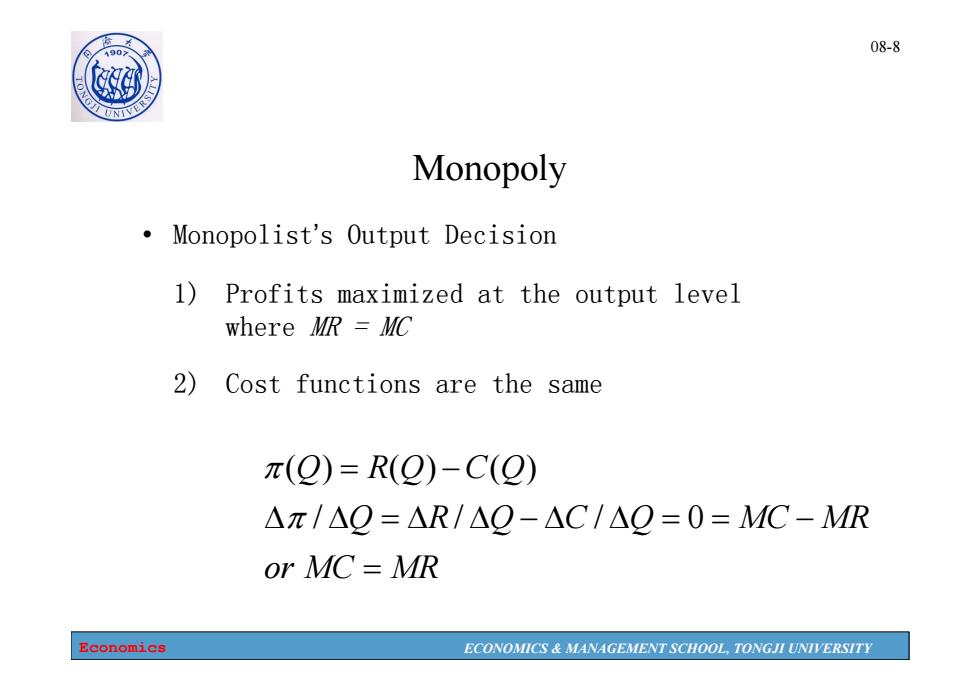
08-8 10 Monopoly Monopolist's Output Decision 1)Profits maximized at the output level where MR MC 2)Cost functions are the same π(Q)=R(Q)-C(Q) Aπ/AQ=△R/△Q-△C/△Q=0=MC-MR or MC=MR Economics ECONOMICS MANAGEMENT SCHOOL,TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Economics ECONOMICS & MANAGEMENT SCHOOL, TONGJI UNIVERSITY 08-8 Monopoly • Monopolist’s Output Decision 1) Profits maximized at the output level where MR = MC 2) Cost functions are the same or MC MR Q R Q C Q MC MR Q R Q C Q / / / 0 ( ) ( ) ( )

490 08-9 Maximizing Profit When Marginal Revenue Equals Marginal Cost The Monopolist's Output Decision At output levels below Mr=MC the decrease in revenue is greater than the decrease in cost (MR MC). At output levels above MR=MC the increase in cost is greater than the decrease in revenue (MR MC) Economics ECONOMICS MANAGEMENT SCHOOL,TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Economics ECONOMICS & MANAGEMENT SCHOOL, TONGJI UNIVERSITY 08-9 Maximizing Profit When Marginal Revenue Equals Marginal Cost • At output levels below MR = MC the decrease in revenue is greater than the decrease in cost (MR > MC). • At output levels above MR = MC the increase in cost is greater than the decrease in revenue (MR < MC) The Monopolist’s Output Decision The Monopolist’s Output Decision

08-10 0 Maximizing Profit When Marginal Revenue Equals Marginal Cost per unit of output MC P* AC P2 Lost profit D=AR 、Lost MR profit Q* Q2 Quantity Economics ECONOMICS MANAGEMENT SCHOOL,TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Economics ECONOMICS & MANAGEMENT SCHOOL, TONGJI UNIVERSITY 08-10 Lost profit P1 Q1 Lost profit MC AC Quantity $ per unit of output D = AR MR P* Q* Maximizing Profit When Marginal Revenue Equals Marginal Cost P2 Q2