
0 Ch13 Money Market Equilibrium Economics ECONOMICS MANAGEMENT SCHOOL,TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Economics ECONOMICS & MANAGEMENT SCHOOL, TONGJI UNIVERSITY Ch13 Money Market Equilibrium

1907 16-2 13.1 Money Supply Money is the set of assets in an economy that people regularly use to buy goods and services from other people. Money has three functions in the economy: Medium of exchange Unit of account -Store of value Economics ECONOMICS MANAGEMENT SCHOOL,TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Economics ECONOMICS & MANAGEMENT SCHOOL, TONGJI UNIVERSITY 16-2 13.1 Money Supply • Money is the set of assets in an economy that people regularly use to buy goods and services from other people. • Money has three functions in the economy: – Medium of exchange – Unit of account – Store of value

16-3 Three Primary Functions of the Central Bank -Regulates banks to ensure they follow federal laws intended to promote safe and sound banking practices Acts as a banker's bank,making loans to banks and as a lender of last resort. Conducts monetary policy by controlling the money supply Economics ECONOMICS MANAGEMENT SCHOOL,TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Economics ECONOMICS & MANAGEMENT SCHOOL, TONGJI UNIVERSITY 16-3 The Federal Open Market Committee • Three Primary Functions of the Central Bank – Regulates banks to ensure they follow federal laws intended to promote safe and sound banking practices. – Acts as a banker’s bank, making loans to banks and as a lender of last resort. – Conducts monetary policy by controlling the money supply

190 16-4 BANKS AND THE MONEY SUPPLY Banks can influence the quantity of demand deposits in the economy and the money supply. Reserves are deposits that banks have received but have not loaned out. ·Reserve ratio The reserve ratio is the fraction of deposits that banks hold as reserves. In a fractional-reserve banking system,banks hold a fraction of the money deposited as reserves and lend out the rest. Economics ECONOMICS MANAGEMENT SCHOOL,TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Economics ECONOMICS & MANAGEMENT SCHOOL, TONGJI UNIVERSITY 16-4 BANKS AND THE MONEY SUPPLY • Banks can influence the quantity of demand deposits in the economy and the money supply. • Reserves are deposits that banks have received but have not loaned out. • Reserve Ratio – The reserve ratio is the fraction of deposits that banks hold as reserves. • In a fractional-reserve banking system, banks hold a fraction of the money deposited as reserves and lend out the rest
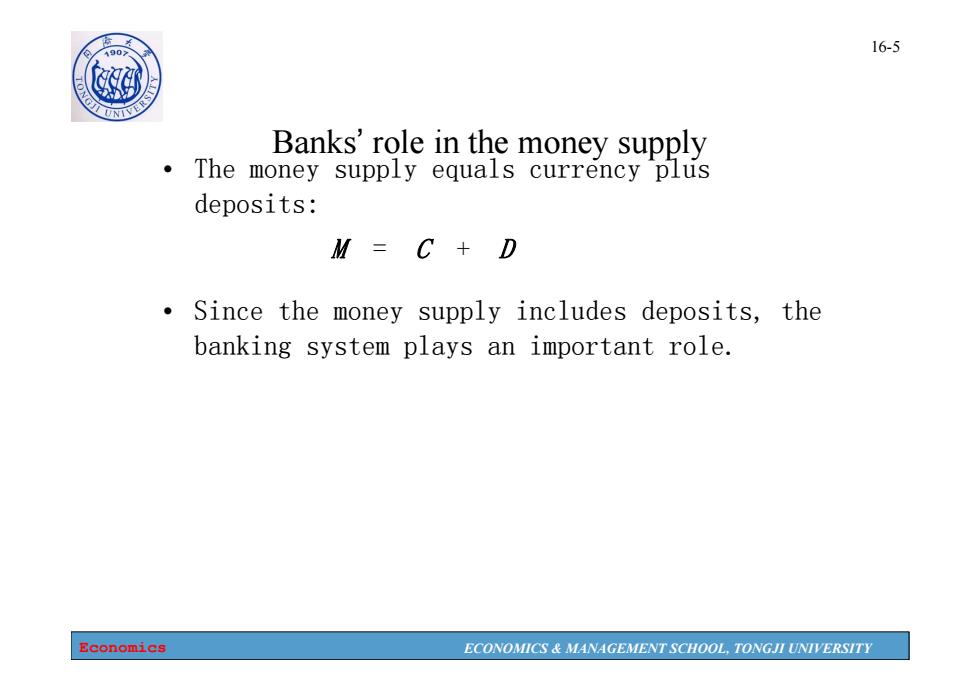
16-5 Banks'role in the money supply The money supply equals currency plus deposits: M=C+D Since the money supply includes deposits,the banking system plays an important role. Economics ECONOMICS MANAGEMENT SCHOOL,TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Economics ECONOMICS & MANAGEMENT SCHOOL, TONGJI UNIVERSITY 16-5 Banks’ role in the money supply • The money supply equals currency plus deposits: M = C + D • Since the money supply includes deposits, the banking system plays an important role

1907 16-6 Money Creation When a bank makes a loan from its reserves,the money supply increases. -The money supply is affected by the amount deposited in banks and the amount that banks loan. Deposits into a bank are recorded as both assets and liabilities. The fraction of total deposits that a bank has to keep as reserves is called the reserve ratio. Loans become an asset to the bank Economics ECONOMICS MANAGEMENT SCHOOL,TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Economics ECONOMICS & MANAGEMENT SCHOOL, TONGJI UNIVERSITY 16-6 Money Creation – When a bank makes a loan from its reserves, the money supply increases. – The money supply is affected by the amount deposited in banks and the amount that banks loan. • Deposits into a bank are recorded as both assets and liabilities. • The fraction of total deposits that a bank has to keep as reserves is called the reserve ratio. • Loans become an asset to the bank

16-7 Money Creation Suppose banks hold 20%of deposits in reserve,making loans with the rest. Firstbank will make $800 in loans. The money supply FIRSTBANK'S now equals $1800: balance sheet The depositor still Assets Liabilities has $1000 in demand reserves $200 deposits $1000 deposits, loans $800 but now the borrower holds $800 in currency. Economics ECONOMICS MANAGEMENT SCHOOL,TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Economics ECONOMICS & MANAGEMENT SCHOOL, TONGJI UNIVERSITY 16-7 The money supply now equals $1800: The depositor still has $1000 in demand deposits, but now the borrower holds $800 in currency. FIRSTBANK’S balance sheet Assets Liabilities deposits $1000 • Suppose banks hold 20% of deposits in reserve, making loans with the rest. • Firstbank will make $800 in loans. reserves $1000 reserves $200 loans $800 Money Creation

1907 16-8 Money Creation Suppose the borrower deposits the $800 in Secondbank. Initially,Secondbank's balance sheet is: SECONDBANK'S ·But then balance sheet Secondbank will loan 80%of this Assets Liabilities deposit reserves $160 deposits $800 and its balance loans $640 sheet will look like this: Economics ECONOMICS MANAGEMENT SCHOOL,TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Economics ECONOMICS & MANAGEMENT SCHOOL, TONGJI UNIVERSITY 16-8 • But then Secondbank will loan 80% of this deposit • and its balance sheet will look like this: SECONDBANK’S balance sheet Assets Liabilities reserves $800 loans $0 deposits $800 • Suppose the borrower deposits the $800 in Secondbank. • Initially, Secondbank’s balance sheet is: reserves $160 loans $640 Money Creation

16-9 0 Money Creation If this $640 is eventually deposited in Thirdbank, THIRDBANK'S ·then Thirdbank will keep 20%of it in balance sheet reserve,and loan the Assets Liabilities rest out: reserves $128 deposits $640 loans $512 Economics ECONOMICS MANAGEMENT SCHOOL,TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Economics ECONOMICS & MANAGEMENT SCHOOL, TONGJI UNIVERSITY 16-9 THIRDBANK’S balance sheet Assets Liabilities reserves $640 loans $0 deposits $640 • If this $640 is eventually deposited in Thirdbank, reserves $128 loans $512 • then Thirdbank will keep 20% of it in reserve, and loan the rest out: Money Creation
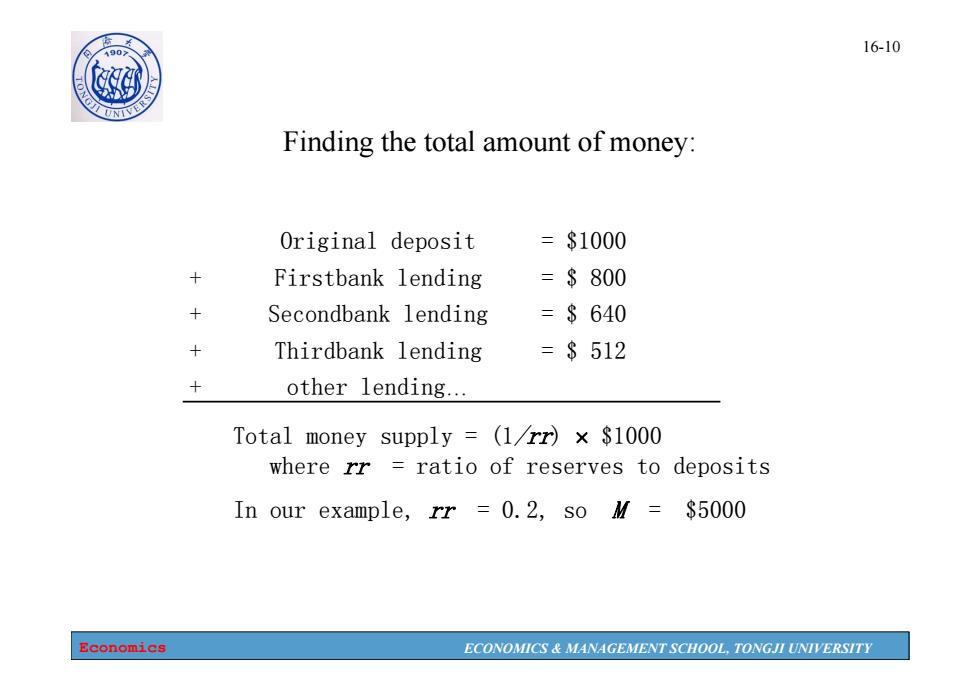
1907 16-10 Finding the total amount of money: Original deposit =$1000 Firstbank lending =$800 Secondbank lending =$640 Thirdbank lending =$512 other lending... Total money supply (1rr)x $1000 where rr ratio of reserves to deposits In our example,rr =0.2,so M=$5000 Economics ECONOMICS MANAGEMENT SCHOOL,TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Economics ECONOMICS & MANAGEMENT SCHOOL, TONGJI UNIVERSITY 16-10 Finding the total amount of money: Original deposit = $1000 + Firstbank lending = $ 800 + Secondbank lending = $ 640 + Thirdbank lending = $ 512 + other lending… Total money supply = (1/rr) $1000 where rr = ratio of reserves to deposits In our example, rr = 0.2, so M = $5000