
1907 Ch06-1 Analysis of Perfectly Competitive Markets Economics ECONOMICS MANAGEMENT SCHOOL,TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Economics ECONOMICS & MANAGEMENT SCHOOL, TONGJI UNIVERSITY Ch06-1 Analysis of Perfectly Competitive Markets

07-2 0 例 Topics to be Discussed Perfectly Competitive Markets ·Profit Maximization Marginal Revenue,Marginal Cost,and Profit Maximization Choosing Output in the Short-Run The Competitive Firm's Short-Run Supply Curve Short-Run Market Supply Choosing Output in the Long-Run The Industry's Long-Run Supply Curve Economics ECONOMICS MANAGEMENT SCHOOL,TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Economics ECONOMICS & MANAGEMENT SCHOOL, TONGJI UNIVERSITY 07-2 Topics to be Discussed • Perfectly Competitive Markets • Profit Maximization • Marginal Revenue, Marginal Cost, and Profit Maximization • Choosing Output in the Short-Run • The Competitive Firm’s Short-Run Supply Curve • Short-Run Market Supply • Choosing Output in the Long-Run • The Industry’s Long-Run Supply Curve

1907 07-3 树 6.1 Perfectly Competitive Markets Characteristics of Perfectly Competitive Markets 1)Price taking 2)Product homogeneity 3)Free entry and exit Economics ECONOMICS MANAGEMENT SCHOOL,TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Economics ECONOMICS & MANAGEMENT SCHOOL, TONGJI UNIVERSITY 07-3 6.1 Perfectly Competitive Markets • Characteristics of Perfectly Competitive Markets 1) Price taking 2) Product homogeneity 3) Free entry and exit

07-4 0 Perfectly Competitive Markets ·Price Taking -The individual firm sells a very small share of the total market output and,therefore,cannot influence market price. The individual consumer buys too small a share of industry output to have any impact on market price. Economics ECONOMICS MANAGEMENT SCHOOL,TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Economics ECONOMICS & MANAGEMENT SCHOOL, TONGJI UNIVERSITY 07-4 Perfectly Competitive Markets • Price Taking – The individual firm sells a very small share of the total market output and, therefore, cannot influence market price. – The individual consumer buys too small a share of industry output to have any impact on market price

190 07-5 Perfectly Competitive Markets ·Product Homogeneity -The products of all firms are perfect substitutes. -Examples Agricultural products,oil,copper,iron,lumber Economics ECONOMICS MANAGEMENT SCHOOL,TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Economics ECONOMICS & MANAGEMENT SCHOOL, TONGJI UNIVERSITY 07-5 Perfectly Competitive Markets • Product Homogeneity – The products of all firms are perfect substitutes. – Examples • Agricultural products, oil, copper, iron, lumber

07-6 10 Perfectly Competitive Markets ·Free Entry and Exit -Buyers can easily switch from one supplier to another. -Suppliers can easily enter or exit a market. Economics ECONOMICS MANAGEMENT SCHOOL,TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Economics ECONOMICS & MANAGEMENT SCHOOL, TONGJI UNIVERSITY 07-6 Perfectly Competitive Markets • Free Entry and Exit – Buyers can easily switch from one supplier to another. – Suppliers can easily enter or exit a market

1907 07-7 6.2 Profit Maximization Do firms maximize profits? -Possibility of other objectives Revenue maximization Dividend maximization Short-run profit maximization Economics ECONOMICS MANAGEMENT SCHOOL,TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Economics ECONOMICS & MANAGEMENT SCHOOL, TONGJI UNIVERSITY 07-7 6.2 Profit Maximization • Do firms maximize profits? – Possibility of other objectives • Revenue maximization • Dividend maximization • Short-run profit maximization

07-8 10 © Profit Maximization Do firms maximize profits? Long-run profit maximization is valid and does not exclude the possibility of altruistic behavior. Economics ECONOMICS MANAGEMENT SCHOOL,TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Economics ECONOMICS & MANAGEMENT SCHOOL, TONGJI UNIVERSITY 07-8 Profit Maximization • Do firms maximize profits? – Long-run profit maximization is valid and does not exclude the possibility of altruistic behavior
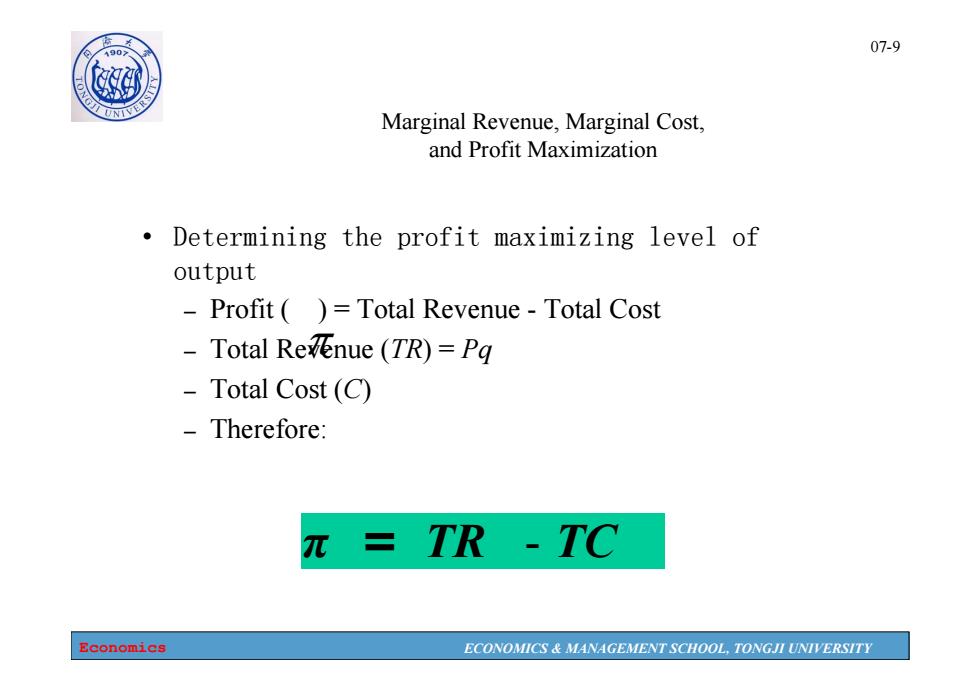
1907 07-9 Marginal Revenue,Marginal Cost, and Profit Maximization Determining the profit maximizing level of output -Profit()=Total Revenue-Total Cost Total Revenue (TR)=Pg Total Cost (C) -Therefore: TR -TC Economics ECONOMICS MANAGEMENT SCHOOL,TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Economics ECONOMICS & MANAGEMENT SCHOOL, TONGJI UNIVERSITY 07-9 Marginal Revenue, Marginal Cost, and Profit Maximization • Determining the profit maximizing level of output – Profit ( ) = Total Revenue - Total Cost – Total Revenue (TR) = Pq – Total Cost (C) – Therefore: π = TR - TC
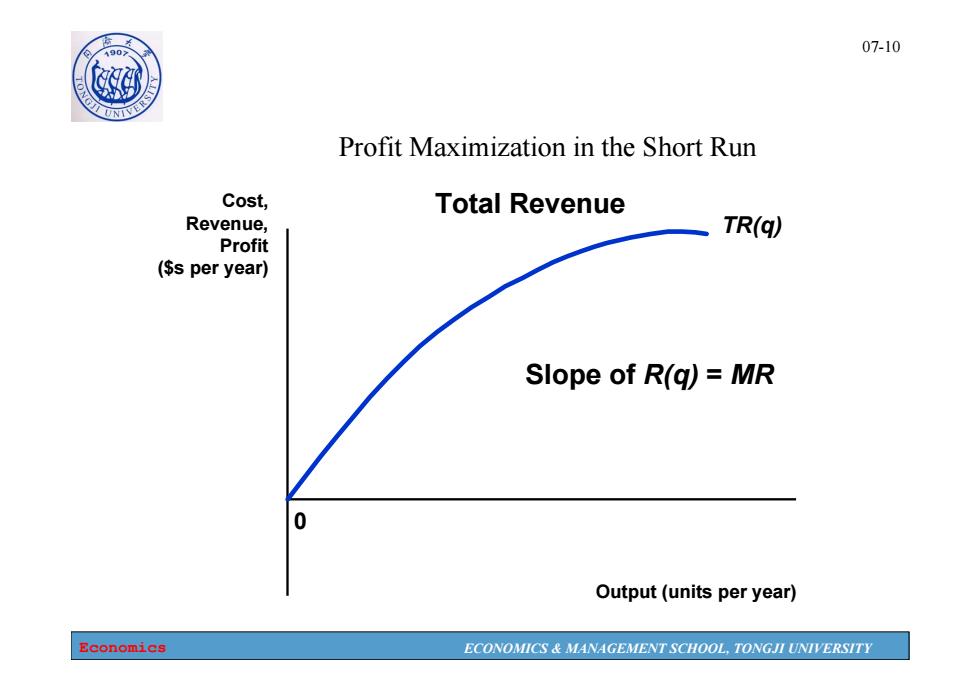
07-10 Profit Maximization in the Short Run Cost, Total Revenue Revenue, TR(q) Profit ($s per year) Slope of R(g)=MR Output(units per year) Economics ECONOMICS MANAGEMENT SCHOOL,TONGJI UNIVERSITY
Economics ECONOMICS & MANAGEMENT SCHOOL, TONGJI UNIVERSITY 07-10 Profit Maximization in the Short Run 0 Cost, Revenue, Profit ($s per year) Output (units per year) TR(q) Total Revenue Slope of R(q) = MR