
同济大学经济与管理学院试卷 (A卷答案) 单选题:40分(每小题2分) cbdcb:bbaad:bcbad:aadcb 二、计算题:40分(每小题20分) 1.answer 1).If the market,and they olude,they will face a marginal ith twice the slope of the demand curve: MR=10.2Q Setting marginal revenue equal to marginal cost(the marginal cos of Pirm 1.sinc it is lower than that of Firm 2)to determine the profit-maximizing quantity, 10.2Q=2.0rQ=4 SubstitutingQ=4into the demand function to determine price P=10.4=$6. The profit for Firm 1 will be: 元1=(6(④-(4+(24)=$12. The profit for Firm 2 will be: 2=(60)-6+30)=3. Total industry profit will be: 元r=元1+元2=12.3=$9. If Firm 1 were the only entrant,its profits would be $12 and Firm 2's would be0. If Firm 2 were the only entrant,then it would equate marginal revenue with its 10.20=3.0rQ=3.5. Substituting a.into the demand equation to determine price P=10.35=86.5. The profits for Firm 2 will be: 2=6.53.5)6+36.5=9.25 2)In the Cournot model,Firm 1 takes as given and maximizes profits.Theprof function derived in2a becomes 1=(10.Q,Q2-4+20,0r π=-4+8Q1-Q2-,Q2
1 同济大学经济与管理学院试卷 ( A 卷答案) 一、单选题:40 分(每小题 2 分) cbdcb;bbaad;bcbad;aadcb 二、计算题:40 分(每小题 20 分) 1. answer 1).If both firms enter the market, and they collude, they will face a marginal revenue curve with twice the slope of the demand curve: MR = 10 - 2Q. Setting marginal revenue equal to marginal cost (the marginal cost of Firm 1, since it is lower than that of Firm 2) to determine the profit-maximizing quantity, Q: 10 - 2Q = 2, or Q = 4. Substituting Q = 4 into the demand function to determine price: P = 10 - 4 = $6. The profit for Firm 1 will be: 1 = (6)(4) - (4 + (2)(4)) = $12. The profit for Firm 2 will be: 2 = (6)(0) - (3 + (3)(0)) = -$3. Total industry profit will be: T = 1 + 2 = 12 - 3 = $9. If Firm 1 were the only entrant, its profits would be $12 and Firm 2’s would be 0. If Firm 2 were the only entrant, then it would equate marginal revenue with its marginal cost to determine its profit-maximizing quantity: 10 - 2Q2 = 3, or Q2 = 3.5. Substituting Q2 into the demand equation to determine price: P = 10 - 3.5 = $6.5. The profits for Firm 2 will be: 2 = (6.5)(3.5) - (3 + (3)(3.5)) = $9.25 2). In the Cournot model, Firm 1 takes Firm 2’s output as given and maximizes profits. The profit function derived in 2.a becomes 1 = (10 - Q1 - Q2 )Q1 - (4 + 2Q1 ), or 4 8 1 1 2 Q Q QQ1 2

Setting the derivative of the profit function with reapect to to zero we find Firm I'sreaction function 8-20-0.=0wg=4(2 a0 Similarly,Firm2s reaction function is 0=35-(g) To find the.we substitute Firm function into Firm I's reaction function a=4-s-号}8=3 Substituting this value for into the reaction function for Firm 2.we find=2. Substituting the values for and into the demand function to determine the P=10-3-2=5. The profits for Firms 1and 2are equal to 元1=(63)-(1+(23)=iand 元2=6)2☒·(3+(32)=1. 0=4- 及=6-号 2.Answer 1)The efficient number of hours is the amount such that the sum of the marginal benefits to marginal cost.Given the demand curves representing the marginal benefits to each individual, we sum these demand curves vertically to determine the sum of all marginal benefits.Figure 18.6.a shows each demand curve and the summation
2 Setting the derivative of the profit function with respect to Q1 to zero, we find Firm 1’s reaction function: . 2 = 8 2 - = 0, or = 4 - 2 1 2 1 1 Q Q Q Q Q Similarly, Firm 2’s reaction function is . 2 3.5 1 2 Q Q To find the Cournot equilibrium, we substitute Firm 2’s reaction function into Firm 1’s reaction function: , or 3. 2 3.5 2 1 4 1 1 1 Q Q Q Substituting this value for Q1 into the reaction function for Firm 2, we find Q2 = 2. Substituting the values for Q1 and Q2 into the demand function to determine the equilibrium price: P = 10 - 3 - 2 = $5. The profits for Firms 1 and 2 are equal to 1 = (5)(3) - (4 + (2)(3)) = 5 and 2 = (5)(2) - (3 + (3)(2)) = 1. Q1 5 10 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Q2 1 2 3 4 6789 Q Q 1 2 4 2 Q Q 2 1 35 2 . Reaction Functions 2. Answer: 1) The efficient number of hours is the amount such that the sum of the marginal benefits is equal to marginal cost. Given the demand curves representing the marginal benefits to each individual, we sum these demand curves vertically to determine the sum of all marginal benefits. Figure 18.6.a shows each demand curve and the summation
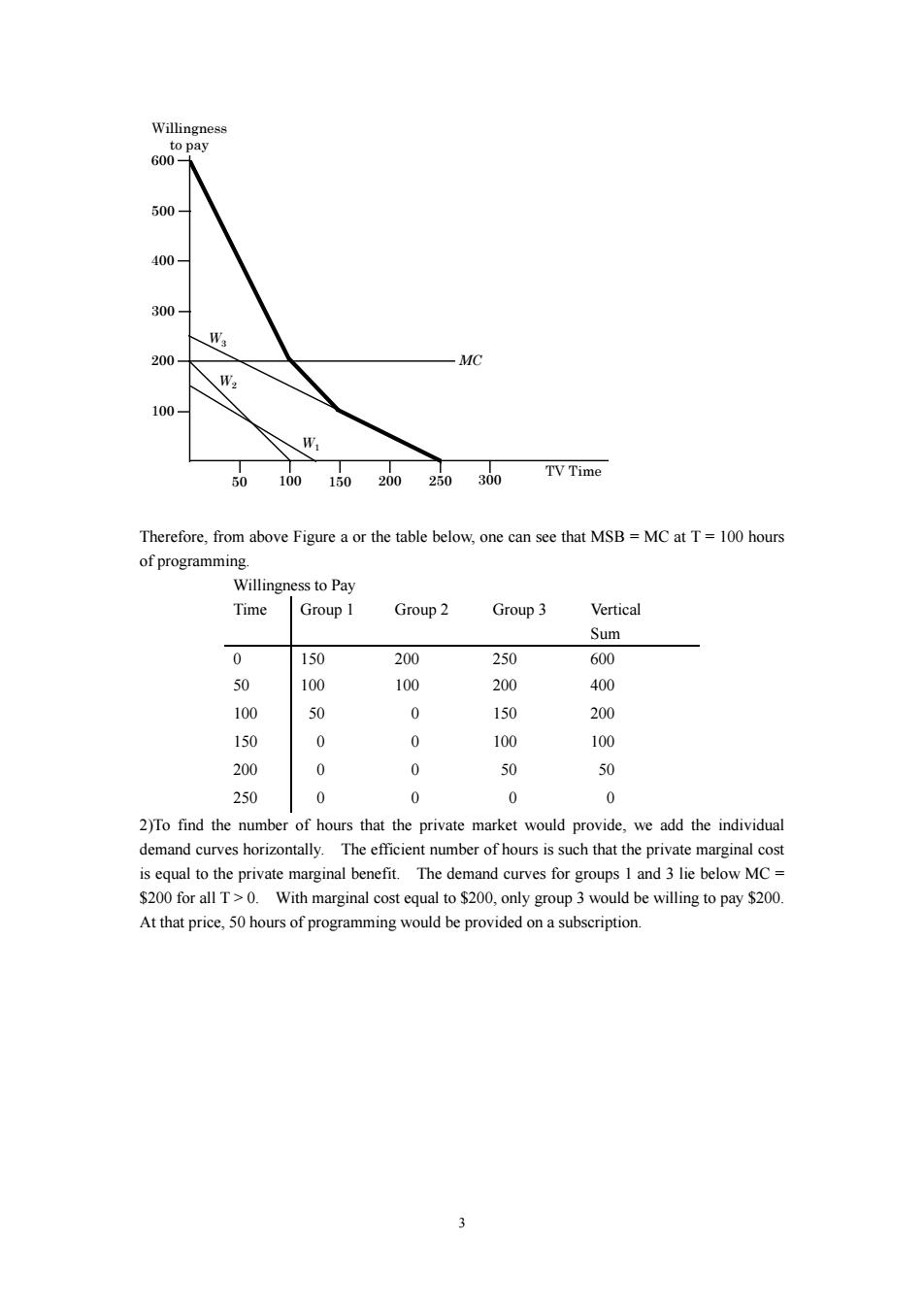
500 4100 300 200 W 010102025030vTme Therefore from above figure a or the table below one can see that msb MC at t=100 hours of programmin Willingness to Pay Time Group I Group2 Group3 Vertical Sum 0 150 200 250 600 200 100 50 0 150 200 150 0 0 100 100 200 0 0 50 250 0 0 0 0 2)To find the number of hours that the private market would provide.we add the individual The ata marginal $200 for allT>.With marginal cost equal to $200,only group 3 would be willing to pay $200. At that price,50 hours of programming would be provided on a subscription
3 Willingness to pay TV Time 250 100 200 300 400 500 50 100 150 200 300 600 MC W1 W2 W3 Therefore, from above Figure a or the table below, one can see that MSB = MC at T = 100 hours of programming. Willingness to Pay Time Group 1 Group 2 Group 3 Vertical Sum 0 150 200 250 600 50 100 100 200 400 100 50 0 150 200 150 0 0 100 100 200 0 0 50 50 250 0 0 0 0 2)To find the number of hours that the private market would provide, we add the individual demand curves horizontally. The efficient number of hours is such that the private marginal cost is equal to the private marginal benefit. The demand curves for groups 1 and 3 lie below MC = $200 for all T > 0. With marginal cost equal to $200, only group 3 would be willing to pay $200. At that price, 50 hours of programming would be provided on a subscription
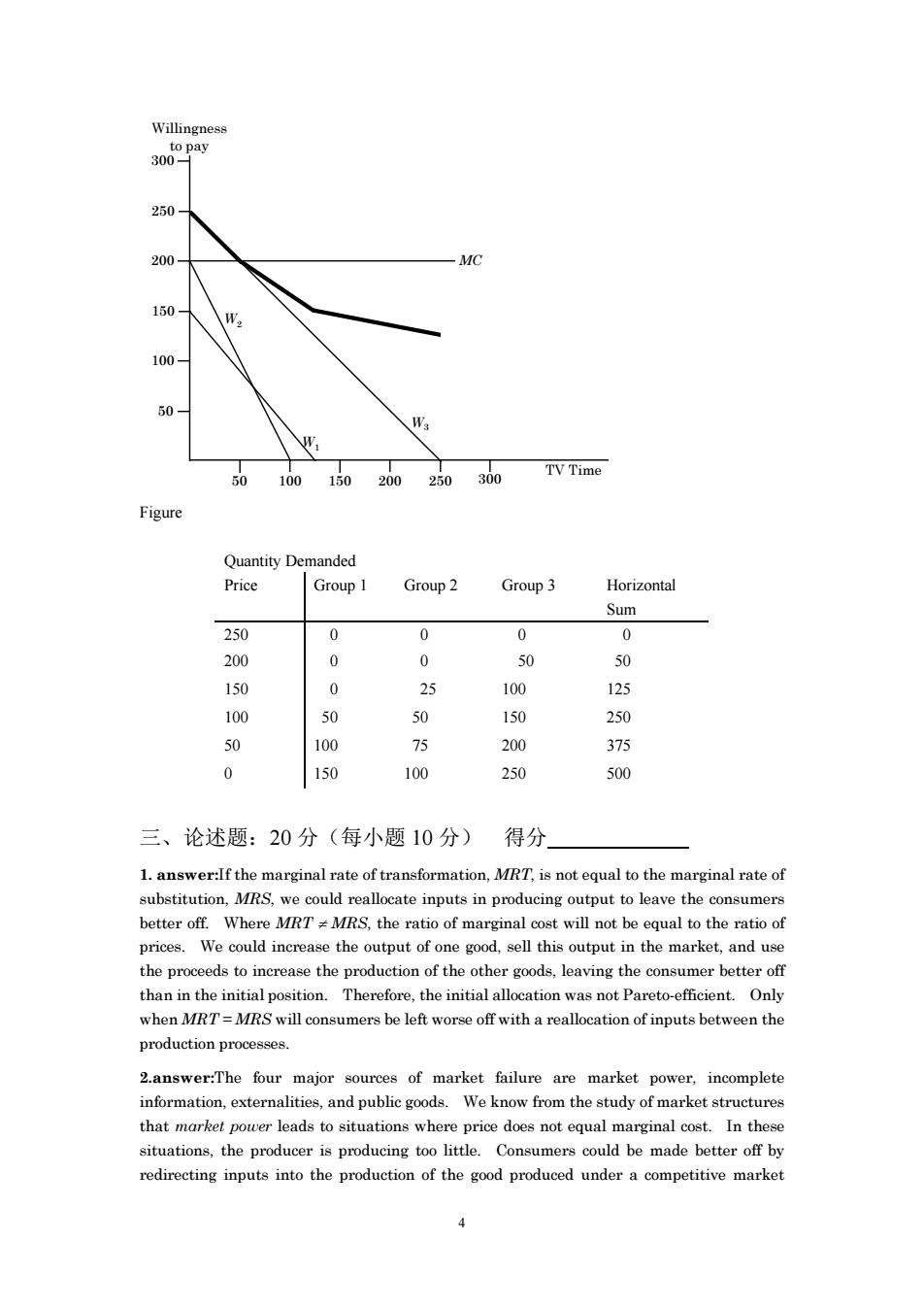
250 150 5010150200250300 TVTime Figure Quantity Demanded Price Group 1 Group2 Group3 Horizontal Sum 250 0 0 0 0 200 0 0 150 0 25 100 125 100 50 0 250 50 100 200 375 0 150 250 500 三、论述题:20分(每小题10分)得分 1.answer:If the marginal rate of transformation,MRT.is not equal to the marginal rate of substitution,MRS,we could reallocate inputs in producing output to leave the consumers better off.Where MRTzMRS,the ratio of marginal cost will not be equal to the ratio of .of than in the initial position.Therefore,the initial allocation was not Pareto-efficient.Only when MRT=MRS will consumers be left worse off with a reallocation of inputs between the production processes. 2.answer:The four major sources of market failure are market power,incomplete information,externalities,and public goods.We know from the study of market structures rginal cost.In these situations,the producer is producing too little.Consumers could be made better off by redirecting inputs into the production of the good produced under a competitive market
4 Willingness to pay TV Time 250 50 100 150 200 250 50 100 150 200 300 300 MC W1 W2 W3 Figure Quantity Demanded Price Group 1 Group 2 Group 3 Horizontal Sum 250 0 0 0 0 200 0 0 50 50 150 0 25 100 125 100 50 50 150 250 50 100 75 200 375 0 150 100 250 500 三、论述题:20 分(每小题 10 分) 得分 1. answer:If the marginal rate of transformation, MRT, is not equal to the marginal rate of substitution, MRS, we could reallocate inputs in producing output to leave the consumers better off. Where MRT MRS, the ratio of marginal cost will not be equal to the ratio of prices. We could increase the output of one good, sell this output in the market, and use the proceeds to increase the production of the other goods, leaving the consumer better off than in the initial position. Therefore, the initial allocation was not Pareto-efficient. Only when MRT = MRS will consumers be left worse off with a reallocation of inputs between the production processes. 2.answer:The four major sources of market failure are market power, incomplete information, externalities, and public goods. We know from the study of market structures that market power leads to situations where price does not equal marginal cost. In these situations, the producer is producing too little. Consumers could be made better off by redirecting inputs into the production of the good produced under a competitive market

structure.thereby lowering price until price is equal to marginal cost.Incomplete impies that prices do the marginalos of productionor the change in utility from changes in consumption.Either r too much or too little (at the extreme,none)is produced and consumed.Externalities occur when a consumption or production activity influences other consumption of production activities,and these effects are not reflected in market prices.Public goods are goods that can be consumed at prices below marginal cost (at the extreme,freely)because consumers cannot be excluded.In these four ases prices do not send the prope signals to either producers or consumers to increase or decrease production or consumption. Thus,the market mechanism cannot equate social marginal costs with social marginal benefits
5 structure, thereby lowering price until price is equal to marginal cost. Incomplete information implies that prices do not reflect either the marginal cost of production or the change in utility from changes in consumption. Either too much or too little (at the extreme, none) is produced and consumed. Externalities occur when a consumption or production activity influences other consumption of production activities, and these effects are not reflected in market prices. Public goods are goods that can be consumed at prices below marginal cost (at the extreme, freely) because consumers cannot be excluded. In these four cases, prices do not send the proper signals to either producers or consumers to increase or decrease production or consumption. Thus, the market mechanism cannot equate social marginal costs with social marginal benefits