
本次课内容 1.3高分子材料的结构与性能2金属材料组织和性能的控制 1.3.1高分子材料的结构 大分子链的结构 2.1纯金属的结晶★ 大分子链的构象及柔性 2.1.1纯金属的结晶 高分子材料的聚集态 纯金属结晶的条件 1.3.2高分子材料的性能 纯金属结晶的过程 高分子材料的机械性能 2.1,2同素异构转变 高分子材料的理化性能特点 2.1.3细化铸态金属晶粒的措施 2.1.4铸锭的结构 1.4陶瓷材料的结构与性能 1.4.1陶瓷材料的结构 晶体相 玻璃相 气相 1.4.2陶瓷材料的性能 陶瓷的机械性能 陶瓷的理化性能
本次课内容 1.3 高分子材料的结构与性能 1.3.1 高分子材料的结构 大分子链的结构 大分子链的构象及柔性 高分子材料的聚集态 1.3.2 高分子材料的性能 高分子材料的机械性能 高分子材料的理化性能特点 1.4 陶瓷材料的结构与性能 1.4.1 陶瓷材料的结构 晶体相 玻璃相 气相 1.4.2 陶瓷材料的性能 陶瓷的机械性能 陶瓷的理化性能 2 金属材料组织和性能的控制 2.1 纯金属的结晶 2.1.1 纯金属的结晶 纯金属结晶的条件 纯金属结晶的过程 2.1.2 同素异构转变 2.1.3 细化铸态金属晶粒的措施 2.1.4 铸锭的结构
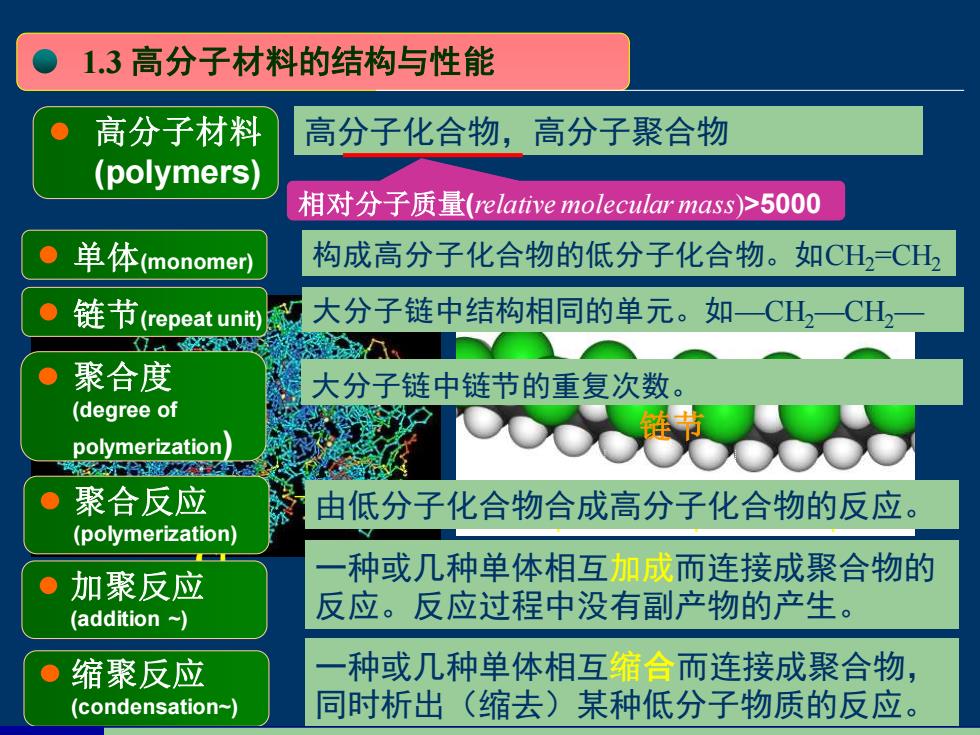
1.3高分子材料的结构与性能 高分子材料 高分子化合物,高分子聚合物 (polymers) 相对分子质量(relative molecular mass)>5000 单体(monomer) 构成高分子化合物的低分子化合物。如CH2CH2 链节(repeat unit))魔 大分子链中结构相同的单元。如CH2CH, 人。 ● 聚合度 大分子链中链节的重复次数 (degree of polymerization 公器 ● 聚合反应 由低分子化合物合成高分子化合物的反应。 (polymerization) 种或几种单体相互加成而连接成聚合物的 ● 加聚反应 (addition ~ 反应。反应过程中没有副产物的产生。 ● 缩聚反应 种或几种单体相互缩合而连接成聚合物, (condensation-) 同时析出(缩去)某种低分子物质的反应
PVC分子三维模型 高分子材料 (polymers) 单体(monomer) 链节(repeat unit) 构成高分子化合物的低分子化合物。如CH2=CH2 大分子链中结构相同的单元。如—CH2—CH2— 高分子化合物,高分子聚合物 相对分子质量(relative molecular mass)>5000 1.3 高分子材料的结构与性能 n CH2 = CH − Cl 氯乙烯 CH2 −CH−CH2−CH−CH2−CH − Cl 聚氯乙烯 − Cl − Cl 单体 聚合物 链节 聚合反应 (polymerization) 加聚反应 (addition ~) 缩聚反应 (condensation~) 一种或几种单体相互缩合而连接成聚合物, 同时析出(缩去)某种低分子物质的反应。 一种或几种单体相互加成而连接成聚合物的 反应。反应过程中没有副产物的产生。 由低分子化合物合成高分子化合物的反应。 聚合度 (degree of polymerization) 大分子链中链节的重复次数
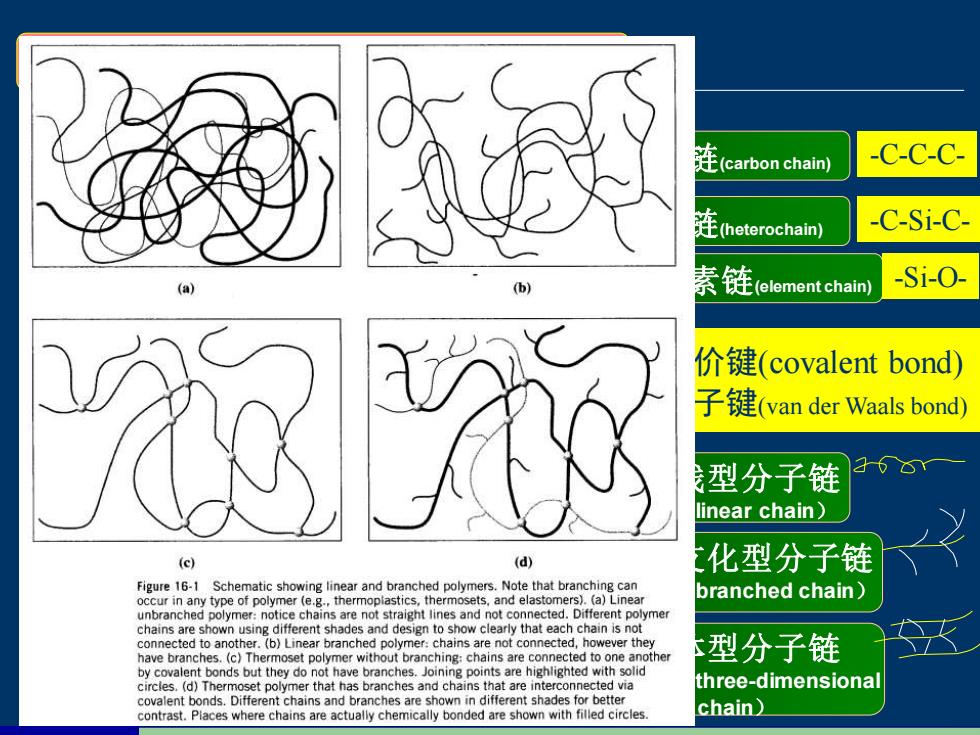
(carbon chain) -C-C-C- (heterochain) C-Si-C- 链(mnhn) -Si-0- 羽网 价键(covalent bond) 子键(van der Waals bond 型分子链 linear chain) (c) (d) 化型分子链 Figure 16-1 Schematic showing linear and branched polymers.Note that branching can occur in any type of polymer (e.g.,thermoplastics,thermosets,and elastomers).(a)Linear branched chain) unbranched polymer:notice chains are not straight lines and not connected.Different polymer chains are shown using different shades and design to show clearly that each chain is not connected to another.(b)Linear branched polymer:chains are not connected,h owever they have branches.(c)Thermoset polymer without branching:chains are connected to one another 型分子链 by covalent bonds but they do not have branches.Joining points are highlighted with solid circles.(d)Thermoset polymer that has branches and chains that are interconnected via three-dimensional covalent bonds.Different chains and branches are shown in different shades for better contrast.Places where chains are actually chemically bonded are shown with filled circles. chain)
1、大分子链(chain)结构 1) 大分子链的化学组成 碳链(carbon chain) 杂链(heterochain) 元素链(element chain) 2) 大分子链的结合键 线型分子链 (linear chain) 支化型分子链 (branched chain) 体型分子链 (three-dimensional chain) 3)大分子链的形态 以主链上是否全部、部分 和全无碳原子分三种类型。 以大分子链的几何形态分 三种类型。 1.3.1 高分子材料的结构 -C-C-C- -C-Si-C- -Si-O- 链内为共价键(covalent bond) 链间为分子键(van der Waals bond)
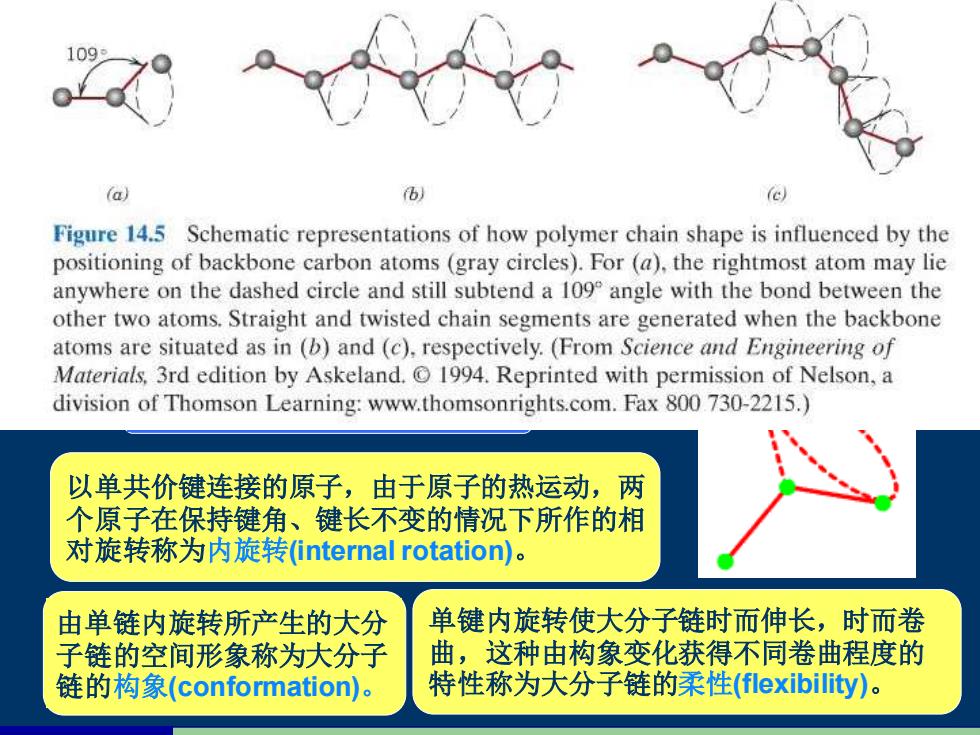
109 (a 韧 e Figure 14.5 Schematic representations of how polymer chain shape is influenced by the positioning of backbone carbon atoms(gray circles).For(a),the rightmost atom may lie anywhere on the dashed circle and still subtend a 109 angle with the bond between the other two atoms.Straight and twisted chain segments are generated when the backbone atoms are situated as in (b)and(c),respectively.(From Science and Engineering of Materials,3rd edition by Askeland.1994.Reprinted with permission of Nelson,a division of Thomson Learning:www.thomsonrights.com.Fax 800 730-2215.) 以单共价键连接的原子,由于原子的热运动,两 个原子在保持键角、键长不变的情况下所作的相 对旋转称为内旋转(internal rotation). 由单链内旋转所产生的大分 单键内旋转使大分子链时而伸长,时而卷 子链的空间形象称为大分子 曲,这种由构象变化获得不同卷曲程度的 链的构象(conformation)。 特性称为大分子链的柔性(flexibility)
1、大分子链结构 4) 大分子链的空间构型 (configuration) 5)大分子链的构象及柔性 将主链上的C原子拉成锯齿状固 定在平面上,以取代基在空间的 排列方式分。 1.3.1 高分子材料的结构 H R H R HH H H C C C C H R H H HH H R C C C C H R H H HH H H C C C C 全同立构 (isotactic) 间同立构 (syndiotactic) 无规立构 (atactic) 以单共价键连接的原子,由于原子的热运动,两 个原子在保持键角、键长不变的情况下所作的相 对旋转称为内旋转(internal rotation)。 由单链内旋转所产生的大分 子链的空间形象称为大分子 链的构象(conformation)。 单键内旋转使大分子链时而伸长,时而卷 曲,这种由构象变化获得不同卷曲程度的 特性称为大分子链的柔性(flexibility)
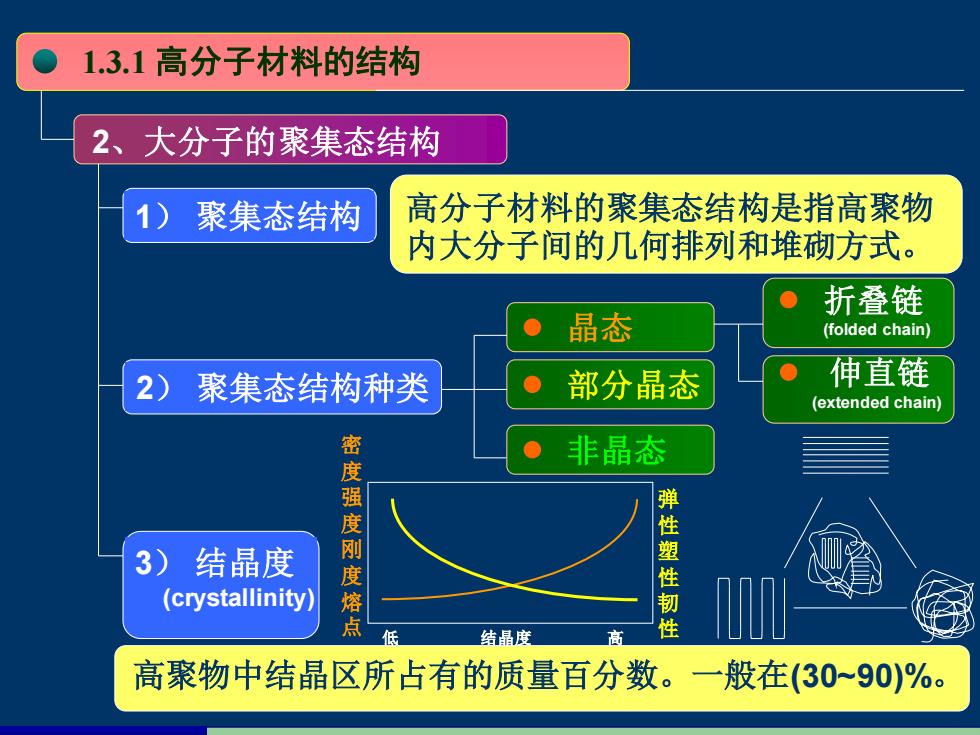
1.3.1高分子材料的结构 2、大分子的聚集态结构 1) 聚集态结构 高分子材料的聚集态结构是指高聚物 内大分子间的几何排列和堆砌方式。 折叠链 晶态 (folded chain) 2)》 聚集态结构种类 部分晶态 伸直链 (extended chain) 非晶态 度强度刚 3)结晶度 弹性 度 (crystallinity) 熔 性 点 低 结晶度 性 高聚物中结晶区所占有的质量百分数。一般在(30-90)%
1.3.1 高分子材料的结构 2、大分子的聚集态结构 1) 聚集态结构 2) 聚集态结构种类 3) 结晶度 (crystallinity) 高分子材料的聚集态结构是指高聚物 内大分子间的几何排列和堆砌方式。 晶态 部分晶态 非晶态 折叠链 (folded chain) 伸直链 (extended chain) 高聚物中结晶区所占有的质量百分数。一般在(30~90)%。 密 度 强 度 刚 度 熔 点 低 结晶度 高 弹 性 塑 性 韧 性

1.3.2高分子材料的性能 1、高分子材料的工艺性能 热压 高分子 注塑 热挤 切削加工 喷射 件 料 真空成型 热处理、焊接等 高分子材料导热性差,切削热易使热塑性材料变软, 热固性材料变焦
1、高分子材料的工艺性能 1.3.2 高分子材料的性能 高 分 子 材 料 热压 注塑 热挤 喷射 真空成型 切削加工 零 件 热处理、焊接等 高分子材料导热性差,切削热易使热塑性材料变软, 热固性材料变焦
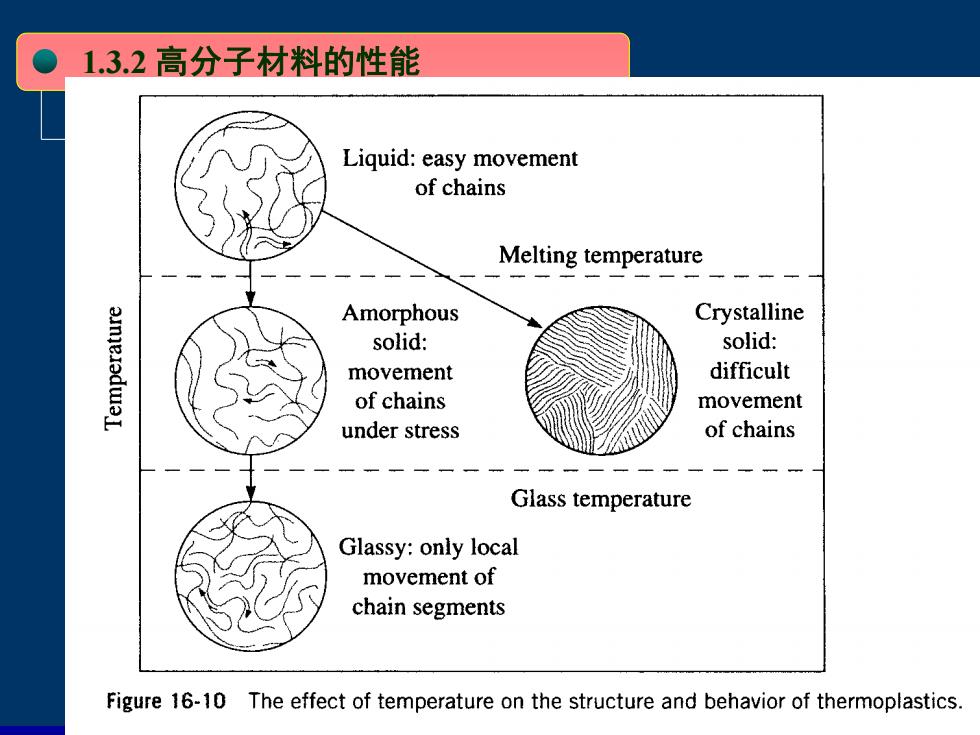
● 1.3.2高分子材料的性能 Liquid:easy movement of chains Melting temperature Amorphous Crystalline aIeladwaI solid: solid: movement difficult of chains movement under stress of chains Glass temperature Glassy:only local movement of chain segments Figure 16-10 The effect of temperature on the structure and behavior of thermoplastics
侧基、链节、小支链运动 链段“冻结”,应力应变同步 2、高分子材料的机械性能 线型非晶态高聚物的三种力学状态 线型晶态高聚物的力学状态 1) 高聚物的力学状态 温度 变形 玻璃态 高弹态 粘流态 Tb Tg Tf Td 体型高聚物的力学状态 线型晶态高聚 物没有高弹态 随着交联点密度的提高, 高聚物的高弹态越来越少 室温下处于 玻璃态、高 弹态和粘流 态的高聚物 一般为塑料、 橡胶和流动 树脂。 1.3.2 高分子材料的性能 链段“解冻” ,链间不滑动 整链舒展与卷曲,应变不同步 链间滑动 变形不可逆
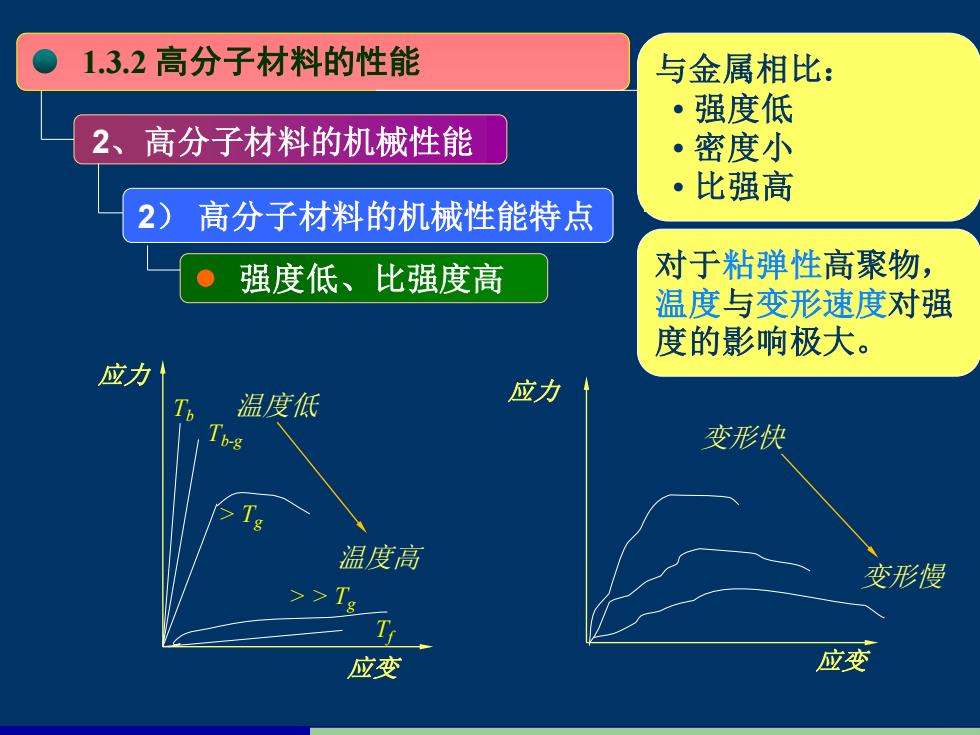
1.3.2高分子材料的性能 与金属相比: 强度低 。 2、高分子材料的机械性能 ·密度小 比强高 2 高分子材料的机械性能特点 强度低、比强度高 对于粘弹性高聚物, 温度与变形速度对强 度的影响极大。 应力 温度低 应力 变形快 温度高 变形馒 ≥>1 应变 应变
2、高分子材料的机械性能 2) 高分子材料的机械性能特点 强度低、比强度高 对于粘弹性高聚物, 温度与变形速度对强 度的影响极大。 变形快 变形慢 应变 应力 1.3.2 高分子材料的性能 与金属相比: • 强度低 • 密度小 • 比强高 温度低 温度高 应变 应力 Tb Tb-g > Tg Tf > > Tg
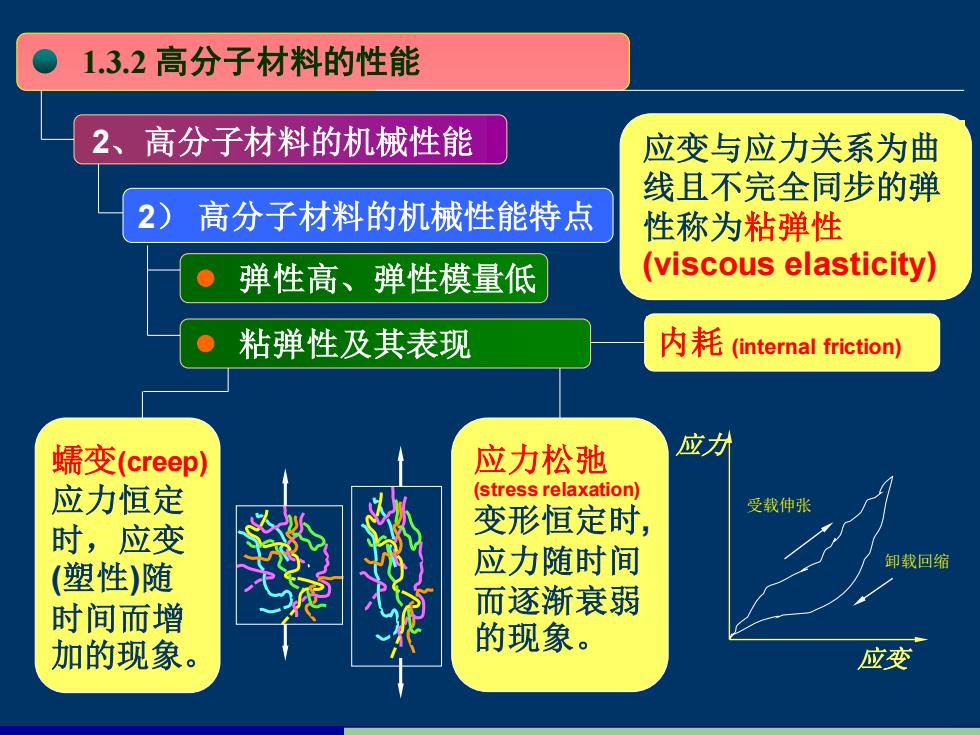
1.3.2高分子材料的性能 2、高分子材料的机械性能 应变与应力关系为曲 线且不完全同步的弹 2 高分子材料的机械性能特点 性称为粘弹性 ● 弹性高、弹性模量低 (viscous elasticity) 粘弹性及其表现 内耗((internal friction) 蠕变(creep) 应力松弛 应力 应力恒定 (stress relaxation) 时,应变 变形恒定时, 受载伸张 应力随时间 卸载回缩 (塑性)随 时间而增 而逐渐衰弱 加的现象。 的现象。 应变
1.3.2 高分子材料的性能 2、高分子材料的机械性能 2) 高分子材料的机械性能特点 应变与应力关系为曲 线且不完全同步的弹 性称为粘弹性 弹性高、弹性模量低 (viscous elasticity) 粘弹性及其表现 应力松弛 (stress relaxation) 变形恒定时, 应力随时间 而逐渐衰弱 的现象。 内耗 (internal friction) 应变 应力 受载伸张 卸载回缩 蠕变(creep) 应力恒定 时,应变 (塑性)随 时间而增 加的现象

Figure 8-4 (a) In an undeformed thermoplastic polymer tensile bar,(a)the polymer chains are randomly oriented. (b)When a stress is applied,a neck Polymer chains develops as chains become aligned before deformation locally.The neck continues to grow until the chains in the entire gage length have aligned.(c)The strength of the polymer is increased. (b) Stress Alignment of chains by deformation
2、高分子材料的机械性能 2) 高分子材料的机械性能特点 塑性 塑性: 1、屈服应变高 达20% 2、颈缩变形阶 段长,断裂 前变形高达 1000% 1.3.2 高分子材料的性能 Necking and crystallization