
Interference of light waves
Interference of light waves

Agenda Today 1.Two-slit experiment 2.Film interference 3.Newton's rings
Agenda Today 1. Two-slit experiment 2. Film interference 3. Newton’s rings

Conditions for interference 1 the source should be monochromatic(单色) same frequency 2 the sources must maintain a constant phase difference. Why is there no interference pattern caused by two bulbs?
Conditions for interference 1 the source should be monochromatic(单色) same frequency 2 the sources must maintain a constant phase difference. Why is there no interference pattern caused by two bulbs?
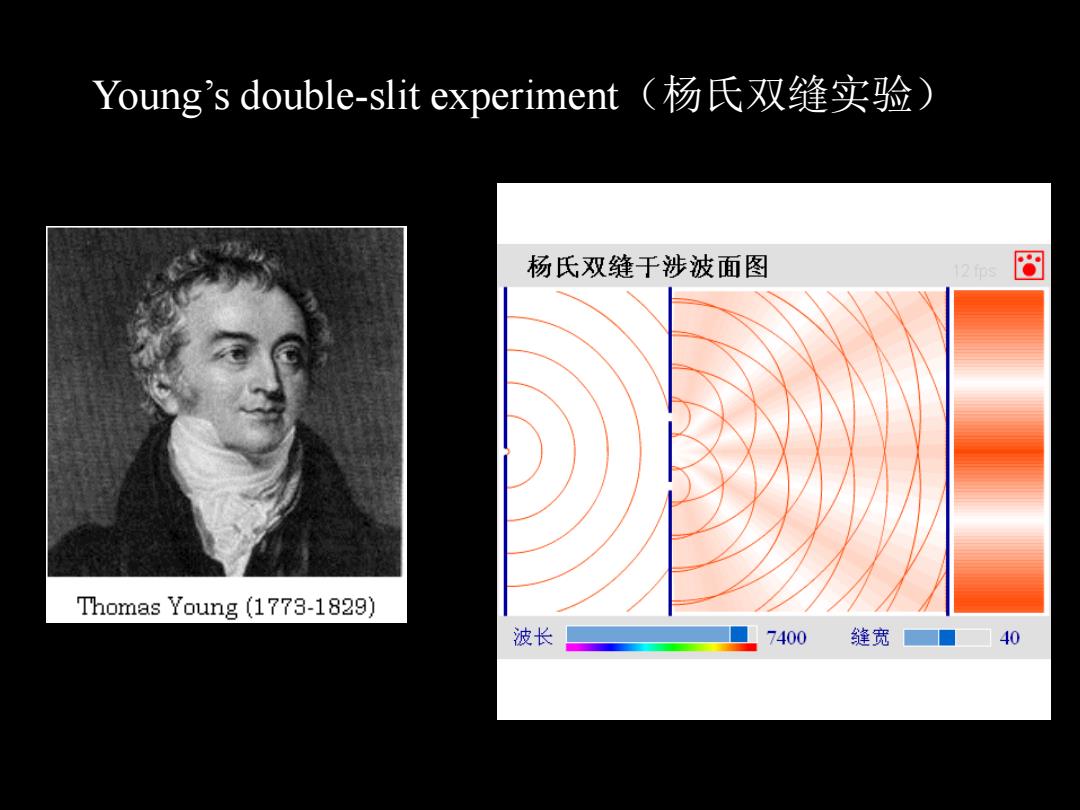
Young's double-slit experiment(杨氏双缝实验 杨氏双缝于涉波面图 回 Thomas Young (1773-1829) 波长 7400 缝宽■ 40
Young’s double-slit experiment(杨氏双缝实验)

In the case the double slits δ=h-K≈dsin8 D>a is very small s08=g9-d月 疗=k=02) Constructive bright fringes 号=-&-123) Destructive dark fringes
In the case the double slits: r1 r2 x P S s1 s2 D d o P S s1 s2 D d o Constructive bright fringes Destructive dark fringes

Intensity distribution of the double-slit interference leKcot
Intensity distribution of the double-slit interference

Example:white light passes through two slits 0.50 mm apart and an interference pattern is observed on a screen 2.5 m away.The first-order fringe resembles a rainbow with violet and red light at either end.The violet light falls about 2.0 mm and the red 3.5 mm from the center of the central white fringe.Estimate the wavelengths of the violet and red lights Solution: since k=1 for violet light,we will have: 元400400 For red light: 1
Example: white light passes through two slits 0.50 mm apart and an interference pattern is observed on a screen 2.5 m away. The first-order fringe resembles a rainbow with violet and red light at either end. The violet light falls about 2.0 mm and the red 3.5 mm from the center of the central white fringe. Estimate the wavelengths of the violet and red lights Solution: since k=1 , for violet light , we will have: For red light:
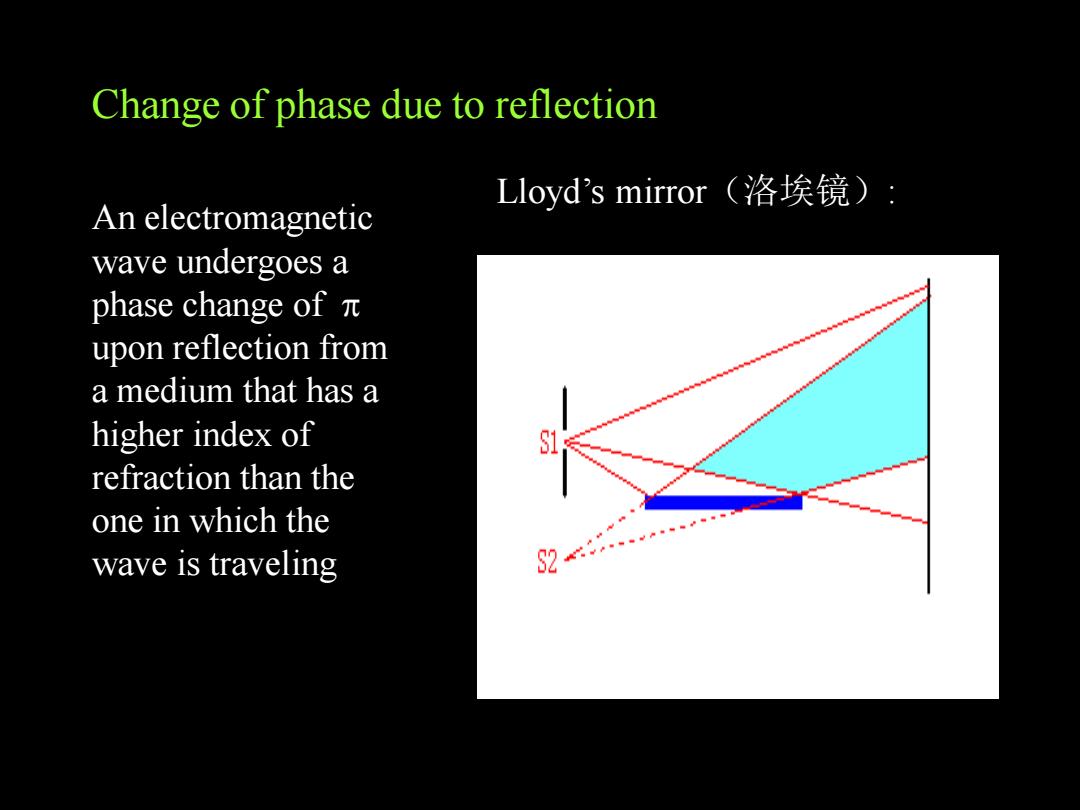
Change of phase due to reflection Lloyd's mirror(洛埃镜) An electromagnetic wave undergoes a phase change ofπ upon reflection from a medium that has a higher index of refraction than the one in which the wave is traveling
Change of phase due to reflection Lloyd’s mirror(洛埃镜): An electromagnetic wave undergoes a phase change of upon reflection from a medium that has a higher index of refraction than the one in which the wave is traveling

Interference in thin films(薄膜干涉) Two things must be noted: 1.The phase shift due to reflection. 2.The wavelength of light An in a medium whose refraction index is n is n Where A is the wavelength of the light in free space
Interference in thin films(薄膜干涉): Two things must be noted: 1. The phase shift due to reflection. 2. The wavelength of light n in a medium whose refraction index is n is Where is the wavelength of the light in free space

Antireflective coatings(增透膜〉 A coating material must have an index of refraction between that of air and the glass to be coated. Where A is the wavelength in min vacuum of the rays that we want pass through the coating n is the refraction index
Antireflective coatings(增透膜) A coating material must have an index of refraction between that of air and the glass to be coated. Where is the wavelength in vacuum of the rays that we want pass through the coating , n is the refraction index