
Faraday's Law C20BANKENGLAND 820 TWENTY
Faraday’s Law

Agenda Today 1.Faraday's Law of induction 2.Motional EMF 3.Induced electric Field
Agenda Today 1. Faraday’s Law of induction 2. Motional EMF 3. Induced electric Field
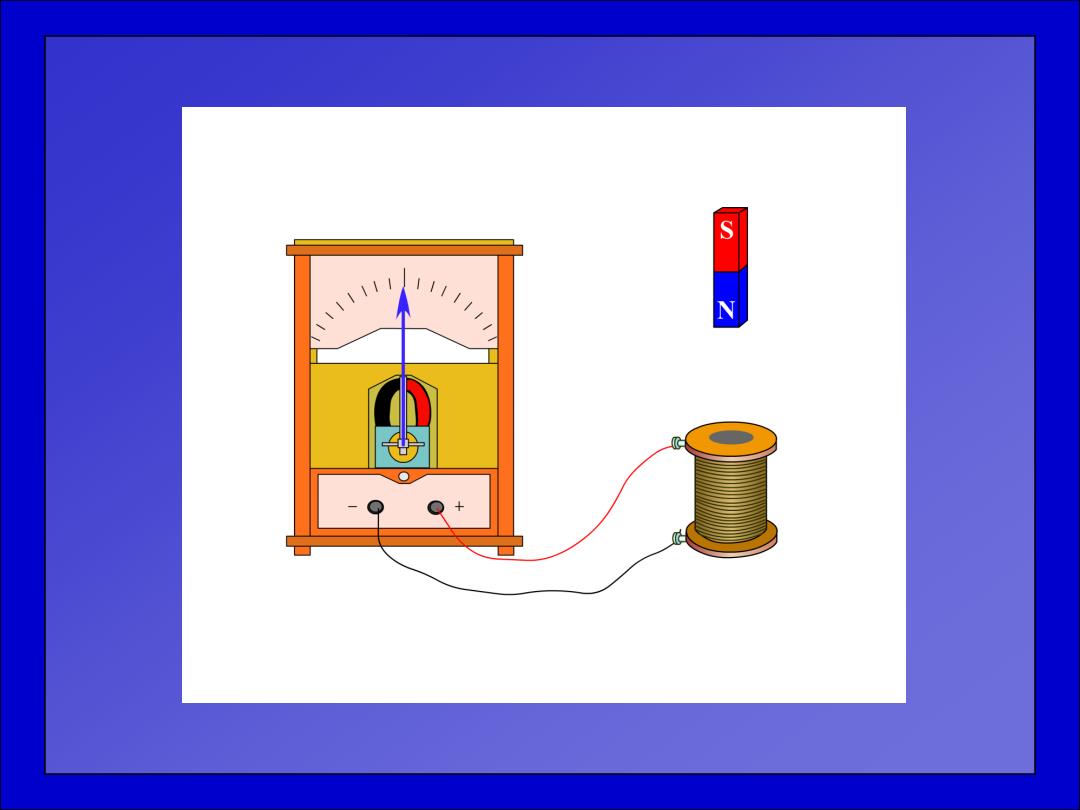
111 N Q+
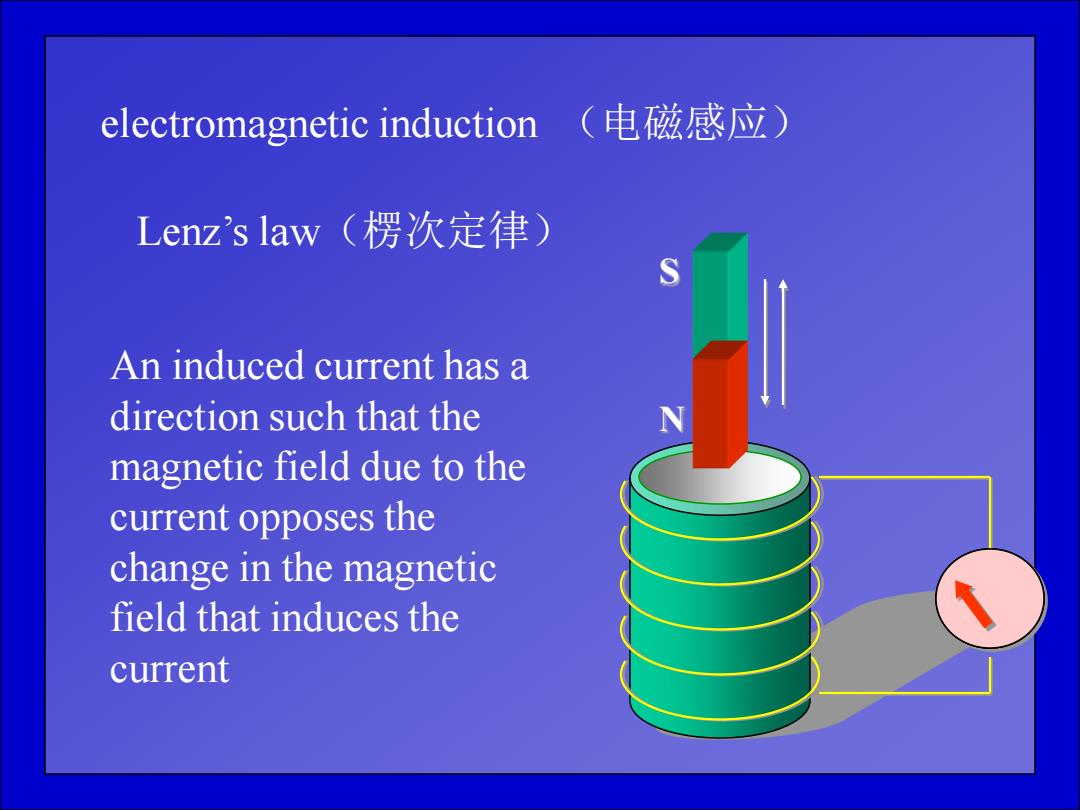
electromagnetic induction (电磁感应) Lenz's law(楞次定律) An induced current has a direction such that the magnetic field due to the current opposes the change in the magnetic field that induces the current
electromagnetic induction (电磁感应) S N Lenz’s law(楞次定律) An induced current has a direction such that the magnetic field due to the current opposes the change in the magnetic field that induces the current

Lenz's Law from viewpoint of energy
Lenz’s Law : from viewpoint of energy v a b c d B

Magnetic flux(磁通量) I%=∫Bd 1Wb=1T*m2 Gauss's law for magnetic field ∮Bk=0
Magnetic flux(磁通量) Gauss’s law for magnetic field 1Wb=1T*m2
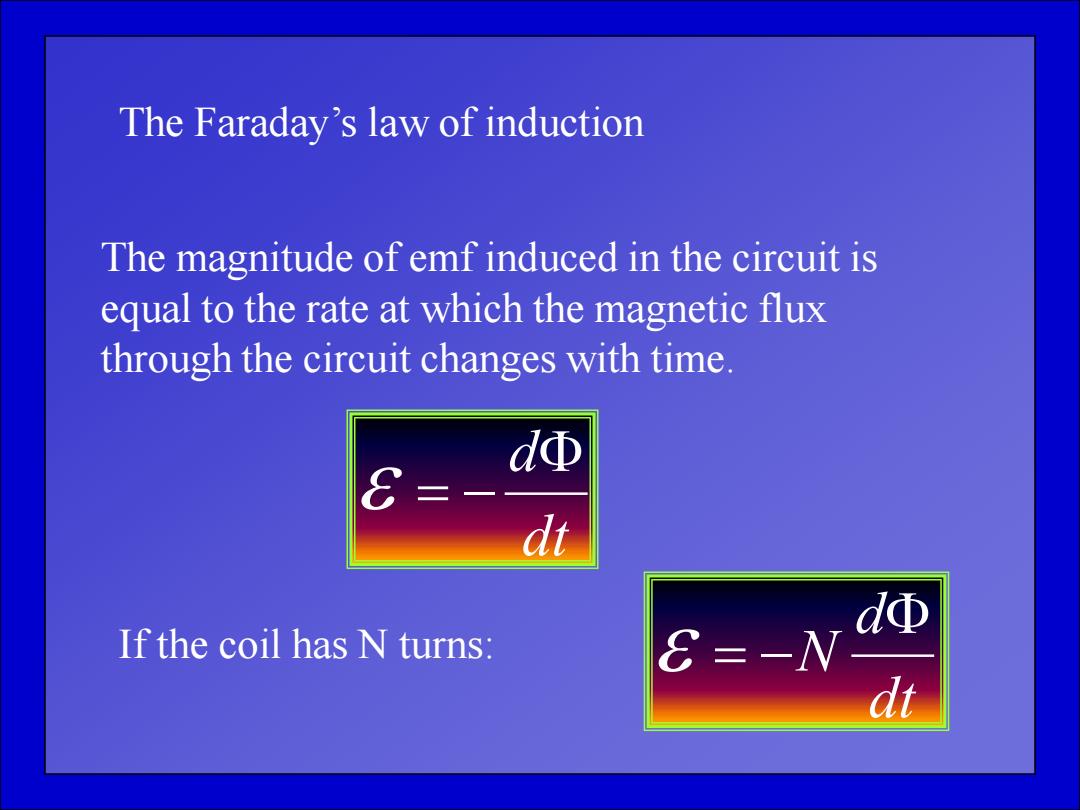
The Faraday's law of induction The magnitude of emf induced in the circuit is equal to the rate at which the magnetic flux through the circuit changes with time. dΦ dt dΦ If the coil has N turns: =-W
The Faraday’s law of induction The magnitude of emf induced in the circuit is equal to the rate at which the magnetic flux through the circuit changes with time. dt d If the coil has N turns: dt d N
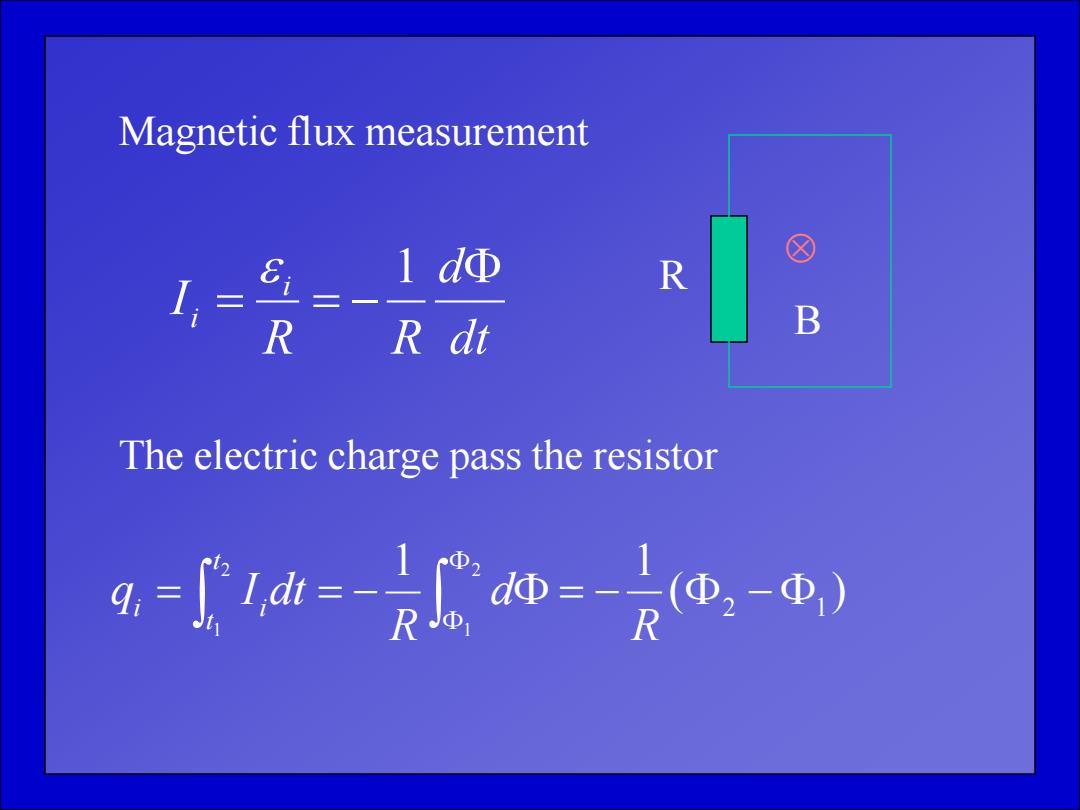
Magnetic flux measurement 1dΦ ④ I = = R RR dt The electric charge pass the resistor g=1h=-m=-R@,-)
Magnetic flux measurement dt d R R I i i 1 The electric charge pass the resistor ( ) 1 1 2 1 2 1 2 1 R d R q I dt t t i i R B
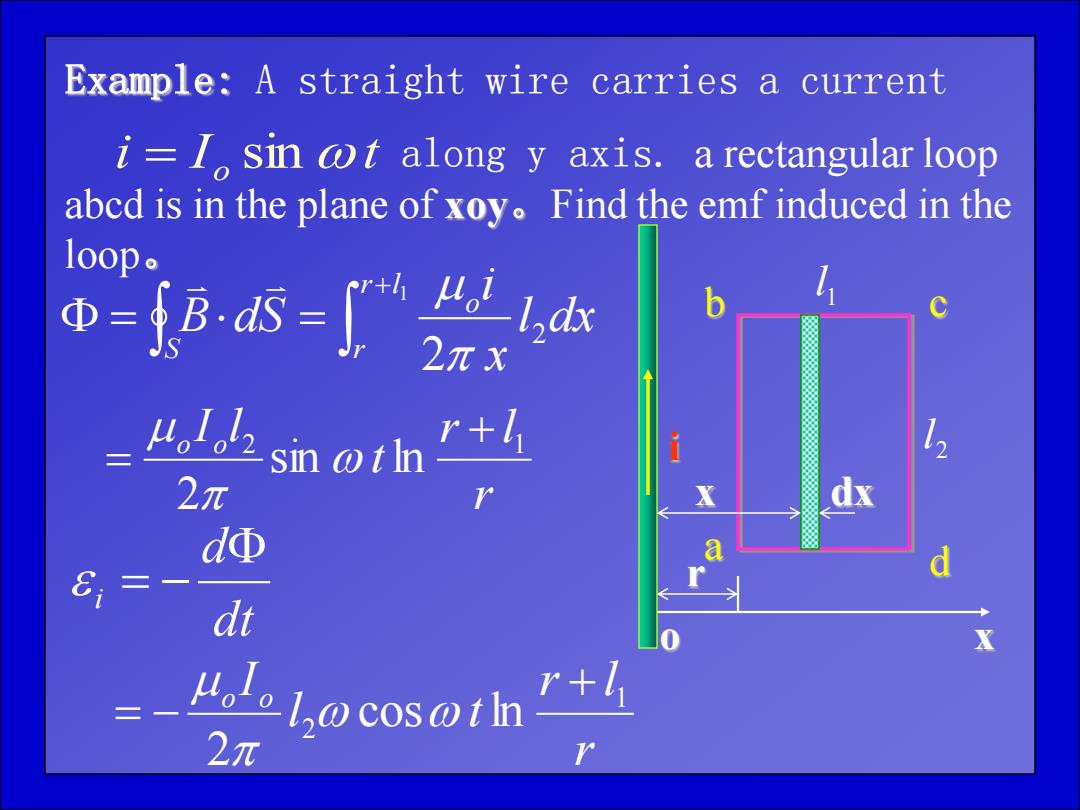
Example:A straight wire carries a current i=I sin ot along y axis.a rectangular loop abed is in the plane of xoy.Find the emf induced in the Bs-兴a loop 42 2π sin t+☑ dΦ E 三一 dt 2元 hocosotth
Example: A straight wire carries a current along y axis. a rectangular loop abcd is in the plane of xoy。Find the emf induced in the loop。 i I t o sin o 1 l 2 l d b c a r x i x dx 1 2 2 r l r o S l dx x i B dS r r l t I l o o 2 1 sin ln 2 dt d i r r l l t Io o 1 2 cos ln 2