
CH2 PSD Estimation “Spectral Estimation is···an Art” Petre Stoica
CH2 PSD Estimation “ Spectral Estimation is ···an Art ” Petre Stoica

Content o Introduction o Periodogram and correlogram o Nonparametric methods o Parametric methods for Rational spectra o Parametric methods for line spectra o Filter-bank approach o Spatial methods P.Stoica,R.Moses-Spectral Analysis of Signals,Prentice Hall,2005(ISBN:0-13-113956-8) o Petre Stoica,Uppsala University o Randolph L.Moses,Ohio State University 2020-01-18 2
2020-01-18 2 Content Introduction Periodogram and correlogram Nonparametric methods Parametric methods for Rational spectra Parametric methods for line spectra Filter-bank approach Spatial methods P. Stoica, R. Moses-Spectral Analysis of Signals, Prentice Hall, 2005 (ISBN: 0-13-113956-8) Petre Stoica, Uppsala University Randolph L. Moses, Ohio State University

S1.Introduction o Spectral Estimation Problem o Applications o Deterministic Signals o Random Signals Two definitions of PSD ●Two main approaches 2020-01-18 3
2020-01-18 3 S1. Introduction Spectral Estimation Problem Applications Deterministic Signals Random Signals Two definitions of PSD Two main approaches
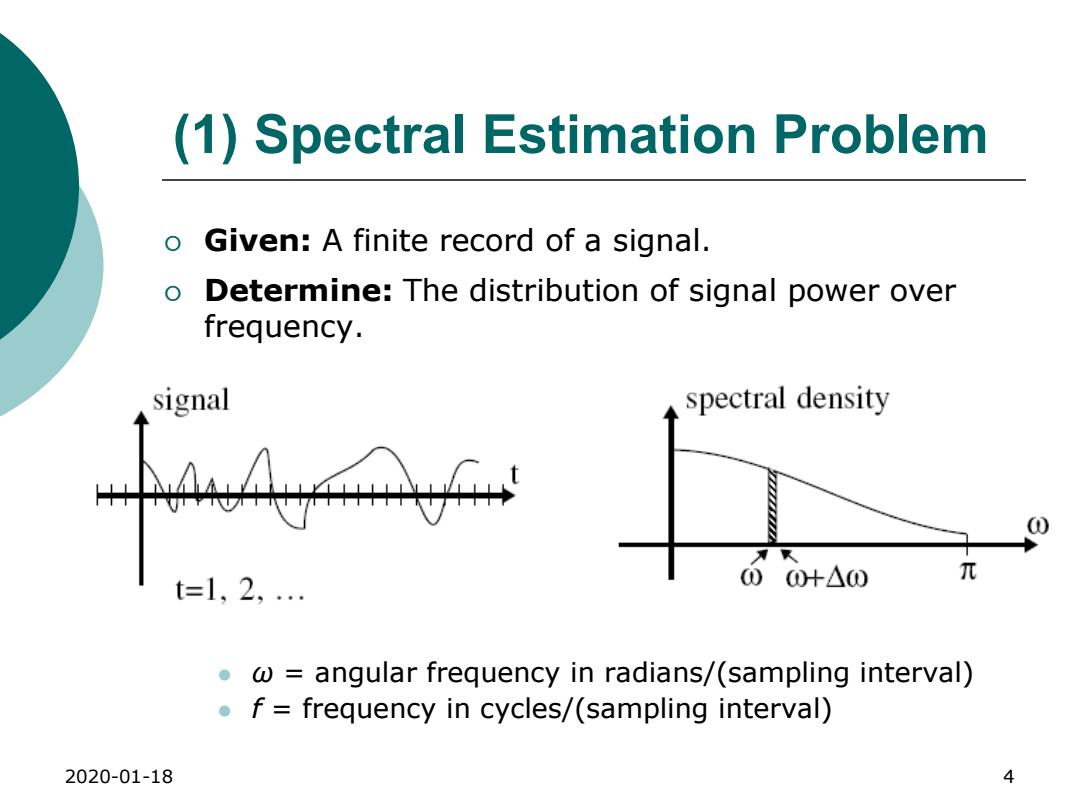
(1)Spectral Estimation Problem o Given:A finite record of a signal. o Determine:The distribution of signal power over frequency. signal spectral density 0+△0 兀 t=1.2 .@angular frequency in radians/(sampling interval) f frequency in cycles/(sampling interval) 2020-01-18 4
2020-01-18 4 (1) Spectral Estimation Problem Given: A finite record of a signal. Determine: The distribution of signal power over frequency. ω = angular frequency in radians/(sampling interval) f = frequency in cycles/(sampling interval)

(2)Applications o Temporal Spectral Analysis ● Vibration monitoring and fault detection Hidden periodicity finding Speech processing and audio devices ● Medical diagnosis Seismology and ground movement study ● Control systems design 。Radar,Sonar 0 Spatial Spectral Analysis Source location using sensor arrays 2020-01-18 5
2020-01-18 5 (2) Applications Temporal Spectral Analysis Vibration monitoring and fault detection Hidden periodicity finding Speech processing and audio devices Medical diagnosis Seismology and ground movement study Control systems design Radar, Sonar Spatial Spectral Analysis Source location using sensor arrays ……
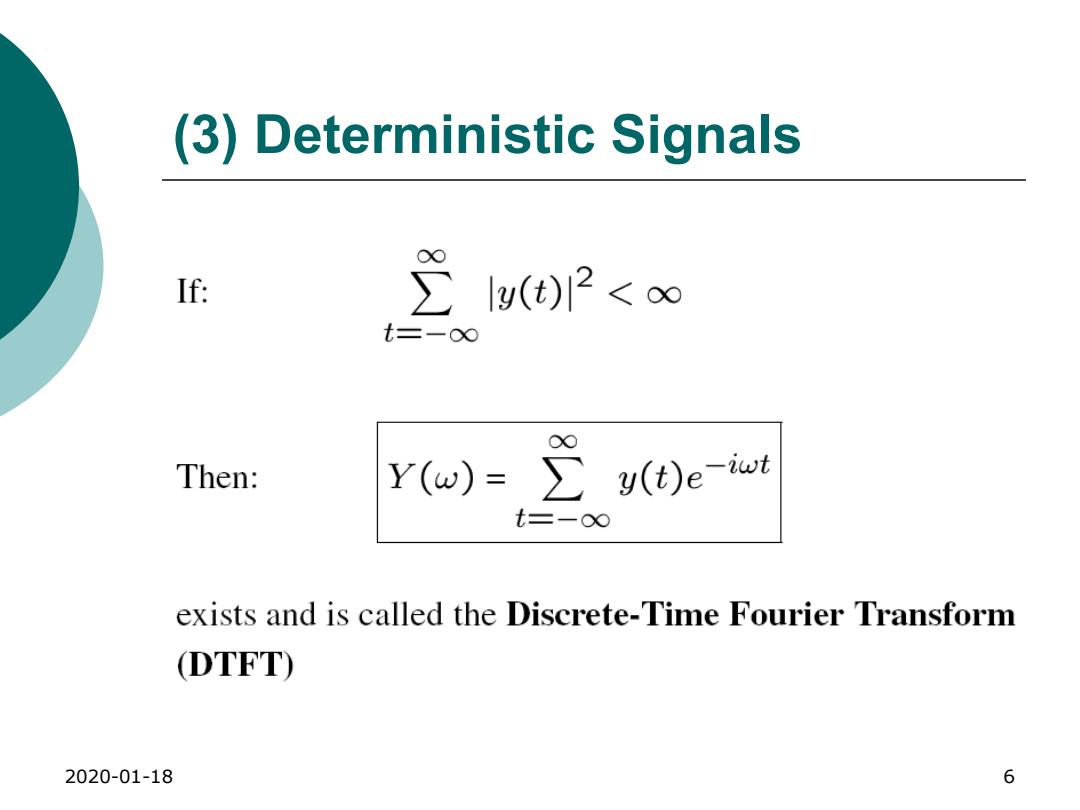
(3)Deterministic Signals If: ∑1g(t)2<o∞ 0o Then: Y(w)=∑y(t)e-iwt t=-o∞ exists and is called the Discrete-Time Fourier Transform DTFT) 2020-01-18 6
2020-01-18 6 (3) Deterministic Signals
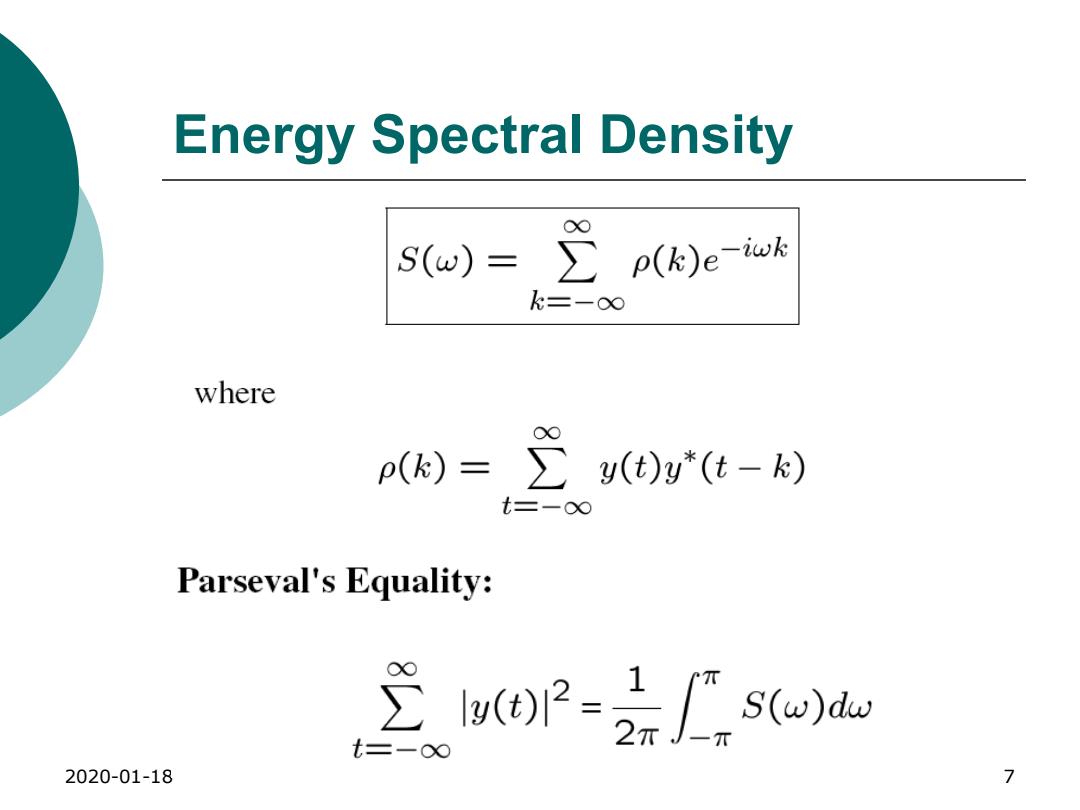
Energy Spectral Density O0 S(w)=∑p(k)eiwk k=-0∞ where p(k)=∑y(t)y*(t-k) t=-0 Parseval's Equality: 22-2 S(w)dw 2020-01-18 7
2020-01-18 7 Energy Spectral Density
(3)Random Signals Random Signal random signal probabilistic statements about future variations △M2 current observation time 2020-01-18 8
2020-01-18 8 (3) Random Signals
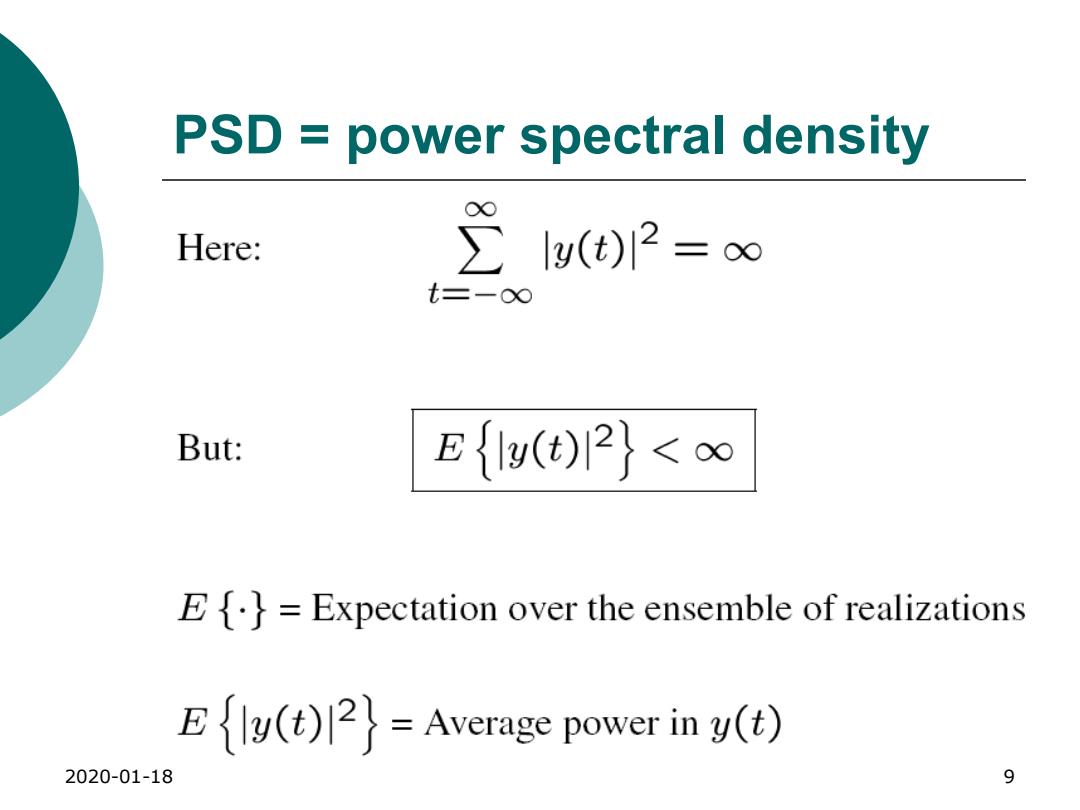
PSD power spectral density Here: 21(e)2=∞ t三-O∞ But: E{(t)12<∞ E{.}=Expectation over the ensemble of realizations (t)2=Average power in y(t) 2020-01-18 9
2020-01-18 9 PSD = power spectral density
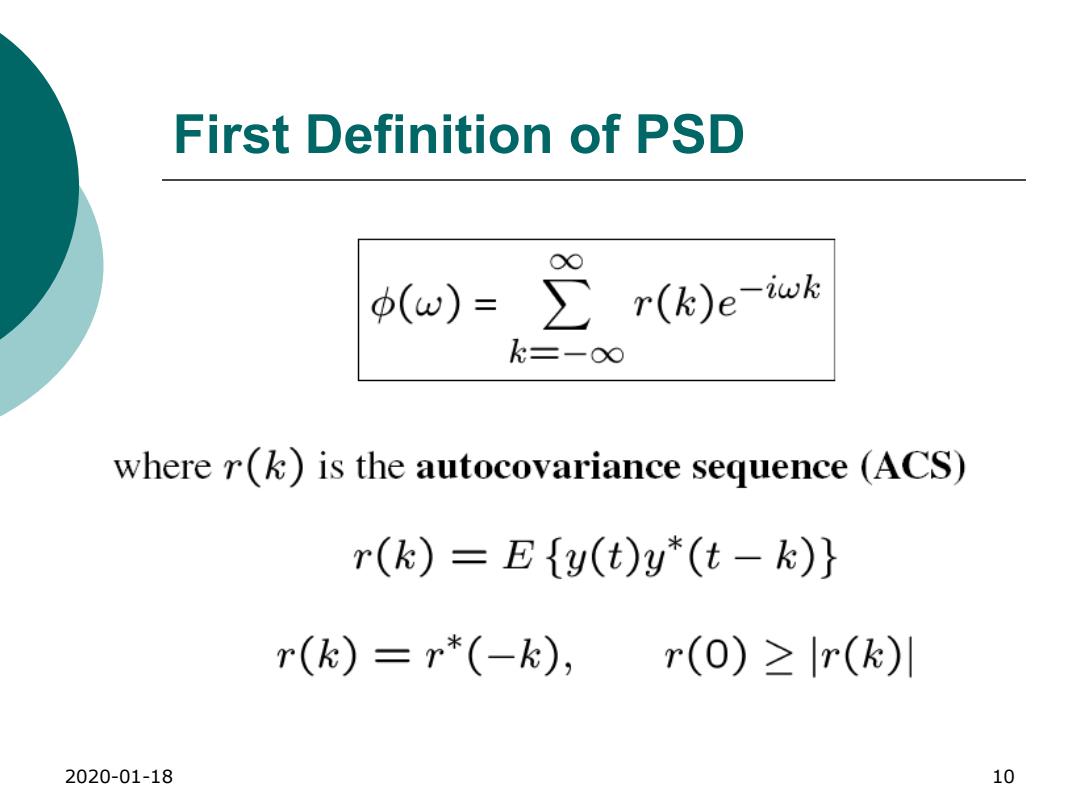
First Definition of PSD (w)=∑r(k)e-iwk k=-0∞ where r(k)is the autocovariance sequence (ACS) r(k)=E{y(t)y*(t-k)} r(k)=r*(-k), r(0)≥r(k) 2020-01-18 10
2020-01-18 10 First Definition of PSD