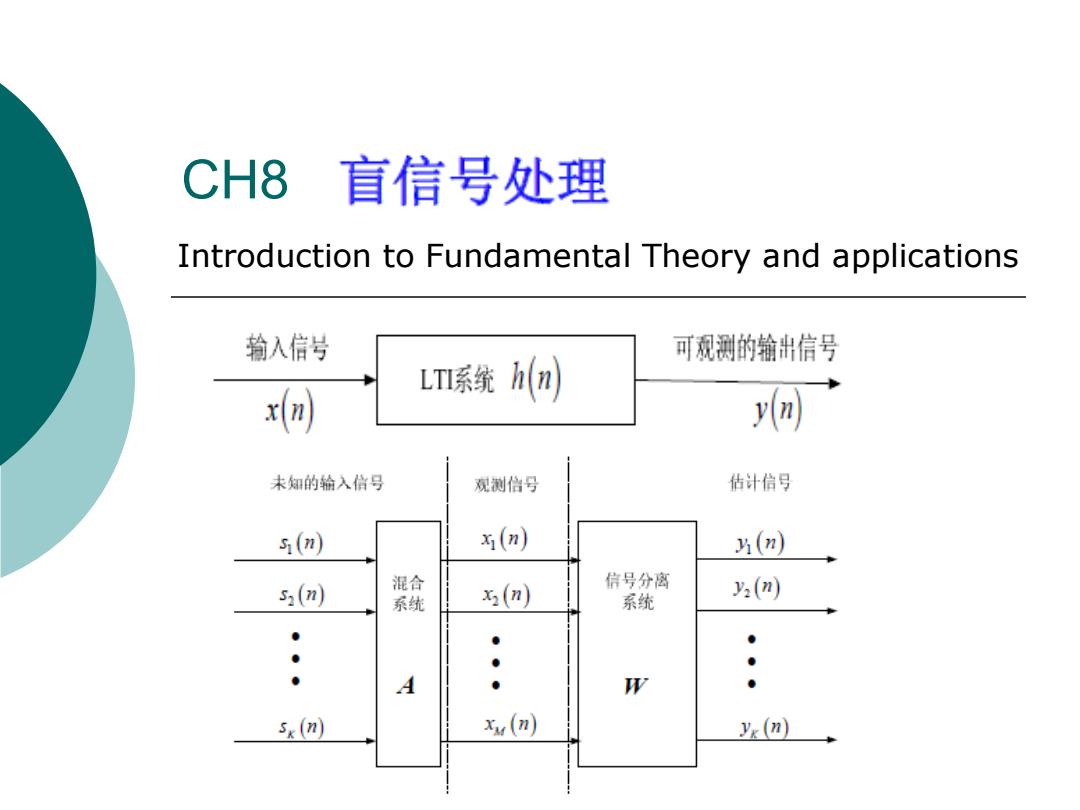
CH8 盲信号处理 Introduction to Fundamental Theory and applications 输入信号 可观测的输出信号 LT系绕h) x(n) 未知的输入信号 观测倍号 估计信号 s(n) (n) 3(n) 信号分离 5(n 混合 系统 (n) 系统 2(m A V s.(n) x (n) y(n)
CH8 Introduction to Fundamental Theory and applications

Contents 盲系统辨识 盲源分离(BSS, Blind Source Separation) 独立分量分析 (ICA, Independent Component Analysis) 信道盲均衡 盲波束形成 2020-01-18 2
2020-01-18 2 Contents
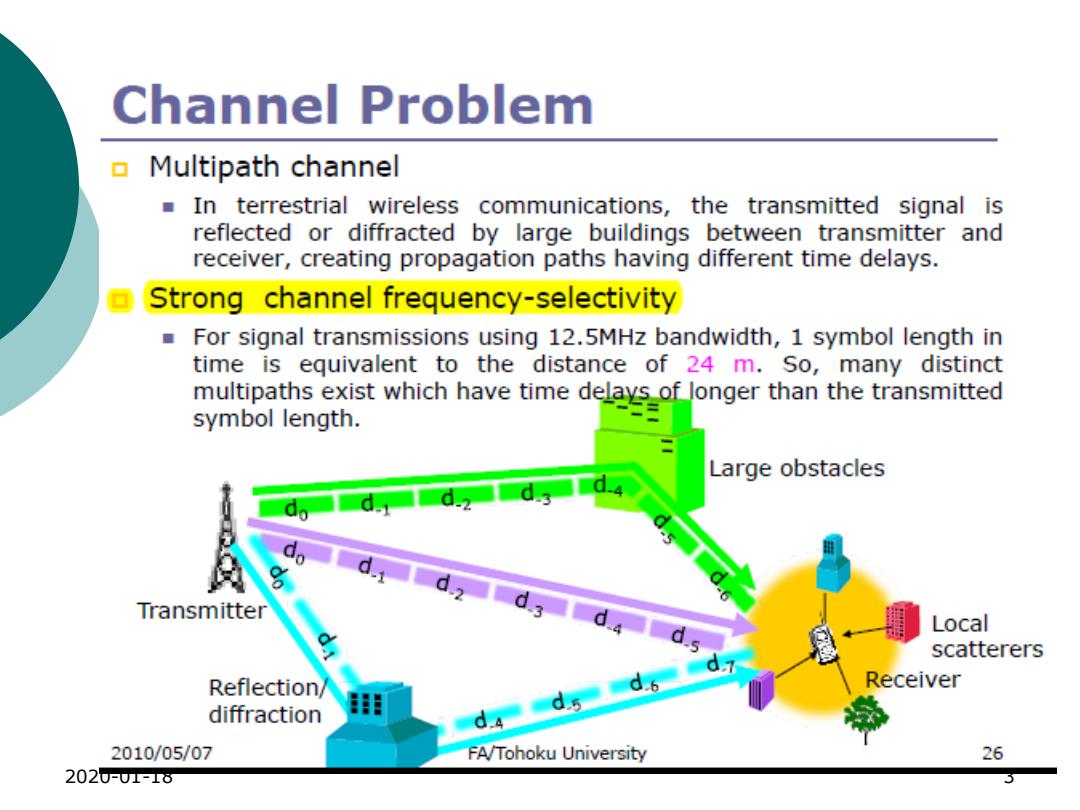
Channel Problem Multipath channel ■ In terrestrial wireless communications,the transmitted signal is reflected or diffracted by large buildings between transmitter and receiver,creating propagation paths having different time delays. 回 Strong channel frequency-selectivity For signal transmissions using 12.5MHz bandwidth,1 symbol length in time is equivalent to the distance of 24 m.So,many distinct multipaths exist which have time delays of longer than the transmitted symbol length. Large obstacles d Transmitter Local scatterers Reflection/ Receiver diffraction 进 d.4d.s 2010/05/07 FA/Tohoku University 26 2020-U1-18 5】
2020-01-18 3

Blind system identification o Time-varying radio channel ●( Channel identification has to be repeated continuously o Training bits constitute a significant portion (roughly 18%)of the transmitted sequence GSM system is based on burst mode communication, where bursts of 148 bits each are transmitted.Each burst has a 26 bit training sequence,which is used to update the channel model. o Fewer training bits,or even without them blind identification/estimation 2020-01-18 4
2020-01-18 4 Blind system identification Time-varying radio channel Channel identification has to be repeated continuously Training bits constitute a significant portion (roughly 18%) of the transmitted sequence GSM system is based on burst mode communication, where bursts of 148 bits each are transmitted. Each burst has a 26 bit training sequence, which is used to update the channel model. Fewer training bits, or even without them blind identification/estimation
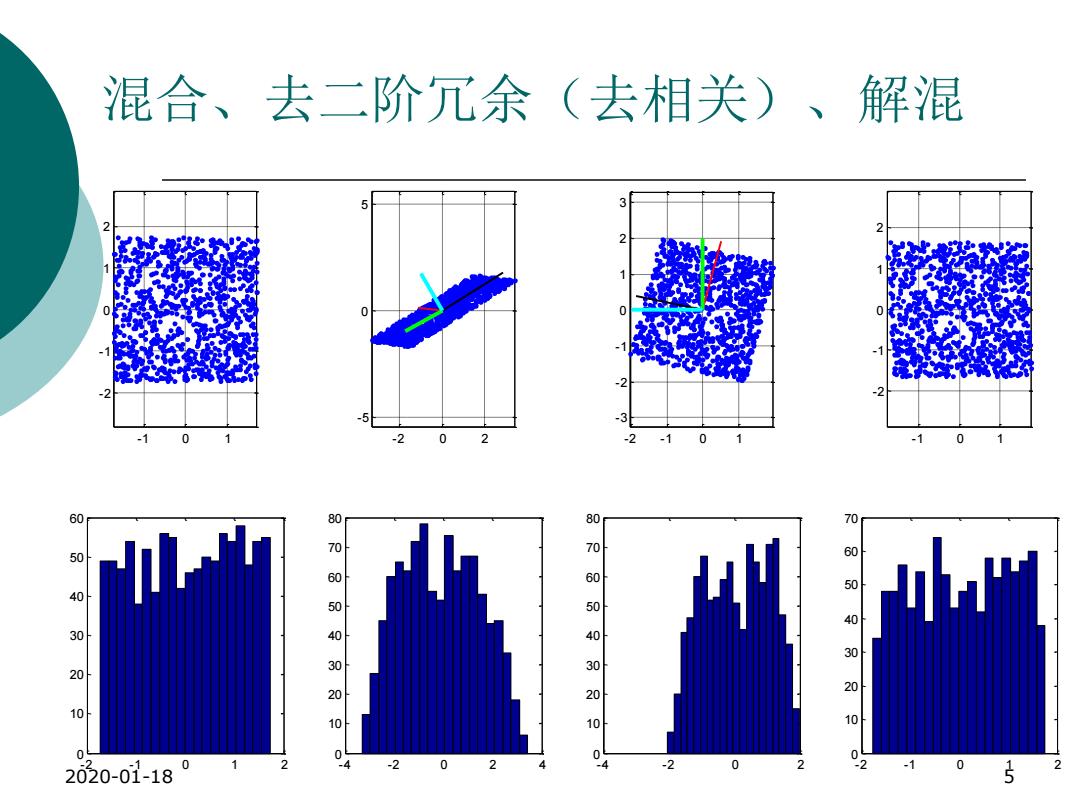
混合、去二阶冗余(去相关)、解混 0 -2 0 -2 -1 0 -1 0 60 50 00000000 000000010 50 40 n 0 30 30 20 20 10 10 0 2020-01-18 0 2 -2 0 0 0 15
混合、去二阶冗余(去相关)、解混 2020-01-18 5 - 1 0 1 - 2 - 1 0 1 2 - 2 - 1 0 1 2 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 - 2 0 2 - 5 0 5 - 4 - 2 0 2 4 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 - 2 - 1 0 1 - 3 - 2 - 1 0 1 2 3 - 4 - 2 0 2 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 - 1 0 1 - 2 - 1 0 1 2 - 2 - 1 0 1 2 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70

[x)-x灯p(x) Kurtosis峭度 -0.6 -3 -0.7 -0.8 -0.9 -1 -1.1 -1.2 -1.3 -1.4 0 100 200 300 400 2020-01-18 6
Kurtosis 峭度 2020-01-18 6 0 100 200 300 400 -1.4 -1.3 -1.2 -1.1 - 1 -0.9 -0.8 -0.7 -0.6

混合、解混、效果 0.2563 -0.9336 0.9581 0.1988 0.2588 0.9659 -0.9659 0.2588 0.9918 -0.0496 0.0004 0.9533 2020-01-18 7
混合、解混、效果 0.2563 -0.9336 0.9581 0.1988 0.2588 0.9659 -0.9659 0.2588 0.9918 -0.0496 0.0004 0.9533 2020-01-18 7

混合、去二阶冗余(去相关)、解混 5 2 .2 2 0 120 120 150 100 o 00 80 100 60 60 40 10 440000000 50 20 20 0 0 -2 0 4 .2 .2 0 2020-01-18 8
混合、去二阶冗余(去相关)、解混 2020-01-18 8 - 2 0 2 - 4 - 3 - 2 - 1 0 1 2 3 4 - 4 - 2 0 2 4 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 - 2 0 2 - 5 0 5 - 4 - 2 0 2 4 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 - 2 0 2 - 4 - 2 0 2 4 - 4 - 2 0 2 4 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 - 2 0 2 - 5 0 5 - 4 - 2 0 2 4 0 50 100 150

Kurtosis峭度 0.15 0.1 0.05 0 -0.05 -0.1 -0.15 -0. 0 100 200 300 400 2020-01-18 9
Kurtosis 峭度 2020-01-18 9 0 100 200 300 400 -0.2 -0.15 -0.1 -0.05 0 0.05 0.1 0.15

混合、解混、效果 1.0144-0.2655 0.2832 0.9441 -0.2079 0.9781 -0.9744 0.2250 0.0662 0.9787 -0.9246 0.4711 2020-01-18 10
混合、解混、效果 1.0144 -0.2655 0.2832 0.9441 -0.2079 0.9781 -0.9744 0.2250 0.0662 0.9787 -0.9246 0.4711 2020-01-18 10