
上游充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY Engineering Thermodynamics I Lectures 14 Spring,3/21/2018 Prof.,Dr.Yonghua HUANG 强 MAMLLLAMAAA http://cc.sjtu.edu.cn/G2S/site/thermo.html 1日G
Engineering Thermodynamics I Lectures 14 Spring, 3/21/2018 Prof., Dr. Yonghua HUANG http://cc.sjtu.edu.cn/G2S/site/thermo.html

△u,△h,cy,and cp relations for ideal gas ideal gas:uAT);hfT) kJ/kg.K →c,definition: du c,(T)= (ideal gas) 0 du=c,(T)dT ()-u()c(TdT (ideal gas) dh →C,definition: dT (ideal gas) The key is to ↓ find c,(T dh=c,(T)dT and cp(T) h()h()TdT Adeal gas) 上游充通大学 March 21,2018 2 SHANGHAI JLAO TONG UNIVERSITY
March 21, 2018 2 Δu, Δh, cv , and cp relations for ideal gas ideal gas: u~f(T); h~f(T) cv definition: cp definition: d ( ) (ideal gas) d v u c T T ( )d v du c T T d ( ) (ideal gas) d p h c T T d ( )d p h c T T 2 1 2 1 ( ) ( ) ( )d (ideal gas) T v T u T u T c T T 2 1 2 1 ( ) ( ) ( )d (ideal gas) T p T h T h T c T T The key is to find cv(T) and cp(T) kJ/kg·K
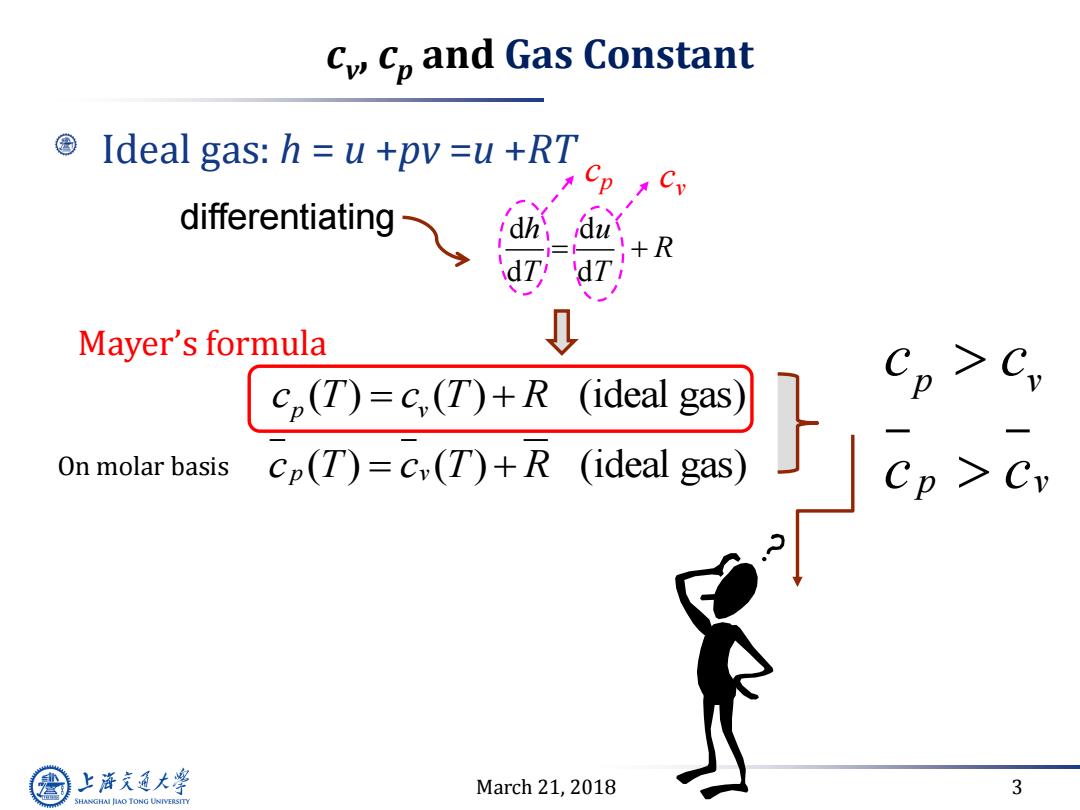
cy Cp and Gas Constant Ideal gas:h u +pv =u +RT differentiating +R dT, 'dT Mayer's formula cp(T)=c,(T)+R (ideal gas) On molar basis cp(T)=c(T)+R (ideal gas) 上游究通大学 March 21,2018 3 SHANGHAI JLAO TONG UNIVERSITY
March 21, 2018 3 cv , cp and Gas Constant Ideal gas: h = u +pv =u +RT d d d d h u R T T cp cv ( ) ( ) (ideal gas) p v c T c T R On molar basis c T c T R p v ( ) ( ) (ideal gas) p v p v c c c c Mayer’s formula differentiating
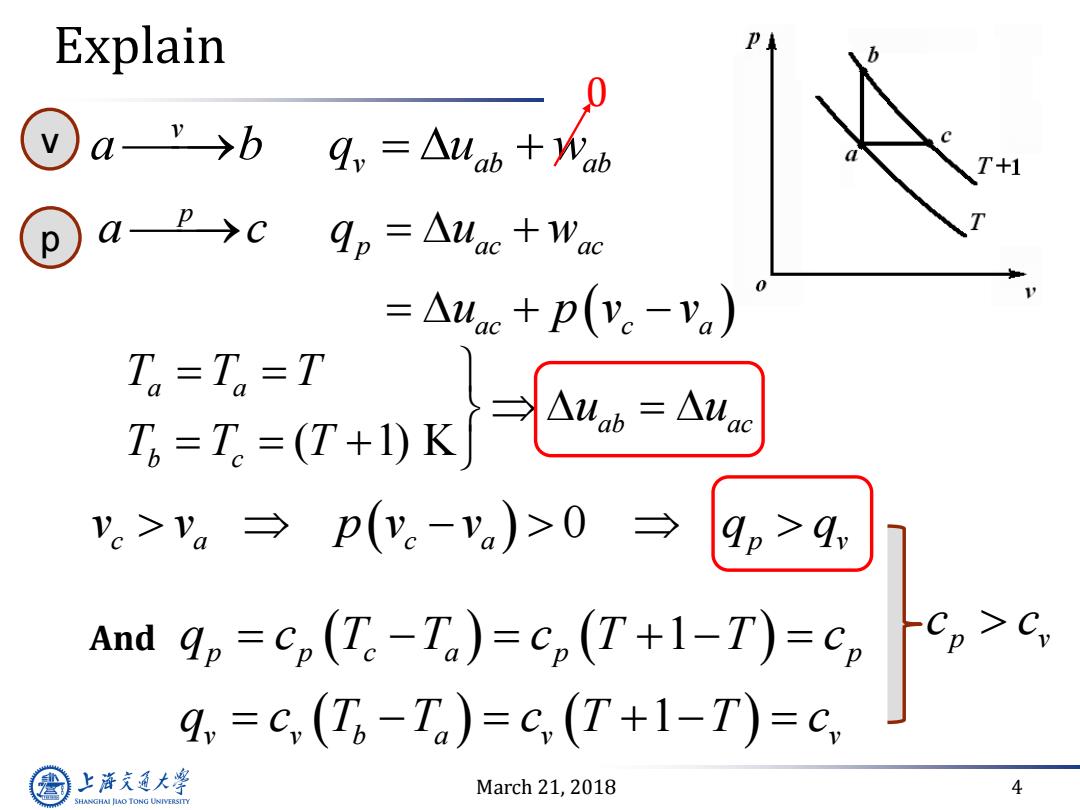
Explain ⊙a→b +1 ap→c qp=△lac+Wac =Auac+p(y。-va) 五=7-行K-= T=T=T .>。→p(.-va)>0→9,>4 And qp =cp(Te-Ta)=Cp(T+1-T)=Cp 4,=C,(T6-Ta)=C(T+1-T)=c, 上游充通大 March 21,2018 4 SHANGHAI JLAO TONG UNIVERSITY
March 21, 2018 4 v v ab ab a b q u w 0 p p ac ac ac c a a c q u w u p v v 0 c a c a p v v v p v v q q And 1 1 p p c a p p v v b a v v q c T T c T T c q c T T c T T c v p Explain ( )1 K ab a a b c a c T T u T T u T T p v c c

Question: Is c,always greater than c,at the same temperature for any phase of any substance 上游充通大学 March 21,2018 5 SHANGHAI JLAO TONG UNIVERSITY
March 21, 2018 5 Is cp always greater than cv at the same temperature ? Question: for any phase of any substance
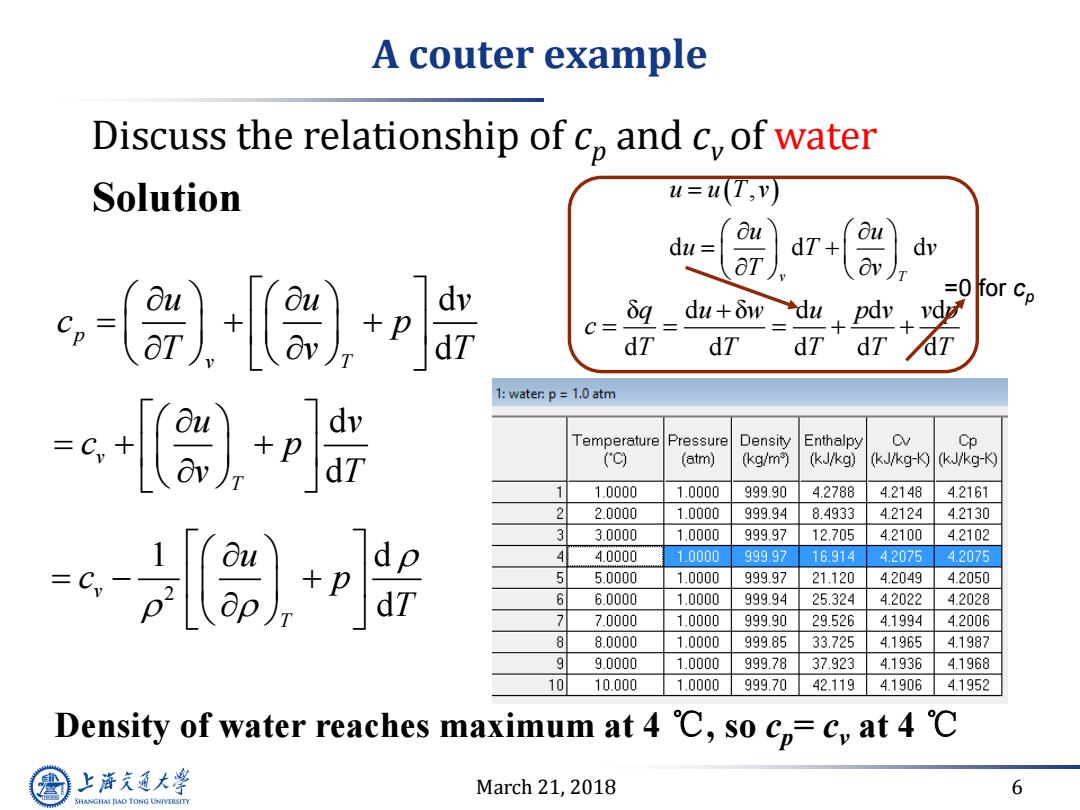
A couter example Discuss the relationship of c,and c,of water Solution u=u(T,v) du= dT dv p δq_du+δw=du+ =0 for Cp dy C= dT dT dT dT 1:water:p=1.0 atm dv T emperature Pressure Density Enthalpy Cp (o (atm) (kg/m) (kJ/kg) (kJ/kg-K(kJ/kg-K) 1.0000 1.0000 999.90 4.2788 4.2148 4.2161 2 2.0000 1.0000 999.94 8.4933 4.2124 4.2130 3 3.0000 1.0000 999.97 12.705 4.2100 4.2102 +p 4 4.0000 1.0000 999.97 16.914 42075 4.2075 5 5.0000 1.0000 999.97 21.120 4.2049 4.2050 6 6.0000 1.0000 999.94 25.324 4.2022 4.2028 7.0000 1.0000 999.90 29.526 4.1994 4.2006 8 8.0000 1.0000 999.85 33.725 4.1965 4.1987 9.0000 1.0000 999.78 37.923 4.1936 4.1968 10.000 1.0000 999.70 42.119 4.1906 4.1952 Density of water reaches maximum at 4 C,so cp=c,at 4 C 上游充通大学 March 21,2018 6 SHANGHAI JLAO TONG UNIVERSITY
March 21, 2018 6 Discuss the relationship of cp and cv of water d d p v T u u v c p T v T Density of water reaches maximum at 4 ℃, so cp= cv at 4 ℃ Solution d d v T u v c p v T 2 1 d d v T u c p T A couter example , d d d v T u u T v u u u T v T v δ d δ d d d d d d d d q u w u p v v p c T T T T T =0 for cp
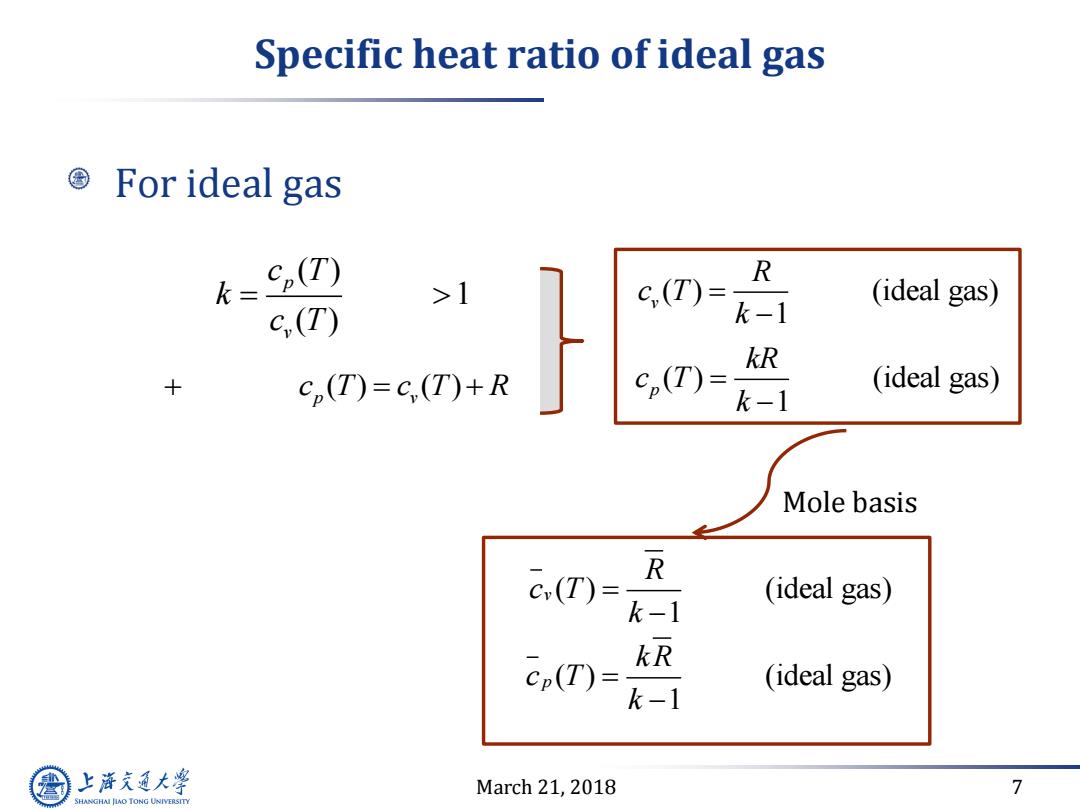
Specific heat ratio of ideal gas For ideal gas h=. ,(T) c(T)= R >1 c,(T) k-1 (ideal gas) kR + cp(T)=c(T)+R c(T)= k-1 (ideal gas) Mole basis c(T)= R (ideal gas) k-1 kR cp(T) (ideal gas) k-1 上游充通大学 March 21,2018 7 SHANGHAI JLAO TONG UNIVERSITY
March 21, 2018 7 Specific heat ratio of ideal gas For ideal gas ( ) 1 ( ) p v c T k c T ( ) ( ) p v c T c T R Mole basis ( ) (ideal gas) 1 p kR c T k ( ) (ideal gas) 1 v R c T k ( ) (ideal gas) 1 p k R c T k ( ) (ideal gas) 1 v R c T k
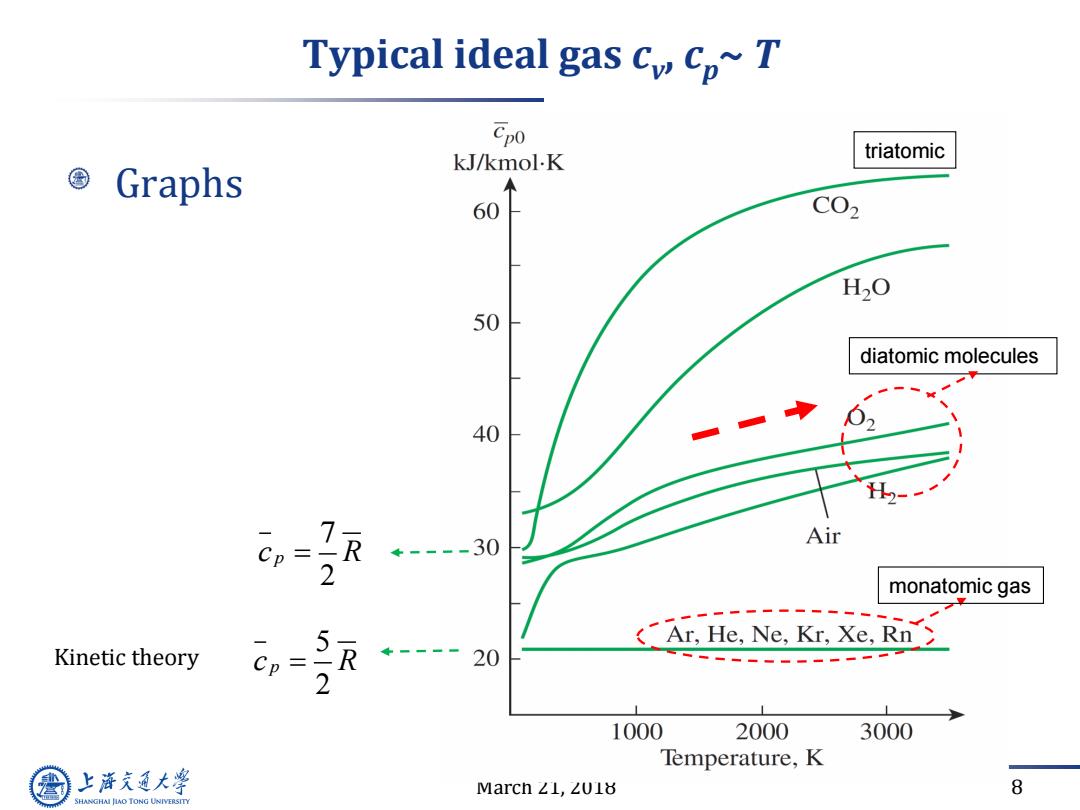
Typical ideal gas cy cp~T Cpo triatomic ©Graphs kJ/kmol.K 60 C02 H2O 50 diatomic molecules 40 H2- R ÷----30 Air 2 monatomic gas 5 R ----20 (Ar.He.Ne,Kr.Xe.Rn Kinetic theory 2 1000 2000 3000 Temperature,K 上游充通大 Marcn∠L,ZU1 8 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
March 21, 2018 8 Typical ideal gas cv , cp~ T Graphs monatomic gas Kinetic theory 5 2 c R p 7 2 c R p diatomic molecules triatomic
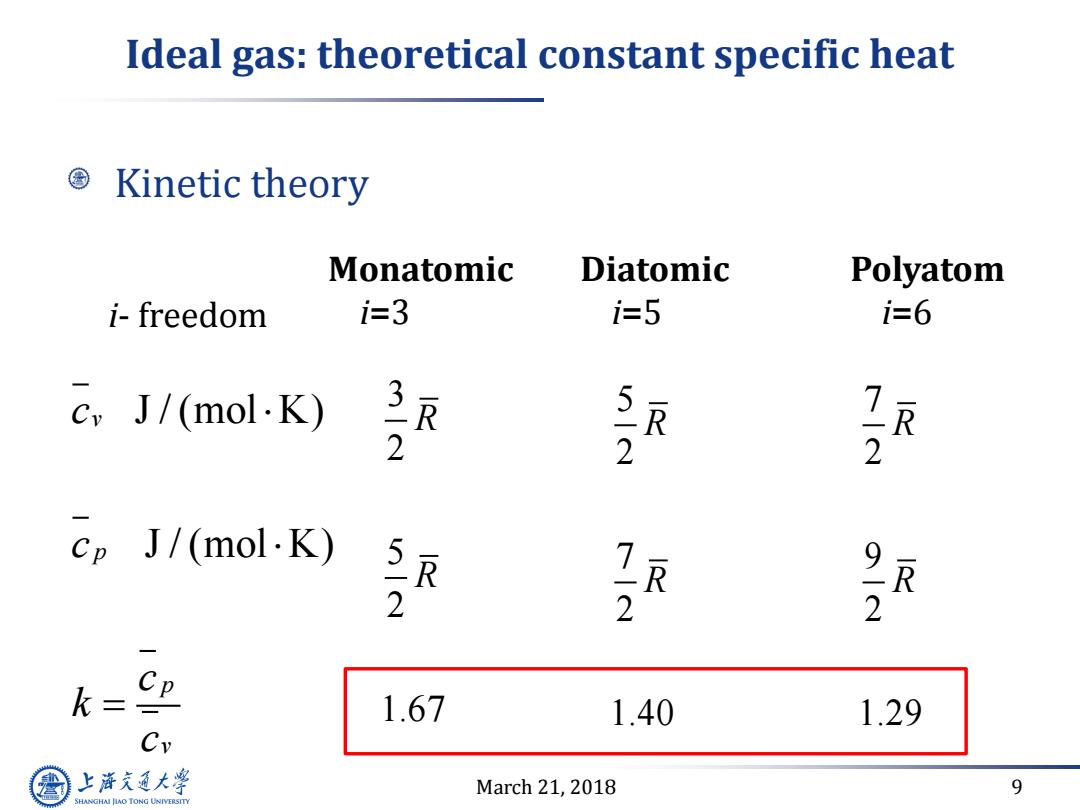
Ideal gas:theoretical constant specific heat Kinetic theory Monatomic Diatomic Polyatom i-freedom i=3 i-5 i=6 cvJ/(mol·K) 7 2 2 2 ep J/(mol.K) R 2 2 2 k= CP 1.67 1.40 1.29 Cy 上游通大学 March 21,2018 9 SHANGHAI JLAO TONG UNIVERSITY
March 21, 2018 9 Ideal gas: theoretical constant specific heat Kinetic theory Monatomic i=3 Diatomic i=5 Polyatom i=6 J / (mol K) J / (mol K) v p p v c c c k c 3 2 5 2 1.67 R R i- freedom 5 2 7 2 1.40 R R 7 2 9 2 1.29 R R
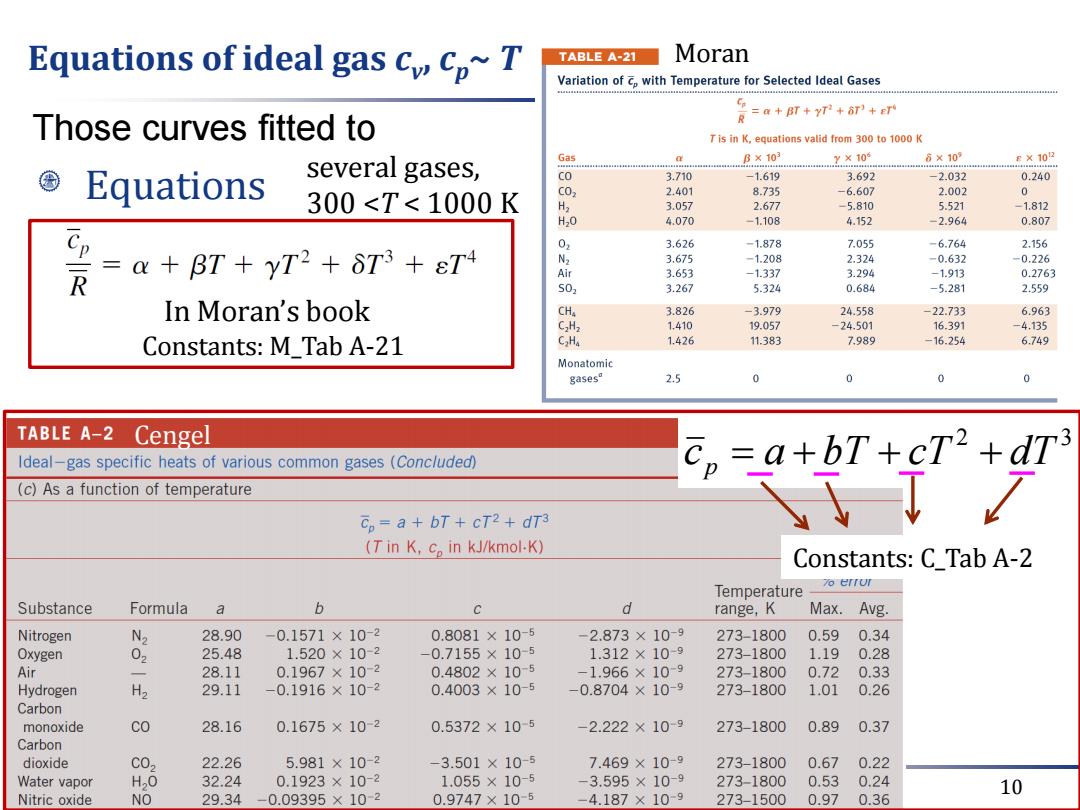
Equations of ideal gas c cp~T TABLE A-21 Moran Variation of Cp with Temperature for Selected Ideal Gases a BT +yT+6T)e Those curves fitted to R Tis in K,equations valid from 300 to 1000 K several gases, Gas B×103 y×10s 6×109 e×102 Equations CO 3.710 -1.619 3.692 -2.032 0.240 300<T<1000K C0 2.401 8.735 -6.607 2.002 0 3.057 2.677 -5.810 5.521 -1.812 H20 4.070 -1.108 4.152 -2.964 0.807 2R 0 3.626 -1.878 7.055 -6.764 2.156 =a+BT+yT2+6T3+εT4 N2 3.675 -1.208 2.324 -0.632 -0.226 r 3.653 -1.337 3.294 -1.913 0.2763 502 3.267 5.324 0.684 -5.281 2.559 In Moran's book CHa 3.826 -3.979 24.558 -22.733 6.963 CxHz 1.410 19.057 -24.501 16.391 -4.135 Constants:M Tab A-21 CaHa 1.426 11.383 7.989 -16.254 6.749 Monatomic gasesa 2.5 0 0 TABLE A-2 Cengel Ideal-gas specific heats of various common gases (Conc/uded) C,=a+bT+cT2+dT (c)As a function of temperature Cp=a+bT+cT2+dT3 (T in K,c in kJ/kmol-K) Constants:C_Tab A-2 7o errur Temperature- Substance Formula a b d range,K Max.Avg. Nitrogen N2 28.90 -0.1571×10-2 0.8081×10-5 -2.873×10-9 273-1800 0.59 0.34 Oxygen 25.48 1.520×10-2 -0.7155×10-5 1.312×10-9 273-1800 1.19 0.28 Air 28.11 0.1967×102 0.4802×10-5 -1.966×109 273-1800 0.72 0.33 Hydrogen H2 29.11 0.1916×10-2 0.4003×10-5 -0.8704×10-9 273-1800 1.01 0.26 Carbon monoxide co 28.16 0.1675×10-2 0.5372×10-5 -2.222×109 273-1800 0.89 0.37 Carbon dioxide C02 22.26 5.981×10-2 -3.501×10-5 7.469×10-9 273-1800 0.670.22 Water vapor H20 32.24 0.1923×10-2 1.055×10-5 -3.595×10-9 273-1800 0.530.24 Nitric oxide NO 29.34-0.09395×10-2 0.9747×10-5 -4.187×10-9 10 273-1500 0.970.36
March 21, 2018 10 Equations of ideal gas cv , cp~ T Equations several gases, 300 <T < 1000 K Those curves fitted to In Moran’s book Moran Constants: C_Tab A-2 2 3 c p a bT cT dT Cengel Constants: M_Tab A-21