
How is antibody diversity generated? Two early theories: Germline hypothesis The genome contains many loci encoding antibody molecules B cells express one of these loci. Different B cells express different loci. Somatic mutation hypothesis There are a small number of antibody genes which undergo mutation as the B cell matures -thus giving rise to B cells expressing antibody of different specificity
How is antibody diversity generated? Two early theories: Germline hypothesis The genome contains many loci encoding antibody molecules. B cells express one of these loci. Different B cells express different loci. Somatic mutation hypothesis There are a small number of antibody genes which undergo mutation as the B cell matures - thus giving rise to B cells expressing antibody of different specificity

Three genetic loci encode immunoglobulin molecules: two loci encoding the light chains kappa locus lambda locus -one locus encoding the heavy chain These three loci are located on different chromosomes TABLE 5-1 CHROMOSOMAL LOCATIONS OF IMMUNOGLOBULIN GENES IN HUMAN AND MOUSE Chromosome Gene Human Mouse λLight chain 22 16 K Light chain 2 6 Heavy chain 14 12
Three genetic loci encode immunoglobulin molecules: - two loci encoding the light chains - kappa locus - lambda locus - one locus encoding the heavy chain These three loci are located on different chromosomes
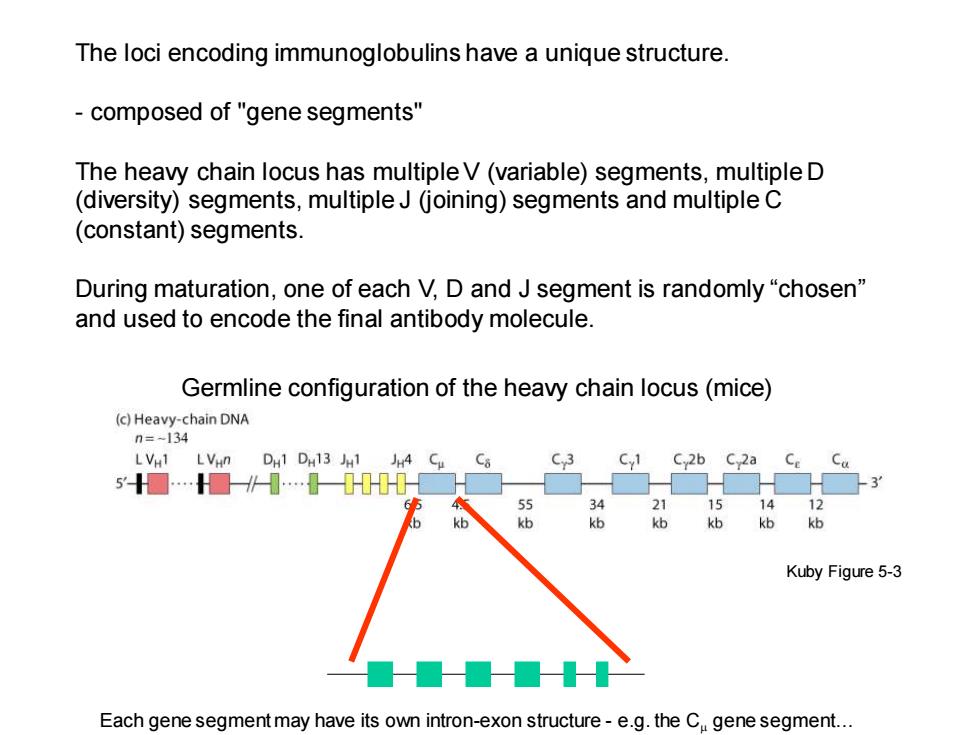
The loci encoding immunoglobulins have a unique structure. composed of "gene segments" The heavy chain locus has multiple V(variable)segments,multiple D (diversity)segments,multiple J(joining)segments and multiple C (constant)segments. During maturation,one of each V,D and J segment is randomly "chosen" and used to encode the final antibody molecule. Germline configuration of the heavy chain locus(mice) (c)Heavy-chain DNA n=-134 LVH1 LVHn DH1 DH13 JH1 JH4 Cu C Cy1 C:2b C 2a 5□…■∥…0 55 34 21 15 kb kb kb kb kb kb kb Kuby Figure 5-3 ■■■■ Each gene segment may have its own intron-exon structure-e.g.the Cu gene segment
The loci encoding immunoglobulins have a unique structure. - composed of "gene segments" The heavy chain locus has multiple V (variable) segments, multiple D (diversity) segments, multiple J (joining) segments and multiple C (constant) segments. During maturation, one of each V, D and J segment is randomly “chosen” and used to encode the final antibody molecule. Germline configuration of the heavy chain locus (mice) Each gene segment may have its own intron-exon structure - e.g. the Cm gene segment… Kuby Figure 5-3
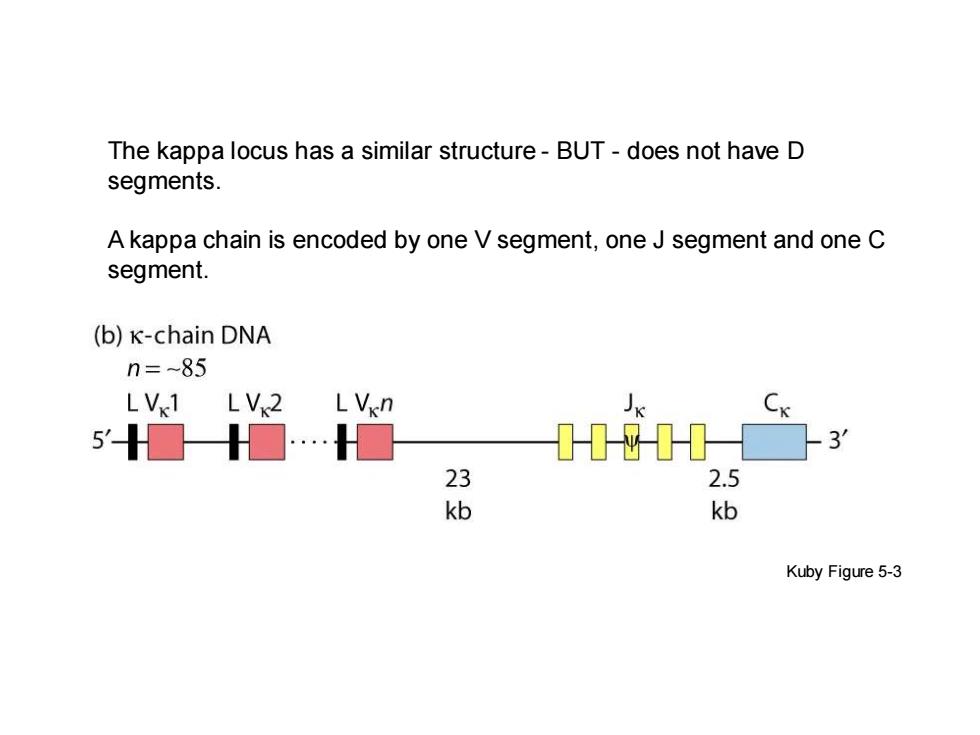
The kappa locus has a similar structure-BUT-does not have D segments A kappa chain is encoded by one V segment,one J segment and one C segment. (b)K-chain DNA n=~85 L Vx1 LVx2 LVikn ☐☐…☐ 1-1-11☐3 23 2.5 kb kb Kuby Figure 5-3
The kappa locus has a similar structure - BUT - does not have D segments. A kappa chain is encoded by one V segment, one J segment and one C segment. Kuby Figure 5-3
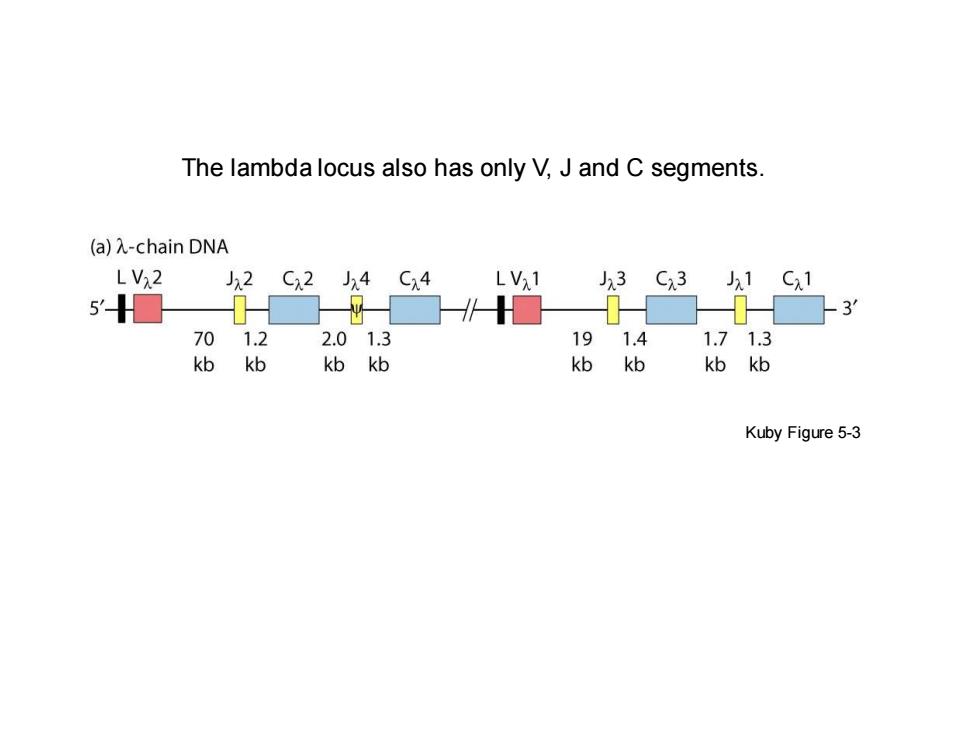
The lambda locus also has only V,J and C segments. (a)λ-chain DNA 。1 LV2 2 C22 J4 C4 LVx1 J3 Cx3 J1 Cx1 701.22.01.3 191.4 1.71.3 kbkbkbkb kbkb kbkb Kuby Figure 5-3
The lambda locus also has only V, J and C segments. Kuby Figure 5-3
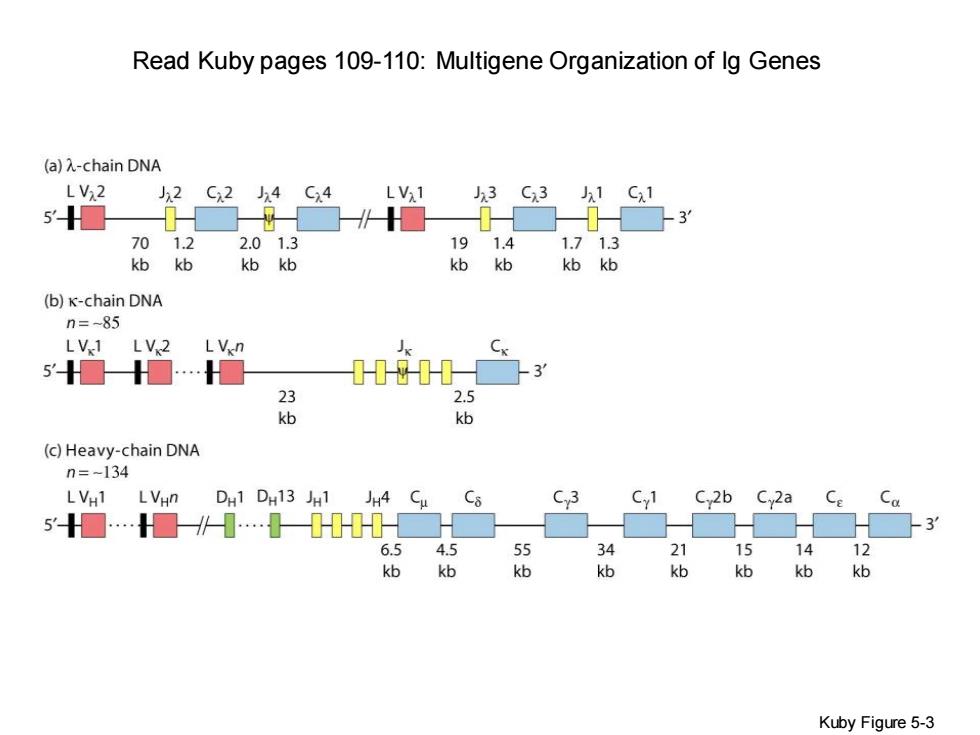
Read Kuby pages 109-110:Multigene Organization of Ig Genes (a)A-chain DNA LV22 Jx2 Cx2 J4 C24 LVx1 Jx3 Cx3 J1 C.1 5☐ 701.2 2.01.3 191.41.713 kbkb kbkb kbkb kbkb (b)K-chain DNA n=-85 LV1 LV 2 LVen (4 ☐☐… 1-181☐3 23 2.5 kb kb (c)Heavy-chain DNA n=-134 LVH1 LVHn DH1 DH13 JH1 JH4 Cu C8 C3 C,1 C 2b Cy2a Ce ☐…a∥-…H☐ -3 6.54.5 55 34 21 15 14 12 kbkb kb kb kb kbkb kb Kuby Figure 5-3
Read Kuby pages 109-110: Multigene Organization of Ig Genes Kuby Figure 5-3
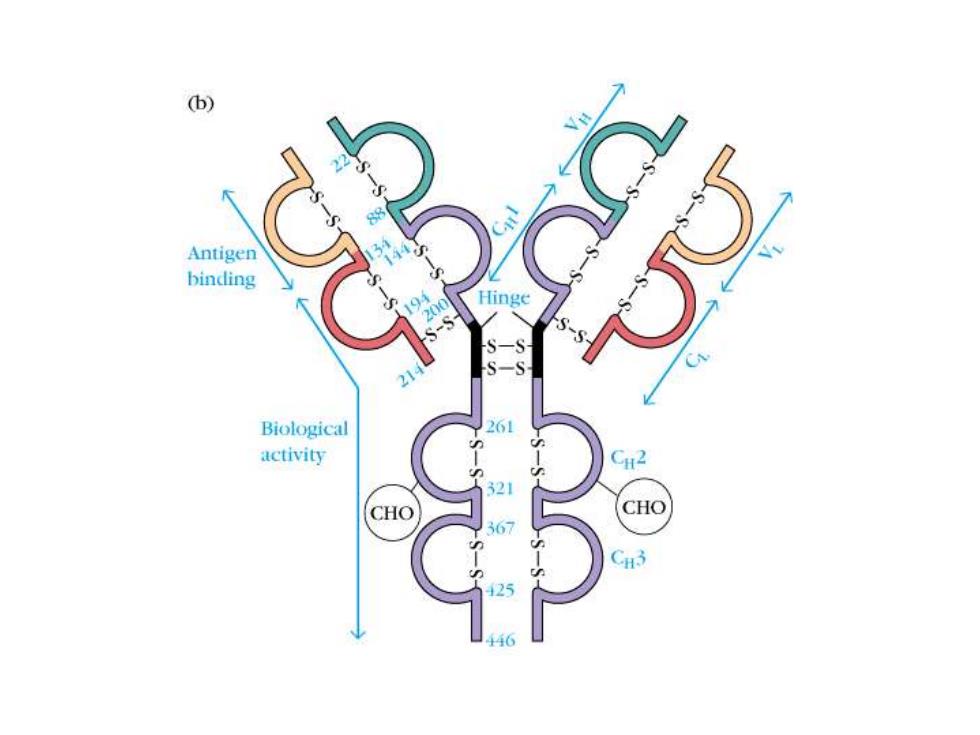
(b) Antigen binding Biological activity CHO CHO 6
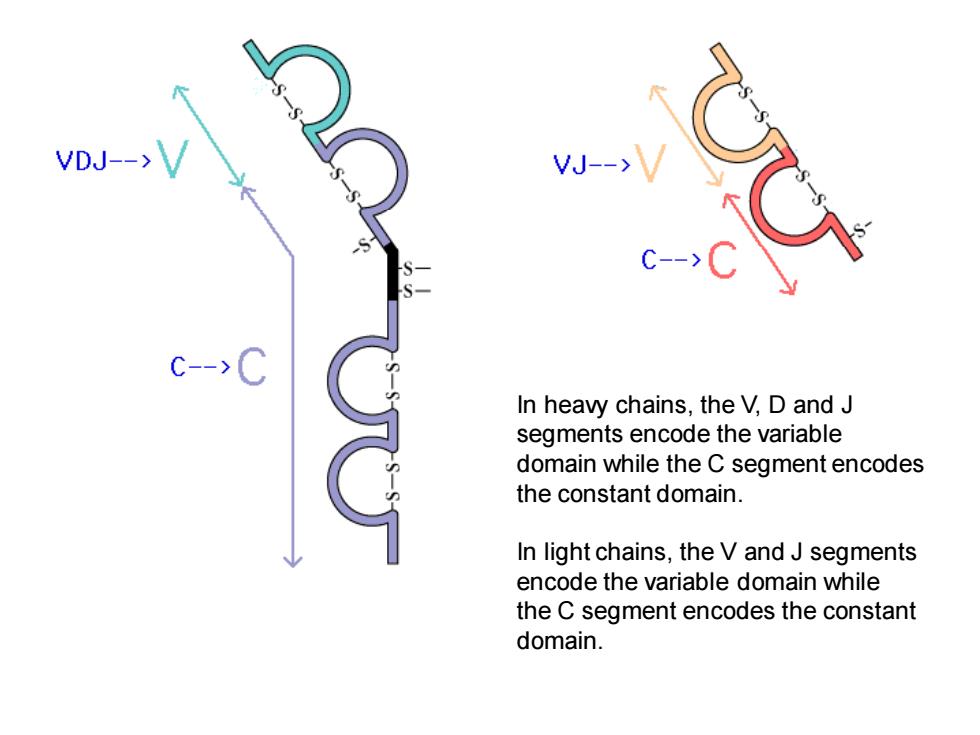
VDJ--> W- C-- c-->C In heavy chains,the V,D and J segments encode the variable domain while the C segment encodes the constant domain. In light chains,the V and J segments encode the variable domain while the C segment encodes the constant domain
In heavy chains, the V, D and J segments encode the variable domain while the C segment encodes the constant domain. In light chains, the V and J segments encode the variable domain while the C segment encodes the constant domain
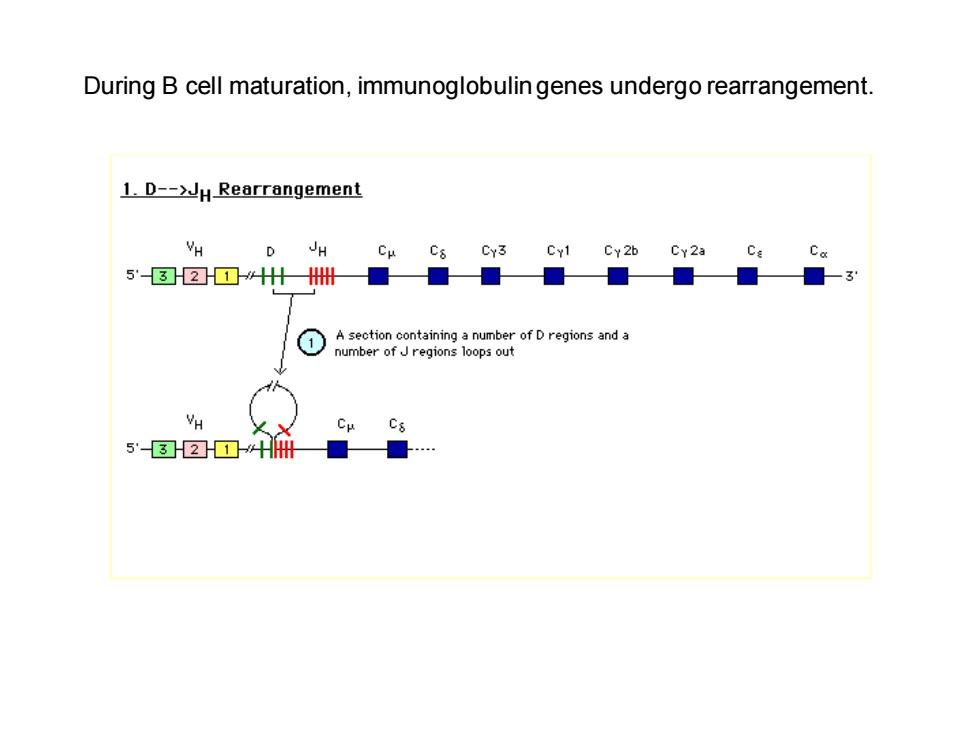
During B cell maturation,immunoglobulin genes undergo rearrangement. 1.D-->JH Rearrangement H D JH Cy3 Cy1 Cy2b Cy2a Ca 5'32☒什H州■■■ -3 A section containing a number of D regions and a number of Jregions loops out H Cs 5'☒2☒☐中H册
During B cell maturation, immunoglobulin genes undergo rearrangement
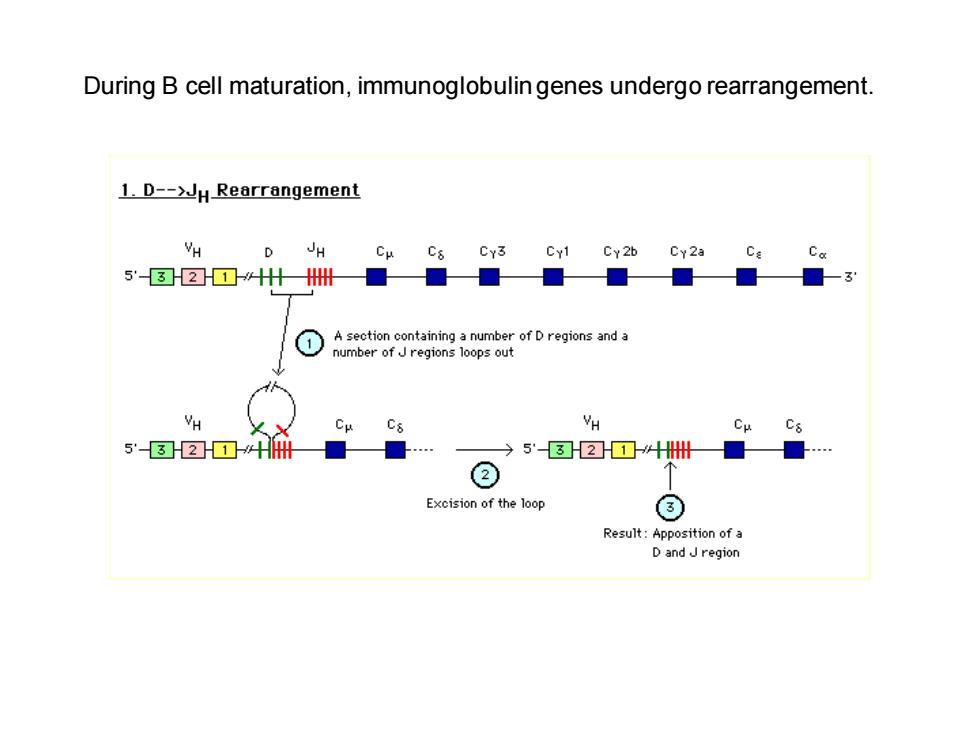
During B cell maturation,immunoglobulin genes undergo rearrangement. 1.D-->JH Rearrangement D JH Cμ Cs Cy3 Cy1 Cy2b Cy2a 5'32☒什州■■■ A section containing a number of D regions and a number of J regions loops out Cμ Cμ 5'3☒2☒□HH州 5'☒2☒HHH Excision of the loop Result:Apposition of a D and J region
During B cell maturation, immunoglobulin genes undergo rearrangement