
Lecture 20 Hypersensitivity Reactions Immune responses that result in tissue injury
Lecture 20 Hypersensitivity Reactions ◼ Immune responses that result in tissue injury
Immune-mediated hypersensitivity reactions Type I-Anaphylactic/Atopic Type IⅡ-Cytotoxic ·Type IlⅢ-Toxic Complex Type IV-T-cell mediated
Immune-mediated hypersensitivity reactions ◼ Type I - Anaphylactic/Atopic ◼ Type II - Cytotoxic ◼ Type III - Toxic Complex ◼ Type IV - T-cell mediated
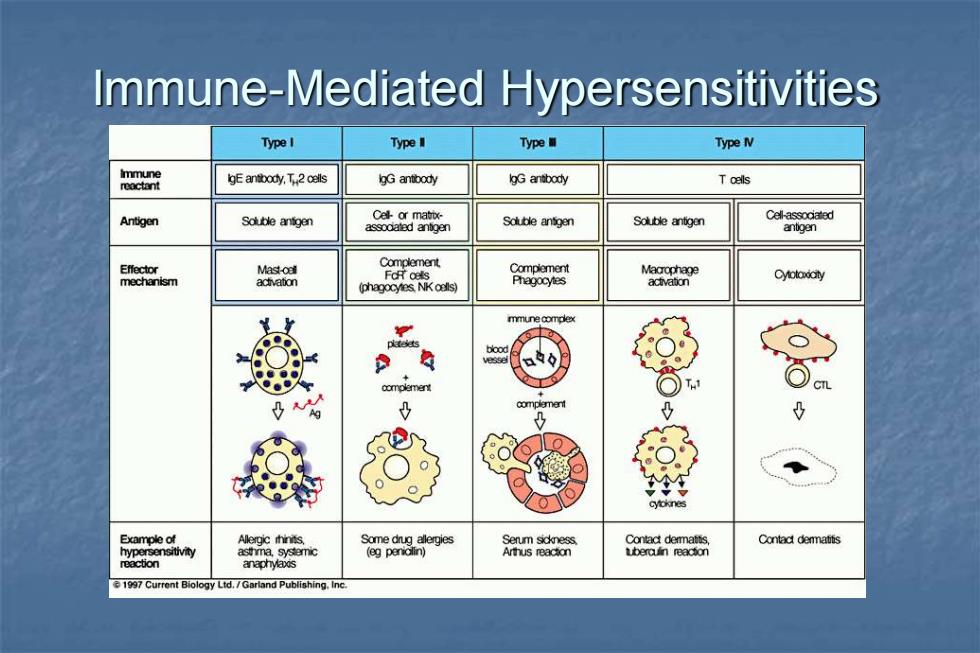
Immune-Mediated Hypersensitivities TypeI TypeI Type Type I immune reactant gE antbody,T2 clls lgG antibody lgG antbody Toells Antigen Soluble antigen Cel or mattx- assodated antigen Souble antigen Soluble antigen Cell-assocated antoen Effector Mast-oel 08o Macrophage mechanism actvation actvation 6 Example of Allergic hnits. 阳8o Senm sickness. n ncon Contad demattis hypersensitivity asthma,systemic Arthus reaction reacton anaphyaxis 1997 Current Biology Ltd./Garland Publishing.In
Immune-Mediated Hypersensitivities

Anaphylactic/Atopic Hypersensitivity (Type I
Anaphylactic/Atopic Hypersensitivity (Type I )

Atopy Describes the clinical features of individuals who develop Type I hypersensitivity increased vascular permeability ·local edema 。itching Strong hereditary linkages Mediated by a serum factor termed "reagin" "Wheal and flare"reaction
Atopy ◼ Describes the clinical features of individuals who develop Type I hypersensitivity ◼ increased vascular permeability ◼ local edema ◼ itching ◼ Strong hereditary linkages ◼ Mediated by a serum factor termed "reagin" ◼ "Wheal and flare" reaction
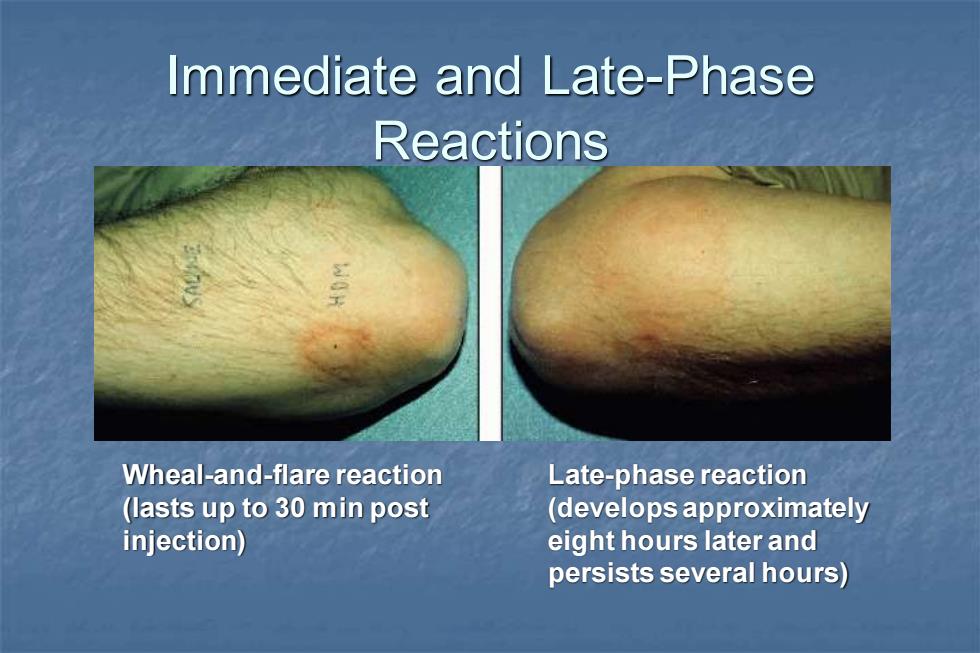
Immediate and Late-Phase Reactions Wheal-and-flare reaction Late-phase reaction (lasts up to 30 min post (develops approximately injection) eight hours later and persists several hours)
Immediate and Late-Phase Reactions Wheal-and-flare reaction (lasts up to 30 min post injection) Late-phase reaction (develops approximately eight hours later and persists several hours)

IgE response is a local event site of allergen entry local synthesis results in sensitization of local mast cells spillover of IgE enters circulation and sensitizes mast cells and basophils systemically
IgE response is a local event ◼ site of allergen entry ◼ local synthesis results in sensitization of local mast cells ◼ spillover of IgE enters circulation and sensitizes mast cells and basophils systemically

Characteristics of IgE Heat labile ■Fe binding destroyed by heating at56°Cfor 30 min antigen binding is not lost Half-life serum half-life is 2 1/2 days (IgG is 21 days) mast cell bound half-life is 12 weeks
Characteristics of IgE ◼ Heat labile ◼ Fc binding destroyed by heating at 56°C for 30 min ◼ antigen binding is not lost ◼ Half-life ◼ serum half-life is 2 1/2 days (IgG is 21 days) ◼ mast cell bound half-life is 12 weeks

IgE Levels in Disease Normal levels do not preclude atopy 30%of random population allergic to at least one common allergen Genetic background puts individual at risk family history indicates predisposition for atopy cannot predict specific reactions(s) higher level of IgE associated with increased risk of atopy
IgE Levels in Disease ◼ Normal levels do not preclude atopy ◼ 30% of random population allergic to at least one common allergen ◼ Genetic background puts individual at risk ◼ family history indicates predisposition for atopy ◼ cannot predict specific reactions(s) ◼ higher level of IgE associated with increased risk of atopy
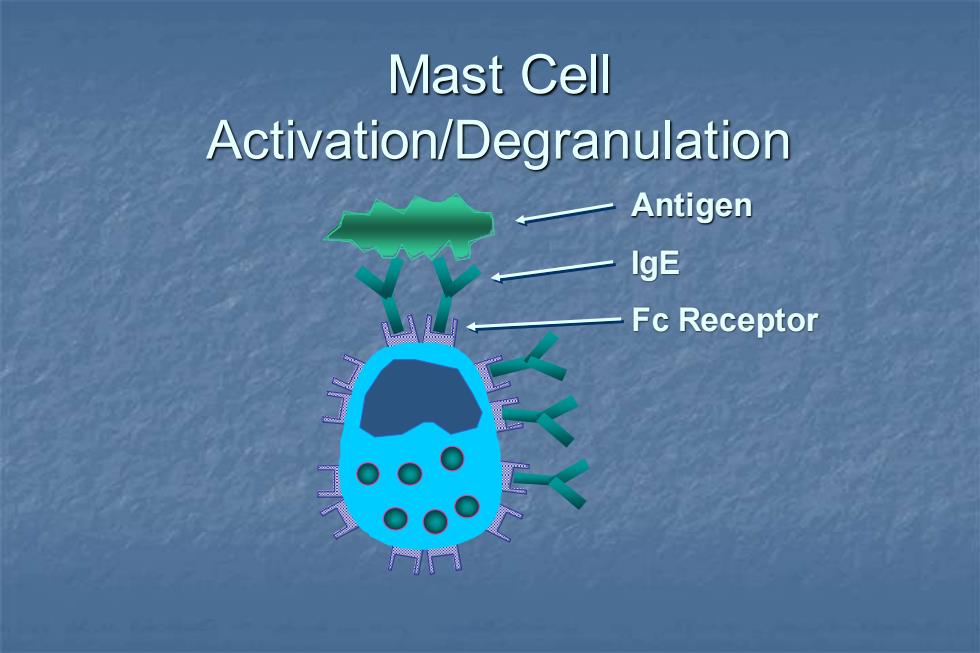
Mast Cell Activation/Degranulation Antigen IgE Fc Receptor
Mast Cell Activation/Degranulation Antigen IgE Fc Receptor