
Lecture 21 Hypersensitivity Types II-V Type II:Cytotoxic (ITH) Type III:Toxic Complex(ITH) Type IV:T Cell-Mediated (DTH) Type V:Stimulatory
Lecture 21 Hypersensitivity Types II-V ◼ Type II: Cytotoxic (ITH) ◼ Type III: Toxic Complex (ITH) ◼ Type IV: T Cell-Mediated (DTH) ◼ Type V: Stimulatory

Cytotoxic Hypersensitivity (Type ll) 最
Cytotoxic Hypersensitivity (Type II)

Characteristics of Cytotoxic Hypersensitivity Directed against cell surface or tissue antigen Characterized by complement cascade activation and various effector cells
Characteristics of Cytotoxic Hypersensitivity ◼ Directed against cell surface or tissue antigen ◼ Characterized by complement cascade activation and various effector cells

Complement Formation of membrane attack complex (lytic enzymes) Activated C3 forms opsonin recognized by phagocytes Formation of chemotactic factors Effector cells possess Fc and complement receptors macrophages/monocytes neutrophils NK cells
Complement ◼ Formation of membrane attack complex (lytic enzymes) ◼ Activated C3 forms opsonin recognized by phagocytes ◼ Formation of chemotactic factors ◼ Effector cells possess Fc and complement receptors ◼ macrophages/monocytes ◼ neutrophils ◼ NK cells

Examples of Type lI Hypersensitivity Blood transfusion reactions Hemolytic disease of the newborn (Rh disease) Autoimmune hemolytic anemias Drug reactions Drug-induced loss of self-tolerance Hyperacute graft rejection Myasthenia gravis(acetylcholine receptor) Sensitivity to tissue antigens
Examples of Type II Hypersensitivity ◼ Blood transfusion reactions ◼ Hemolytic disease of the newborn (Rh disease) ◼ Autoimmune hemolytic anemias ◼ Drug reactions ◼ Drug-induced loss of self-tolerance ◼ Hyperacute graft rejection ◼ Myasthenia gravis (acetylcholine receptor) ◼ Sensitivity to tissue antigens
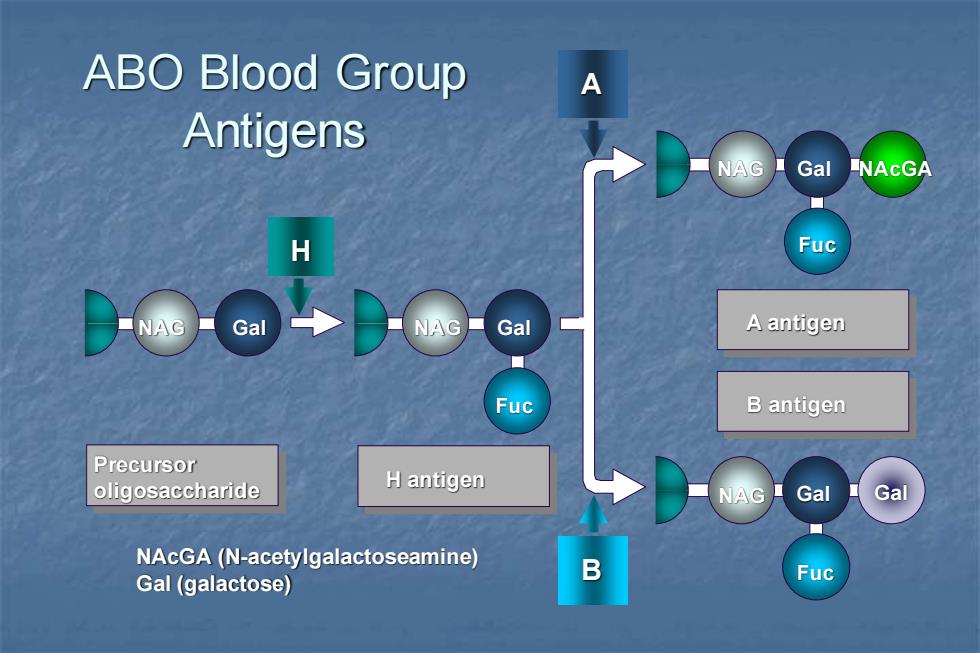
ABO Blood Group Antigens NAG Gal NACGA Fuc NAG Gal NAG Gal A antigen Fuc B antigen Precursor oligosaccharide Hantigen NAG Gal Gal NAcGA(N-acetylgalactoseamine) Gal (galactose) B Fuc
ABO Blood Group Antigens Precursor oligosaccharide H antigen B antigen NAG Gal NAcGA Fuc NAG Gal NAG Gal Fuc H Fuc NAG Gal Gal B A A antigen NAcGA (N-acetylgalactoseamine) Gal (galactose)

ABO Blood Group Reactivity blood group genotypes antigens a antibodies to (phenotype) ABO in serum A AA,AO A anti-B B BB,BO B anti-A AB AB A and B none 0 00 H anti-A/B
ABO Blood Group Reactivity blood group genotypes antigens antibodies to (phenotype) ABO in serum A AA, AO A anti-B B BB, BO B anti-A AB AB A and B none O OO H anti-A/B
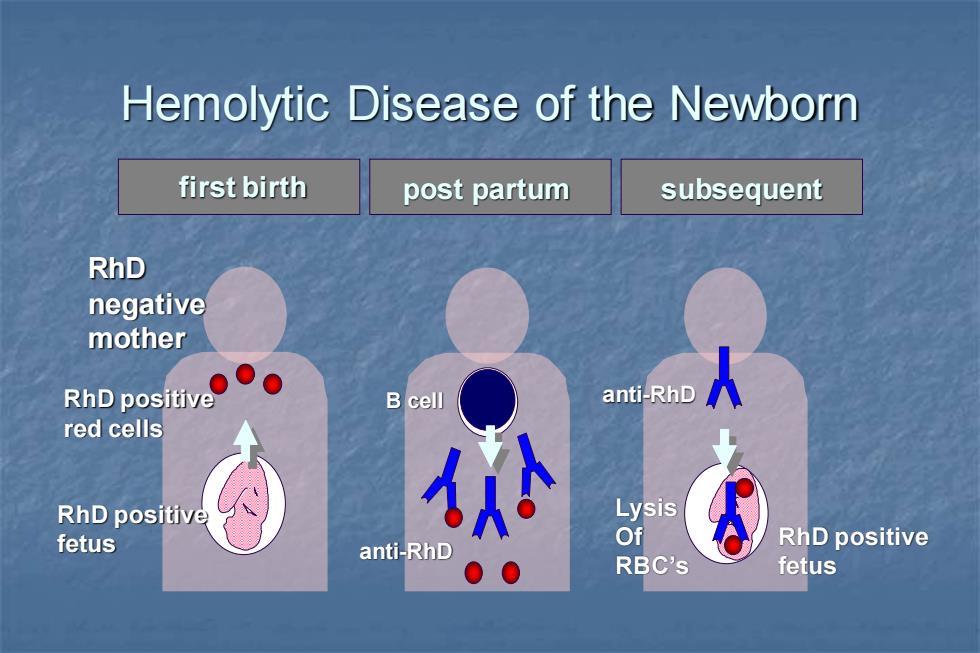
Hemolytic Disease of the Newborn first birth post partum subsequent RhD negative mother RhD positive Bcell anti-RhD red cells RhD positive Lysis fetus Of anti-RhD RhD positive 00 RBC's fetus
Hemolytic Disease of the Newborn RhD positive red cells RhD negative mother RhD positive fetus Lysis Of RBC’s B cell anti-RhD first birth post partum subsequent anti-RhD RhD positive fetus
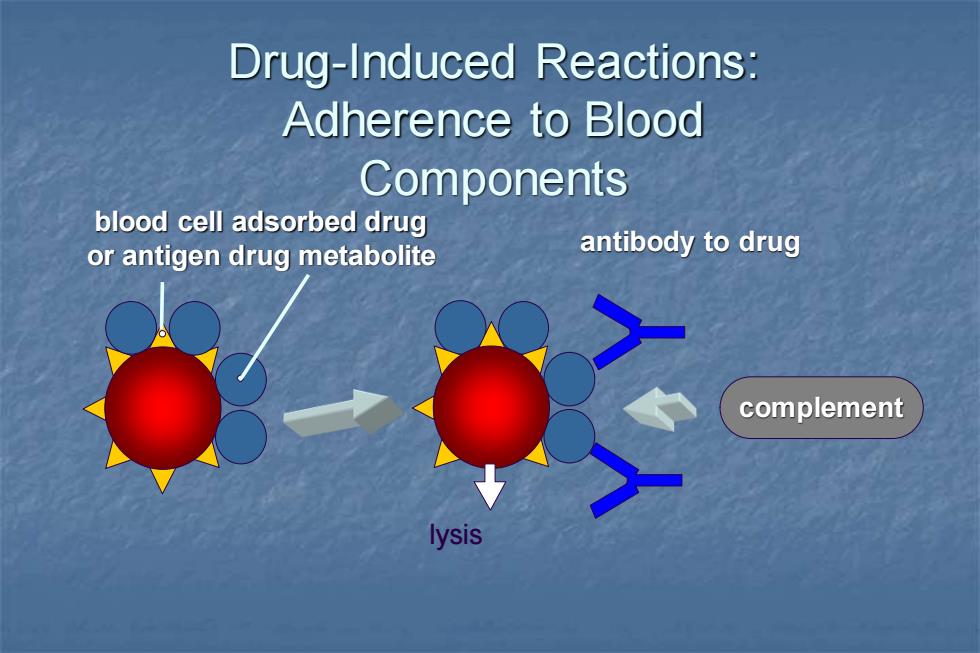
Drug-Induced Reactions: Adherence to Blood Components blood cell adsorbed drug or antigen drug metabolite antibody to drug complement lysis
Drug-Induced Reactions: Adherence to Blood Components complement blood cell adsorbed drug or antigen drug metabolite antibody to drug lysis
Toxic Complex Hypersensitivity (Type Ill) ☒无法显示该图片
Toxic Complex Hypersensitivity (Type III)