
Lecture 13 Antigens,Receptors and Immunoglobulins
Lecture 13 Antigens, Receptors and Immunoglobulins
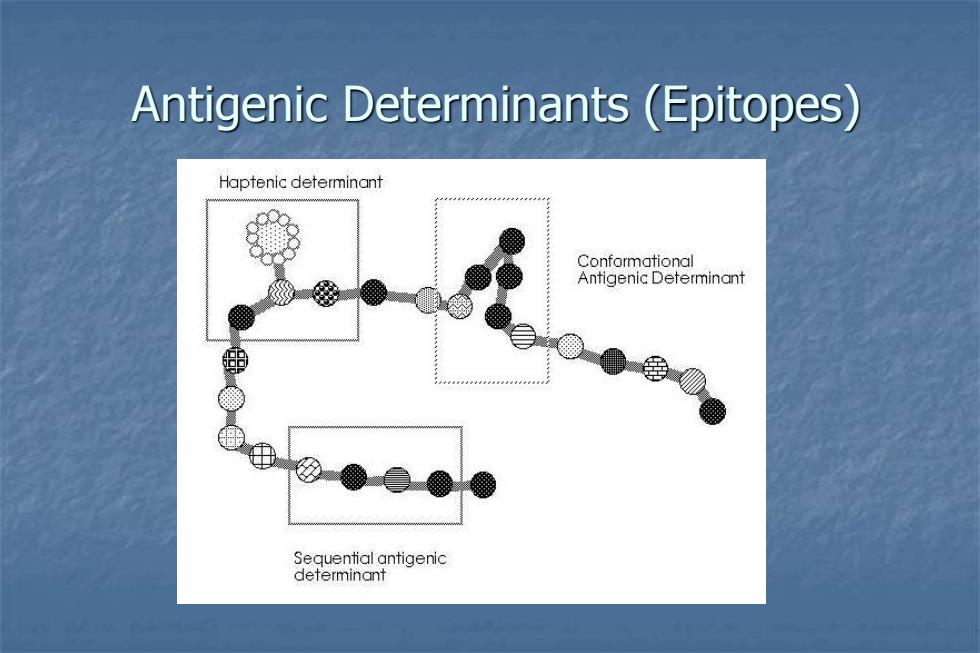
Antigenic Determinants(Epitopes) Haptenic determinant Conformational Antigenic Determinant ●舍 Sequential antigenic deferminant
Antigenic Determinants (Epitopes)

Receptor-Epitope Concepts Most biological systems can be viewed in terms of interactions between receptors and epitopes (hand and glove"). Specificity of the interaction between the receptor and epitope is determined by the amino acid sequence of the receptor ("tailoring the glove"). If the glove is too big,the glove falls off. If the glove is too small,you can't get your hand into it. If the glove is missing fingers
Receptor-Epitope Concepts ◼ Most biological systems can be viewed in terms of interactions between receptors and epitopes (“hand and glove”). ◼ Specificity of the interaction between the receptor and epitope is determined by the amino acid sequence of the receptor (“tailoring the glove”). ◼ If the glove is too big, the glove falls off. ◼ If the glove is too small, you can’t get your hand into it. ◼ If the glove is missing fingers…
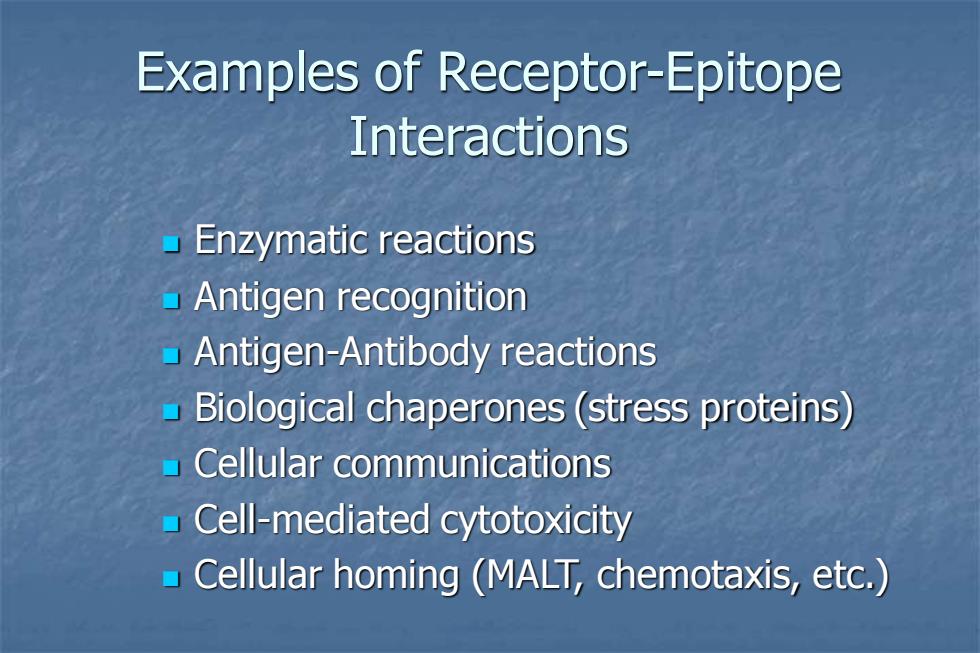
Examples of Receptor-Epitope Interactions Enzymatic reactions Antigen recognition Antigen-Antibody reactions Biological chaperones(stress proteins) Cellular communications Cell-mediated cytotoxicity Cellular homing (MALT,chemotaxis,etc.)
Examples of Receptor-Epitope Interactions ◼ Enzymatic reactions ◼ Antigen recognition ◼ Antigen-Antibody reactions ◼ Biological chaperones (stress proteins) ◼ Cellular communications ◼ Cell-mediated cytotoxicity ◼ Cellular homing (MALT, chemotaxis, etc.)

Basic Immunoglobulin Structure light chain disufide bridges heavy chain @1997 Current Biology Ltd./Garland Publishing,Inc
Basic Immunoglobulin Structure
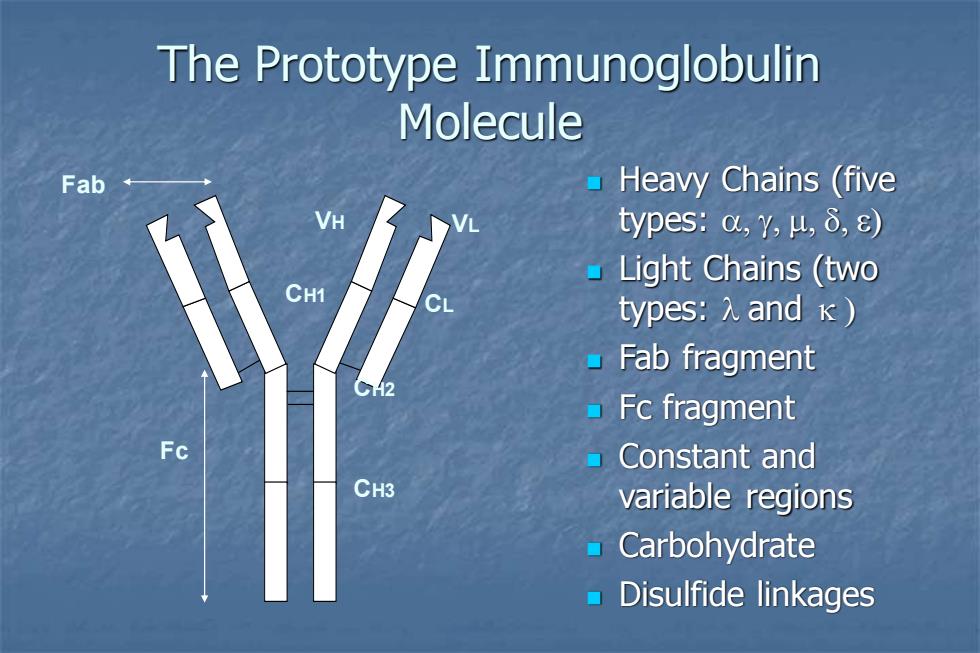
The Prototype Immunoglobulin Molecule Fab Heavy Chains(five VH types:a,y,u,8,s) Light Chains (two CH1 types:7 and Fab fragment 42 Fc fragment Fc Constant and CH3 variable regions Carbohydrate Disulfide linkages
The Prototype Immunoglobulin Molecule Fab Fc VH CH1 CH2 CH3 VL CL ◼ Heavy Chains (five types: ) ◼ Light Chains (two types: and ) ◼ Fab fragment ◼ Fc fragment ◼ Constant and variable regions ◼ Carbohydrate ◼ Disulfide linkages
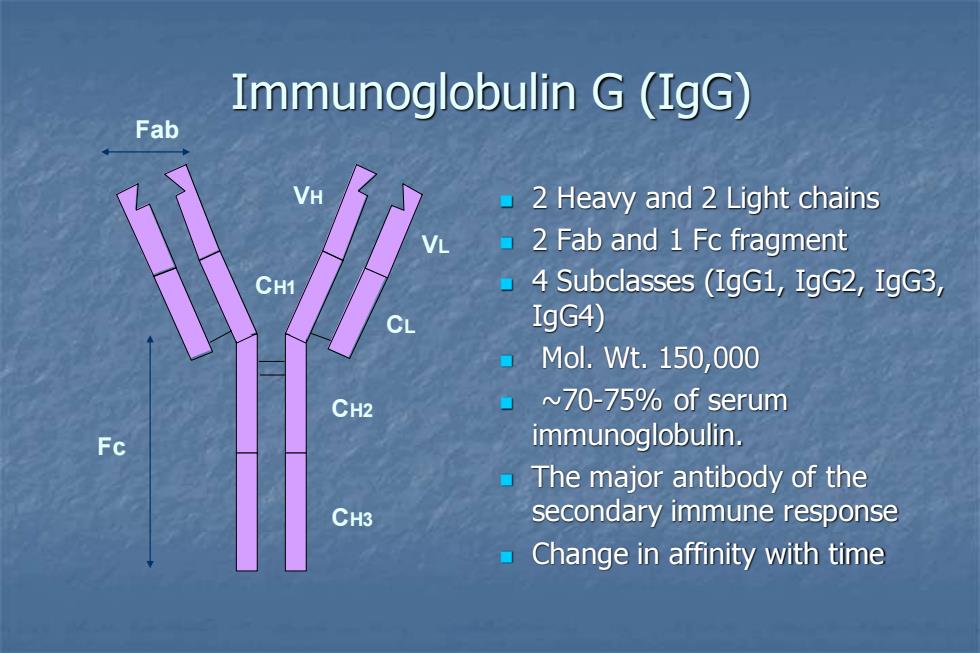
Immunoglobulin G(IgG) Fab 2 Heavy and 2 Light chains VL 2 Fab and 1 Fc fragment CH1 4 Subclasses (IgG1,IgG2,IgG3, CL IgG4) ▣Mol.Wt.150,000 CH2 ~70-75%of serum Fc immunoglobulin. The major antibody of the CH3 secondary immune response Change in affinity with time
Immunoglobulin G (IgG) ◼ 2 Heavy and 2 Light chains ◼ 2 Fab and 1 Fc fragment ◼ 4 Subclasses (IgG1, IgG2, IgG3, IgG4) ◼ Mol. Wt. 150,000 ◼ ~70-75% of serum immunoglobulin. ◼ The major antibody of the secondary immune response ◼ Change in affinity with time Fab Fc VH CH1 CH2 CH3 VL CL
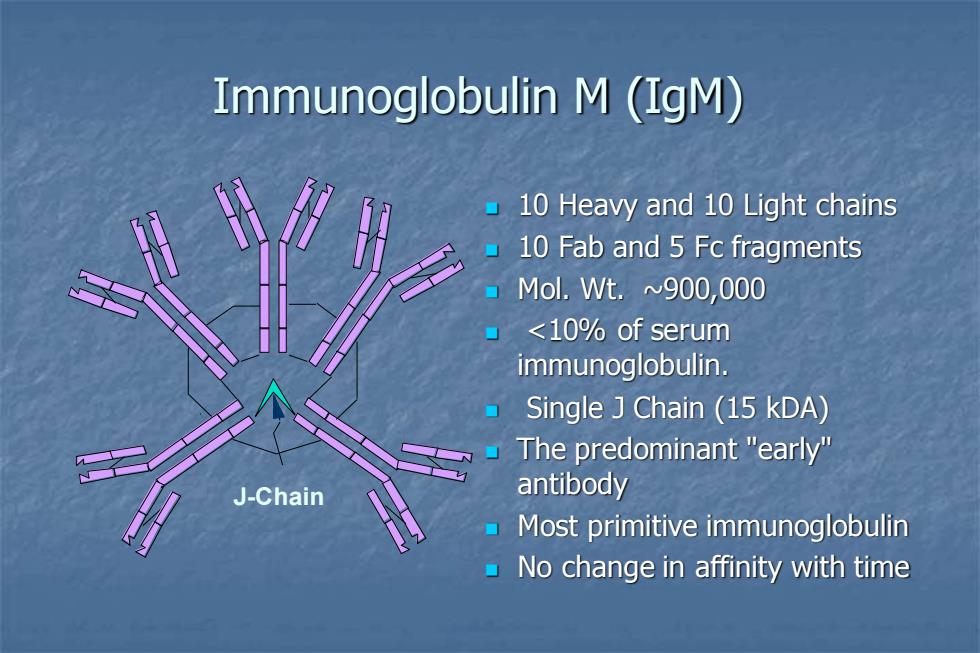
Immunoglobulin M (IgM) 10 Heavy and 10 Light chains 10 Fab and 5 Fc fragments ▣Mol.Wt.~900,000 <10%of serum immunoglobulin. Single Chain(15 kDA) The predominant "early" J-Chain antibody Most primitive immunoglobulin No change in affinity with time
Immunoglobulin M (IgM) ◼ 10 Heavy and 10 Light chains ◼ 10 Fab and 5 Fc fragments ◼ Mol. Wt. ~900,000 ◼ <10% of serum immunoglobulin. ◼ Single J Chain (15 kDA) ◼ The predominant "early" antibody ◼ Most primitive immunoglobulin ◼ No change in affinity with time J-Chain
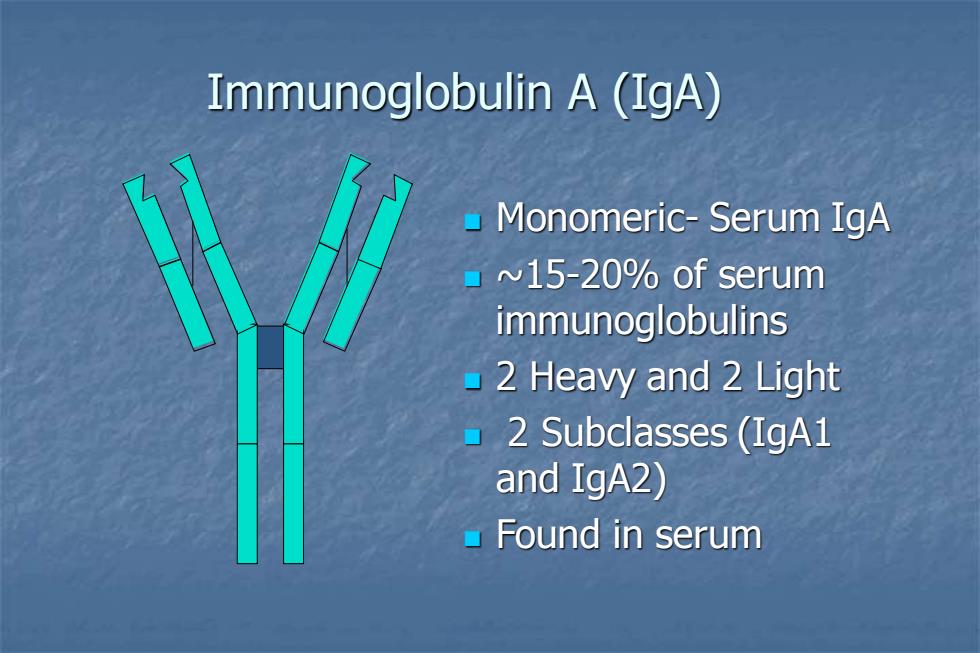
Immunoglobulin A (IgA) Monomeric-Serum IgA ~15-20%of serum immunoglobulins 2 Heavy and 2 Light ·2 Subclasses(IgA1 and IgA2) Found in serum
Immunoglobulin A (IgA) ◼ Monomeric- Serum IgA ◼ ~15-20% of serum immunoglobulins ◼ 2 Heavy and 2 Light ◼ 2 Subclasses (IgA1 and IgA2) ◼ Found in serum
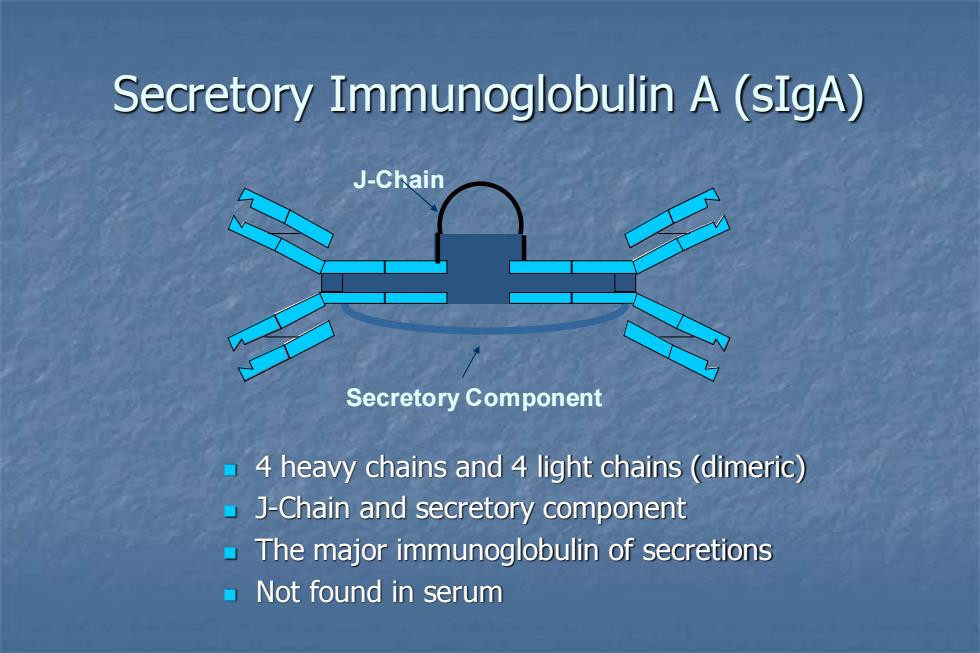
Secretory Immunoglobulin A(sIgA) J-Chain Secretory Component 4 heavy chains and 4 light chains (dimeric) J-Chain and secretory component The major immunoglobulin of secretions Not found in serum
Secretory Immunoglobulin A (sIgA) ◼ 4 heavy chains and 4 light chains (dimeric) ◼ J-Chain and secretory component ◼ The major immunoglobulin of secretions ◼ Not found in serum Secretory Component J-Chain