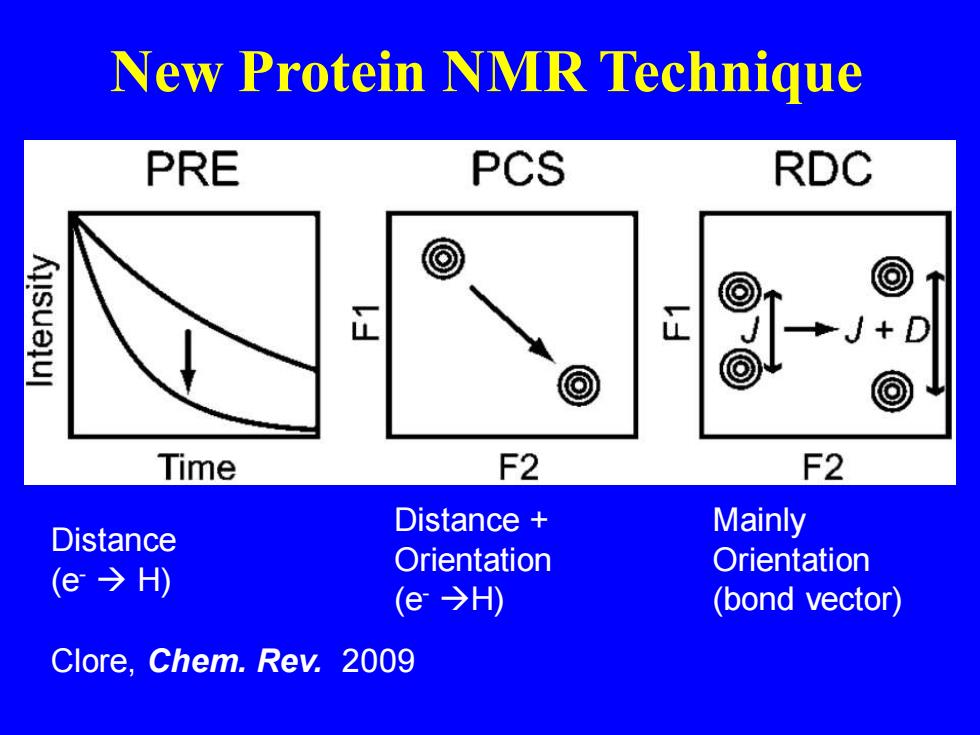
New Protein NMR Technique PRE PCS RDC @ 正 正 Time F2 F2 Distance Distance Mainly Orientation (e→H) Orientation (e→H) (bond vector) Clore,Chem.Rev.2009
Long range structural restraints Distance (e- → H) Distance + Orientation (e- →H) Mainly Orientation (bond vector) Clore, Chem. Rev. 2009 New Protein NMR Technique

Residual Dipolar Couplings Bo isotropic anisotropic 118 119 94.2Hz@ 74.9Hz奇 120 E007V @93.9Hz 84.6Hz 121 122 7.57.4 7.3 7.27.57.4 7.3 7.2 1H ppm Residual Dipolar Couplings(RDC)are measured as contributions to lines splittings in anisotropic solution relative to isotropic solution
Residual Dipolar Couplings Residual Dipolar Couplings (RDC) are measured as contributions to lines splittings in anisotropic solution relative to isotropic solution
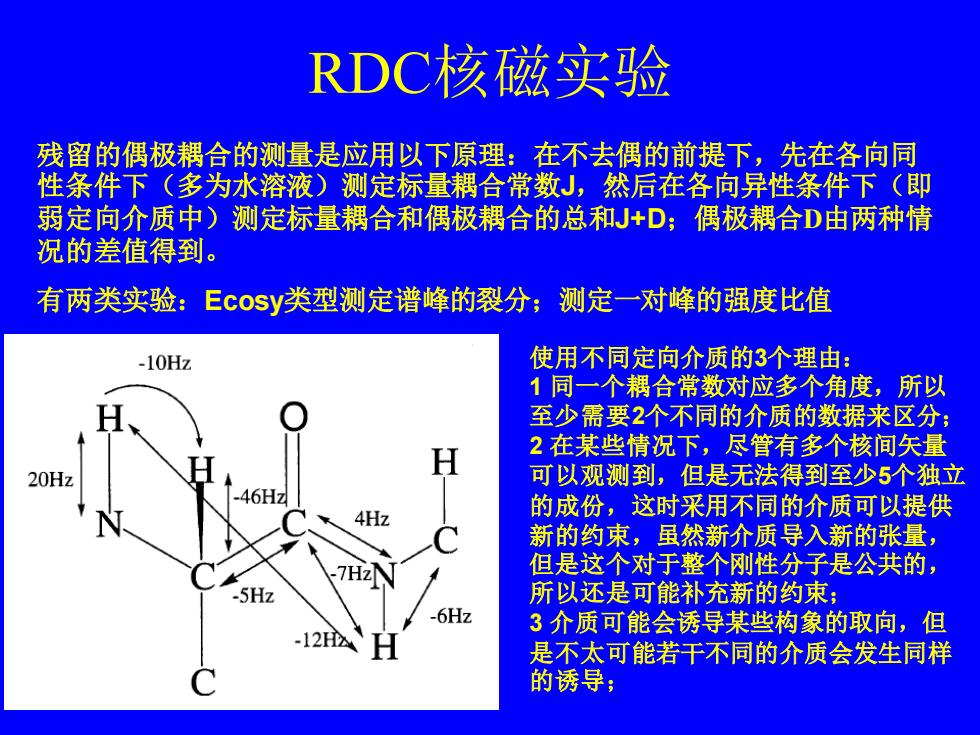
RDC核磁实验 残留的偶极耦合的测量是应用以下原理:在不去偶的前提下,先在各向同 性条件下(多为水溶液)测定标量耦合常数J,然后在各向异性条件下(即 弱定向介质中)测定标量耦合和偶极耦合的总和J+D;偶极耦合D由两种情 况的差值得到。 有两类实验:Ecosy类型测定谱峰的裂分;测定一对峰的强度比值 -10Hz 使用不同定向介质的3个理由: 1同一个耦合常数对应多个角度,所以 至少需要2个不同的介质的数据来区分; H 2在某些情况下,尽管有多个核间矢量 20Hz 可以观测到,但是无法得到至少5个独立 .46Hz 4Hz 的成份,这时采用不同的介质可以提供 新的约束,虽然新介质导入新的张量, 7H2 但是这个对于整个刚性分子是公共的, -5Hz 所以还是可能补充新的约束; -6Hz 3介质可能会诱导某些构象的取向,但 -12 是不太可能若干不同的介质会发生同样 的诱导;
RDC核磁实验 残留的偶极耦合的测量是应用以下原理:在不去偶的前提下,先在各向同 性条件下(多为水溶液)测定标量耦合常数J,然后在各向异性条件下(即 弱定向介质中)测定标量耦合和偶极耦合的总和J+D;偶极耦合D由两种情 况的差值得到。 有两类实验:Ecosy类型测定谱峰的裂分;测定一对峰的强度比值 使用不同定向介质的3个理由: 1 同一个耦合常数对应多个角度,所以 至少需要2个不同的介质的数据来区分; 2 在某些情况下,尽管有多个核间矢量 可以观测到,但是无法得到至少5个独立 的成份,这时采用不同的介质可以提供 新的约束,虽然新介质导入新的张量, 但是这个对于整个刚性分子是公共的, 所以还是可能补充新的约束; 3 介质可能会诱导某些构象的取向,但 是不太可能若干不同的介质会发生同样 的诱导;
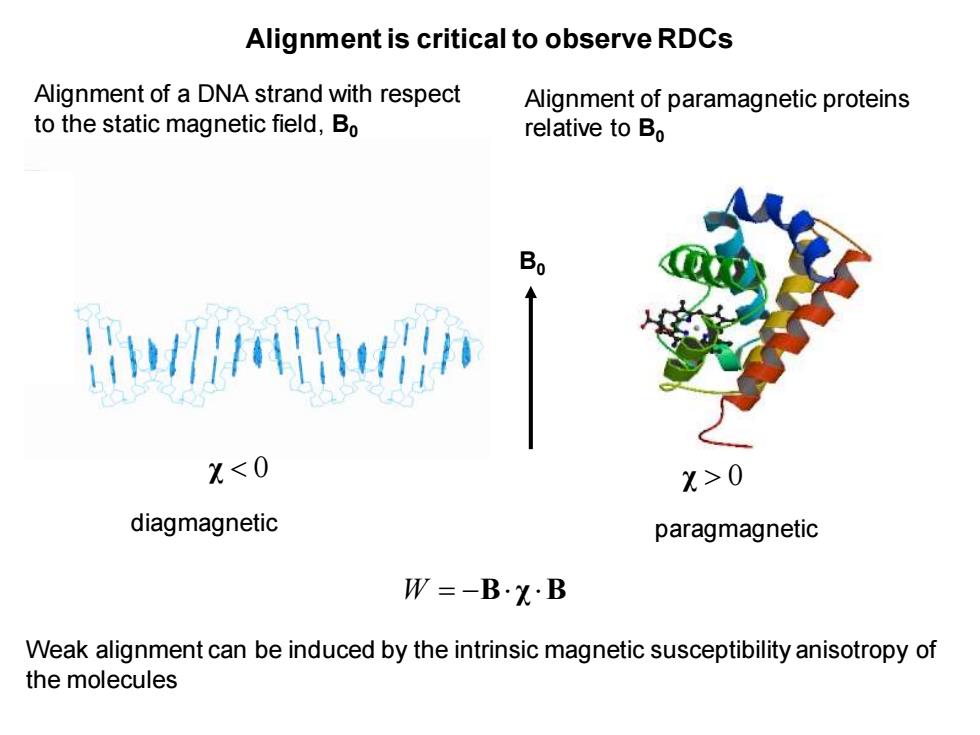
Alignment is critical to observe RDCs Alignment of a DNA strand with respect Alignment of paramagnetic proteins to the static magnetic field,Bo relative to Bo X0 diagmagnetic paragmagnetic W=-B·X·B Weak alignment can be induced by the intrinsic magnetic susceptibility anisotropy of the molecules
Alignment is critical to observe RDCs Alignment of a DNA strand with respect to the static magnetic field, B0 Weak alignment can be induced by the intrinsic magnetic susceptibility anisotropy of the molecules W = − B χ B χ 0 Alignment of paramagnetic proteins relative to B0 χ 0 B0 diagmagnetic paragmagnetic

External alignment media Bicelle Bacteriophage Pf1 Orientation of the uniaxial alignment media is described by a director Purple Membrane Alignment of the target molecules is dictated by the interactions between the molecules and the alignment media Better control over the alignment level Multiple aligning conditions
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - Bicelle Bacteriophage Pf1 Alignment of the target molecules is dictated by the interactions between the molecules and the alignment media ❑ Better control over the alignment level ❑ Multiple aligning conditions External alignment media Purple Membrane Orientation of the uniaxial alignment media is described by a director
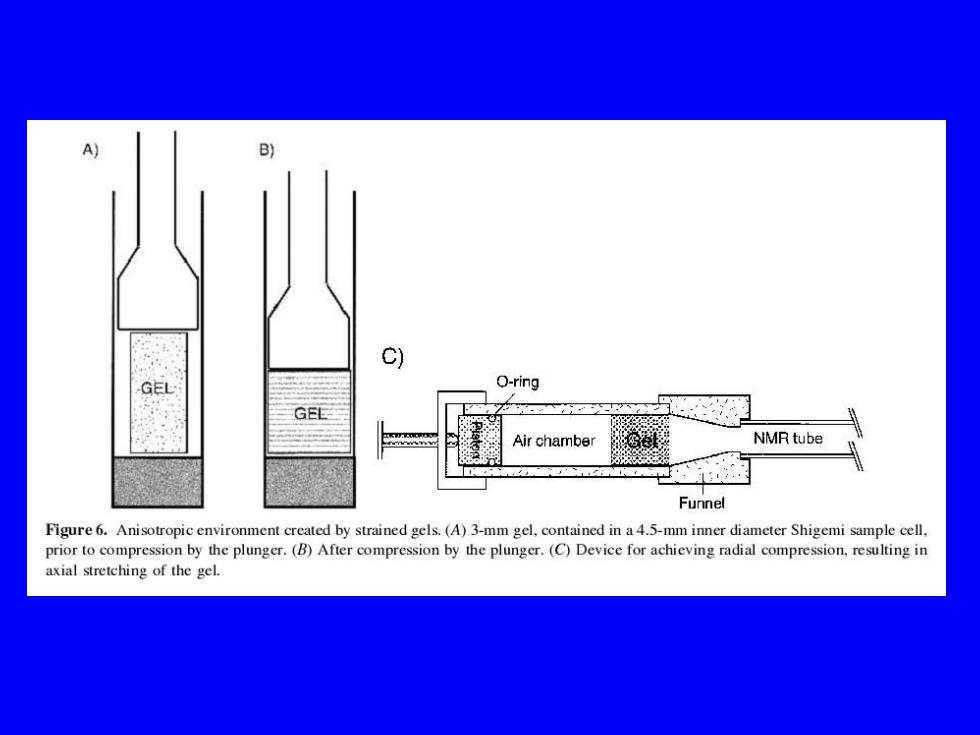
A) B) c) GEL O-ring GEL Air chamber NMR tube Funnel Figure6.Anisotropic environment created by strained gels.(A)3-mm gel,contained in a4.5-mm inner diameter Shigemi sample cell. prior to compression by the plunger.(B)After compression by the plunger.(C)Device for achieving radial compression,resulting in axial stretching of the gel
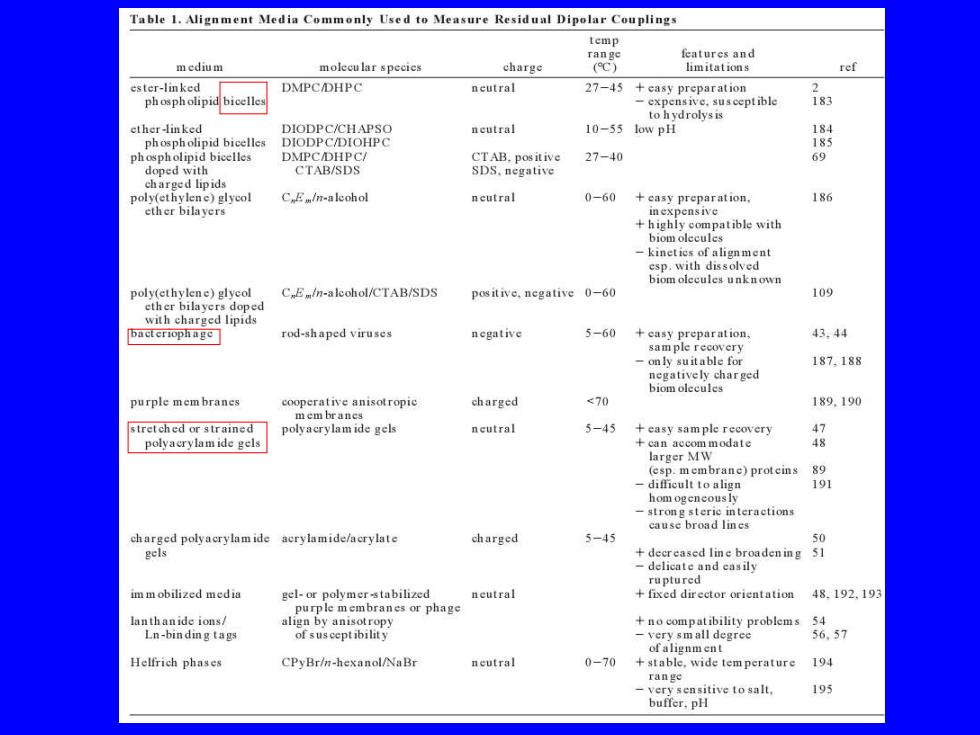
Table 1.Alignment Media Commonly Used to Measure Residual Dipolar Couplings temp features and medium molecu lar species charge (C) limitations ref ester-linked DMPC/DHPC neutral 27-45 +easy preparation phospholipid bicelles -expensive.susceptible 183 to hydrol小ysis ether-linked DIODPC/CHAPSO ncutral 10-55 low pH 184 phospholipid bicelles DIODPC/DIOHPC 185 pp CTAB.positive 27-40 69 CTAB/SDS SDS.negative charged lipids poly(ethylene)glycol C Em/n-aleohol neutral 0-60 +casy preparation, 186 ether bilayers inexpensive +highly compatible with biom olec kineties of alignment esp.with dissolved biom olecules unknown poly(ethylene)glycol C E/n-aleohol/CTAB/SDS positive.negative 0-60 109 ether bilayers doped with charged lipids rod-shaped viruses 5-60 +a 43.44 -only suitable for 187,188 negatively charged biomolecules purple mem branes cooperative anisotropic charged <70 189.190 mem brancs stretched or strained polyacrylam ide gels ncutral 5-45 +easy sample recovery polyacrylamide gels +nNmodae 4极 (esp.membrane)proteins 89 191 interactions charged polyacrylam ide acrylamide/acrylate charged 5-45 50 gels +decreased line broadening 51 -delicate and casily ruptured im m obilized media neutral +fixed director orientation 48.192,19 purple membranes or phage lanthanide ions/ align by anisotropy no compatibility problems 54 Ln-binding tags of susceptibility -very small degree 6.57 ofalignment Helfrich phases CPyBr/n-hexanol/NaBr neutral 0-70 +stable,wide tem perature 194 「ange very sensitive to salt, 195 buffer.pH
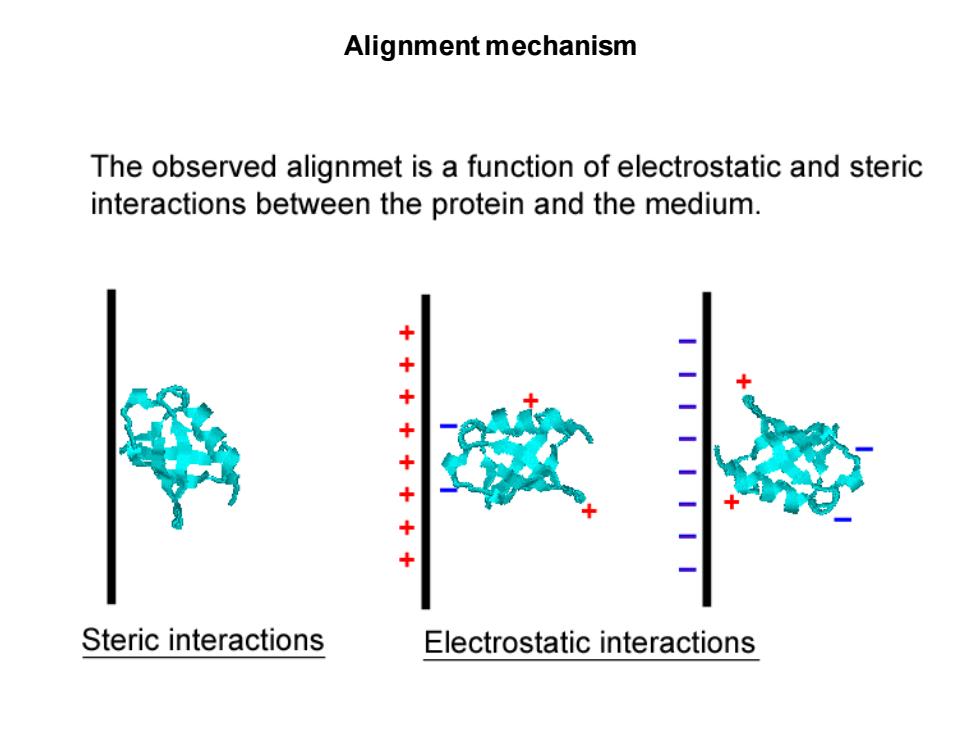
Alignment mechanism The observed alignmet is a function of electrostatic and steric interactions between the protein and the medium. ++ -- + Steric interactions Electrostatic interactions
Alignment mechanism
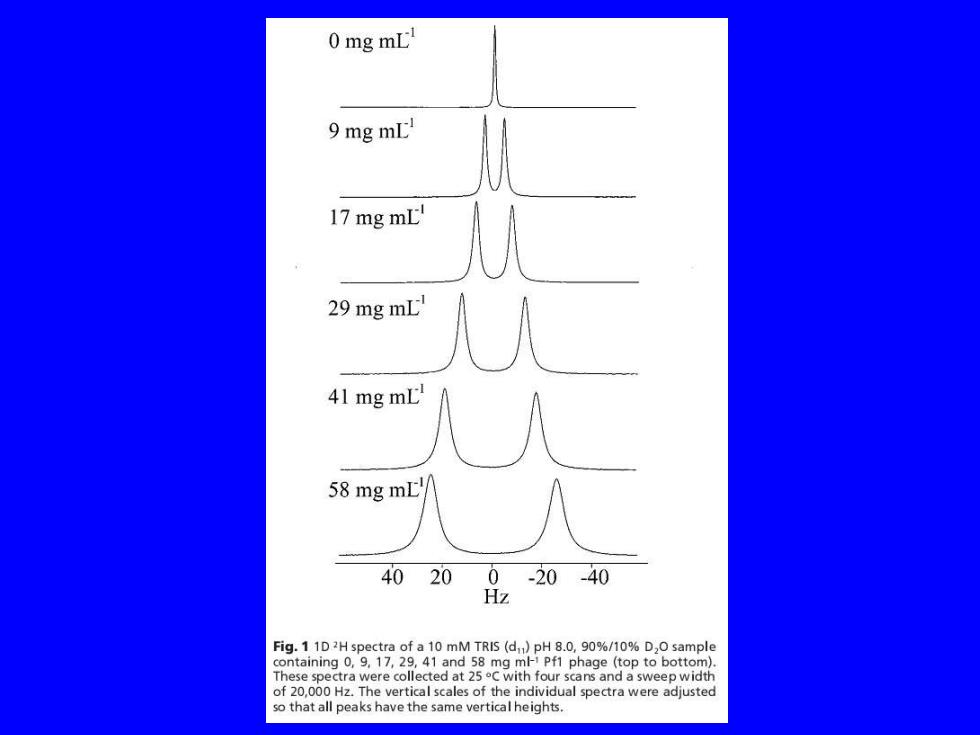
0 mg mL 9 mg mL 17 mg mL! 29 mg mL 41 mg mL 58 mg mLt 40 200-20-40 Hz Fig.1 1D2H spectra of a 10 mM TRIS (d)pH 8.0,90%/10%D,O sample containing 0,9.17,29,41 and 58 mg ml Pf1 phage (top to bottom). These spectra were collected at 25C with four scans and a sweep width of 20,000 Hz.The vertical scales of the individual spectra were adjusted so that all peaks have the same vertical heights
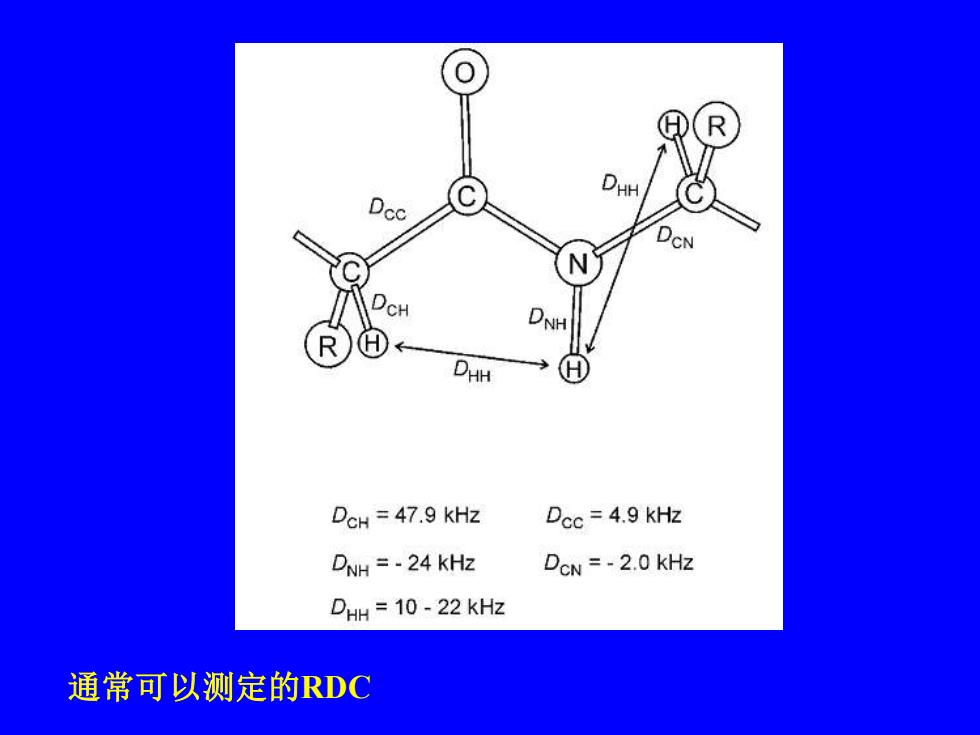
CN H DHH DCH 47.9 kHz Dcc=4.9 KHz DNH =-24 KHz DoN =-2.0 KHz DHH 10-22 kHz 通常可以测定的RDC
通常可以测定的RDC