
Chapter 11 Solution thermodynamics: Theory
Chapter 11 Solution thermodynamics: Theory

Purpose: To develop the theoretical foundation for applications of thermodynamics to gas mixtures and liquid solutions 且的 1、了解溶液热力学的基本概念 2、学习溶液热力学的基本原理 3、为相平衡的学习打下基础
Purpose: To develop the theoretical foundation for applications of thermodynamics to gas mixtures and liquid solutions 目的 1、了解溶液热力学的基本概念 2、学习溶液热力学的基本原理 3、为相平衡的学习打下基础

Purpose: To develop the theoretical foundation for applications of thermodynamics to gas mixtures and liquid solutions Main idea: Property relations for mixture Chemical potential Partial properties Fugacity and fugacity coefficient Ideal solution Excess properties
Purpose: To develop the theoretical foundation for applications of thermodynamics to gas mixtures and liquid solutions Main idea: Property relations for mixture Fugacity and fugacity coefficient Partial properties Chemical potential Ideal solution Excess properties

content 11.1 Fundamental Property Relation 11.2 The chemical Potential and Phase Equilibrium 11.3 Partial Properties 11.4 Ideal-Gas Mixture 11.5 Fugacity and Fugacity Coefficient:Pure Species 11.6 Fugacity and Fugacity Coefficient:Species in Solution 11.7 Generalized Correlations for the Fugacity Coefficient 11.8 The Ideal Solution 11.9 Excess Properties
content 11.1 Fundamental Property Relation 11.2 The chemical Potential and Phase Equilibrium 11.3 Partial Properties 11.4 Ideal-Gas Mixture 11.5 Fugacity and Fugacity Coefficient: Pure Species 11.6 Fugacity and Fugacity Coefficient: Species in Solution 11.7 Generalized Correlations for the Fugacity Coefficient 11.8 The Ideal Solution 11.9 Excess Properties

11.1 Fundamental Property Relation REVIEW Fundamental Property Relations of Thermodynamics for Homogeneous Phase System For one mol For n mol dU TdS-Pdv d(nU)=Td(nS)-Pd(nv) (nG) dH TdS+Vap d(nH)=Td(nS)+(nV)d(nP) OP dA=-Pdv-SdT d(nA)=-Pd(nV)-(nS)d(nT) anG) P n =-nS dG =Vdp-SdT d(nG)=(nV)dp-(nS)dT 四个微分方程式,是我们常用到的微分方程, 使用这些方程时一定要注意以下几,点: 1.恒组分、恒质量体系,也就是封闭体系; 2.均相体系(单相); 3.平衡态间的变化; 4.常用于1摩尔时的性质
11.1 Fundamental Property Relation REVIEW Fundamental Property Relations of Thermodynamics for Homogeneous Phase System dU TdS PdV dH TdS VdP dA PdV SdT dG VdP SdT = − = + =− − = − For one mol For n mol ( ) () ( ) ( ) ( ) ( )( ) ( ) ( ) ( )( ) ( )( ) () d nU Td nS Pd nV d nH Td nS nV d nP d nA Pd nV nS d nT d nG nV dP nS dT = − = + =− − = − , , ( ) [ ] ( ) [ ] T n P n nG nV P nG nS T ∂ = ∂ ∂ = − ∂
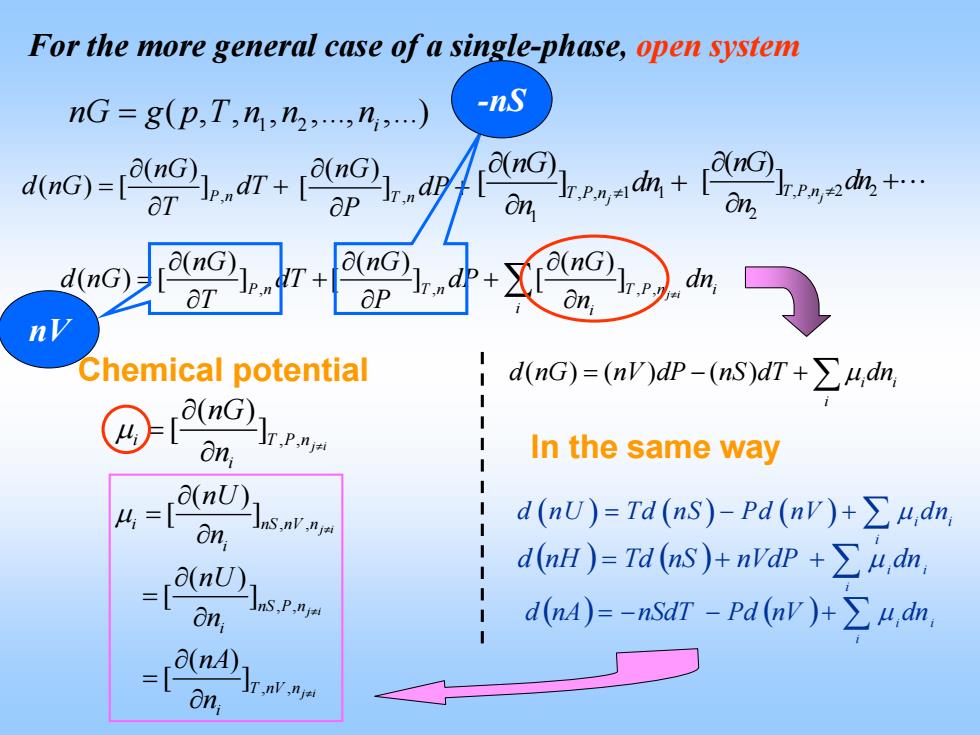
For the more general case of a single-phase,open system nG=g(p,T,h,n2,n,) -nS (nG) on, n Chemical potential dnG)=(n)dp-(nS)dT+∑4,dn (nG)1 On In the same way 4=en0) nS.nv.nja d(nU)=Td(nS)-Pd(nv)+>u,dn, -[n) d(aH)=Td(s)+ndP+∑从,dn, On; nS,P.nja d(nA)=-nSdT-Pd (nv)+udn, a(nA) on
For the more general case of a single-phase, open system 1 2 ( , , , ,., ,.) i nG g p T n n n = , , , () () () ( )[ ] [ ] [ ] P j i n T n T P n i i i nG nG nG d nG dT dP dn TP n ≠ ∂∂ ∂ = ++ ∂∂ ∂ ∑ , ( ) [ ]T n nG dP P ∂ + ∂ , 1 1 1 ( ) [ ]T Pnj nG dn n ≠ ∂ + ∂ , 2 2 2 ( ) [ ]TPnj nG dn n ≠ ∂ + ∂ d nG( )[ ] ( ) nG P n, dT L T ∂ = + ∂ , , ( ) [ ] j i i T P n i nG n μ ≠ ∂ = ∂ Chemical potential ( )( ) ( ) i i i d nG nV dP nS dT dn = −+ ∑ μ nV -nS ( ) ( ) ++= ∑i nVdPnSTdnHd μ dnii ( ) ( )+−−= ∑i nAd nVPdnSdT μ dnii ( ) ( ) ( ) i i i d nU Td nS Pd nV dn =− + ∑ μ In the same way , , , , , , ( ) [ ] ( ) [ ] ( ) [ ] j i j i j i i n S n V n i nS P n i T nV n i nU n nU n nA n μ ≠ ≠ ≠ ∂ = ∂ ∂ = ∂ ∂ = ∂

dnG)=(nWdp-(nS)dT+∑4,dn For the case of one mole of solution n-1 nxi dG=dP-SdT+∑4,a G=G(P,T,x1,x2,x,.) T )pn=-S
( )( ) ( ) i i i d nG nV dP nS dT dn = −+∑μ For the case of one mole of solution n=1 ni=xi i i i dG VdP SdT dx =−+∑μ 1 2 ( , , , ,., ,.) G GPT x x x = i , , () () T n P n G G V S P T ∂ ∂ = =− ∂ ∂
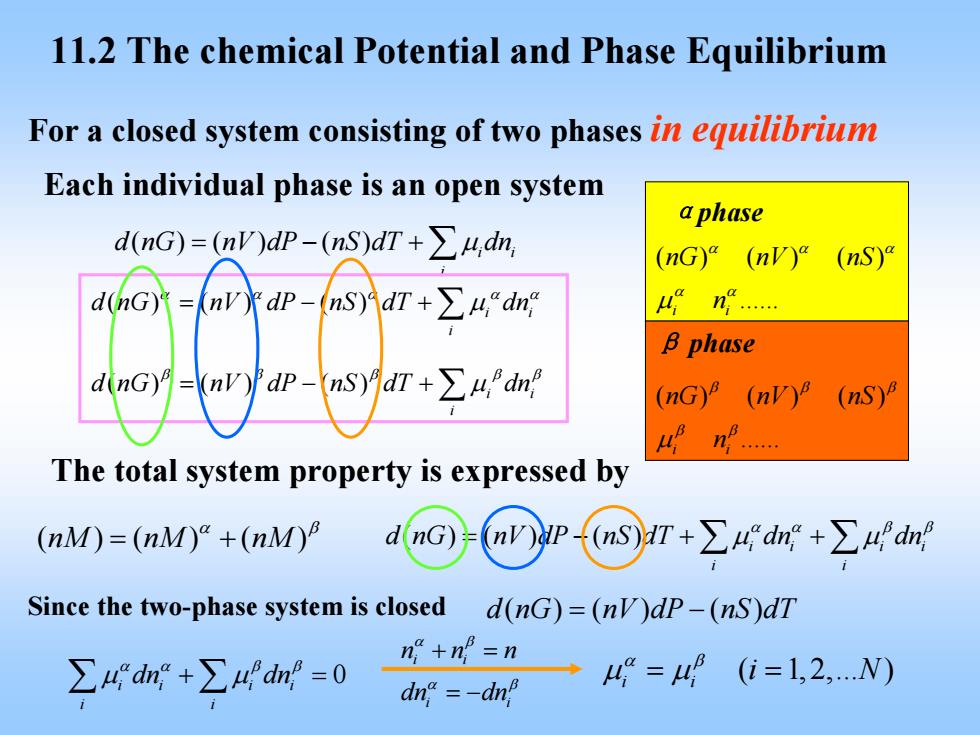
11.2 The chemical Potential and Phase Equilibrium For a closed system consisting of two phases in equilibrium Each individual phase is an open system aphase dnG)=nVdP-(nS)dT+∑4,dn (nG)"(nV) (nS) d(nG) (n水dP-ns)idr+∑4dn B phase dinG)=(nv) dP-ns)月dr+∑h,dn (nG)(nV)8 (nS) The total system property is expressed by (nM)=(nM)+(nM) Since the two-phase system is closed d(nG)=(nV)dp-(nS)dT ∑4dr+∑Adn=0 n+no=n →42=4(i=1,2,.N) dna=-dn
11.2 The chemical Potential and Phase Equilibrium For a closed system consisting of two phases in equilibrium Each individual phase is an open system αphase β phase ( ) ( ) () . i i nG nV nS n α αα α α μ ( ) ( ) () . i i nG nV nS n β ββ β β μ ( )( ) ( ) i i i d nG nV dP nS dT dn = −+ ∑ μ ( ) ( ) () i i i d nG nV dP nS dT dn α αα α α = −+ ∑ μ ( ) ( ) () i i i d nG nV dP nS dT dn β ββ β β = −+ ∑ μ The total system property is expressed by ( )( ) ( ) nM nM nM α β = + ( )( ) ( ) ii ii i i d nG nV dP nS dT dn dn α α ββ = −+ + ∑μ μ ∑ Since the two-phase system is closed d nG nV dP nS dT ( )( ) ( ) = − 0 ii ii i i dn dn αα ββ ∑ ∑ μ μ + = i i i i nnn dn dn α β α β + = = − ( 1, 2,. ) i i i N α β μ μ = =

For n-phase system 4=4==4(i=1,2,N) Multiple phases at the same T and P are in equilibrium when the chemical potential of each species is the same in all phases
For π-phase system . ( 1, 2,. ) ii i i N αβ π μμ μ = == = Multiple phases at the same T and P are in equilibrium when the chemical potential of each species is the same in all phases
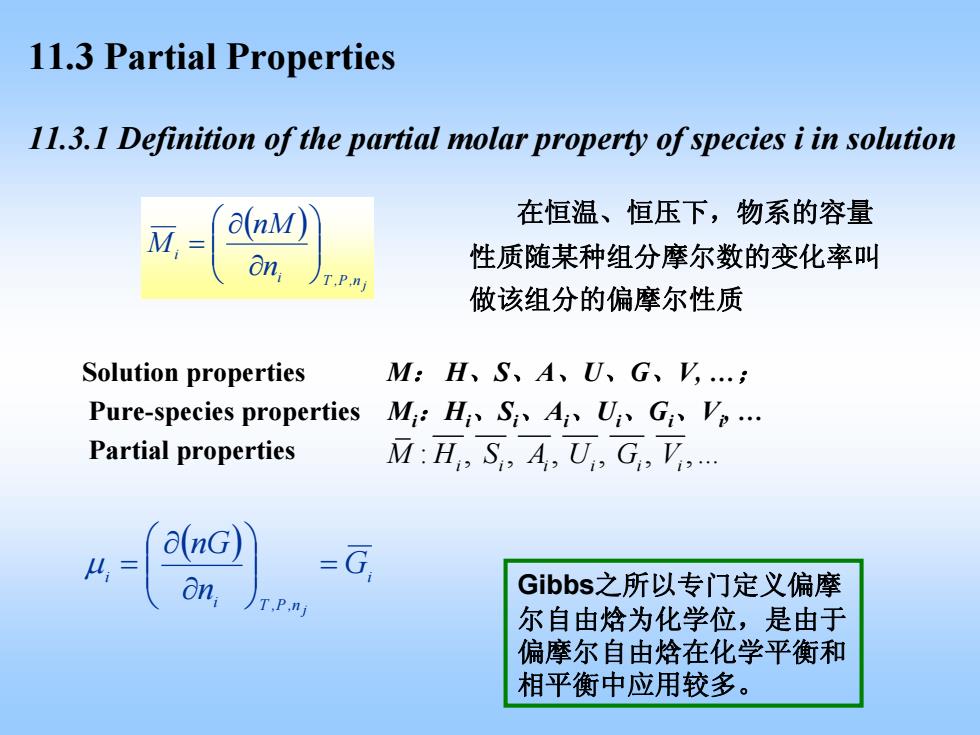
11.3 Partial Properties 11.3.1 Definition of the partial molar property of species i in solution 在恒温、恒压下,物系的容量 M, a(nM 8n, 性质随某种组分摩尔数的变化率叫 TP.n 做该组分的偏摩尔性质 Solution properties M:H、S、A、U、G、,.; Pure-species properties M:H、Si、A、U、G、V,. Partial properties M:H S,A U G,V. a(nG) 4= on, -G Gibbs.之所以专门定义偏摩 尔自由焓为化学位,是由于 偏摩尔自由焓在化学平衡和 相平衡中应用较多
11.3 Partial Properties ( ) n,P,T j i i n nM M ⎟ ⎟ ⎠ ⎞ ⎜ ⎜ ⎝ ⎛ ∂ ∂ = 11.3.1 Definition of the partial molar property of species i in solution 在恒温、恒压下,物系的容量 性质随某种组分摩尔数的变化率叫 做该组分的偏摩尔性质 ( ) i i n,P,T i G n nG j = ⎟ ⎟ ⎠ ⎞ ⎜ ⎜ ⎝ ⎛ ∂ ∂ μ = Gibbs之所以专门定义偏摩 尔自由焓为化学位,是由于 偏摩尔自由焓在化学平衡和 相平衡中应用较多。 Solution properties M : H 、 S 、 A 、 U 、 G 、V, . ; Pure-species properties Mi : Hi 、 Si 、 Ai 、 Ui 、 Gi 、 Vi, . Partial properties : , , , , , , . MH S AU GV ii i i ii