
Chapter 2 The First Law and Other Basic Concepts 2.1 The First Law of Thermodynamics 2.2 Energy Balance for Closed System 2.3 Mass and Energy Balance for Open System 2.1 The First Law of Thermodynamics (1)Statement of the first law of thermodynamics Although energy assumes many forms.the total quantity of energy is constant.and when energy disappears in one form it appears simulaneously in other forms (2)The basic form of the first law of thermodynamics: A(Energy of the system)+A(Energy of surroundings)=0 Characteristics of energies (1)Heat and work ()Potential,kinetic,and intemal energy 能量分类: ()系统蓄积的能量,如动能、势能和热力学能,是系统状态的函数。 (2)过程中系统和环境传递的能量,如功、热量,不是状态函数,与过程有关。 2.2 Energy Balance for Closed System Definition of closed system ifthe boundary of a system does not permit the transfer of matter between the system and its surroundings.the system is said to be closed system Energy Balance for Closed System A(Energy of the system)=0+W State That is E=Q+W E2 Energies of a system include System intemal,potential,kinetic energy. surroundings etc. Closed systems often undergo processes that cause no change in the system other than in its intemal energy. 4E=O+W Attention! △U=Q+W O and W,transferring into the system from and du do+dw the surroundings,are positive
Chapter 2 The First Law and Other Basic Concepts 2.1 The First Law of Thermodynamics 2.2 Energy Balance for Closed System 2.3 Mass and Energy Balance for Open System 2.1 The First Law of Thermodynamics (1) Statement of the first law of thermodynamics: Although energy assumes many forms, the total quantity of energy is constant, and when energy disappears in one form it appears simultaneously in other forms. (2) The basic form of the first law of thermodynamics: △( Energy of the system) + △( Energy of surroundings) =0 Characteristics of energies (1) Heat and work (2) Potential, kinetic, and internal energy 能量分类: (1)系统蓄积的能量,如动能、势能和热力学能,是系统状态的函数。 (2)过程中系统和环境传递的能量,如功、热量,不是状态函数,与过程有关。 2.2 Energy Balance for Closed System Definition of closed system if the boundary of a system does not permit the transfer of matter between the system and its surroundings, the system is said to be closed system Energy Balance for Closed System △( Energy of the system) =Q+W That is Energies of a system include internal, potential, kinetic energy, etc. Closed systems often undergo processes that cause no change in the system other than in its internal energy. System surroundings State 2 E2 State 1 E1 Q W E = Q +W Q and W, transferring into the system from the surroundings, are positive Attention! and = + U Q W dU dQ dW = + E = Q +W
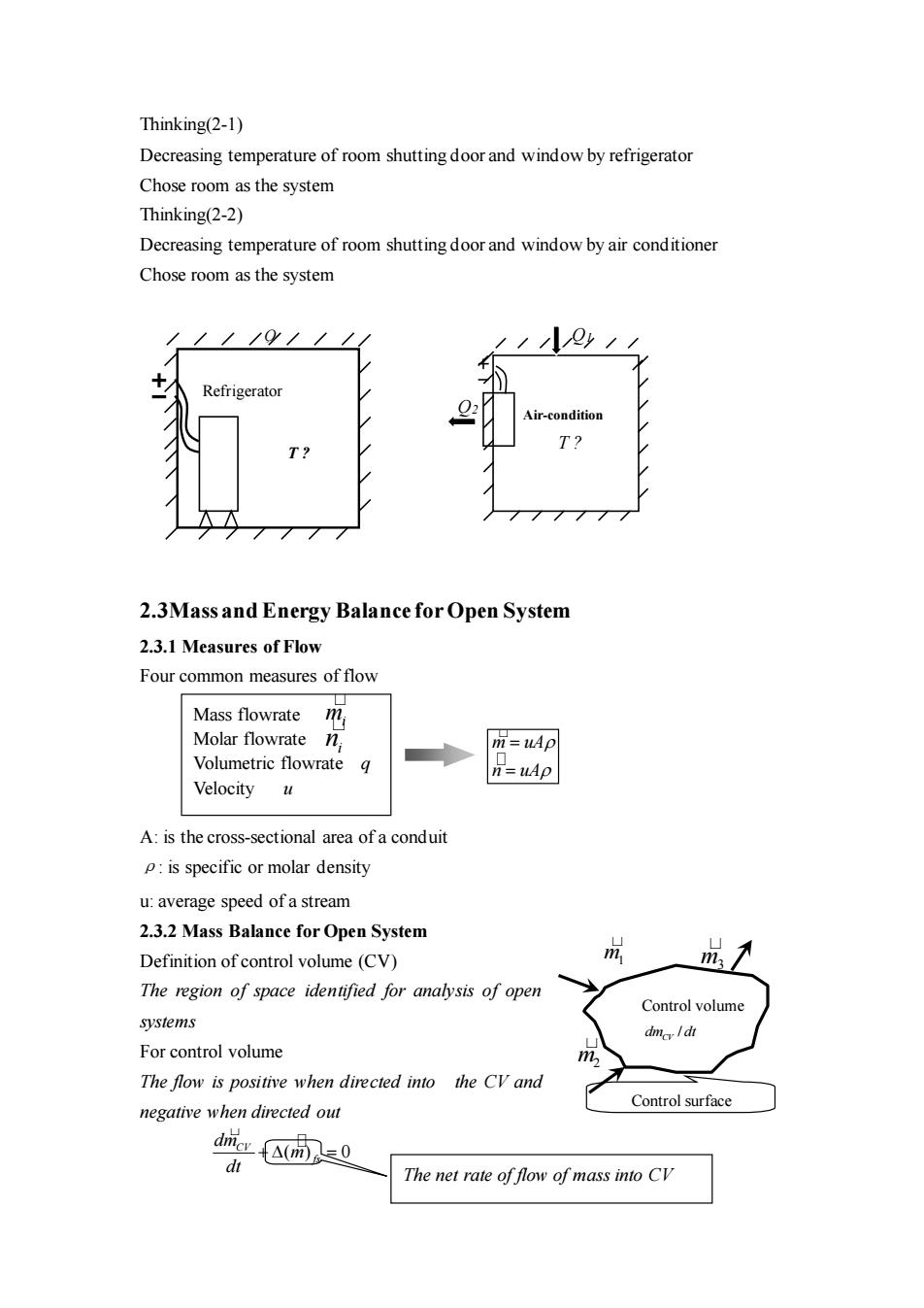
Thinking(2-1) Decreasing temperature of room shutting door and window by refrigerator Chose room as the system Thinking(2-2) Decreasing temperature of room shutting door and window by air conditioner Chose room as the system ir-conditio T T 777 2.3Mass and Energy Balance for Open System 2.3.1 Measures of Flow Four common measures of flow Mass flowrate Molar flowrate n m=uAp Volumetric flowrate q n=uAp Velocity u A:is the cross-sectional area ofa conduit p:is specific or molar density u:average speed ofa stream 2.3.2 Mass Balance for Open System Definition of control volume (CV) The region of space identified for analysis of open Control volume systems dmc/dt For control volume The fow is positive when directed into the CV and negative when directed out Control surface dries( d山 The net rate of flow of mass into CV
Thinking(2-1) Decreasing temperature of room shutting door and window by refrigerator Chose room as the system Thinking(2-2) Decreasing temperature of room shutting door and window by air conditioner Chose room as the system 2.3Mass and Energy Balance for Open System 2.3.1 Measures of Flow Four common measures of flow A: is the cross-sectional area of a conduit ρ: is specific or molar density u: average speed of a stream 2.3.2 Mass Balance for Open System Definition of control volume (CV) The region of space identified for analysis of open systems For control volume The flow is positive when directed into the CV and negative when directed out Mass flowrate Molar flowrate Volumetric flowrate q Velocity u mi i n m uA n uA = = Q2 Air-condition Q1 T ? ( ) 0 CV fs dm m dt + = Control volume Control surface m3 m2 m1 / dm dt CV Q T ? Refrigerator The net rate of flow of mass into CV
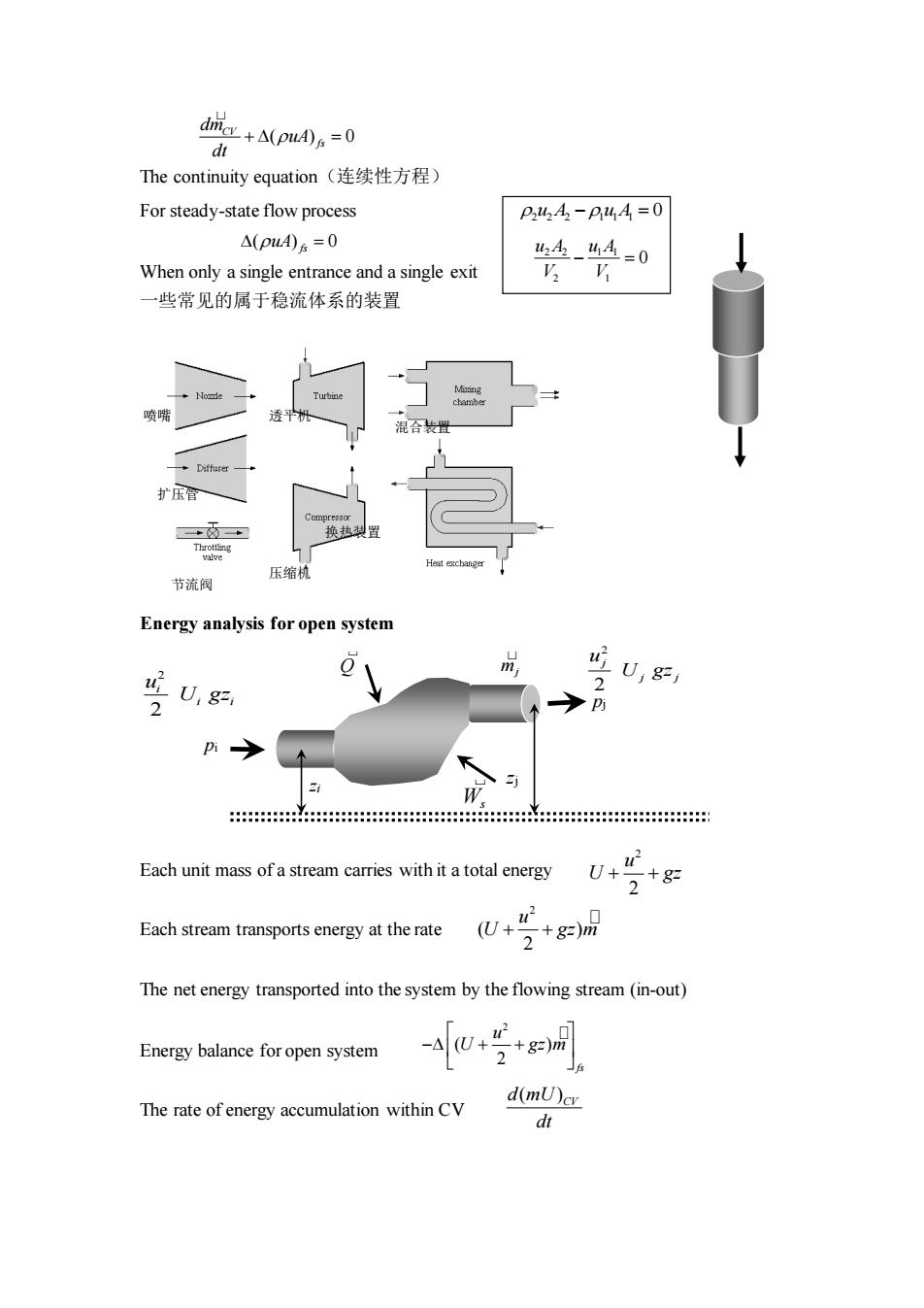
d城+A(pu0a=0 The continuity equation(连续性方程) For steady-state flow process P44,-P44=0 △(pu4)6=0 h4-44=0 When only a single entrance and a single exit 一些常见的属于稳流体系的装置 扩压 节流阀 压缩材 Energy analysis for open system m U,g= 0 U,g=, 2 Each unit mass of a stream carries with it a total energy 2+& Each stream transports energy at the rate U+ 2+8 The net energy transported into the system by the flowing stream(in-out) Energy balance for open system The rate of energy accumulation within CV d(mU)cv dt
The continuity equation(连续性方程) For steady-state flow process When only a single entrance and a single exit 一些常见的属于稳流体系的装置 Energy analysis for open system Each unit mass of a stream carries with it a total energy Each stream transports energy at the rate The net energy transported into the system by the flowing stream (in-out) Energy balance for open system The rate of energy accumulation within CV zi 2 2 i i i u U gz zj mj 2 2 j j j u U gz Ws Q pi pj ( ) 0 CV fs dm uA dt + = = ( ) 0 uA fs 2 2 2 1 1 1 u A u A − = 0 2 2 1 1 2 1 0 u A u A V V − = 换热装置 压缩机 喷嘴 扩压管 透平机 混合装置 节流阀 2 2 u U gz + + 2 ( ) 2 u U gz m + + 2 ( ) 2 fs u U gz m − + + ( ) d mU CV dt

Total energy entering Total energy leaving Change in the total the system the system energy of the system d(mU)cr_ -A +ork rate Work rate work rate=the flowing work rate+the other work rate(功传递速率=流动功速率+ 其他功) the flowing work rate:moving the flowing streams through entrances and exits through the entrance p The work rate (pm through the exit p,V The work rate (p,v)m the flowing work rate -A[(pV] the other work rate: =the shaft work rate+the expansion work rate+ contraction work+stirring work rate+. work rate=-A[(plm。+W Energy balance for open system =-[+片+g+-pn+ H=U+pV m-4+号g调+0+ d Omit potential,kinetic energy ma=-A。++ For closed system d(mU)cr dt =0+ 2.3.4 Energy Balance for Steady-State Flow Process Review 稳态流动是指流体流动途径中所有各点的状况都不随时间而变化,系统中没有 物料和能量的积累
Work rate work rate =the flowing work rate + the other work rate(功传递速率=流动功速率+ 其他功) the flowing work rate:moving the flowing streams through entrances and exits through the entrance The work rate through the exit The work rate the flowing work rate the other work rate: =the shaft work rate + the expansion work rate + contraction work + stirring work rate + . Energy balance for open system 2.3.4 Energy Balance for Steady-State Flow Process Review 稳态流动是指流体流动途径中所有各点的状况都不随时间而变化,系统中没有 物料和能量的积累。 H=U+pV 2 ( ) ( ) 2 CV fs d mU u H gz m Q W dt = − + + + + Omit potential, kinetic energy ( )CV fs d mU Hm Q W dt = − + + For closed system ( ) d mU CV Q W dt = + 2 ( ) ( ) 2 CV fs d mU u U gz m Q work rate dt = − + + + + ? Total energy entering the system Total energy leaving the system Change in the total energy of the system - = ( ) pV m i i i pVi i ( ) j j j p V m pVj j ( ) fs − pV m W ( ) fs work rate pV m W = − + 2 ( ) ( ) [( ) ] 2 CV fs fs d mU u U gz m Q pV m W dt = − + + + − +
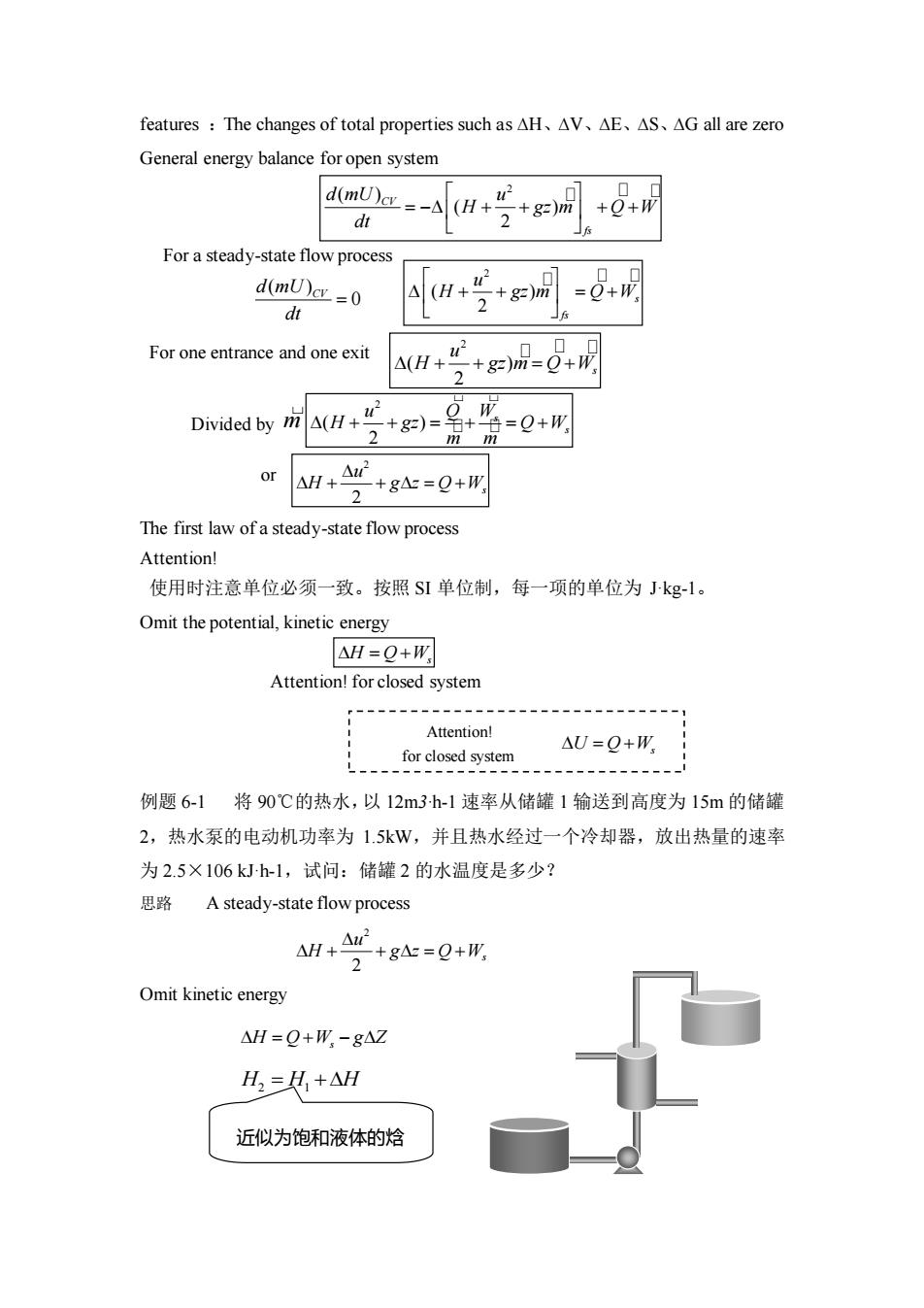
features:The changes of total properties such as AH、AV、△E、AS、△Gall are zero General energy balance for open system am-ah+号+g+ dt For a steady-state flow process d(mUc=0 4(H+ +=0+ dt For one entrance and one exit +gn品-0+ 4(H+4 Divided by(H +)=名 游=0+形 or 4H+4r +g△=Q+W The first law of a steady-state flow process Attention! 使用时注意单位必须一致。按照S单位制,每一项的单位为kg1。 Omit the potential,kinetic energy △H=Q+W Attention!for closed system Attention! for closed system 0-0 例题6-1将90℃的热水,以12m3h-1速率从储罐1输送到高度为15m的储罐 2,热水泵的电动机功率为1.5kW,并且热水经过一个冷却器,放出热量的速率 为2.5×106kJh-1,试问:储罐2的水温度是多少? 思路 A steady-state flow process ANH+A+g4=Q+形 2 Omit kinetic energy △H=Q+W,-gA☑ H,=其+AH 近似为饱和液体的焓
features :The changes of total properties such as ∆H、∆V、∆E、∆S、∆G all are zero General energy balance for open system The first law of a steady-state flow process Attention! 使用时注意单位必须一致。按照 SI 单位制,每一项的单位为 J·kg-1。 Omit the potential, kinetic energy Attention! for closed system 例题 6-1 将 90℃的热水,以 12m3·h-1 速率从储罐 1 输送到高度为 15m 的储罐 2,热水泵的电动机功率为 1.5kW,并且热水经过一个冷却器,放出热量的速率 为 2.5×106 kJ·h-1,试问:储罐 2 的水温度是多少? 思路 A steady-state flow process Omit kinetic energy For one entrance and one exit For a steady-state flow process ( ) 0 d mU CV dt = 2 ( ) 2 s fs u H gz m Q W + + = + 2 ( ) 2 s u + + = + H gz m Q W Divided by m 2 ( ) 2 s s u Q W H gz Q W m m + + = + = + 2 ( ) ( ) 2 CV fs d mU u H gz m Q W dt = − + + + + 2 2 s u H g z Q W + + = + or = + H Q Ws Attention! for closed system = + U Q Ws 2 2 s u H g z Q W + + = + = + − H Q W g Z s H H H 2 1 = + 近似为饱和液体的焓

Solution 从水性质表中可查得 90℃时水的密度为 965.3kgm-3 水的质量流率为 965.3×12=11583.6kg-h-1 得到放出的热量Q=-25x10 =-215.8kJkg 11583.6 1.5×3600 轴功 W=11583.6 =0.466kJ-kg 势能 g4=9.8×15×10-3=0.147kJ.kg △H=Q+W,-g4=-215.8+0.466-0.147=-215.48kJ-kg 从附录C-1饱和水性质表中可查得90℃时饱和液体的焓 H1=376.92kJ.kg H2=△H+H1=-215.48+376.92=161.44kJkg 再从饱和水性质表中可内插查到此时的温度约为38.5℃ 5.1.3 Application for energy balance equation (I))For closed system δml(U+p+2/2+gl-δm2(U+pp+u22+g=2+δQ+δW形=d(mE/system 6ml=6m2=dm=0 6Q+6形=mdE E=U+Ep+Ek mdE=mdU du =60+8W AU=0+W (2)For Steady-State Flow System d(mE)s=0 6m =6m,=6m 80+6m+(H+g2+5r),6m-(H+gZ+5r2,6m=0 -+g=Q+W Forl+ Attention! +g止=6Q+6W, 2 使用时要注意单位必须 dH+udu+gd=δQ+6w, 致。按照S1单位制.每一项的 单位为Jkg'。动能和位能的 单位
Solution 从水性质表中可查得 90℃时水的密度为 965.3kg·m-3 水的质量流率为 965.3×12 = 11583.6 kgh-1 得到放出的热量 从附录 C-1 饱和水性质表中可查得 90℃时饱和液体的焓 再从饱和水性质表中可内插查到此时的温度约为 38.5℃。 5.1.3 Application for energy balance equation (1) For closed system m1(U + pv+u2/2 + gz)1- m2(U + pv+u2/2 + gz)2 + Q + Ws = d(mE)system δm1=δm2=dm=0 δQ+δWs=mdE E=U+EP+EK mdE=mdU δW=δWs (2) For Steady-State Flow System 1 6 215.8kJ kg 11583.6 2.5 10 − = − Q = − 1 0.466kJ kg 11583.6 1.5 3600 − = = s 轴功 W 3 1 9.8 15 10 0.147kJ kg − − 势能 gz = = 1 215.8 0.466 0.147 215.48kJ kg− H = Q +W − gz = − + − = − S 1 1 376.92kJ kg − H = 1 2 1 215.48 376.92 161.44kJ kg − H = H + H = − + = dU Q W = + U = Q +W 1 2 ( ) 0 sys d mE m m m = = = 2 2 1 2 1 1 ( ) ( ) 0 2 2 Q W H gZ u m H gZ u m S + + + + − + + = Q Ws g z u H + + = + 2 2 For differential process 2 2 s du dH gdz Q W + + = + s dH udu gdz Q W + + = + Attention! 使用时要注意单位必须一 致。按照SI单位制,每一项的 单位为 J·kg-1。动能和位能的 单位

稳态流动是指流体流动途径中所有各点的状况都不随时间而变化,系统中没 有物料和能量的积累。 features:The changes of total properties such as AH、AV、aE、AS、AG all are zero DFor eqipment such as turbine and compresser,etc. g4Z≈0 △u2/2≈ 4++=Q+ △H=W,+g Foreqipment such as valve,pipe,heat-exchange chamber,etc 620”+等t=0 gAZ≈0 △WH=g For adiabatic reaction,adiabatic mixing.etc. 管-0 Q=0△u22≈0 Balance equation of mechanical energy dH+udu+gd=0+W dH=TdS+Vdp For reversible process=Tds dP+udu+gt=δW For real fluid,Consider energy lost owing to friction VdP+udu+gd+F=&W Fora non-viscous,non-compressible fluid,and Ws=0 Vdp+udu+gd=0 ++g=0 Bemoulli equation P1 =2 MPa T.=400°0 For example Turbine and compresser,etc. Virom gAZ=?≈0 △u2/2=?≈0 STEAM H+u +84=Q+形 TURBINE =5M1W △H=W,+Q 透平机是借助流体的减压和降温过程来产 P2-15 kPa 出功 180 m/s
稳态流动是指流体流动途径中所有各点的状况都不随时间而变化,系统中没 有物料和能量的积累。 features :The changes of total properties such as ∆H、∆V、∆E、∆S、∆G all are zero ①For eqipment such as turbine and compresser, etc. g∆Z ≈0 ∆u2/2 ≈0 ②For eqipment such as valve, pipe, heat- exchange chamber, etc. g∆Z ≈0 ∆u2/2 ≈0 Ws=0 ③For adiabatic reaction, adiabatic mixing, etc. Ws=0 g∆Z= ≈0 Q=0 ∆u2/2 ≈0 ④ Balance equation of mechanical energy dH=TdS+Vdp For reversible processδQ=TdS For real fluid, Consider energy lost owing to friction For a non-viscous, non-compressible fluid, and Ws=0 Bernoulli equation For example Turbine and compresser,etc. g∆Z=? ≈0 ∆u2/2 =? ≈0 透平机是借助流体的减压和降温过程来产 出功 Q Ws g z u H + + = + 2 2 = + H W Q s Q Ws g z u H + + = + 2 2 = H Q Q Ws g z u H + + = + 2 2 = H 0 s dH udu gdz Q W + + = + VdP udu gdz Ws + + = VdP udu gdz F W + + + = s VdP udu gdz + + = 0 2 0 2 P u g z + + = Q Ws g z u H + + = + 2 2 = + H W Q s
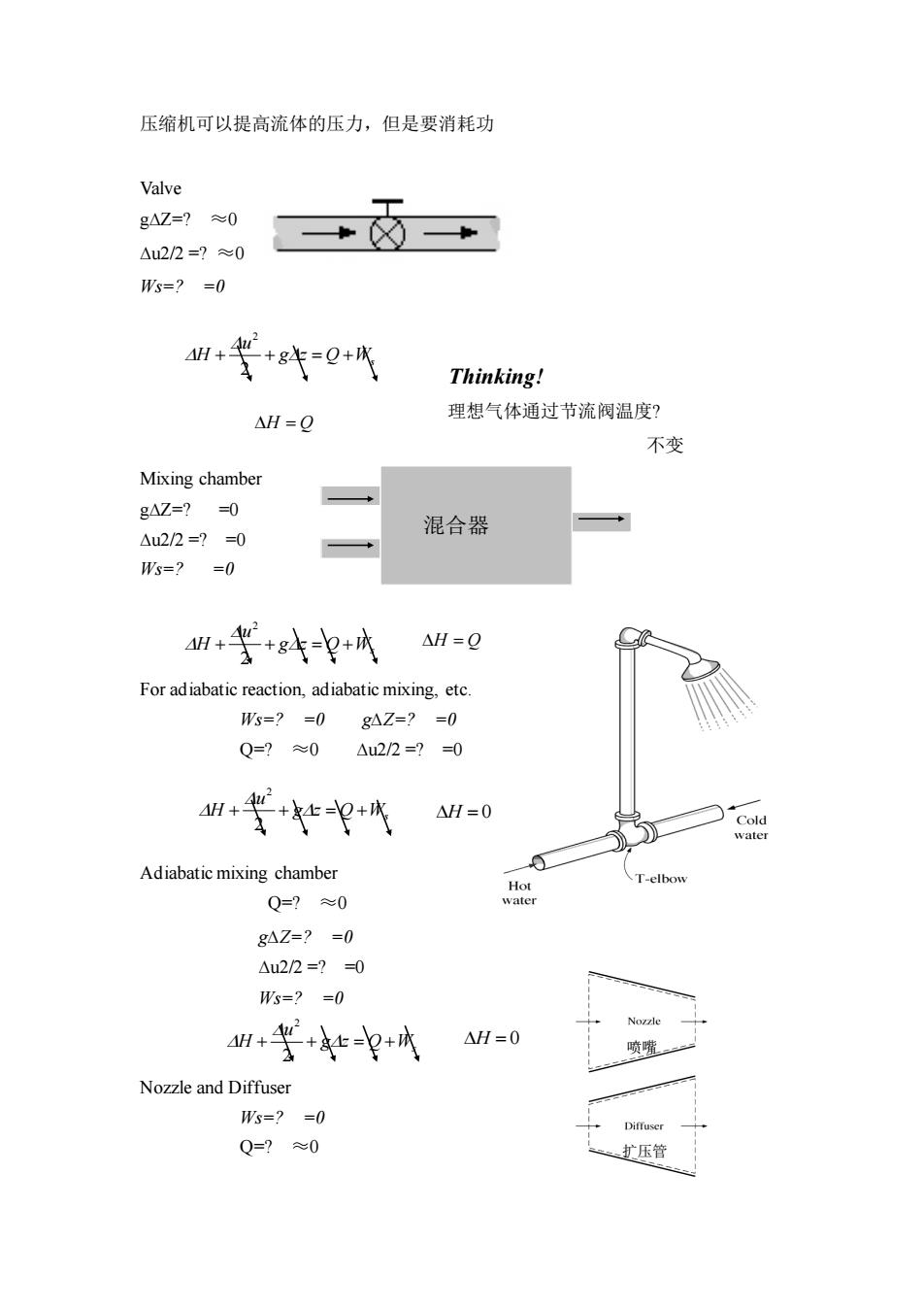
压缩机可以提高流体的压力,但是要消耗功 Valve g4Z=?≈0 Au22=?≈0 W5=?=0 4H+2 +件0+代 Thinking! △H=Q 理想气体通过节流阀温度? 不变 Mixing chamber gAZ=?=0 △u2/2=?=0 混合器 Ws=?=0 +等+4 △H=Q For adiabatic reaction,adiabatic mixing,etc. s=?=0g4Z=?=0 Q=?≈0 △u2/2=?=0 M+等+火水=0 Adiabatic mixing chamber T-elbow Q=?≈0 gAZ=?-0 △u22=?0 W=?=0 1+等++ △H=0 Nozzle and Diffuser W=?=0 Q=≈0 扩压管
压缩机可以提高流体的压力,但是要消耗功 Valve g∆Z=? ≈0 ∆u2/2 =? ≈0 Ws=? =0 Thinking! 理想气体通过节流阀温度? 不变 Mixing chamber g∆Z=? =0 ∆u2/2 =? =0 Ws=? =0 For adiabatic reaction, adiabatic mixing, etc. Ws=? =0 g∆Z=? =0 Q=? ≈0 ∆u2/2 =? =0 Adiabatic mixing chamber Q=? ≈0 g∆Z=? =0 ∆u2/2 =? =0 Ws=? =0 Nozzle and Diffuser Ws=? =0 Q=? ≈0 Q Ws g z u H + + = + 2 2 = H Q 混合器 Q Ws g z u H + + = + 2 2 = H Q Q Ws g z u H + + = + 2 2 = H 0 Q Ws g z u H + + = + 2 2 = H 0 喷嘴 扩压管

gAZ=?=0 m+实女 4-H= 2 流体通过焓值的改变来换取动能的调整 喷嘴与扩压管的结构特点是进出口截面积变化很大。流体通过时,使压力沿着 流动方向降低,而使流速加快的部件称为喷嘴。反之,使流体流速减缓,压力升 高的部件称为扩压管。 例5-11.5MPa的湿蒸汽在量热计中被节流到0.1MPa和403.15K,求湿蒸汽的 干度 解:节流过程无功的传递,忽略散热、动能变化和位能变化 4+等+t+ H,=H T C H kJ/kg 130-120_H2-2716.6 120 2716.6 160-120-2796.2-2716.6 130 H2 H2=2736.5kJ/kg 160 2796.2 H2=H1=2736.5 1.5MPa饱和液体焓值H=844.9饱和蒸汽培值Hg=2792.2 H=H,(1-x)+Hx 例5-2 4+答+g=0+代 m4H=mC(亿2-T)=50×1.005×(423-303)=6030k 将空气当作理想气体,并忽略压降时 4=4号-5铝-68m:
g∆Z=? =0 流体通过焓值的改变来换取动能的调整 喷嘴与扩压管的结构特点是进出口截面积变化很大。流体通过时,使压力沿着 流动方向降低,而使流速加快的部件称为喷嘴。反之,使流体流速减缓,压力升 高的部件称为扩压管。 例 5-1 1.5MPa 的湿蒸汽在量热计中被节流到 0.1MPa 和 403.15K,求湿蒸汽的 干度 解:节流过程无功的传递,忽略散热、动能变化和位能变化 T ℃ H kJ/kg 120 2716.6 130 H2 160 2796.2 1.5MPa 饱和液体焓值 Hl=844.9 饱和蒸汽焓值 Hg=2792.2 例 5-2 将空气当作理想气体,并忽略压降时 Q Ws g z u H + + = + 2 2 2 0 2 u H + = 2 2 1 2 2 1 2 u u H H − − = Q Ws g z u H + + = + 2 2 H H 2 1 = 2796 2 2716 6 2716 6 160 120 130 120 2 . . H . − − = − − H2 = 2736.5kJ / kg H H 2 1 = = 2736.5 H H ( x) H x 1 = l 1− + g 0 9709 2792 2 844 9 1 2736 5 844 9 . . . . . H H H H x g l l = − − = − − = Q Ws g z u H + + = + 2 2 m H mC (T T ) . ( ) k J = P 2 − 1 = 501 005 423−303 = 6030 1 1 2 2 V T V T = u A T u A T 1 1 2 2 = . m / s T T u u 6 98 303 423 5 1 2 2 = 1 = =

m54r=50x698-5=59J=0593 2 mgL=50×9.81×3=1472J=1.472kJ Q=6030+0.593+1.472=6032kJ 换热器的动能变化和位能变化可以忽略不计
换热器的动能变化和位能变化可以忽略不计 J . k J . m u 593 0 593 2 6 98 5 50 2 1 2 2 2 = = − = mgz = 509.813 =1472J =1.472k J Q = 6030 + 0.593+1.472 = 6032kJ