
Chapter 13 Chemical-Reaction Equilibria content 13.1 The Reaction Coordinate 13.2 Application of Equilibrium Criteria to Chemical Reactions 13.3 The Standard Gibbs-Energy Change and Equilibrium Constants 13.4 Effect of Temperature on EquilibriumConstants 13.5 Evaluation of Equilibrium Constants 13.6 Relation of Equilibrium Constant to Composition
Chapter 13 Chemical-Reaction Equilibria content 13.1 The Reaction Coordinate 13.2 Application of Equilibrium Criteria to Chemical Reactions 13.3 The Standard Gibbs-Energy Change and Equilibrium Constants 13.4 Effect of Temperature on EquilibriumConstants 13.5 Evaluation of Equilibrium Constants 13.6 Relation of Equilibrium Constant to Composition

13.1 The Reaction Coordinate The general chemical reaction A+A+.=4+A+. b,stoichiometric coefficient(化学计量系数) Positive(+)for products negative(-)for reactants For example CH4+H20→C0+3H2 veH,=-1H,0=-1H,=3ao=l dh_血_恤_恤-.=d血=dG :⅓V 典=s·血=吹 the reaction coordinate 4+4+.=4+l心A+. =v©-∫dm=jydc %=m°+yE0r△%=%-m°=y,E Summation over all species n=n+va The mole fractionyiyv nn+Ve Mutireaction stoichiomerry the stoichiometric number of species i in reactionj
13.1 The Reaction Coordinate The general chemical reaction 1 1 2 2 3 3 4 4 A A A A + + = + + i stoichiometric coefficient (化学计量系数 ) Positive(+) for products negative (-) for reactants For example CH4 + H2O →CO + 3H2 CH H O H CO 4 2 2 ν = − = − = = 1 1 3 1 ν ν ν 1 2 4 3 1 2 3 4 N N dn dn dn dn dn d = = = = = = i i dn d = → i i dn d = the reaction coordinate 1 1 2 2 3 3 4 4 A A A A + + = + + i i dn d = → 0 0 i i n i i n dn d = 0 i i i n n = + or 0 i i i i = − = n n n Summation over all species n n = + The mole fraction yi 0 i i i i n n y n n + = = + Mutireaction stoichiomerry i i,j j j 1 d ( ) n ν dε = = the stoichiometric number of species i in reaction j
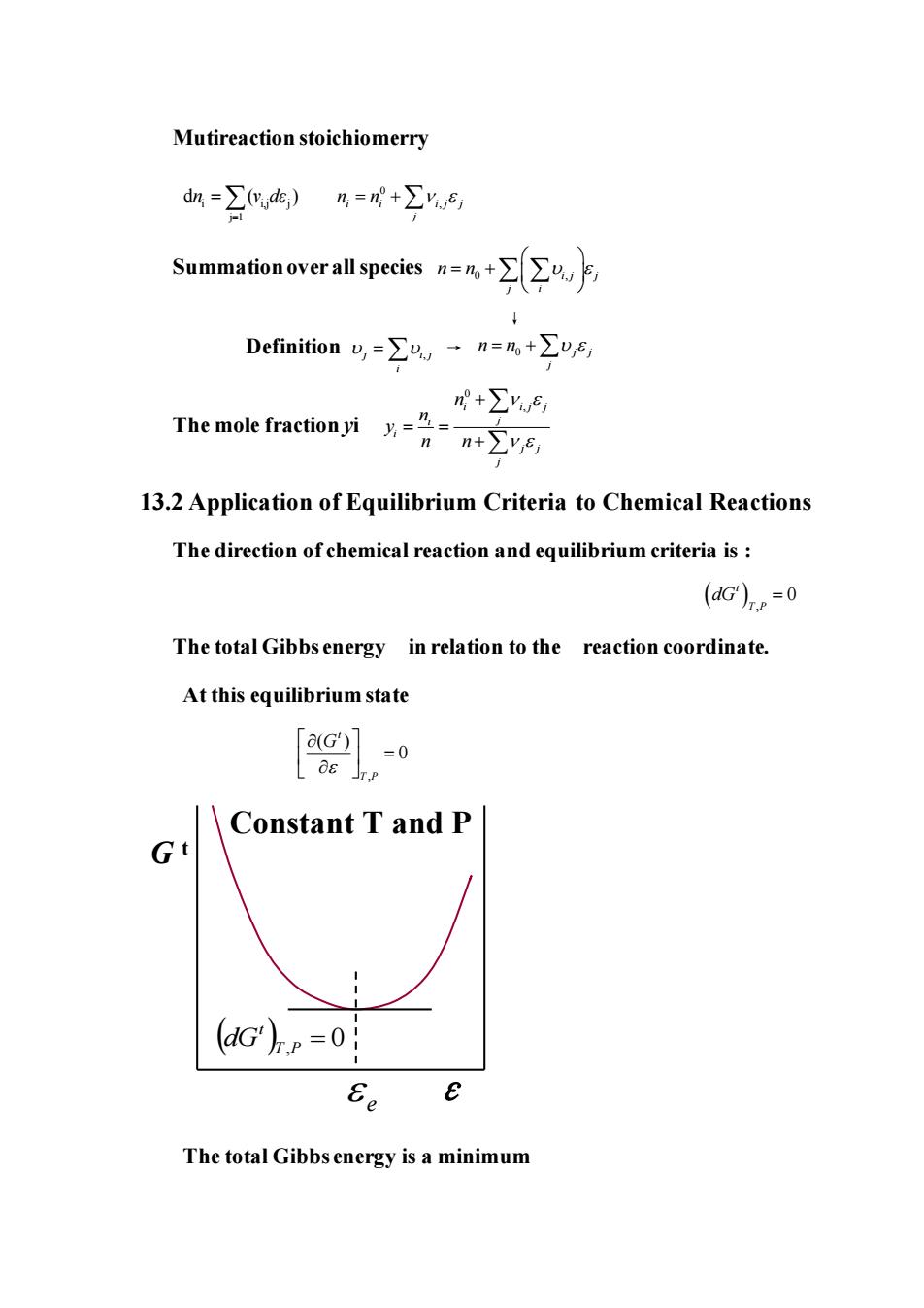
Mutireaction stoichiomerry d血=∑)%=+∑F Summationoverall species=%+∑∑F Definition=∑,·n=%+∑"ys n+∑y) The mole fractionyi nn+∑ys 13.2 Application of Equilibrium Criteria to Chemical Reactions The direction of chemical reaction and equilibrium criteria is (dG)=0 The total Gibbs energy in relation to the reaction coordinate. At this equilibrium state [G]-0 Constant T and P G (dG')p=0 Ee The total Gibbs energy is a minimum
Mutireaction stoichiomerry i i,j j j 1 d ( ) n ν dε = = 0 i i i j j , j n n = + Summation over all species 0 ,i j j j i n n = + ↓ Definition j i j , i = → The mole fraction yi 0 i i j j , j i i j j j n n y n n + = = + 13.2 Application of Equilibrium Criteria to Chemical Reactions The direction of chemical reaction and equilibrium criteria is : ( ) , 0 t T P dG = The total Gibbs energy in relation to the reaction coordinate. At this equilibrium state , ( ) 0 t T P G = ( )T,P = 0 t dG Constant T and P ε G t e The total Gibbs energy is a minimum j j n n j = + 0
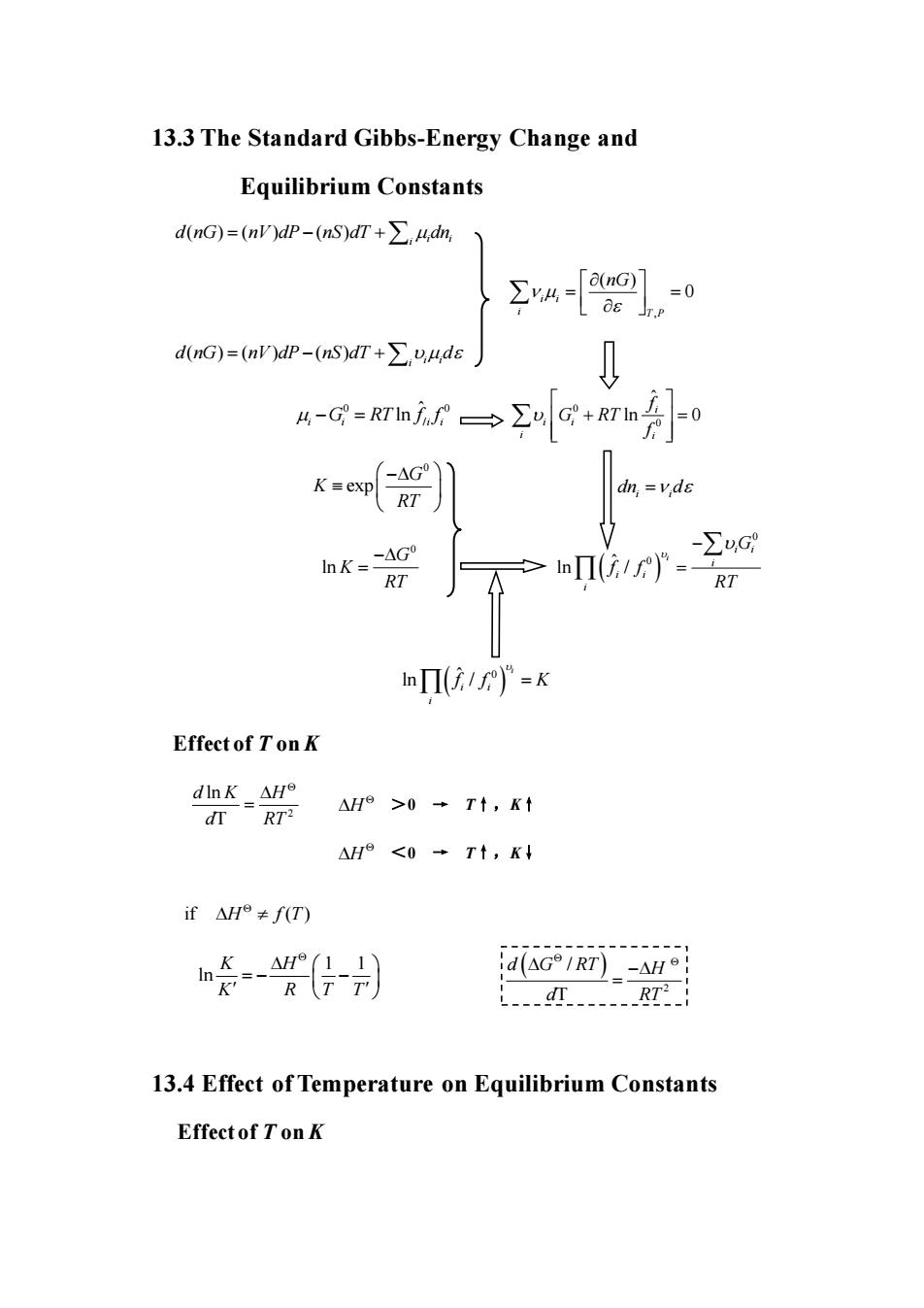
13.3 The Standard Gibbs-Energy Change and Equilibrium Constants dnG)=(nv)dP-(ns)dT+∑,4d d(nG)=(nV)dP-(nS)dT+>vuds 0 -AG° dn,=vds -△G -∑u,G RT oΠi1)° RT nΠi/e)=K Effect of Ton K △He>0→Tt,Kt △H<0+Tt,K if△H9≠fT) 炎}司 d(AGIRT-AH L.-.-RT2 13.4 Effect of Temperature on Equilibrium Constants Effect of Ton K
13.3 The Standard Gibbs-Energy Change and Equilibrium Constants ( ) ( ) ( ) i i i d nG nV dP nS dT dn = − + , ( ) 0 i i i T P nG = = ( ) ( ) ( ) i i i d nG nV dP nS dT d = − + 0 0 / ˆ ln i i i i − = G RT f f 0 0 ˆ ln 0 i i i i i f G RT f + = 0 exp G K RT − i i dn d = 0 ln G K RT − = ( ) 0 ˆ 0 ln / i i i i i i i G f f RT − = ( ) ˆ 0 ln / i i i i f f K = Effect of T on K 2 ln T d K H d RT = >0 → T↑,K↑ <0 → T↑,K↓ 13.4 Effect of Temperature on Equilibrium Constants Effect of T on K H H if ( ) H f T 1 1 ln K H K R T T = − − ( ) 2 / T d G RT H d RT − =
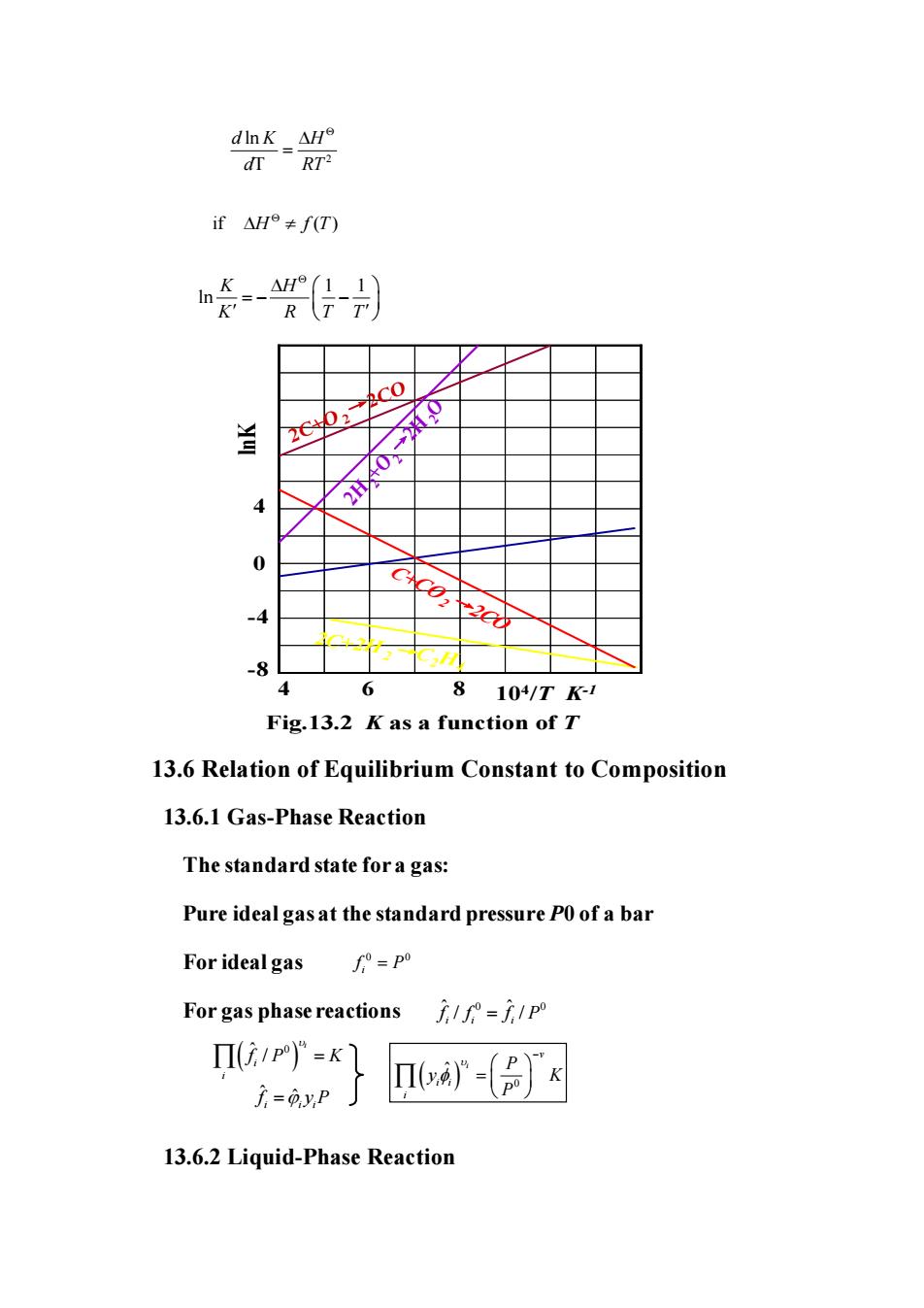
ifH≠fT) 火2c0/ y 2 -8 4 6 810/T1 Fig.13.2 K as a function of T 13.6 Relation of Equilibrium Constant to Composition 13.6.1 Gas-Phase Reaction The standard state for a gas: Pure ideal gas at the standard pressure P0 of a bar For idealgas/°-p For gas phase reactions=/p Π(i1P)°=K 广=0yP nIva- 13.6.2 Liquid-Phase Reaction
2 ln T d K H d RT = 2C+O2→2CO 2H2+O →2 2H2O C+CO2→2CO 2C+2H2→C2H4 lnK 104 /T K-1 0 -4 -8 4 4 6 8 Fig.13.2 K as a function of T 13.6 Relation of Equilibrium Constant to Composition 13.6.1 Gas-Phase Reaction The standard state for a gas: Pure ideal gas at the standard pressure P0 of a bar For ideal gas For gas phase reactions 13.6.2 Liquid-Phase Reaction if ( ) H f T 1 1 ln K H K R T T = − − 0 0 i f P = ˆ 0 0 ˆ / / i i i f f f P = ( ) ˆ 0 / i i i f P K = f ˆ i = ˆ i yiP ( ) 0 ˆ i v i i i P y K P − =
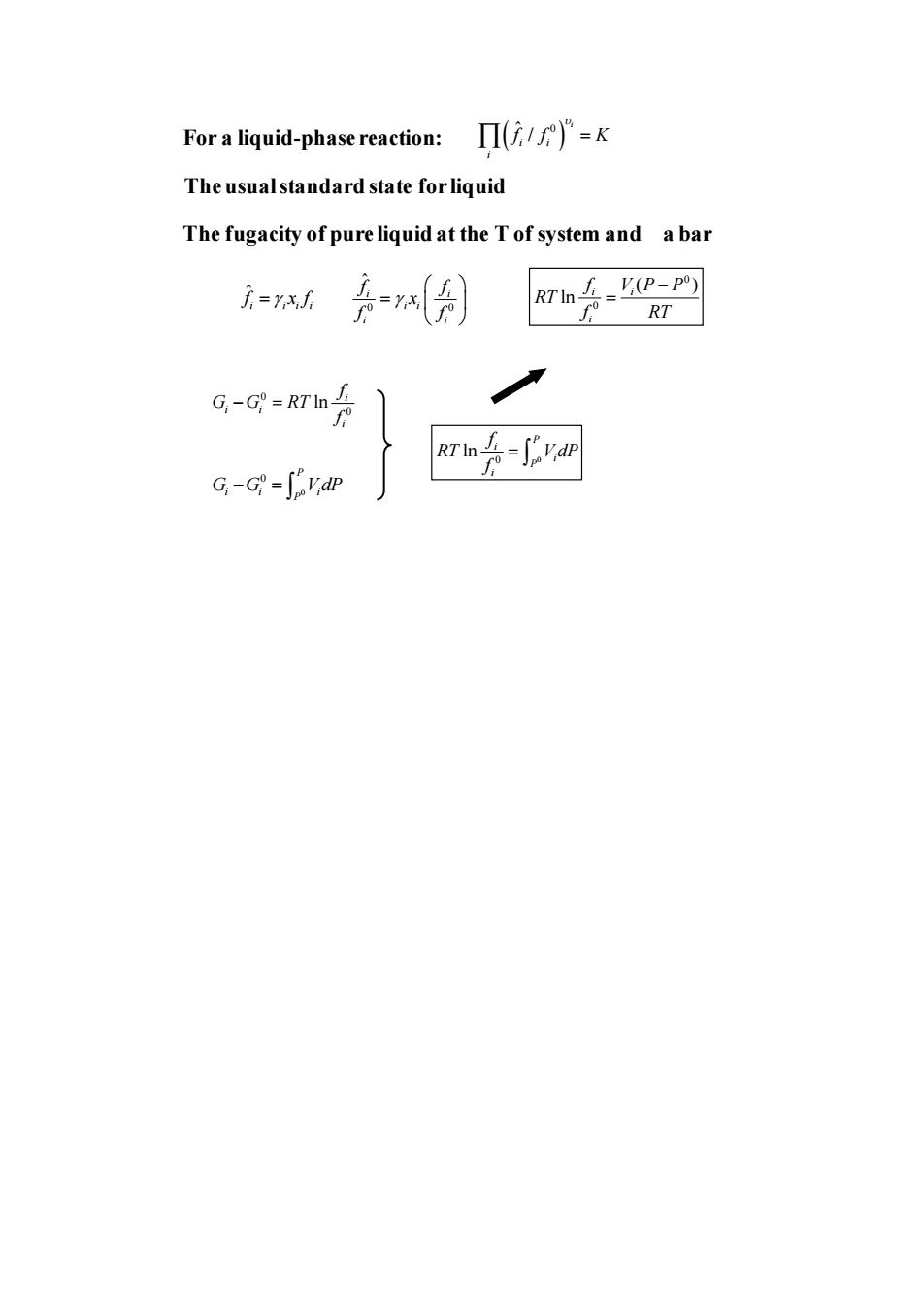
For a liquid-phase reaction::Πi/fW)P=K The usual standard state for liquid The fugacity of pure liquid at the T of system and a bar i-rxh 是月 RT G-G=会 Rrh片-可an G-G-S"vdP
For a liquid-phase reaction: The usual standard state for liquid The fugacity of pure liquid at the T of system and a bar ( ) ˆ 0 / i i i i f f K = ˆ i i i i f x f = 0 0 ˆ i i i i i i f f x f f = 0 0 ( ) ln i i i f V P P RT f RT − = 0 0 ln i i i i f G G RT f − = 0 0 P i i i P G G V dP − = 0 0 ln P i i P i f RT V dP f =