
Chapter 9 Refrigeration and Liquefaction Introduction 使物系的温度降到低于周围环境物质(如大气)的温度的过程称 为制冷过程。 冷冻温度高于100℃称普通冷冻(普冷),低于-100℃称为深度 冷冻(深冷) content 9.1 The Carnot Refrigerator 9.2 The Vapor-Compression Cycle 9.3 The Choice of Refrigerant 9.4 Absorption Refrigeration 9.5 The Heat Pump 9.6 Liquefaction Processes 9.1 The Carnot Refrigerator A refrigeration cycle is a reversed heat-engine cycle 音 3 condenser expander compressor 2 Evaporator
Chapter 9 Refrigeration and Liquefaction Introduction 使物系的温度降到低于周围环境物质(如大气)的温度的过程称 为制冷过程。 冷冻温度高于-100℃称普通冷冻(普冷),低于-100℃ 称为深度 冷冻(深冷) content 9.1 The Carnot Refrigerator 9.2 The Vapor-Compression Cycle 9.3 The Choice of Refrigerant 9.4 Absorption Refrigeration 9.5 The Heat Pump 9.6 Liquefaction Processes 9.1 The Carnot Refrigerator A refrigeration cycle is a reversed heat-engine cycle expander compressor 2 4 3 1 condenser Evaporator
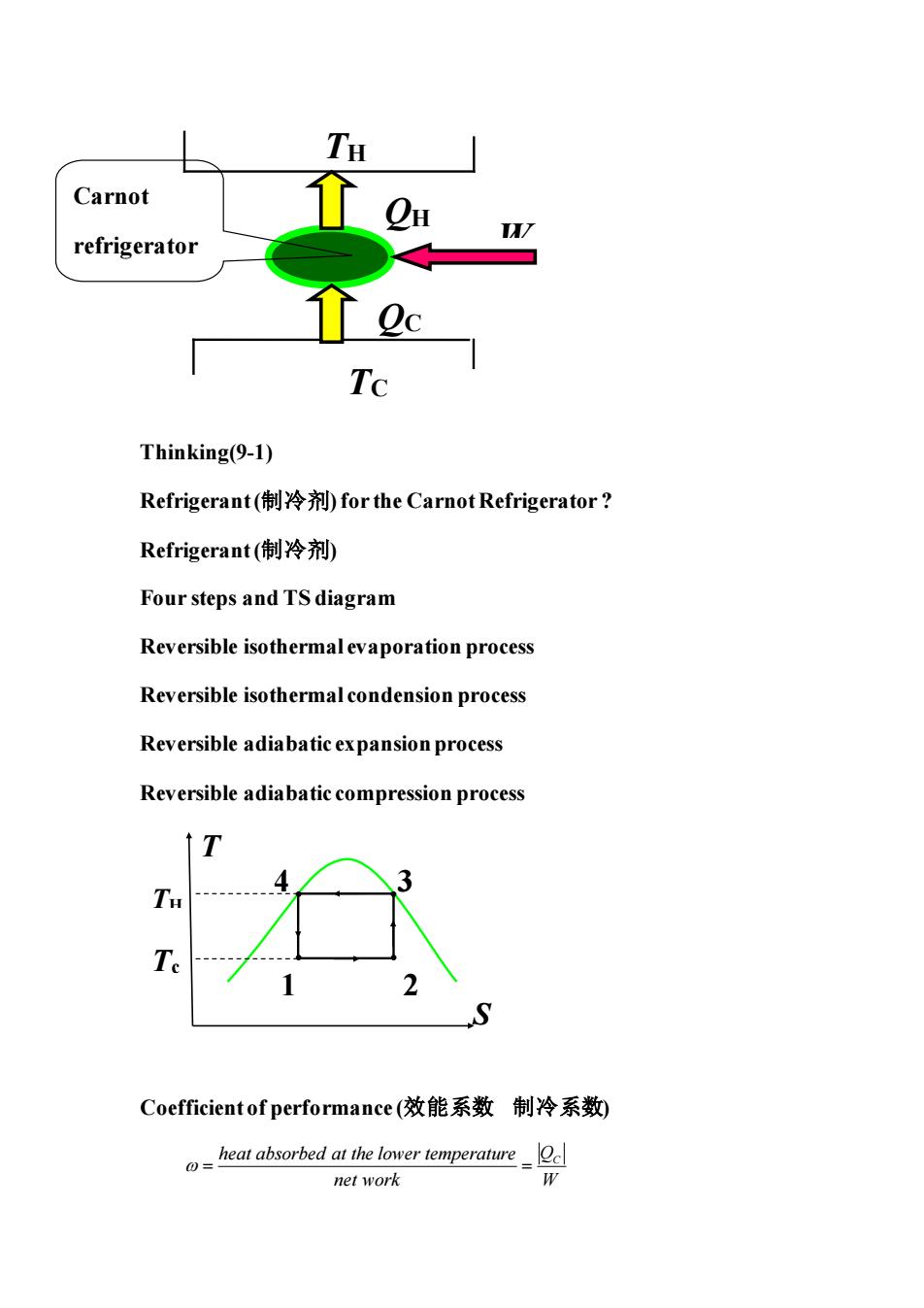
TH Carnot refrigerator Tc Thinking(9-1) Refrigerant(制冷剂for the Carnot Refrigerator? Refrigerant(制冷剂) Four steps and TS diagram Reversible isothermal evaporation process Reversible isothermal condension process Reversible adiabatic expansion process Reversible adiabatic compression process ↑T S Coefficient of performance(效能系数制冷系数) heat absorbed at the lower temperature net work
Thinking(9-1) Refrigerant (制冷剂) for the Carnot Refrigerator ? Refrigerant (制冷剂) Four steps and TS diagram Reversible isothermal evaporation process Reversible isothermal condension process Reversible adiabatic expansion process Reversible adiabatic compression process Coefficient of performance (效能系数 制冷系数) heat absorbed at the lower temperature QC net work W = = TH TC QH QC W 2 4 3 1 T S TH Tc Carnot refrigerator refrigera tor
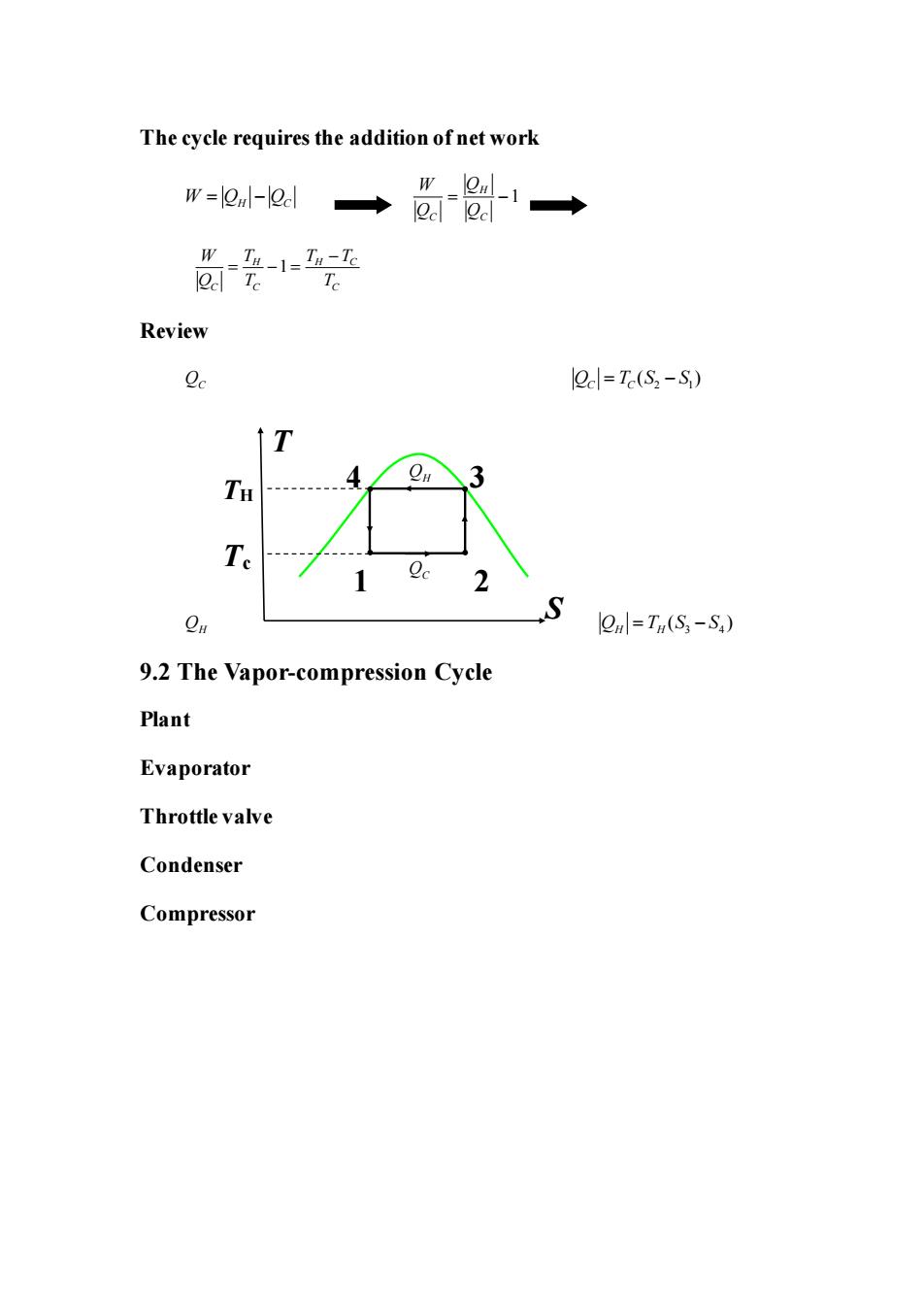
The cycle requires the addition of net work w=l№al-leal 岛受1经 T Review 2=T(S2-S) Te 1 0. S n=T(S;-S.) 9.2 The Vapor-compression Cycle Plant Evaporator Throttle valve Condenser Compressor
The cycle requires the addition of net work W Q Q = − H C 1 H C C W Q Q Q = − 1 H H C C C C W T T T Q T T − = − = Review QC 2 1 ( ) Q T S S C C = − QH 3 4 ( ) Q T S S H H = − 9.2 The Vapor-compression Cycle Plant Evaporator Throttle valve Condenser Compressor 2 4 3 1 T S TH Tc QC QH

condenser 3 Throttle valve compressor 2 evaporator Refrigerant (制冷剂 Four steps Isothermal evaporation process(1-2) Compression process(2-3) Cooled and condension process(3-4) Expansion process(4-1) 3 TS diagram Calculation: On the basis ofa unit mass of fluid
Refrigerant (制冷剂) Four steps Isothermal evaporation process (1→2) Compression process (2→3) Cooled and condension process (3→4 ) Expansion process (4→1) TS diagram Calculation: On the basis of a unit mass of fluid condenser 4 1 2 3 compressor Throttle valve evaporator S T 4 1 2 3

n=H3-H Qc=H,-H 0=4-月 H3-H2 Ws Hs-H2 The rate of circulation of refrigerant HH Ws=△H 4 0 c=△H TS diagram and pH diagram
Q H H H = − 3 4 Q H H C = − 2 1 2 1 3 2 H H H H − = − W H H S = − 3 2 The rate of circulation of refrigerant 2 1 QC m H H = − TS diagram and pH diagram S T 4 1 2 3 QH= △H QC=△H WS =△H
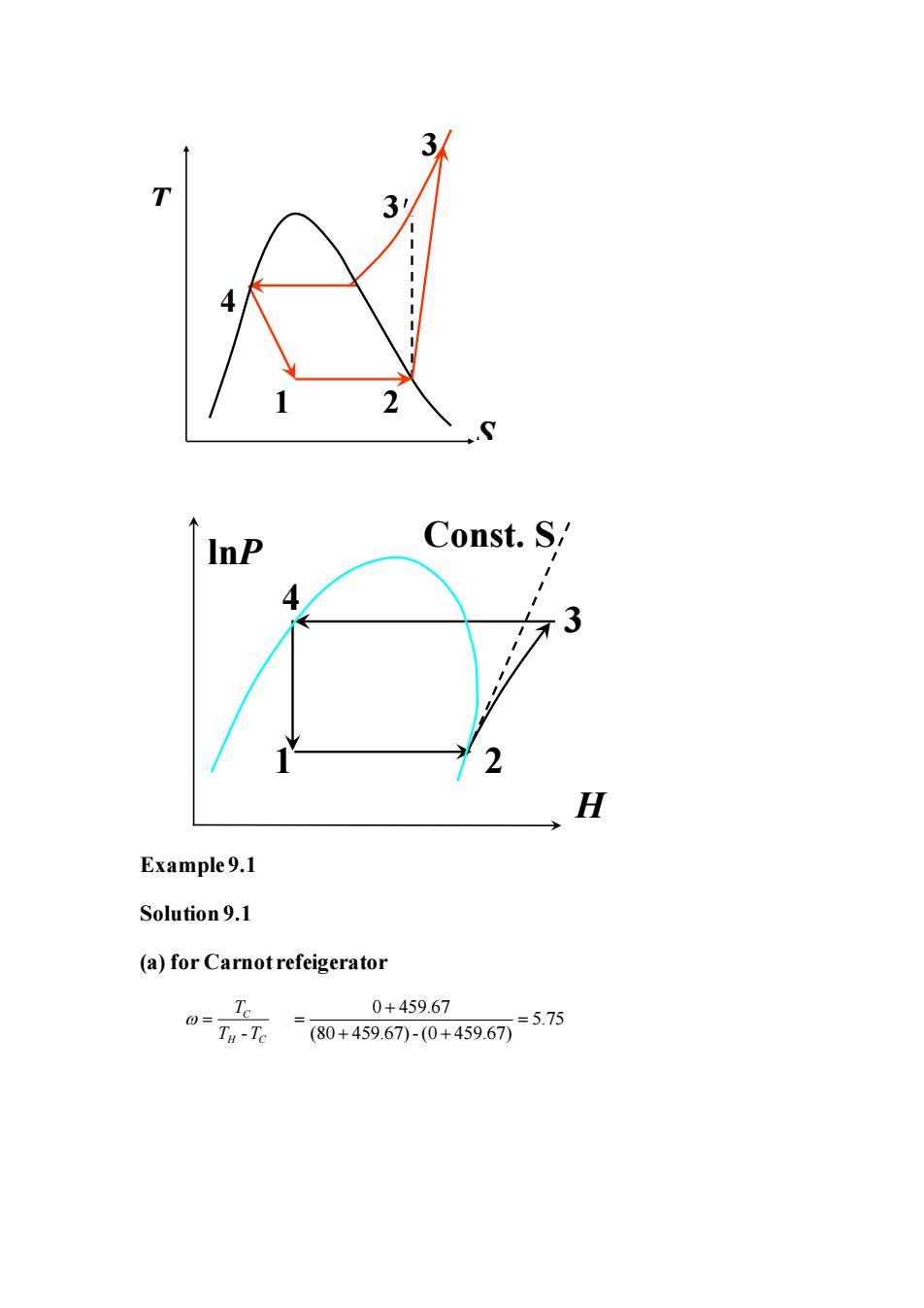
InP Const.S/ 4 2 H Example9.1 Solution9.1 (a)for Carnotrefeigerator 0+459.67 07n元=80+459.671-0+459675.75
Example 9.1 Solution 9.1 (a) for Carnot refeigerator - C H C T T T = 0 459.67 5.75 (80 459.67) - (0 459.67) + = = + + S T 4 1 2 3 3′ lnP H 2 3 4 1 Const. S
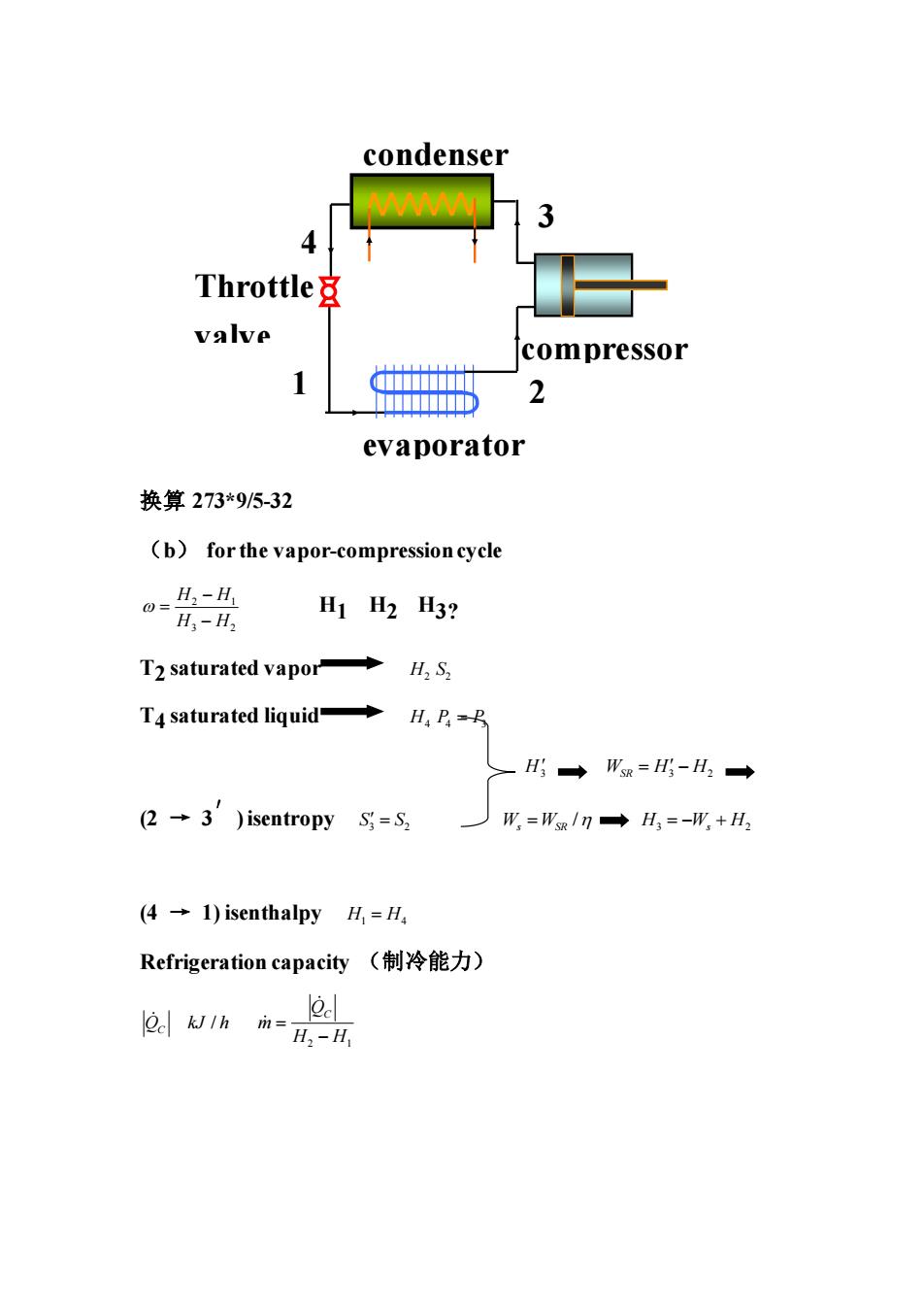
condenser 4 Throttle8 valve compressor 1 t 2 evaporator 换算273*9/5-32 (b)for the vapor-compression cycle H3-H2 H1 H2 H3? T2 saturated vapor S. T4 saturated liquid 用→W=-H,→ 亿→3'))isentropy S=S, W=W/n→H=-用+H2 (4→1)isenthalpy,=H Refrigeration capacity(制冷能力) Qe h
换算 273*9/5-32 (b) for the vapor-compression cycle 2 1 3 2 H H H H − = − H1 H2 H3? T2 saturated vapor H S2 2 T4 saturated liquid H P P 4 4 3 = H3 W H H SR 3 2 = − (2 → 3 ′ ) isentropy 3 2 S S = / W W s SR = H W H 3 2 = − + s (4 → 1) isenthalpy H H 1 4 = Refrigeration capacity (制冷能力) / Q kJ h C 2 1 QC m H H = − condenser 4 1 2 3 compressor Throttle valve evaporator

Thinking(9-1) 1.Coefficient of performance for Carnot refrigerator is the function of temperature only 01n-1 2.在相同温度区间工作的制冷循环,以逆卡诺循环的制冷系数为最 大。 3.制冷循环中,高温下放热量大于低温下吸热量。 4+4 -+g4=Q+W0=Q+用.-l+w=0g.+W= 2 Thinking(9-1) 4.The definition of coefficient of performance is that the heat absorbed at a lower temperature is divided by work that compressor needs heat absorbed at the lower temperatre net work
Thinking(9-1) 1. Coefficient of performance for Carnot refrigerator is the function of temperature only C H C T T T = − 2. 在相同温度区间工作的制冷循环,以逆卡诺循环的制冷系数为最 大。 3. 制冷循环中,高温下放热量大于低温下吸热量。 2 2 s u H g z Q W + + = + 0 = + Q Ws 0 Q Q W C − + = H s C Q W Q + =s H Thinking(9-1) 4. The definition of coefficient of performance is that the heat absorbed at a lower temperature is divided by work that compressor needs heat absorbed at the lower temperature C net wor Q k W = = S T 4 1 2 3 3 ′

9.3 The Choice of Refrigerant 9.3.1 Theimportant characteristics of Refrigerant Toxicity flammability cost corrosion property vapor pressure in related to temperature 大气压力下沸点低,不仅可获得较低的制冷温度,且在一定制冷温度 下,蒸汽压力高于大气压,防止空气进入 常温下冷凝压力应尽量低,以降低冷凝器的耐压与密封要求 汽化潜热大,减少制冷剂循环量,缩小压缩机尺寸;具有较高临界温 度与较低凝固温度,使大部分放热过程在两相区进行:具有化学稳定 性,不易燃,不分解,无腐蚀。 9.3.2 Refrigerants (1)Conventional refrigerants: NH3 CH3CI C02 C3H8 (2)Chloro Fluoro Carbons CFC's CFCl3(R-11)CF2Cl2(R-12) (3)Hydro Chloro Fluoro Carbons HCFC's: CHCIF(R-22) CHCI2CF3(R-123) (4)(Hydro)Fluoro Carbons HFC's
9.3 The Choice of Refrigerant 9.3.1 Theimportant characteristics of Refrigerant Toxicity flammability cost corrosion property vapor pressure in related to temperature 大气压力下沸点低,不仅可获得较低的制冷温度,且在一定制冷温度 下,蒸汽压力高于大气压,防止空气进入; 常温下冷凝压力应尽量低,以降低冷凝器的耐压与密封要求 汽化潜热大,减少制冷剂循环量,缩小压缩机尺寸;具有较高临界温 度与较低凝固温度,使大部分放热过程在两相区进行;具有化学稳定 性,不易燃,不分解,无腐蚀。 9.3.2 Refrigerants (1) Conventional refrigerants: NH3 CH3Cl CO2 C3H8 (2) Chloro Fluoro Carbons CFC’s CFCl3 (R-11) CF2Cl2 (R-12) (3) Hydro Chloro Fluoro Carbons HCFC’s : CHCl2F (R-22) CHCl2CF3 (R-123) (4) (Hydro) Fluoro Carbons HFC’s

CF4(R-14)CHF3R-23) CF3F3R-116) CHF2CHF2(R-134a) 大气: 02 20 0°+02 O3 ozone CFC's: CFCI3 +UV light CCIF+CI* C+03→02+C10 C10°+0°→Cr+02 9.4 The More Refrigeration Cycle Thinking(9-2) Why is the more refrigeration cycle needed? 3 p
CF4 (R-14) CHF3 (R-23) CF3F3 (R-116) CHF2CHF2 (R-134a) 大气: O2 2 O• O• + O2 O3 ozone CFC’s: CFCl3 + UV light → CCl2F• + Cl• Cl• + O3 → O2 + ClO• ClO• + O•→ Cl• + O2 9.4 The More Refrigeration Cycle Thinking(9-2) Why is the more refrigeration cycle needed? S T 4 1 2 3 3 H H ’ p T c c p T