
Chapter 3 Volumetric Properties of Pure Fluids
Chapter 3 Chapter 3 Volumetric Properties of Volumetric Properties of Pure Fluids Pure Fluids

3.1 PIT behavior of pure substances 3.2 Virial Equations of state 3.3 the ideal gas 3.4 Application of the Virial Equations 3.5 Cubic equation of state 3.6 Generalized Correlations for Gases
3.1 PVT behavior of pure substances 3.2 Virial Equations of state Virial Equations of state 3.3 the ideal gas 3.3 the ideal gas 3.4 Application of the Virial Equations 3.4 Application of the Virial Equations 3.5 Cubic equation of state 3.5 3.6 Generalized Correlations for Gases Generalized Correlations for Gases

Why to study this chapter In industrial processes,we need: Thermodynamic properties, Such as internal energy,enthalpy,entropy,gibbs energy,etc How can we obtain these informations? PVT Two routes: ※measuring directly Xcalculating with other parameters which can be measured directly
Why to study this chapter ? In industrial processes, we need: Thermodynamic properties, Such as internal energy, enthalpy, entropy, gibbs energy, etc. How can we obtain these informations? Two routes : ※measuring directly ※calculating with other parameters which can be measured directly P V T
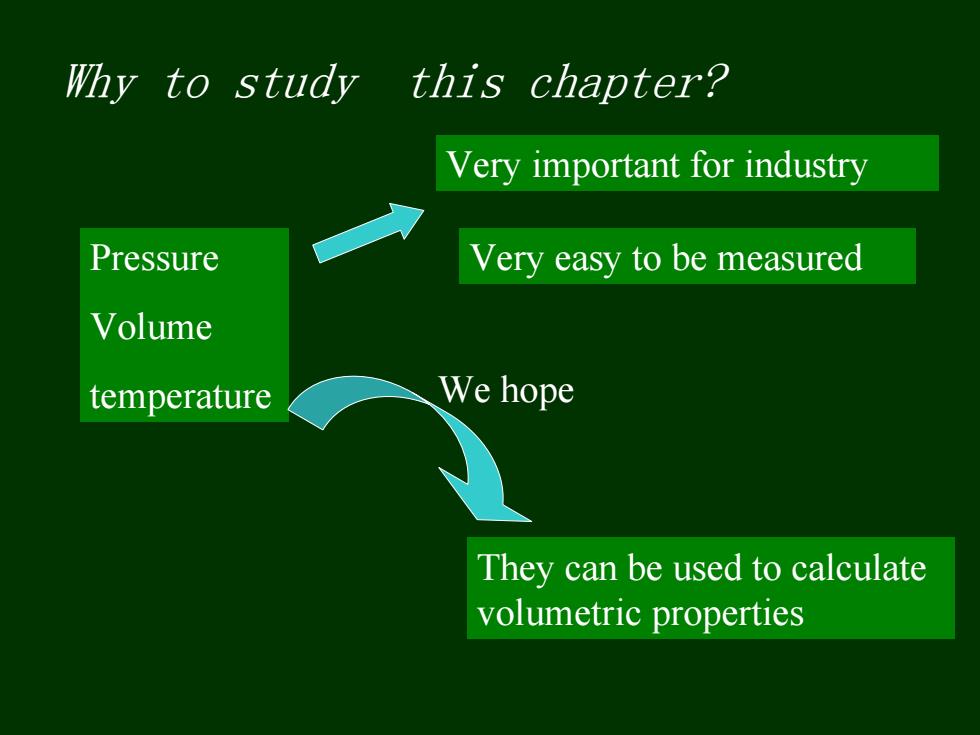
Why to study this chapter? Very important for industry Pressure Very easy to be measured Volume temperature We hope They can be used to calculate volumetric properties
Pressure Volume temperature They can be used to calculate volumetric properties Very easy to be measured Very important for industry We hope Why to study this chapter?
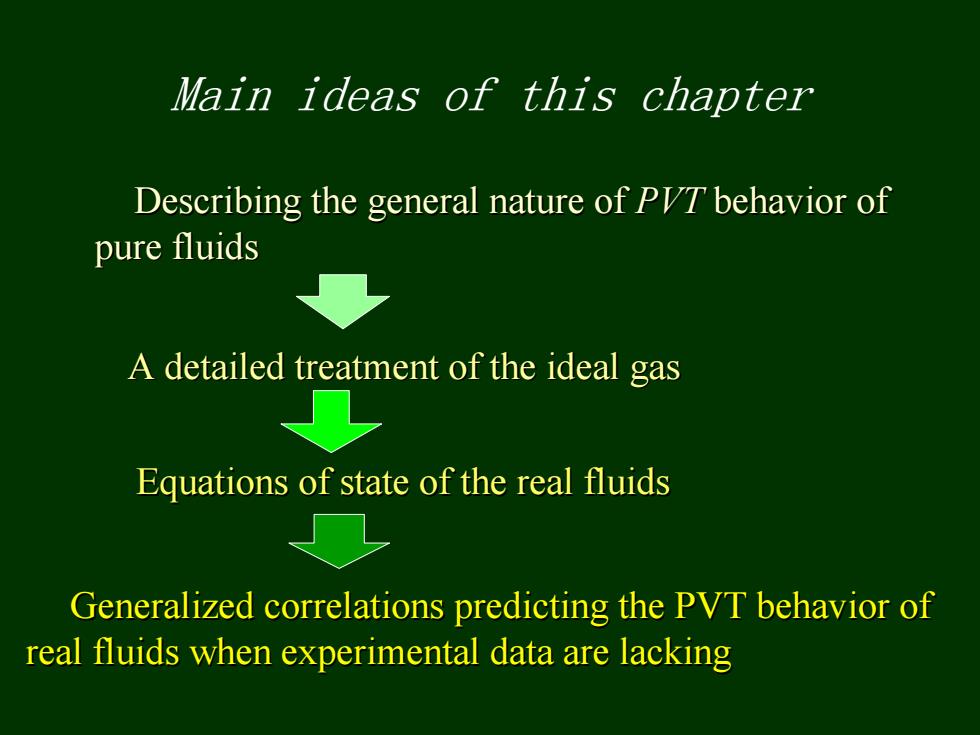
Main ideas of this chapter Describing the general nature of PIT behavior of pure fluids A detailed treatment of the ideal gas Equations of state of the real fluids Generalized correlations predicting the PVT behavior of real fluids when experimental data are lacking
Main ideas of this chapter Describing the general nature of Describing the general nature of PVT behavior of behavior of pure fluids pure fluids A detailed treatment of the ideal gas A detailed treatment of the ideal gas Generalized correlations predicting the PVT behavior of Generalized correlations predicting the PVT behavior of real fluids when experimental data are lacking real fluids when experimental data are lacking Equations of state of the real fluids Equations of state of the real fluids

3.1 PIT behavior of pure substances By measuring the vapor pressure,volume and temperature of a pure substances when different phases achieve equilibrium,we can draw the curve of P-V-T V=constant PT diagram T=constant PV diagram P=constant TV diagram PVT PTV diagram
3.1 PVT behavior of pure substances By measuring the vapor pressure, volume and By measuring the vapor pressure, volume and temperature of a pure substances when different temperature of a pure substances when different phases achieve equilibrium, we can draw the curve of phases achieve equilibrium, we can draw the curve of P-V-T V=constant PT diagram T=constant PV diagram P=constant TV diagram P V T PTV diagram
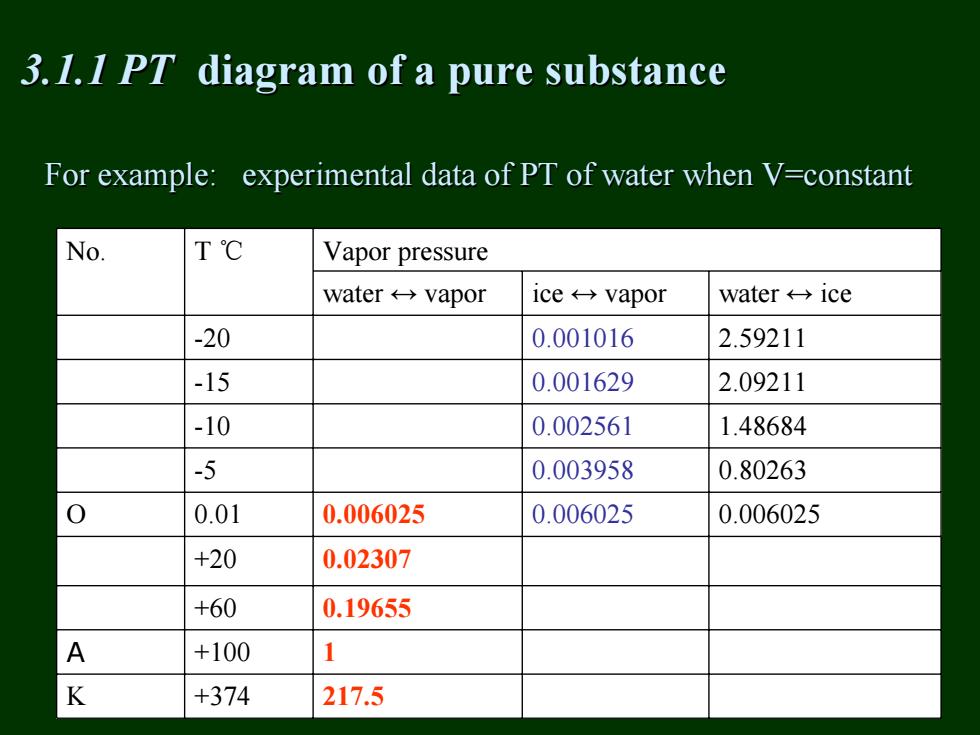
3.1.I PT diagram of a pure substance For example:experimental data of PT of water when V=constant No. T℃ Vapor pressure water←→vapor ice←→vapor water←→ice -20 0.001016 2.59211 -15 0.001629 2.09211 -10 0.002561 1.48684 -5 0.003958 0.80263 0.01 0.006025 0.006025 0.006025 +20 0.02307 +60 0.19655 A +100 1 K +374 217.5
For example: experimental data of PT of water when V=constant For example: experimental data of PT of water when V=constant No. T ℃ Vapor pressure water ↔ vapor ice ↔ vapor water ↔ ice -20 0.001016 2.59211 -15 0.001629 2.09211 -10 0.002561 1.48684 -5 0.003958 0.80263 O 0.01 0.006025 0.006025 0.006025 +20 0.02307 +60 0.19655 A +100 1 K +374 217.5 3.1.1 PT 3.1.1 PT diagram diagram of a pure substance of a pure substance
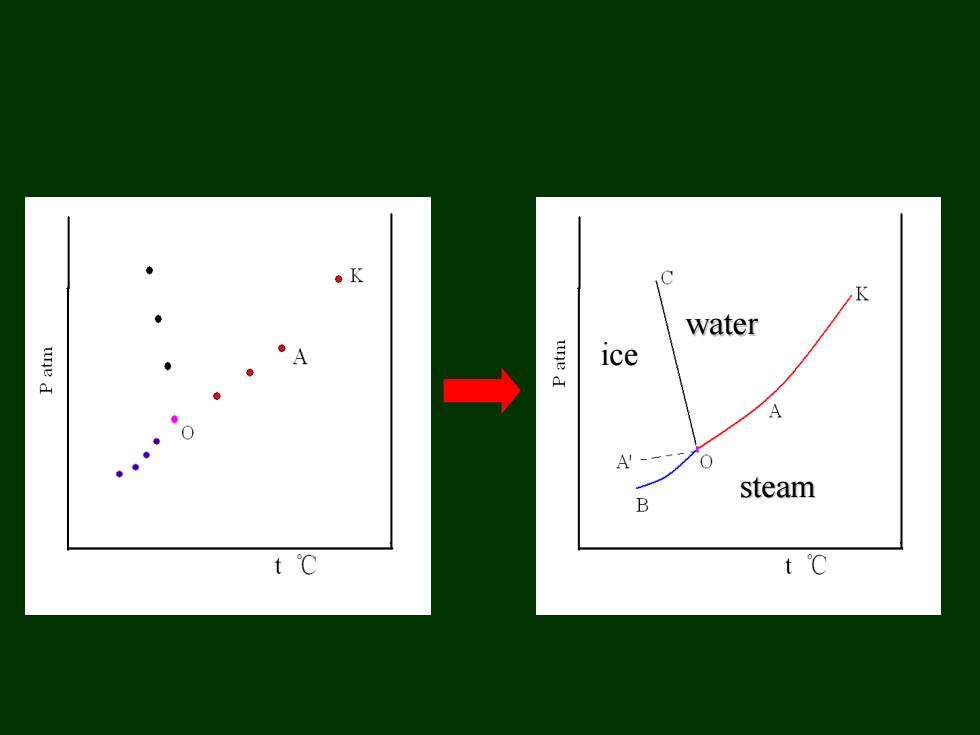
。K C K water une d A ice → 。 A'- 0 steam B t℃ t℃
water steam ice
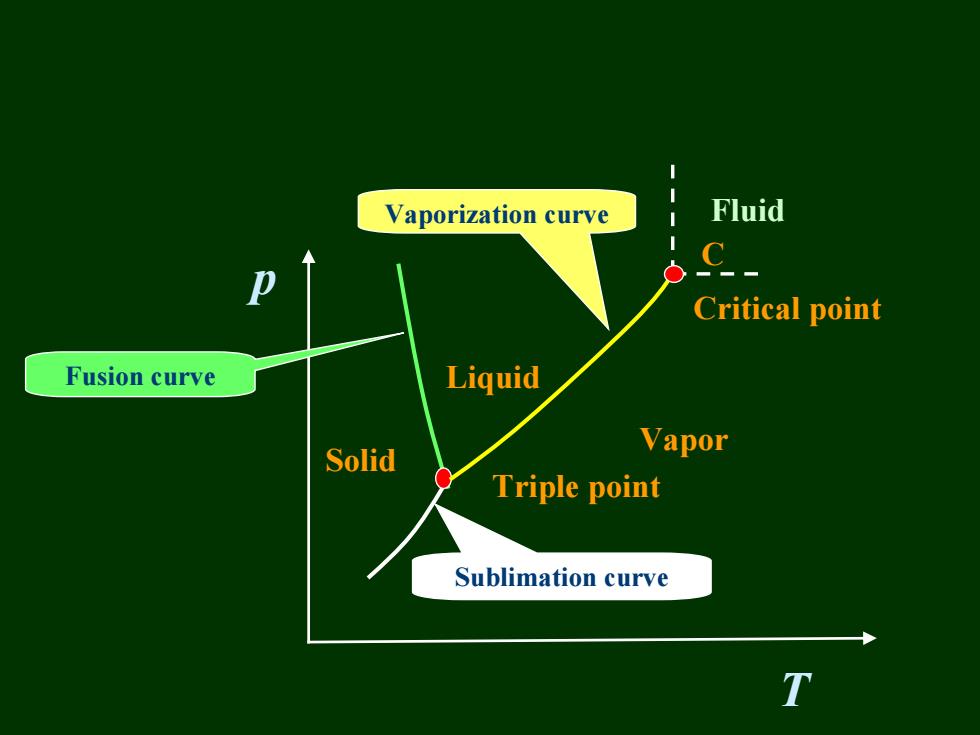
Vaporization curve Fluid Critical point Fusion curve Liquid Solid Vapor Triple point Sublimation curve
p T Liquid Vapor Solid Triple point Critical point Sublimation curve Fusion curve Vaporization curve Fluid C
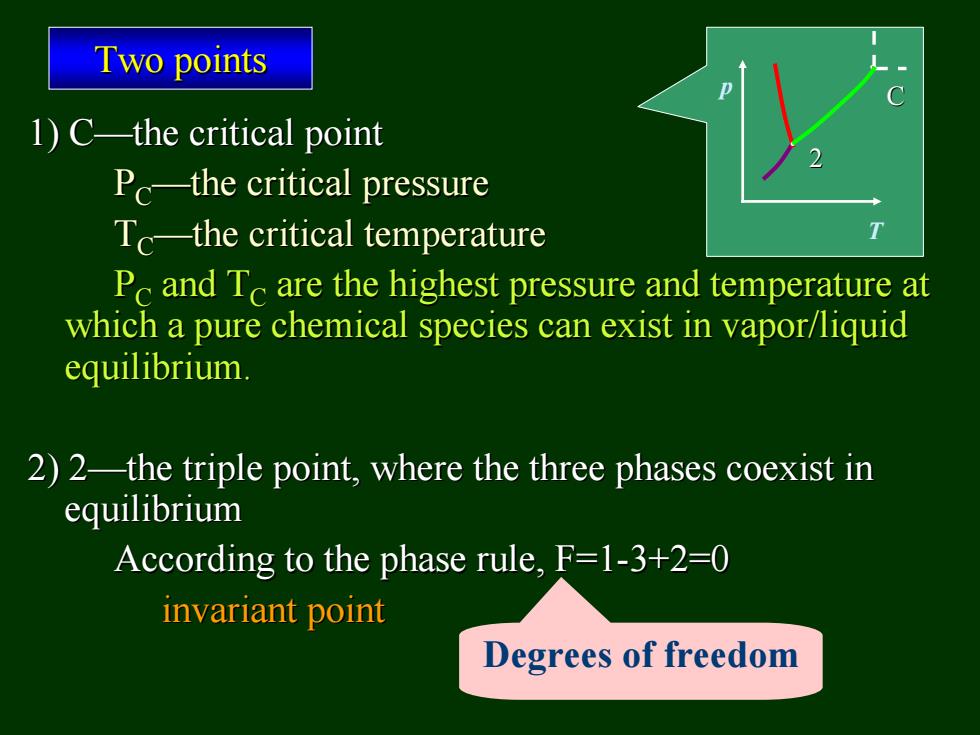
Two points 1)C-the critical point Pc-the critical pressure Tc-the critical temperature Pc and Tc are the highest pressure and temperature at which a pure chemical species can exist in vapor/liquid equilibrium. 2)2-the triple point,where the three phases coexist in equilibrium According to the phase rule,F=1-3+2=0 invariant point Degrees of freedom
1) C—the critical point the critical point PC—the critical pressure the critical pressure TC—the critical temperature the critical temperature PC and TC are the highest pressure and temperature at are the highest pressure and temperature at which a pure chemical species which a pure chemical species can exist in vapor/liquid can exist in vapor/liquid equilibrium. equilibrium. 2) 2—the triple point, where the three phases coexist in the triple point, where the three phases coexist in equilibrium equilibrium According to the phase rule, F=1 According to the phase rule, F=1-3+2=0 3+2=0 invariant point invariant point Two points Two points p T 2 C Degrees of freedom