
Tutorial 5:General Random Variables 1 MENG Yitong ytmeng@cse.cuhk.edu.hk 27,February,2016 1
Tutorial 5: General Random Variables 1 MENG Yitong ytmeng@cse.cuhk.edu.hk 27, February, 2016 1

Outline Continuous random variables,PDFs,CDFs Uniform distributions Exponential distributions Normal distributions Laplace distributions
Outline • Continuous random variables, PDFs, CDFs • Uniform distributions • Exponential distributions • Normal distributions • Laplace distributions 2
Continuous r.v.and PDFs A random variable X is called continuous if there is a functionfx>0, called the probability density function of X,or PDF,s.t. P(X E B)=fx(x)dx for every subset B≤R. In particular,when B [a,b], P(a≤X≤b)=fx(x)dx is the area under the graph of PDF
Continuous r.v. and PDFs • A random variable 𝑋 is called continuous if there is a function 𝑓𝑋 ≥ 0, called the probability density function of 𝑋, or PDF, s.t. 𝑃(𝑋 ∈ 𝐵) = න 𝐵 𝑓𝑋 𝑥 𝑑𝑥 for every subset 𝐵 ⊆ ℝ. • In particular, when 𝐵 = [𝑎, 𝑏], 𝑃(𝑎 ≤ 𝑋 ≤ 𝑏) = න 𝑎 𝑏 𝑓𝑋 𝑥 𝑑𝑥 is the area under the graph of PDF. 3
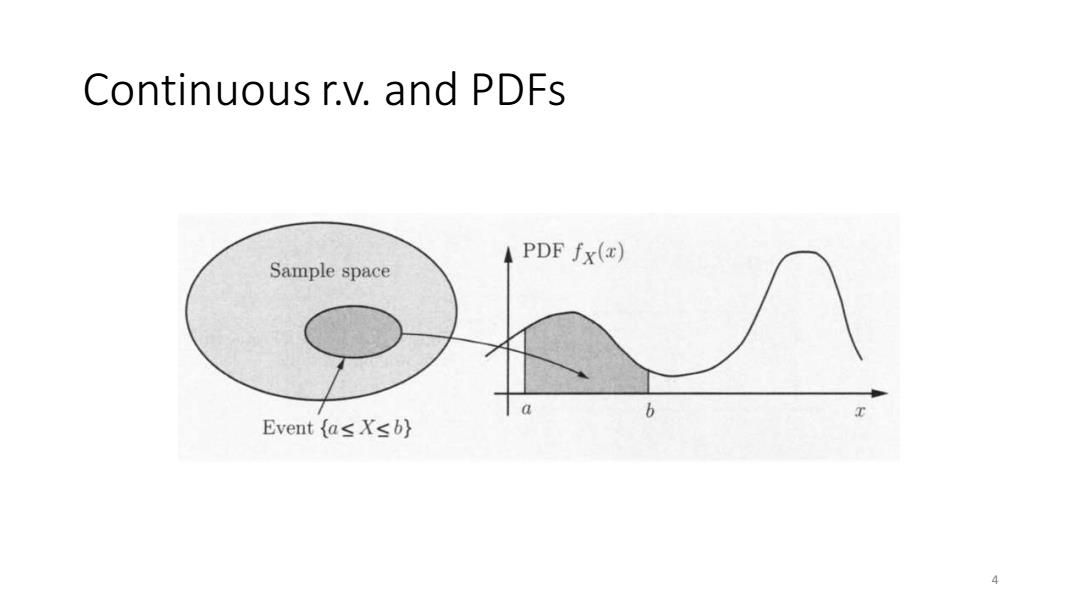
Continuous r.v.and PDFs PDF fx(t) Sample space b Event fas Xsb} 4
Continuous r.v. and PDFs 4
Cumulative Distribution Function The cumulative distribution function,or CDF,of a random variablex is Fx(x)=P(X≤x) ∑ksx Px(x),( discrete fx(x)dx,continuous The CDF Fx(x)"accumulates"probability "up to"the value x
Cumulative Distribution Function • The cumulative distribution function, or CDF, of a random variable 𝑋 is 𝐹𝑋 𝑥 = 𝑃 𝑋 ≤ 𝑥 = ൝ σ𝑘≤𝑥 𝑝𝑋 𝑥 , discrete ∞− 𝑥 𝑓𝑋 𝑥 𝑑𝑥 , continuous • The CDF 𝐹𝑋 𝑥 “accumulates” probability “up to” the value 𝑥
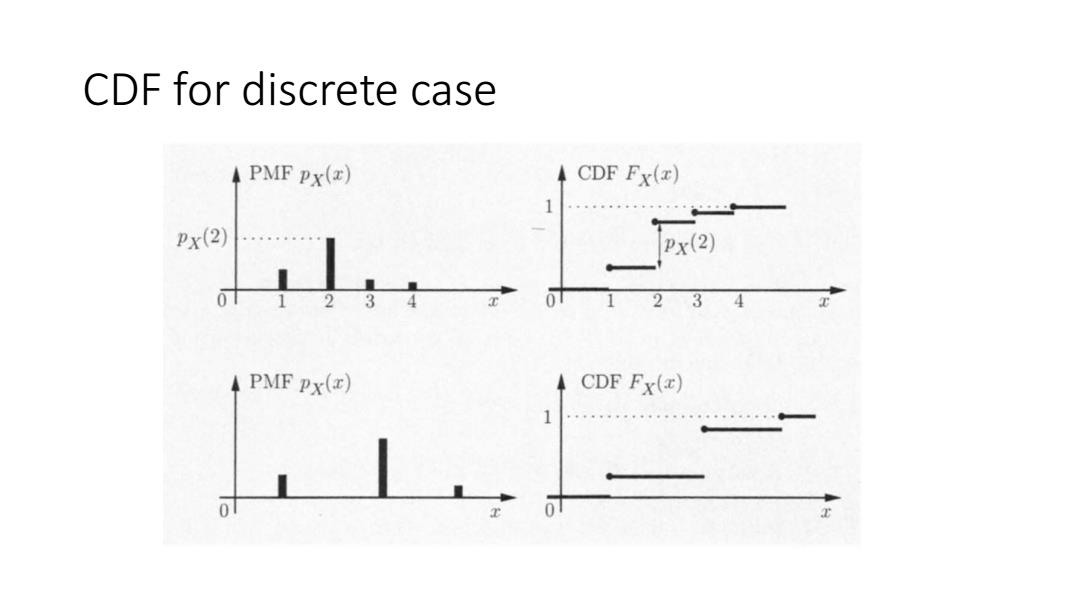
CDF for discrete case ◆PMF Px(x) CDF Fx(x) px(2) Px(2) A PMF Px() CDF Fx() 1
CDF for discrete case
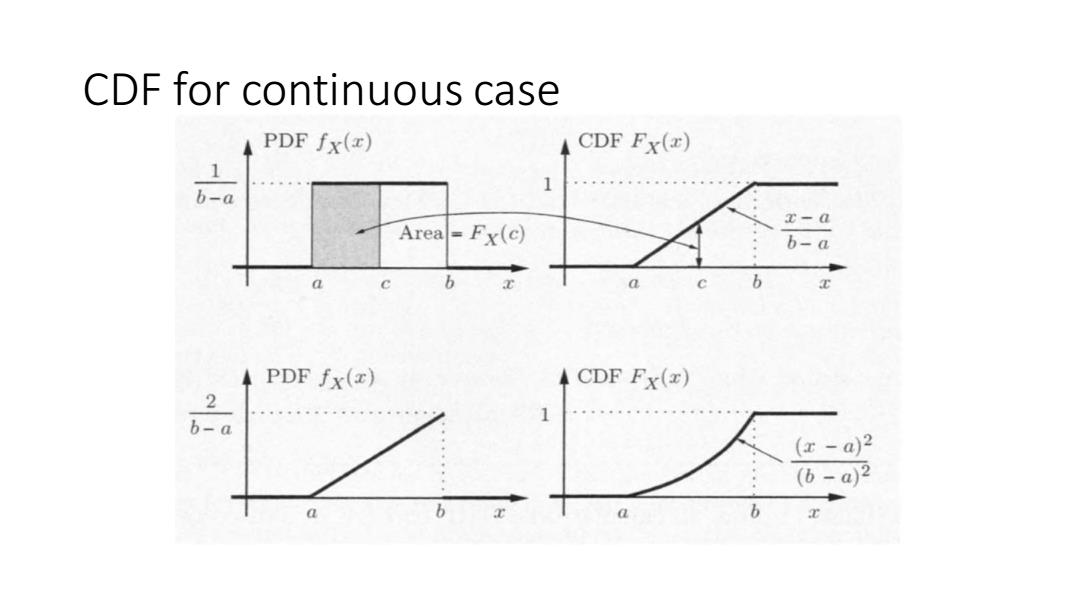
CDF for continuous case PDF fx() CDF Fx(x) 1 b-a x-a Area -Fx(c) b-a a b a c b PDF fx(x) CDF Fx(z) 2 1 b-a (x-a)2 (6-a)2 b a b x
CDF for continuous case

Uniform distributions ·Its PDF has the form (1 fx(x)=3b-a' ifa≤x≤b (0, otherwise PDF fx() 1 b-a a b
Uniform distributions • Its PDF has the form 𝑓𝑋 𝑥 = ቐ 1 𝑏 − 𝑎 , if 𝑎 ≤ 𝑥 ≤ 𝑏 0, otherwise 8
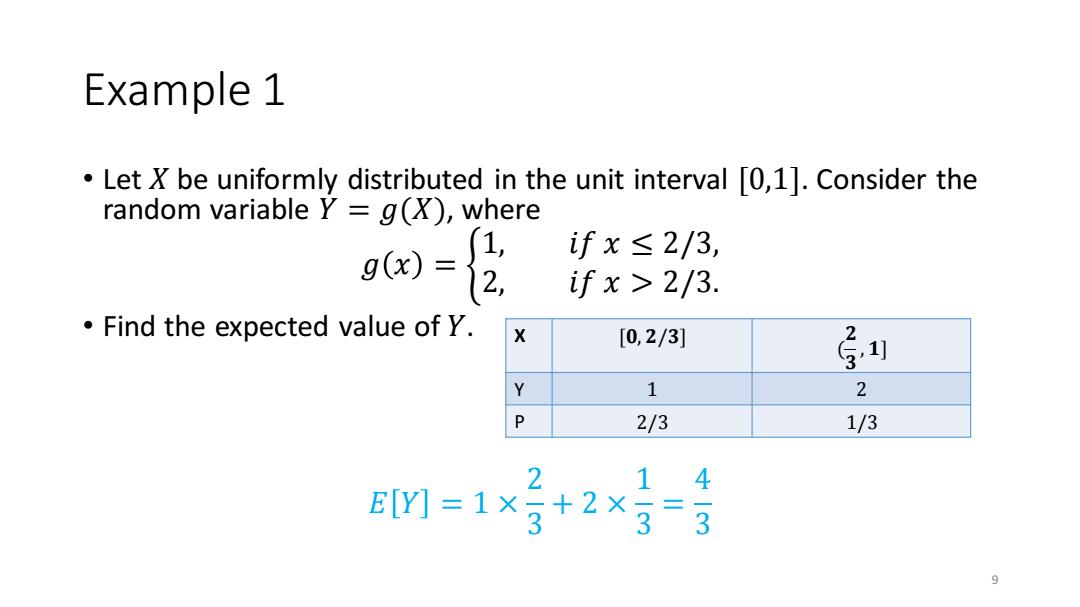
Example 1 Let X be uniformly distributed in the unit interval 0,1.Consider the random variable Y=g(),where g)= ifx≤2/3, 2 ifx>2/3. Find the expected value of Y. X [0,2/3] Y 1 2 P 2/3 1/3 2 14 EY]=1× +2×3=3 9
Example 1 • Let 𝑋 be uniformly distributed in the unit interval [0,1]. Consider the random variable 𝑌 = 𝑔(𝑋), where 𝑔 𝑥 = ቊ 1, 𝑖𝑓 𝑥 ≤ 2/3, 2, 𝑖𝑓 𝑥 > 2/3. • Find the expected value of 𝑌. 𝐸 𝑌 = 1 × 2 3 + 2 × 1 3 = 4 3 9 X [𝟎, 𝟐/𝟑] ( 𝟐 𝟑 , 𝟏] Y 1 2 P 2/3 1/3

Exponential distributions An exponential random variable has PDF fx≥0 otherwise 1.6 1.4 —入=0.5 ,Mean:元mode:0,variance::是 1 1.2 一入=1 λ=1.5 1.0 ·Its CDF is o.8 0.6 B22e=(-e6 o. 2 =1-e-8 10
Exponential distributions • An exponential random variable has PDF 𝑓𝑋 𝑥 = ቊ 𝜆𝑒 −𝜆𝑥 , if 𝑥 ≥ 0 0, otherwise • Mean: 1 𝜆 , mode:0, variance: 1 𝜆 2 • Its CDF is 𝐹𝑋 𝑥 = න 0 𝑥 𝜆𝑒 −𝜆𝑡𝑑𝑡 = −𝑒 −𝜆𝑡 ቤ 𝑥 0 = 1 − 𝑒 −𝜆𝑥 10