
Tutorial 9:Further Topics on Random variables 2 Weiwen LIU wwliu@cuhk.edu.hk March 27,2017 1
Tutorial 9: Further Topics on Random Variables 2 Weiwen LIU wwliu@cuhk.edu.hk March 27, 2017 1

Covariance and Correlation Covariance and correlation describe the degree to which two random variables or sets of random variables tend to deviate from their expected values in similar ways. Independent random variables are uncorrelated,but NOT vice versa
Covariance and Correlation • Covariance and correlation describe the degree to which two random variables or sets of random variables tend to deviate from their expected values in similar ways. • Independent random variables are uncorrelated, but NOT vice versa. 2

Example 1 Let X and Y be continuous random variables with joint pdf fxx(xy) 3x,0≤y≤x≤1, 0,otherwise. ·Compute cov(X,Y); Are X and Y independent?
Example 1 • Let X and Y be continuous random variables with joint pdf 𝑓𝑋,𝑌 𝑥, 𝑦 = ቊ 3𝑥, 0 ≤ 𝑦 ≤ 𝑥 ≤ 1, 0, 𝑜𝑡ℎ𝑒𝑟𝑤𝑖𝑠𝑒. • Compute cov 𝑋,𝑌 ; • Are 𝑋 and 𝑌 independent? 3

Example 1 The marginal pdfs and expectations of X and Y are fx(X)=3xdy=3x2,0≤x≤1, EW=x3x2=居x-子 )=3xdx=)0sys1 m=a-9w=告--君 m=w3d-,=品
Example 1 • The marginal pdfs and expectations of X and Y are 𝑓𝑋 𝑋 = න0𝑥 3𝑥𝑑𝑦 = 3 𝑥 2 , 0 ≤ 𝑥 ≤ 1 , E 𝑋 = න0 1 𝑥 ⋅ 3 𝑥 2𝑑𝑥 = 34 𝑥 4 01 = 34 , 𝑓𝑌 𝑦 = න𝑦 1 3𝑥𝑑𝑥 = 32 𝑥 2 𝑦1 = 32 1 − 𝑦 2 , 0 ≤ 𝑦 ≤ 1 , E 𝑌 = න0 1 𝑦 ⋅ 32 1 − 𝑦 2 𝑑𝑦 = 32 𝑦 22 − 𝑦 44 01 = 38 , E 𝑋𝑌 = න0 1 න0 𝑥 𝑥𝑦 ⋅ 3𝑥𝑑𝑦𝑑𝑥 = 32 𝑥 55 01 = 3 10 4

Example 1 Then the covariance is 3333 COv(X,Y)=E[XY]-E[X]E[Y]= 10 -4×8= 1601 .X and Y are not independent as it is not true that fx.y(x,y)=fx(x)fy(y)
Example 1 • Then the covariance is cov X, Y = E XY − E X E Y = 3 10 − 3 4 × 3 8 = 3 160 . • 𝑋 and 𝑌 are not independent as it is not true that 𝑓𝑋,𝑌 𝑥, 𝑦 = 𝑓𝑋 𝑥 𝑓𝑌 𝑦 . 5
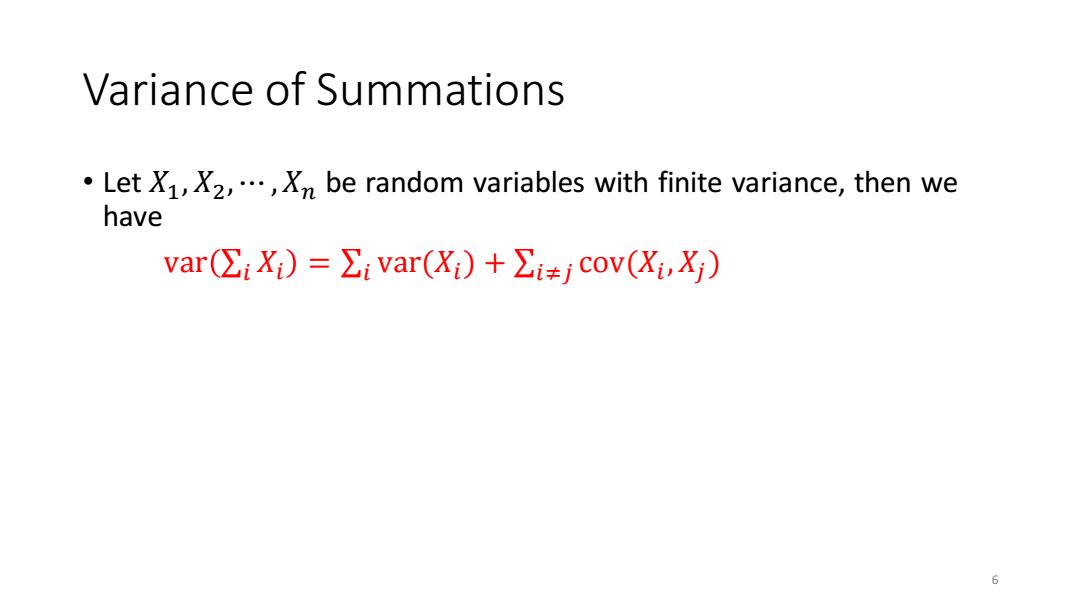
Variance of Summations Let X1,X2,...,Xn be random variables with finite variance,then we have var(∑iXi)=∑ivar(Xi)+∑jCoV(Xi,X) 6
Variance of Summations • Let 𝑋1 , 𝑋2 , ⋯ ,𝑋𝑛 be random variables with finite variance, then we have var σ𝑖 𝑋𝑖 = σ𝑖 var(𝑋𝑖 ) + σ𝑖≠𝑗 cov(𝑋𝑖 ,𝑋𝑗 ) 6

Example 2 If the variance of verbal GRE were 64,the variance of quantitative SAT were 81 and the correlation between these two tests were 0.50,then what is the variance of total SAT(verbal quantitative)?
Example 2 • If the variance of verbal GRE were 64, the variance of quantitative SAT were 81 and the correlation between these two tests were 0.50, then what is the variance of total SAT (verbal + quantitative)? 7

Example 2 Denote X1,X2 as the score for verbal and quantitative respectively, then var(X1 +X2)=var(X1)+var(X2)+2cov(X1,X2) =64+81+2×0.5×V64×V81 =217 8
Example 2 • Denote 𝑋1 , 𝑋2 as the score for verbal and quantitative respectively, then var 𝑋1 + 𝑋2 = var 𝑋1 + var 𝑋2 + 2cov 𝑋1 , 𝑋2 = 64 + 81 + 2 × 0.5 × 64 × 81 = 217 8

Conditional Expectation Revisit The conditional expectation EXY of a random variable X given another random variable y,is a new random variable determined by Y. It's distribution is determined by the distribution of Y
Conditional Expectation Revisit • The conditional expectation E[𝑋|𝑌] of a random variable 𝑋 given another random variable 𝑌, is a new random variable determined by 𝑌. • It’s distribution is determined by the distribution of 𝑌
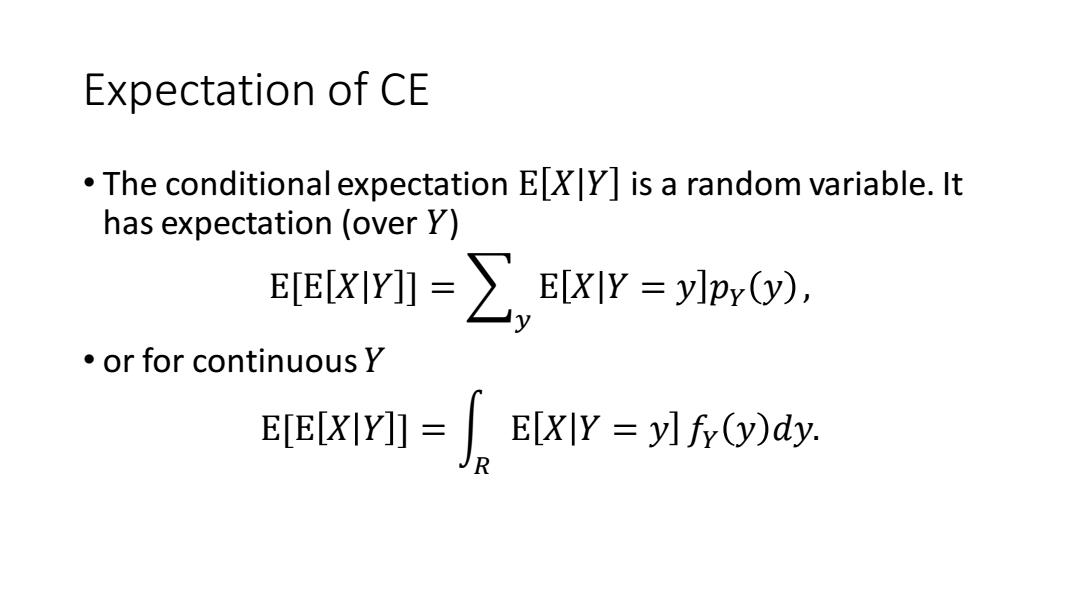
Expectation of CE The conditional expectation EXY]is a random variable.It has expectation (over Y) EEXIY=∑ E[XIY ylpy(y), ●or for continuous y x)dy
Expectation of CE • The conditional expectation E 𝑋 𝑌 is a random variable. It has expectation (over 𝑌) E[E 𝑋 𝑌 ] = 𝑦 E 𝑋 𝑌 = 𝑦 𝑝𝑌 𝑦 , • or for continuous 𝑌 E[E 𝑋 𝑌 ] = න 𝑅 E 𝑋 𝑌 = 𝑦 𝑓𝑌 𝑦 𝑑𝑦