
Public Policy Contents
Public Policy Contents

I.What is Public Policy:Public policy is a goal- directed or purposive course of action taken by government in an attempt to deal with a public problem. 1.Distributive:transportation,public safety,education, recreation,construction of harbors,reservoirs, dams 2 Regulatory:working conditions,minimum wage, industry standards 3 Redistributive:social welfare programs for the poor
I. What is Public Policy: Public policy is a goal- directed or purposive course of action taken by government in an attempt to deal with a public problem. 1. Distributive: transportation, public safety, education, recreation, construction of harbors, reservoirs, dams 2 Regulatory: working conditions, minimum wage, industry standards 3 Redistributive: social welfare programs for the poor

Il.Relationships between Politics and Ecnomy What is politics?Who gets what,when and how (according to Harold Lasswell) What is economics?efficient allocation of scarce resources 1.Three approaches toward political economy 1)Mercantilism or statism:politics determines economics 2)Marxism:economics determines politics 3)Classical liberalism:politics and economics should be separated as much as possible
II. Relationships between Politics and Ecnomy What is politics? Who gets what, when and how (according to Harold Lasswell) What is economics? efficient allocation of scarce resources 1. Three approaches toward political economy 1) Mercantilism or statism: politics determines economics 2) Marxism: economics determines politics 3) Classical liberalism: politics and economics should be separated as much as possible

2.Relationships between politics and economy in the U.S. Classical liberalism(free enterprise system, capitalist market economy)is still the dominant ideology in the U.S.even though it has been declining since the 1930s.On one hand,U.S.is still a regulative and distributive state,not a developmental state.U.S.still maintains,by a large, a Laissez faire capitalist economic system.On the other hand,however,thre is no quesion that the role of government in the U.S.economy has increased significantly since the 1930s
2. Relationships between politics and economy in the U.S. Classical liberalism (free enterprise system, capitalist market economy) is still the dominant ideology in the U.S. even though it has been declining since the 1930s. On one hand, U.S. is still a regulative and distributive state, not a developmental state. U.S. still maintains, by a large, a Laissez faire capitalist economic system. On the other hand, however, thre is no quesion that the role of government in the U.S. economy has increased significantly since the 1930s

The U.S.is still one of the most capitalist countries in the world Extent of government ownership of industry Canada Medium-low France High Great Britain Medium Italy High Japan Medium Sweden High Germany Medium U.S. Low (U.S.government owns postal service,TVA,passenger train,partially owns National Public Radio and PBS)
The U.S. is still one of the most capitalist countries in the world Extent of government ownership of industry Canada Medium-low France High Great Britain Medium Italy High Japan Medium Sweden High Germany Medium U.S. Low (U.S. government owns postal service, TVA, passenger train, partially owns National Public Radio and PBS)
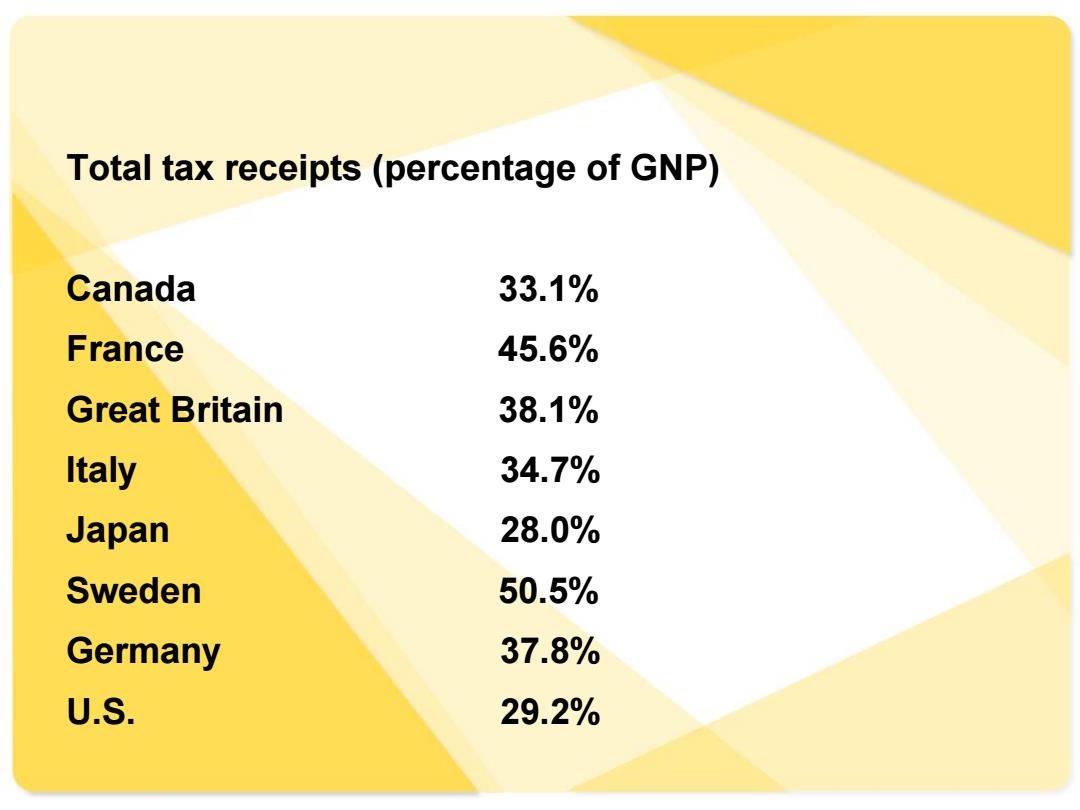
Total tax receipts(percentage of GNP) Canada 33.1% France 45.6% Great Britain 38.1% Italy 34.7% Japan 28.0% Sweden 50.5% Germany 37.8% U.S. 29.2%
Total tax receipts (percentage of GNP) Canada 33.1% France 45.6% Great Britain 38.1% Italy 34.7% Japan 28.0% Sweden 50.5% Germany 37.8% U.S. 29.2%

Ill.Public Policy Contents in the U.S. 1.Domestic policy areas 1)Education a.education system in the U.S.:education is primarily provided by the public sector:federal,state and local governments;U.S.education system is highly decentralized,therefore is highly stratified;child education is compulsory (ending varies by state); kindergarten (one year at age 5),elementary (5 years between 6-11),middle school (3 years between 11- 14),high school (4 years between 14-18),and higher education.The issue of home schooling
III. Public Policy Contents in the U.S. 1. Domestic policy areas 1) Education a. education system in the U.S.: education is primarily provided by the public sector: federal, state and local governments; U.S. education system is highly decentralized, therefore is highly stratified; child education is compulsory (ending varies by state); kindergarten (one year at age 5), elementary (5 years between 6-11), middle school (3 years between 11- 14), high school (4 years between 14-18), and higher education. The issue of home schooling

b.funding for education in the U.S.:According to a 2005 report from the OECD,the United States is tied for first place with Switzerland when it comes to annual spending per student on its public schools, with each of those two countries spending more than $11,000(in U.S.currency).However,the United States is ranked 37th in the world in education spending as a percentage of gross domestic product. The federal government only contributes 6%of total public money on education.The rest is from state and local governments and private funds.Public education for elementary,middle school and high school is completely free
b. funding for education in the U.S.: According to a 2005 report from the OECD, the United States is tied for first place with Switzerland when it comes to annual spending per student on its public schools, with each of those two countries spending more than $11,000 (in U.S. currency). However, the United States is ranked 37th in the world in education spending as a percentage of gross domestic product. The federal government only contributes 6% of total public money on education. The rest is from state and local governments and private funds. Public education for elementary, middle school and high school is completely free

c.college education in the U.S.:public colleges and universities;private colleges and universities.There is a Department of Education at the federal level.But its role in higher education is almost zero
c. college education in the U.S.: public colleges and universities; private colleges and universities. There is a Department of Education at the federal level. But its role in higher education is almost zero

CPI:College Tuition vs. U.S.Home Prices vs. CPI:All Items,1978 to 2010 1.200 1.000- Indexes 10o in 1978 800- CPI:College Tuition and Fees U.S.Home Prices 600- CPI:All Items 400- 200- Sourees:BIS.Census miperry.blogspot.com 0- 1980 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 2010