
CONTENTS 1.Introduction 2.Fire fighting in Metro and Road Tunnels 3.Flooding Prevention in Underground Structures 4.Earthquake Prevention 百年同濟2
2 1. Introduction 2. Fire fighting in Metro and Road Tunnels 3. Flooding Prevention in Underground Structures 4. Earthquake Prevention CONTENTS

1.Introduction Disaster classifications Natural disaster: flooding,earthquake,snow,landslide,etc. 百年同洒/0 TONGJI UNIVERSITY
3 3 /40 1. Introduction Disaster classifications Natural disaster: flooding, earthquake, snow, landslide, etc

1.Introduction Disaster classifications Human disaster: Terrorist attack,traffic accident,fire,poison gas, chemical explosions,etc. 百年同源 4 TONGII UNIVERSITY
4 1. Introduction Disaster classifications Human disaster: Terrorist attack, traffic accident, fire, poison gas, chemical explosions, etc

1.Introduction Main Types of Disasters Protections Fire/Fire fighting Flooding/Waterproofing Terrorist attack/Terrorist prevention Earthquake/Earthquake prevention 百年同海y0 TONGILUNIVERSITY
5 5 /40 1. Introduction Main Types of Disasters & Protections Fire/Fire fighting Flooding/Waterproofing Terrorist attack/Terrorist prevention Earthquake/Earthquake prevention

2.Fire fighting in Metro and Road Tunnels Frequency of fires is approximately 0.05 fires per million vehicle km. Graphic courtesy of Earth Tech The majority of these fires do not result in any serious consequences except for the car itself 百年同濟6
6 Frequency of fires is approximately 0.05 fires per million vehicle km. 2. Fire fighting in Metro and Road Tunnels The majority of these fires do not result in any serious consequences except for the car itself Graphic courtesy of Earth Tech
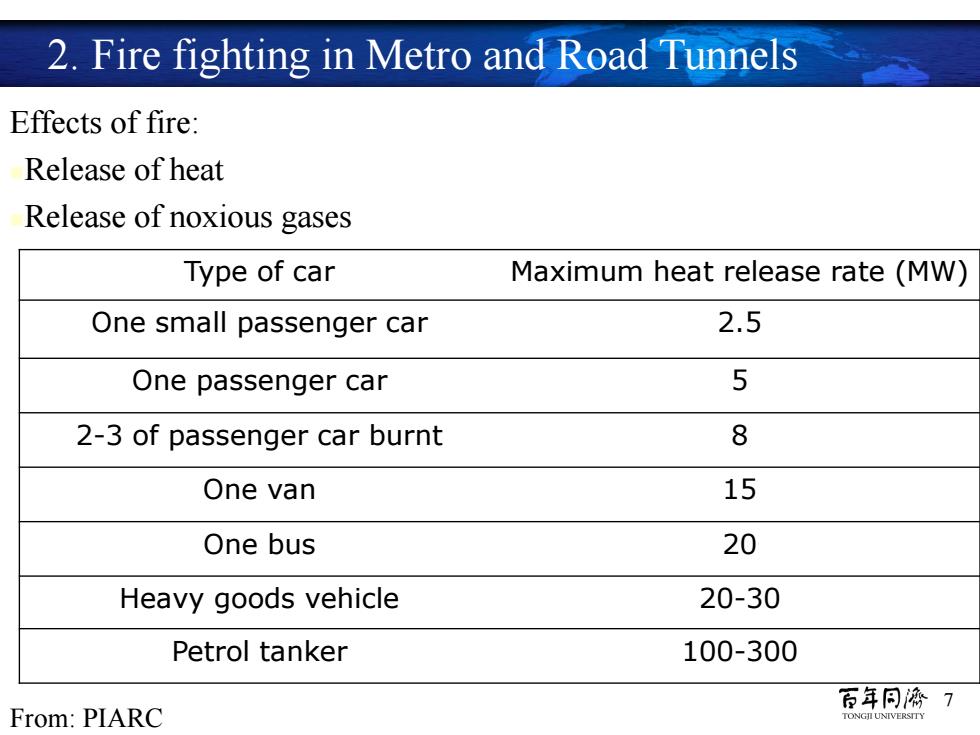
2.Fire fighting in Metro and Road Tunnels Effects of fire: Release of heat Release of noxious gases Type of car Maximum heat release rate(MW) One small passenger car 2.5 One passenger car 5 2-3 of passenger car burnt 8 One van 15 One bus 20 Heavy goods vehicle 20-30 Petrol tanker 100-300 百年同榜7 From:PIARC TONGILUNIVERSITY
7 Fire detection and suppression Peter Reinke 2. Fire fighting in Metro and Road Tunnels Effects of fire: Release of heat Release of noxious gases Type of car Maximum heat release rate (MW) One small passenger car 2.5 One passenger car 5 2-3 of passenger car burnt 8 One van 15 One bus 20 Heavy goods vehicle 20-30 Petrol tanker 100-300 From: PIARC

2.Fire fighting in Metro and Road Tunnels Consequences: Life-threatening conditions Harmful conditions Damage to infrastructure Damage to vehicles Loss of availability of public infrastructure 百年同濟8 TONGII UNIVERSITY
8 Fire detection and suppression Peter Reinke 2. Fire fighting in Metro and Road Tunnels Consequences: Life-threatening conditions Harmful conditions Damage to infrastructure Damage to vehicles Loss of availability of public infrastructure
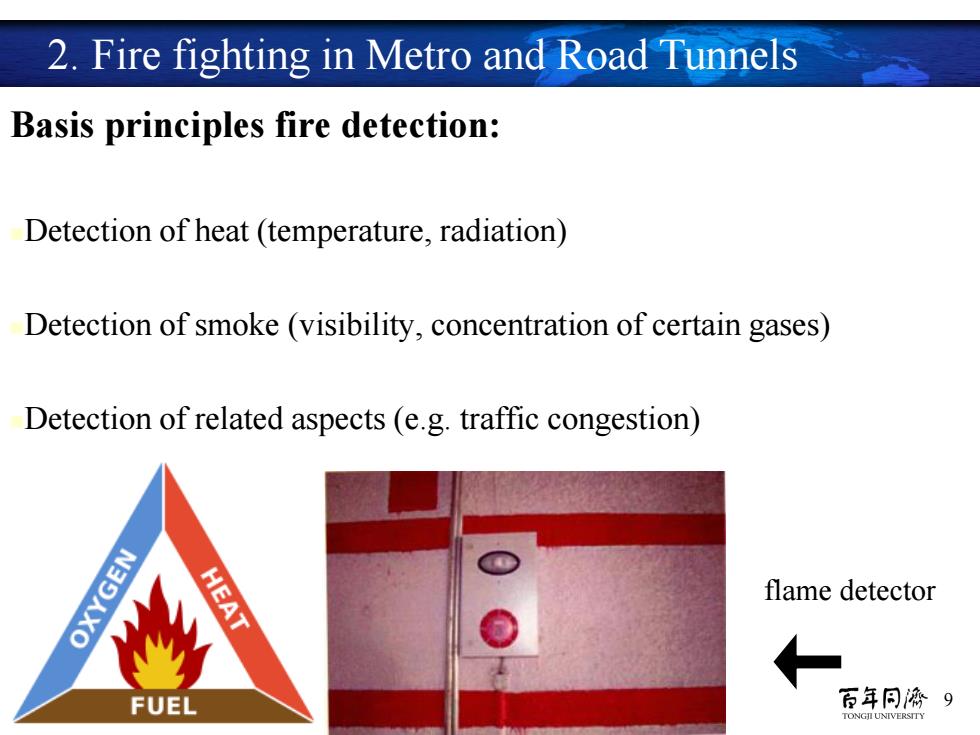
2.Fire fighting in Metro and Road Tunnels Basis principles fire detection: Detection of heat(temperature,radiation) Detection of smoke (visibility,concentration of certain gases) Detection of related aspects (e.g.traffic congestion) OXYGEN HEAT flame detector FUEL 百年同濟9 TONGILUNIVERSITY
9 Basis principles fire detection: Detection of heat (temperature, radiation) Detection of smoke (visibility, concentration of certain gases) Detection of related aspects (e.g. traffic congestion) 2. Fire fighting in Metro and Road Tunnels flame detector ←
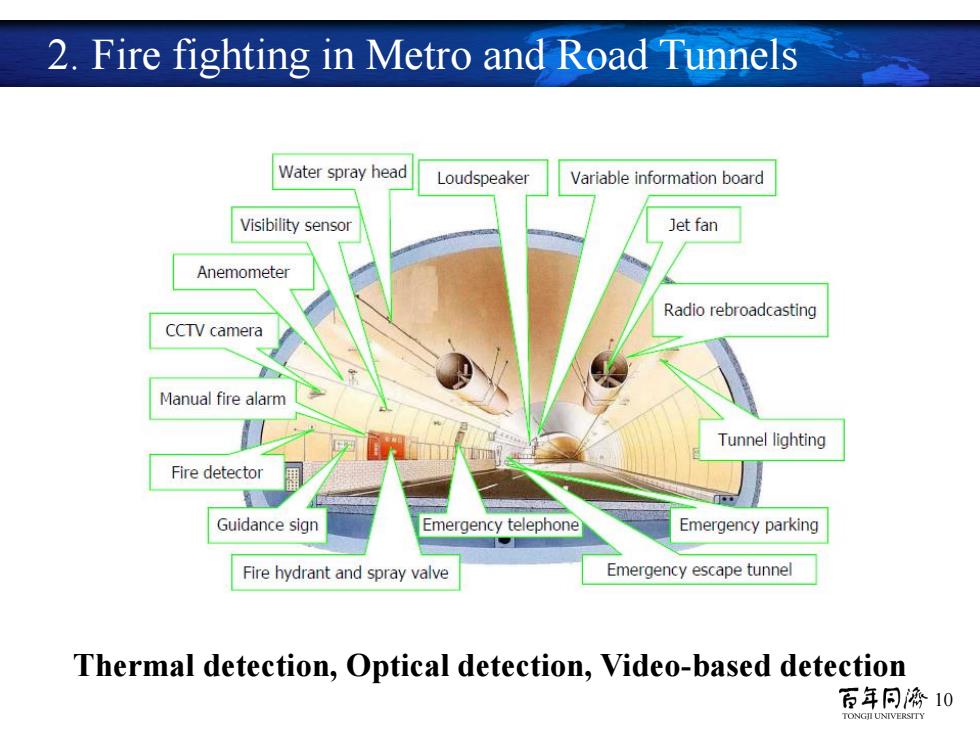
2.Fire fighting in Metro and Road Tunnels Water spray head Loudspeaker Variable information board Visibility sensor Jet fan Anemometer Radio rebroadcasting CCTV camera Manual fire alarm Tunnel lighting Fire detector Guidance sign Emergency telephone Emergency parking Fire hydrant and spray valve Emergency escape tunnel Thermal detection,Optical detection,Video-based detection 百年同濟10
10 2. Fire fighting in Metro and Road Tunnels Thermal detection, Optical detection, Video-based detection

2.Fire fighting in Metro and Road Tunnels Fire prevention or extinguishing by removing any one of: Heat:Supply water,switch off electricity Fuel:Mechanically or chemically remove fuel from the fire Oxidizing agent:Supply aqueous foam,or inert gas or enclose fire Sustained chemical reaction:Supply,e.g.Halon HEAT OXYGEN FVEL RERACTION 百年同濟11 TONGILUNIVERSITY
11 Fire prevention or extinguishing by removing any one of: Heat: Supply water, switch off electricity Fuel: Mechanically or chemically remove fuel from the fire Oxidizing agent: Supply aqueous foam, or inert gas or enclose fire Sustained chemical reaction: Supply, e.g. Halon 2. Fire fighting in Metro and Road Tunnels