
Chapter 1 INTRODUCT ION 1.Physiology its research field Definition of physiology The task of physiological research *How *Why Influence of environment Adaptation and regulation
Chapter 1 § 1. Physiology & its research field • Definition of physiology • The task of physiological research * How * Why * Influence of environment * Adaptation and regulation INTRODUCTION

Relationship between medicine physiology Physiology is one of basic medical sciences Three levels of physiological research Cellular molecular level Organic systemic level Integrative level Methods of physiological research Acute and chronic animal experiment in vitro in vivo experiment molecular biological experiment
• Relationship between medicine & physiology * Physiology is one of basic medical sciences • Three levels of physiological research * Cellular & molecular level * Organic & systemic level * Integrative level • Methods of physiological research * Acute and chronic animal experiment * in vitro & in vivo experiment * molecular biological experiment
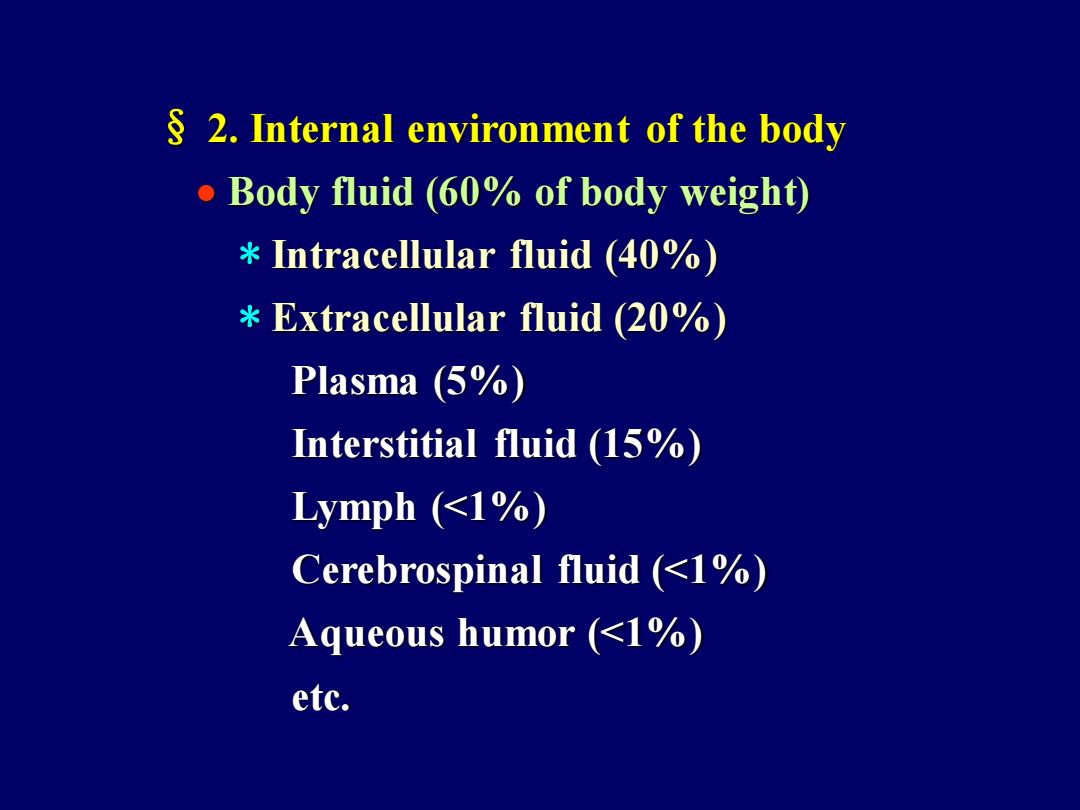
2.Internal environment of the body Body fluid (60%of body weight) Intracellular fluid (40%) Extracellular fluid (20%) Plasma (5%) Interstitial fluid (15%) Lymph (<1%) Cerebrospinal fluid (<1%) Aqueous humor (<1%) etc
§ 2. Internal environment of the body • Body fluid (60% of body weight) * Intracellular fluid (40%) * Extracellular fluid (20%) Plasma (5%) Interstitial fluid (15%) Lymph (<1%) Cerebrospinal fluid (<1%) Aqueous humor (<1%) etc

(占体重的40%) 人体外 Distribution transfusion of body fluid
Distribution & transfusion of body fluid

Concept of internal environment ('1870) By Claude Bernard (1813-1878) milieu interne [mi:ljo:into:n]French Concept of homeostasis ('1920) By W.B.Cannon (1871-1945) Importance of maintaining the homeostasis Enough nutritional substances O2 Low level of metabolic products CO2 Water,electrolyte,acid-base balance Temperature,osmotic pressure,etc. Homeostasis is a dynamic equilibrium Regulation of homeostasis Involve all systems,especially the lung kidney
• Concept of internal environment (’1870) By Claude Bernard (1813-1878) milieu interne [`mi:lj: `int:n] [French] • Concept of homeostasis (’1920) By W. B. Cannon (1871-1945) • Importance of maintaining the homeostasis * Enough nutritional substances & O2 * Low level of metabolic products & CO2 * Water, electrolyte, acid-base balance * Temperature, osmotic pressure, etc. • Homeostasis is a dynamic equilibrium • Regulation of homeostasis * Involve all systems, especially the lung & kidney

3.Regulation of physiological function ●Nervous regulation Definition the characteristics Reflex reflex arc ●Humoral regulation Definition the characteristics Hormone its secretory forms Telecrine,paracrine,neurosecretion,etc. ●Autoregulation Definition the characteristics
§ 3. Regulation of physiological function • Nervous regulation * Definition & the characteristics * Reflex & reflex arc • Humoral regulation * Definition & the characteristics * Hormone & its secretory forms Telecrine, paracrine, neurosecretion, etc. • Autoregulation * Definition & the characteristics

传入神经元 突触-- 人传入纤维 中间神经元 ●一感受器 突触 传出神经元 传出年雄人入 oi- 一-一二效应器 图1013反射弧 Reflex reflex arc
Reflex & reflex arc
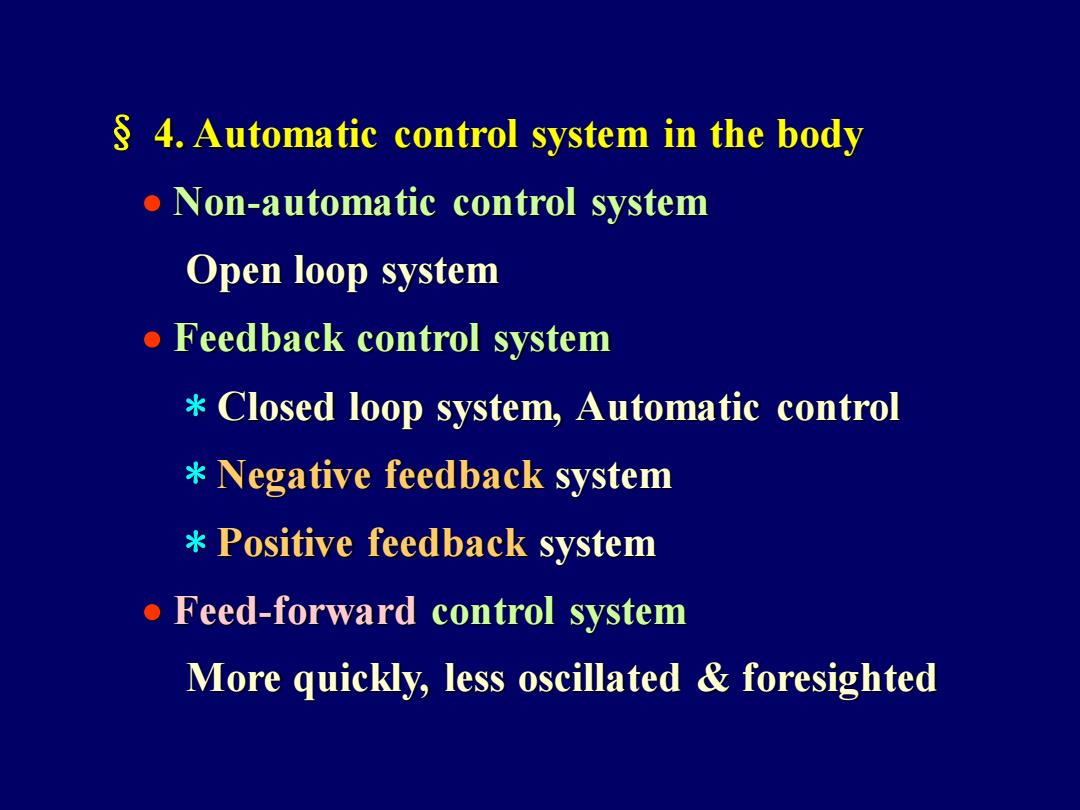
4.Automatic control system in the body Non-automatic control system Open loop system Feedback control system Closed loop system,Automatic control Negative feedback system Positive feedback system Feed-forward control system More quickly,less oscillated foresighted
§ 4. Automatic control system in the body • Non-automatic control system Open loop system • Feedback control system * Closed loop system, Automatic control * Negative feedback system * Positive feedback system • Feed-forward control system More quickly, less oscillated & foresighted
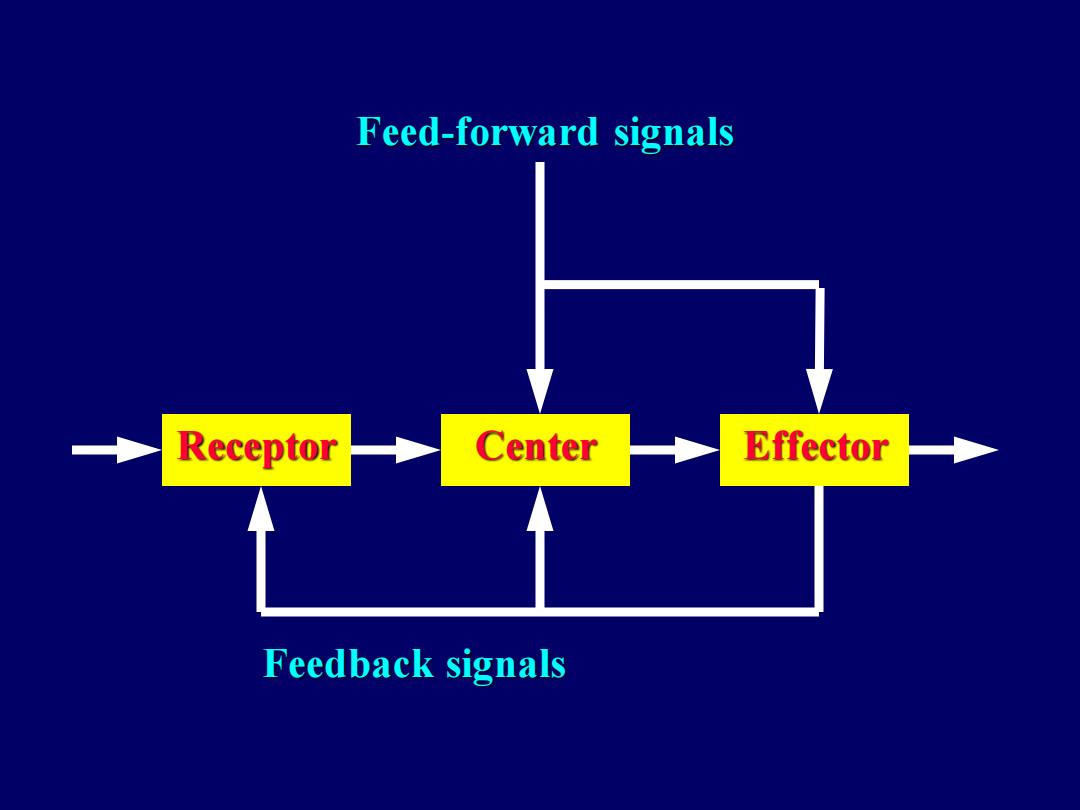
Feed-forward signals Receptor Center Effector Feedback signals
Receptor Center Effector Feed-forward signals Feedback signals