
问题求解 -论题1.1:计算机为什么能解题? 2017年9月28
问题求解 -论题1.1:计算机为什么能解题? 2017年9月28

Computers are amazing machines. They seem to be able to do anything.They fly aircraft and spaceships,and control power stations and hazardous chemical plants.Companies can no longer be run without them,and a growing number of sophisticated medical procedures cannot be performed in their absence.They serve lawyers and judges who seek judicial precedents in scores of documented trials,and help scientists in performing immensely complicated and involved mathematical computations. They route and control millions of telephone calls in networks that span continents.They execute tasks with enormous precision-from map reading and typesetting to graphical picture processing and integrated circuit design.They can relieve us of many boring chores,such as keeping a meticulous track of home expenses,and at the same time provide us with diverse entertainment such as computer games or computerized music.Moreover,the computers of today are hard at work helping design the even more powerful computers of tomorrow
Computers are amazing machines. • They seem to be able to do anything. They fly aircraft and spaceships, and control power stations and hazardous chemical plants. Companies can no longer be run without them, and a growing number of sophisticated medical procedures cannot be performed in their absence. They serve lawyers and judges who seek judicial precedents in scores of documented trials, and help scientists in performing immensely complicated and involved mathematical computations. • They route and control millions of telephone calls in networks that span continents. They execute tasks with enormous precision—from map reading and typesetting to graphical picture processing and integrated circuit design. They can relieve us of many boring chores, such as keeping a meticulous track of home expenses, and at the same time provide us with diverse entertainment such as computer games or computerized music. Moreover, the computers of today are hard at work helping design the even more powerful computers of tomorrow

实际上,计算机是什么? .even the most sophisticated computer is really only a large,well-organized volume of bits,and moreover it can normally carry out only a small number of extremely simple operations on them,such as zeroing, flipping,and testing
实际上,计算机是什么? •even the most sophisticated computer is really only a large, well-organized volume of bits, and moreover it can normally carry out only a small number of extremely simple operations on them, such as zeroing, flipping, and testing
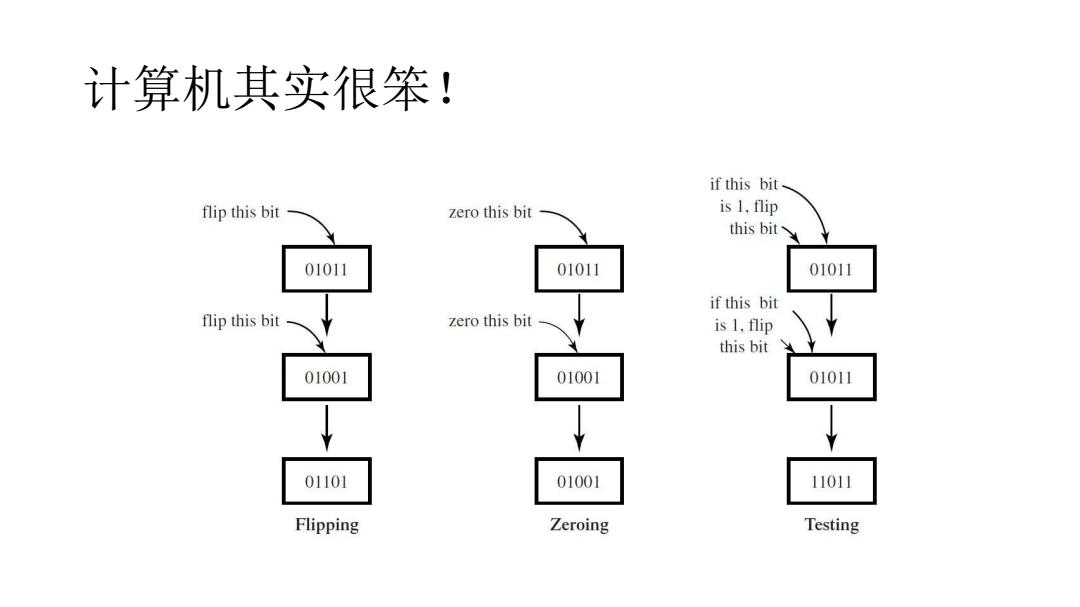
计算机其实很笨! if this bit flip this bit zero this bit is 1.flip this bit 01011 01011 01011 if this bit flip this bit zero this bit is 1,flip this bit 01001 01001 01011 01101 01001 11011 Flipping Zeroing Testing
计算机其实很笨!

但是,计算机确实很神奇! Equality test(x,y) zero eq; flip eq;equality on test x flip eq; test y flip eq;equality on only tum twice eq 你能将这个操作扩展到, If x=y eq=1 比如,32位内的整数吗? Otherwise eq=0 我们用x0,x1,x31表示x的32个bits,用y0,y1,,y31表示y的32个bits
但是,计算机确实很神奇! 我们用x0,x1,…,x31表示x的32个bits,用y0,y1,…,y31表示y的32个bits

一个稍微复杂的例子 ·计算两个1bit的二进制数的和(增加exit和goto操作) add(x,y) 1.zero zO 问题: 2.zero z1 如果只用zero、flip、test 3.equality test(x,y) exit、goto操作,能完成 4.test eq goto 7 这个任务吗? 5.flip zO 6.exit 7.zero t 8.flip t 9.equality test(x,t) 10.test eq flip z1
一个稍微复杂的例子 • 计算两个1bit的二进制数的和(增加exit和goto操作) add(x,y) 1. zero z0 2. zero z1 3. equality test(x,y) 4. test eq goto 7 5. flip z0 6. exit 7. zero t 8. flip t 9.equality test(x,t) 10. test eq flip z1 问题: 如果只用zero、flip、test exit、goto操作,能完成 这个任务吗?

封装+抽象 ·用最原子的操作封装成更“高级”的操作 ·用三个基本操作可以实现“相等”操作 ·用“相等”操作可以实现一位的加法操作 ·用一位的加法“间接操作”可以实现普通加法 ·a:=X+y 实际上,现代计算机内部电路能提供的“原子”操作远不止这5个基 本操作 不同的原子操作==不同的计算机 实际上,我们在编写程序时使用“封装”的高级操作可以“随心所欲” 不同级别的语言、不同级别的软件库
封装+抽象 • 用最原子的操作封装成更“高级”的操作 • 用三个基本操作可以实现“相等”操作 • 用“相等”操作可以实现一位的加法操作 • 用一位的加法“间接操作”可以实现普通加法 • a:= x + y 实际上,现代计算机内部电路能提供的“原子”操作远不止这5个基 本操作 不同的原子操作 == 不同的计算机 实际上,我们在编写程序时使用“封装”的高级操作可以“随心所欲” 不同级别的语言、不同级别的软件库

一段等价的汇编和高级语言程序 /-计算|x-y川的c代码 ∥----汇编代码--- int absdiff(int x,int y) moMl8(%ebp),%edx;取x的值 moM12(%ebp),%eax;取y的值 cmpl%eax,%edx;比较x和y的值 if (x<y) j1.L3 ;如果y<x转到.L3 subl%eax,%edx;计算y-x return y X; mol%edx,%eax;返回值 else jmp .L5 ;跳转到.L5 .L3: y<X return x -y; subl%edx,%eax;计算xy } .L5: ;完成
一段等价的汇编和高级语言程序 //--计算|x-y|的C代码- int absdiff(int x, int y) { if (x < y) return y - x; else return x - y; } //----------汇编代码---------- movl 8(%ebp),%edx ; 取x的值 movl 12(%ebp),%eax ; 取y的值 cmpl %eax,%edx ;比较x和y的值 jl .L3 ;如果y<x 转到.L3 subl %eax,%edx ; 计算y-x movl %edx,%eax ; 返回值 jmp .L5 ; 跳转到.L5 .L3: ;y<x subl %edx,%eax ;计算x-y .L5: ; 完成

但,本质上都是: However,the outward appearance is of peripheral importance when compared to the bits and their internal arrangement.It is the bits that"sense"the external stimuli arriving from the outside world via buttons,levers,keys on a keyboard,electronic communication lines,and even microphones and cameras.It is the bits that"decide" how to react to these stimuli and respond accordingly by directing other stimuli to the outside via displays,screens,printers,loudspeakers,beepers,levers,and cranks
但,本质上都是:

关于问题的广义理解 ·求解3x=6和求解ax=b的区别 ·“哪个x能够满足3x=6”:问题的实例 ·在给定任意的a,b时,哪个x能够满足ax=b:问题! ·计算机解题: ·解一般的题 什么叫解一般的题? ·20万份报纸从印刷厂用50辆汽车,分发到100个小镇的1000个零 售点。如何安排运输?
关于问题的广义理解 • 求解3x=6和求解ax=b的区别 • “哪个x能够满足3x=6”:问题的实例 • 在给定任意的a,b时,哪个x能够满足ax=b:问题! • 计算机解题: • 解一般的题 什么叫解一般的题? • 20万份报纸从印刷厂用50辆汽车,分发到100个小镇的1000个零 售点。如何安排运输?