
计算机问题求解一论题3-7 树 2016年10月12日
计算机问题求解 – 论题3-7 - 树 2016年10月12日

Theorem 4.1 An edge e of a graph G is a bridge if and only if e lies on no cycle of G 推论:Every edge in a tree is a bridge 问题1: 从应用的角度看,上述推论有何 指导意义?
Theorem 4.1 An edge e of a graph G is a bridge if and only if e lies on no cycle of G. 推论:Every edge in a tree is a bridge

For an n-vertex graph G(with n1),the following are equiv- alent(and characterize the trees with n vertices). A)G is connected and has no cycles. B)G is connected and has n-1 edges. C)G hasn-1 edges and no cycles. D)For u,vEV(G),G has exactly one u,v-path 问题2: 如何证明一系列命题等价? 问题3: 不能有回路对最小顶点次 数有什么影响?

树的性质的“极限性” a)Every edge of a tree is a cut-edge. b)Adding one edge to a tree forms exactly one cycle. c)Every connected graph contains a spanning tree. 问题4: 什么样的图生成树是唯一的, 为什么?
树的性质的“极限性

Theorem 4.4 Every tree of order n has size n-1. 问题:有n-1条边的n点连通图,一定是树? 有n-1条边的无环连通图,一定连通n个点? 问题5:如何构造一个连通图的生成树? 无向连通图遍历算法一定得到一棵树
Theorem 4.4 Every tree of order n has size n - 1. 问题:有n-1条边的n点连通图,一定是树? 有n-1条边的无环连通图,一定连通n个点? 问题5:如何构造一个连通图的生成树? 无向连通图遍历算法一定得到一棵树
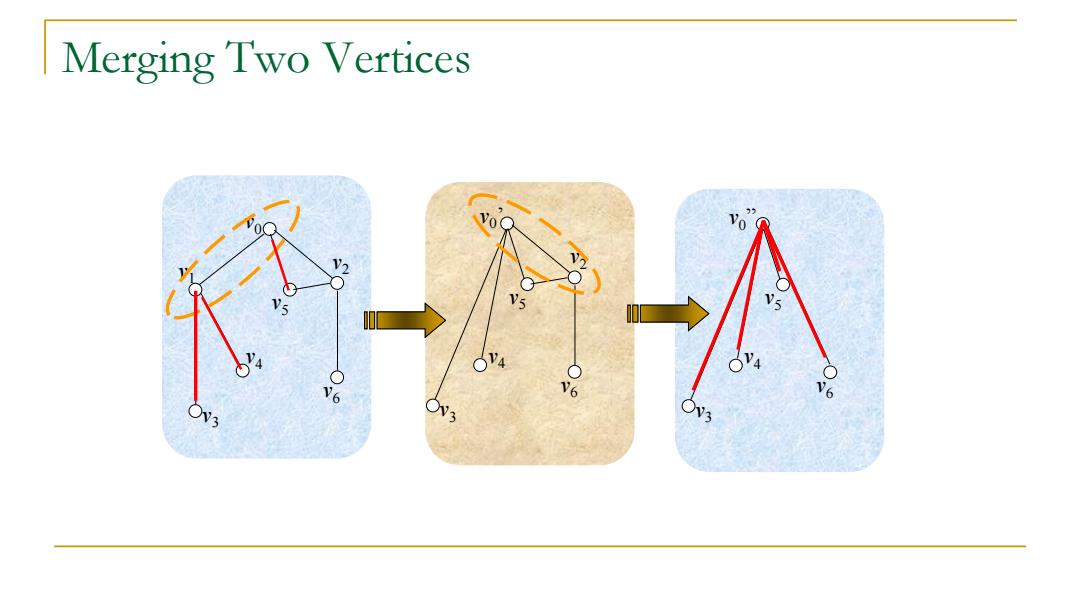
Merging Two Vertices V6
Merging Two Vertices v0 v6 v2 v5 v4 v1 v3 v6 v2 v5 v4 v3 v0 ’ v6 v5 v4 v3 v0
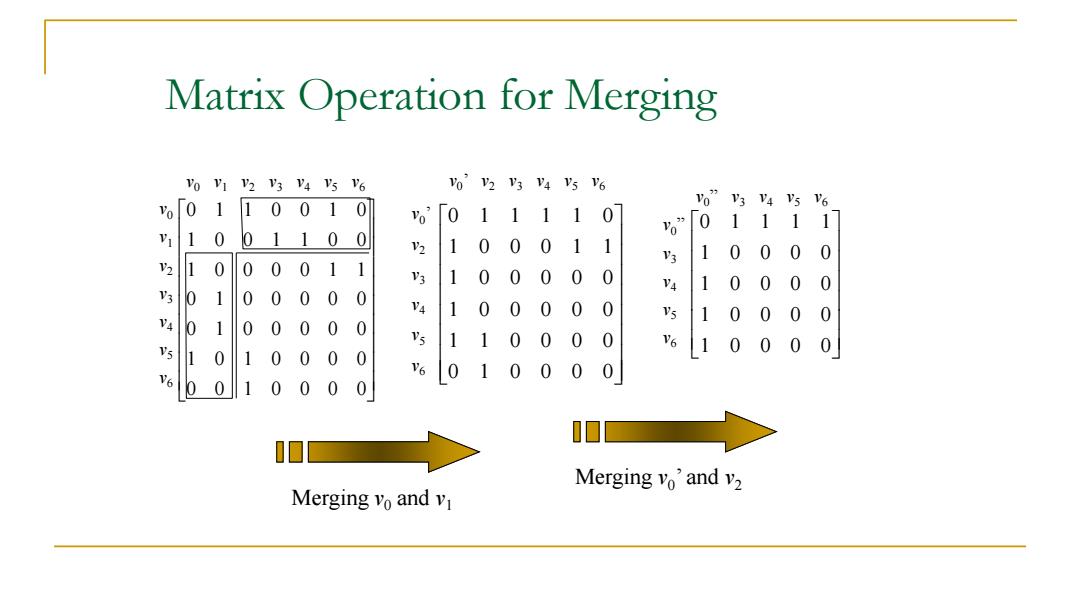
Matrix Operation for Merging Vo VI V2 V3 V4 Vs V6 Vo V2 V3 V4 V5 V6 「01 10010 %” V3 V4 V5 V6 %'「0 1111 07 台 [0 1111 10 01100 210 0 0 11 3 1 0 0 00 5 10 0 0011 3 10000 0 1 5 V4 0 00 0 01 00 0 00 V4 10 00 0 0 女 Vs 1 0 00 0 01 00 00 0 11 0 0 0 0 V6 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 6 V6 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 Merging vo'and v2 Merging vo and vi
Matrix Operation for Merging 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 0 v0 v1 v2 v3 v4 v5 v6 v0 v1 v2 v3 v4 v5 v6 Merging v0 and v1 v0 ” v3 v4 v5 v6 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 v0 ” v3 v4 v5 v6 v0 ’ v2 v3 v4 v5 v6 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 v0 ’ 0 1 1 1 1 0 v2 v3 v4 v5 v6 Merging v0 ’ and v2

Constructing a Spanning Tree a (1 (2 (3 0.Let a be the starting vertex,selecting edges one by one in original R 1.Merging a and c into a'(fa,c)),selecting(a,c) 2.Merging a'and b into a"(fa,c,b)),selecting (c,b) 3.Merging a"and d into a"(a,c,b,d)),selecting (a,d)or(d,b) Ending,as only one vertex left
Constructing a Spanning Tree a b c d a b a b a b c c d c d d 0. Let a be the starting vertex, selecting edges one by one in original R 1. Merging a and c into a’({a,c}), selecting (a,c) 2. Merging a’ and b into a”({a,c,b}), selecting (c,b) 3. Merging a” and d into a”’({a,c,b,d}), selecting (a,d) or (d,b) Ending, as only one vertex left 0. Let a be the starting vertex, selecting edges one by one in original R 1. Merging a and c into a’({a,c}), selecting (a,c) 2. Merging a’ and b into a”({a,c,b}), selecting (c,b) 3. Merging a” and d into a”’({a,c,b,d}), selecting (a,d) or (d,b) Ending, as only one vertex left (0) (1) (2) (3)
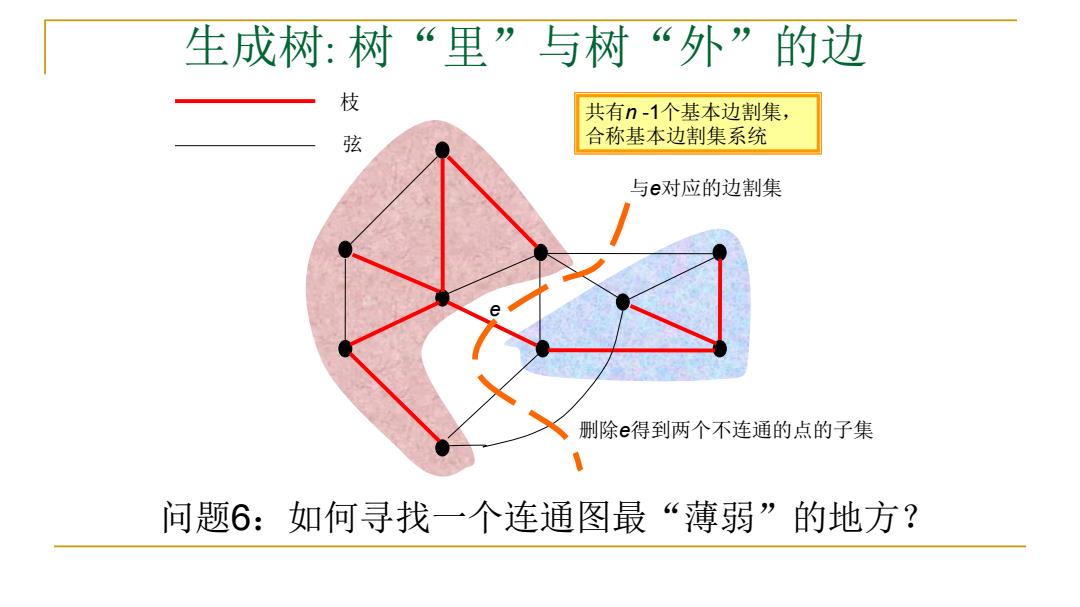
生成树:树“里”与树“外”的边 枝 共有n-1个基本边割集, 弦 合称基本边割集系统 与e对应的边割集 删除e得到两个不连通的点的子集 问题6:如何寻找一个连通图最“薄弱”的地方?
生成树: 树“里”与树“外”的边 枝 弦 e 删除e得到两个不连通的点的子集 与e对应的边割集 共有n -1个基本边割集, 合称基本边割集系统 共有n -1个基本边割集, 合称基本边割集系统 问题6:如何寻找一个连通图最“薄弱”的地方?

暗藏玄机:两棵不同的生成树 T树 T'树 两条边互换 e2 e2
暗藏玄机:两棵不同的生成树 e1 e2 e2 e1 两条边互换 u v u v u v u v x y x y x y x y T树 T’树