
计算机问题求解一论题2-8 -概率分析与随机算法 2016年04月14日
计算机问题求解 – 论题2-8 - 概率分析与随机算法 2016年04月14日
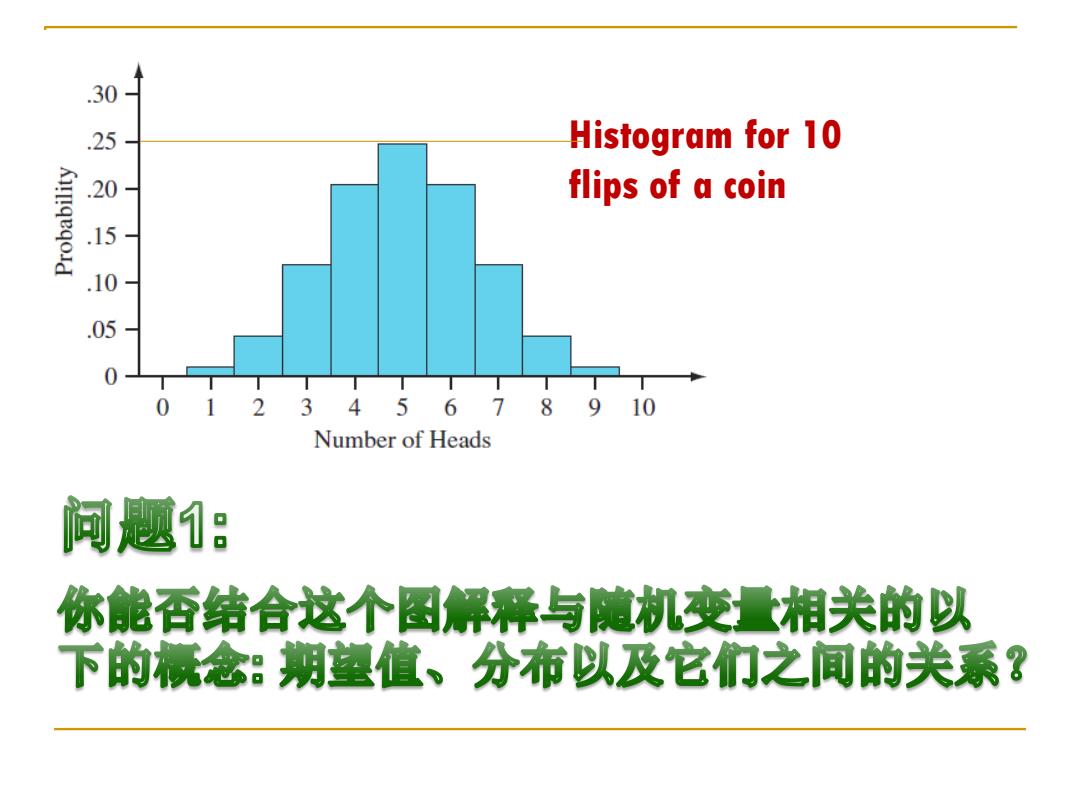
.30 25 Histogram for 10 .20- flips of a coin 1 10 .05 0 0 1 23456789 10 Number of Heads 问题: 你能否结合这个图解释与随机变量相关的以 下的标念:期望值、分布以及它们之间的关系?
Histogram for 10 flips of a coin

Histogram for answers for a 10-problem test 35 .30 .25 问题2 .20 .15 .10 图中纵坐标值是 .05 0 012345678910 怎台得出来的? Number of Right Answers 贝努利试验过程: P(exactly k successes)= (p1-p- 当k=8, 0.88.0.22≈0.302
Histogram for answers for a 10-problem test 贝努利试验过程: 当k=8, 0.8 0.2 0.302 8 10 8 2

HIRE-ASSISTANT (n) best 0 /candidate 0 is a least-qualified dummy candidate 2 for i 1 to n 3 interview candidate i 4 if candidate i is better than candidate best 5 best i 6 hire candidate i 那么,有没有问: 般情况下,代价 问题3: 会如何? 这个算法是“确定”的吗? 什么是“随机”的呢? 它的best和worst case是什么?
那么,有没有问: 一般情况下,代价 会如何?
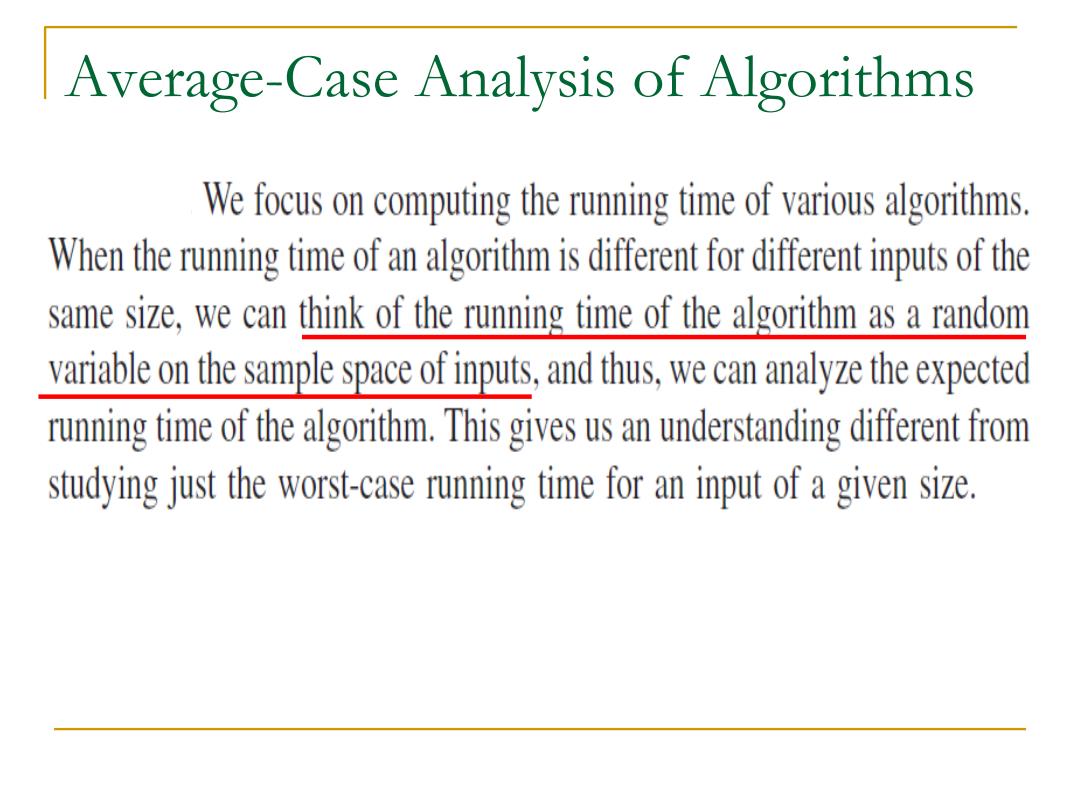
Average-Case Analysis of Algorithms We focus on computing the runing time of various algorithms When the running time of an algorithm is different for different inputs of the same size,we can think of the running time of the algorithm as a random variable on the sample space of inputs,and thus,we can analyze the expected running time of the algorithm.This gives us an understanding different from studying just the worst-case runing time for an input of a given size
Average-Case Analysis of Algorithms
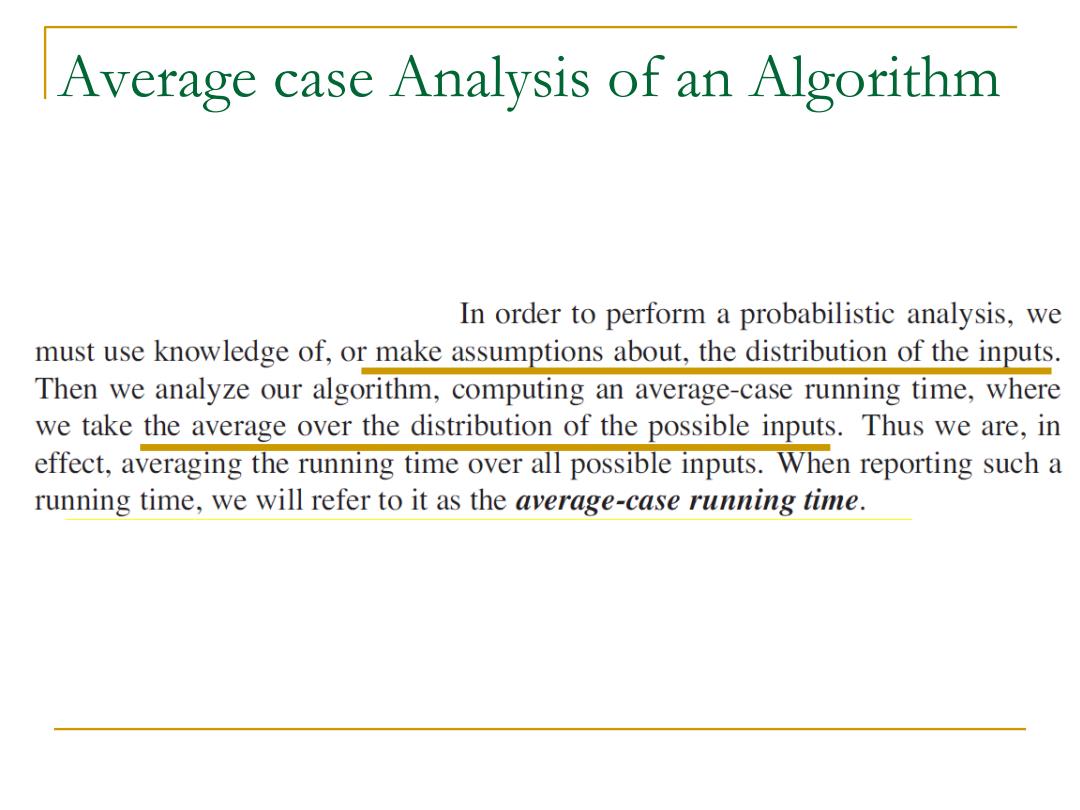
Average case Analysis of an Algorithm In order to perform a probabilistic analysis,we must use knowledge of,or make assumptions about,the distribution of the inputs. Then we analyze our algorithm,computing an average-case running time,where we take the average over the distribution of the possible inputs.Thus we are,in effect,averaging the running time over all possible inputs.When reporting such a running time,we will refer to it as the average-case running time
Average case Analysis of an Algorithm

HIRE-ASSISTANT (n) 1 best =0 /candidate 0 is a least-qualified dummy candidate 2 for i 1 to n 3 interview candidate i 4 if candidate i is better than candidate best 5 best i 6 hire candidate i 问题4: 在hiring problem.算法中假设 应聘者随机到达”意味着什么?

HIRE-ASSISTANT (n) 1 best =0 /candidate 0 is a least-qualified dummy candidate 2 for i 1 to n 3 interview candidate i 4 if candidate i is better than candidate best 5 best i 6 hire candidate i 问题5: 在hiring problem算法中分析算 法所需要的随机变量是什么?

Hiring-Assistant算法的平均情况分析 涉及的随机变量: ·Hiring?操作执行次数:X; E[X]=∑xPr{X=x x=1 ·事件“第个候选人被雇用”的indicator::X; X=X1+X2+…+Xn
Hiring-Assistant算法的平均情况分析 涉及的随机变量: • Hiring操作执行次数:X ; • 事件“第i个候选人被雇用”的indicator:Xi ;

Indicator Random variable if A occurs, if A does not occur Indicator random variables provide a convenient method for onverting between probabilities and expectations. 问题6: 这句话是什么意思?
Indicator Random Variable