
计算机问题求解一论题1-7 不同的程序设计方法 2015年11月5日
计算机问题求解 – 论题1-7 - 不同的程序设计方法 2015年11月5日
检查 Since this information is unavailable to the compiler,the machine code it generates for the expression a[j]just takes the address of a (that is, the first cell of the array),adds j to it,and retrieves the value stored in that address.(In fact,the same expression can also be written in C as *(a +j), which more closely reflects its implementation.)In contrast,when the PL/I compiler encounters the corresponding expression,it will also generate code to check that the index is indeed within the legal bounds
检查 Since this information is unavailable to the compiler, the machine code it generates for the expression a[ j ] just takes the address of a (that is, the first cell of the array), adds j to it, and retrieves the value stored in that address. (In fact, the same expression can also be written in C as ∗(a + j ), which more closely reflects its implementation.) In contrast, when the PL/I compiler encounters the corresponding expression, it will also generate code to check that the index is indeed within the legal bounds

问题0 ■计算机真正能够“识别”和“执行”的程序是什么? o机器代a码,hard wired primitive instructions and it combination instructions ■我们能否编写这样的程序?
问题0 计算机真正能够“识别”和“执行”的程序是什么? 机器代码,hard wired primitive instructions and it combination instructions 我们能否编写这样的程序?

问题1 0 我们常说“高级程序设计”,有没有与之对应的“低级”程序 设计? 如果有,两者是什么区别? o抽象VS具体 口巨大的“细节”鸿沟
问题1 我们常说“高级程序设计”,有没有与之对应的“低级”程序 设计? 如果有,两者是什么区别? 抽象 VS 具体 巨大的“细节”鸿沟
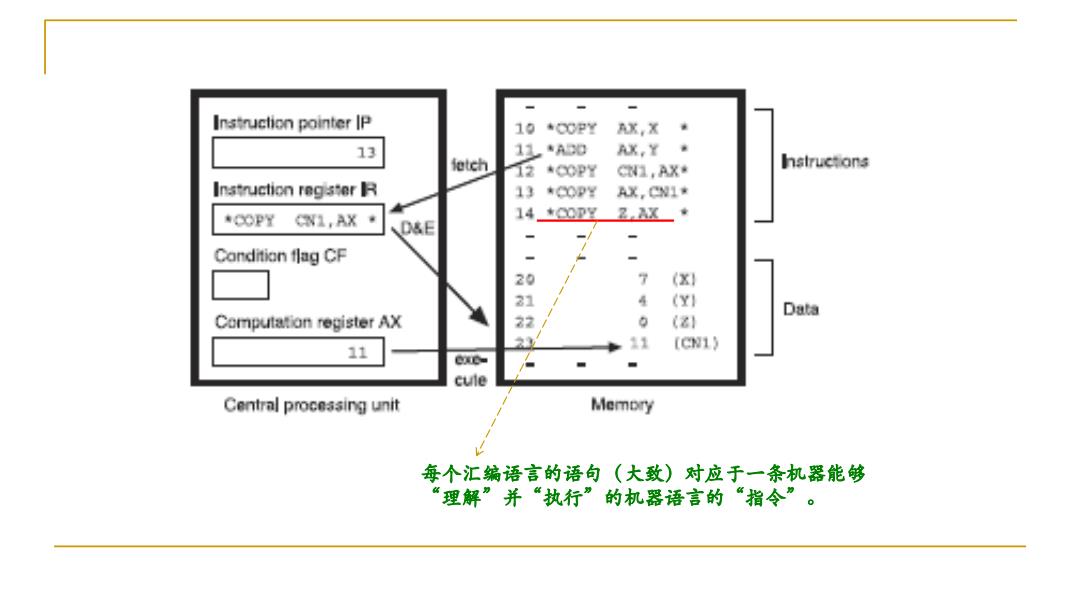
Instruction pointer IP 10 *COPY AX,X 13 11*A0 x,Y· ietch Istructans 12 *COOPY G1,AX· Instruction register 13 *COPY AX,CNI* *COPY CN1,AX 140P厘2X· D&E Candition flag CF 20 (X) 21 (YI Data Computation register AX 22 6 (21 23 11 11 (Cw1) Cx- cule Central processing unit MemDry 每个汇编语言的语句(大致)对应于一条机器能够 “理解”并“执行”的机器语言的“指令
每个汇编语言的语句(大致)对应于一条机器能够 “理解”并“执行”的机器语言的“指令

问题2: 程序设计语言的 “implementation (实现)”是什么意思?

问题2 任意给出一个用该语言书写的合法程序,将 其转换成可以在某台机器上可以运行的机器 语言程序
问题2 任意给出一个用该语言书写的合法程序,将 其转换成可以在某台机器上可以运行的机器 语言程序

问题3: 我们通常用什么手段 来“实现”一个程序 设计语言?

Algorithmic idea algorithm for y from I to N do (body-of-loop) Programmer programming end (human) A program in high-level language MVCO.Y (move constantOto location Y LOOP:CMP N.Y (compre values at locations Nand Y) Compiler compilation (software) JEQ REST (ifequauostatement labelled"REST ADC 1.Y (add ttovaueY 编译 program in A (a-body-of-oop) Compilation assembly language JMP LOOP (jump back to statement labeledLOOP) REST: (restof prgram) AM machine code Computer exccution
编译 Compilation

什么是编译器 ·一个编译器就是一个程序 ■Input:以某一种语言(源语言)编写的程序, Output:与input等价的、用另一种语言(目标语言)编写的程序。 源程序 编译器 目标程序 ■狭义: 程序设计语言→机器代码 ■广义:程序变换C++→C→汇编 Pascal→C
什么是编译器 一个编译器就是一个程序 Input:以某一种语言(源语言)编写的程序, Output:与input等价的、用另一种语言(目标语言)编写的程序。 狭义: 程序设计语言 → 机器代码 广义:程序变换 C++ → C →汇编 Pascal → C 源程序 编译器 目标程序