
Part A.Answer all eight questions(5 marks each). 1.What kind of hybrid orbitals does the S atom use in a molecule of H2S? H、 S The structure of H2S is Since this structure has two lone pairs and two bonding pairs about theS atom,then the S atom must be using sp'hybrid orbitals. 2.In a buffered system composed of (C2Hs)N and(C2Hs)NHCl)will the pH increase or decrease as more (C2Hs)3NHCl(ag)is added?Why? din o the Hendern bIe id sh (C2Hs)3NHCla Adding more of it will therefore lower the pH. 3.Name the strongest intermolecular force between two molecules of(CH3)NH.Be specific. Due to the polar N-H bonds,two molecules of this compound will be attracted by H-bonds. 4.For the reaction MgCO=MgOs+COx),which way will the equilibrium shift if pressure is increased? Why? The equilibrium will shift left so as to reduce the pressure.Note that there is only one gaseous species in the e reaction 5.Define the term"state function"and give three examples of one. e function is one whose value is the same no matter wh path istaken om reactants to products.Some examples are S.H..V. eaction and no matter what Part B.Answer all four questions(20 marks each). 1. For the reaction H+CO=CO+H2O at equilibrium at 25C,the following partial pressures were measured: Pa =0.387atm Pco =0.152atm Peo=.180atm Pu.o=0.252atm (a)Calculate the equilibrium constant Kp K=PcoPu,o PHa Pcoz _01800252=0.71 (0.387)0.152)
Part A. Answer all eight questions (5 marks each). 1. What kind of hybrid orbitals does the S atom use in a molecule of H2S? The structure of H2S is Since this structure has two lone pairs and two bonding pairs about the S atom, then the S atom must be using sp3 hybrid orbitals. S H H .. .. 2. In a buffered system composed of (C2H5)3N(aq) and (C2H5)3NHCl(aq), will the pH increase or decrease as more (C2H5)3NHCl(aq) is added? Why? According to the Henderson Hasslebalch equation, a 10 [acid] pH pK log [base] = + . In this system, the acid is the (C2H5)3NHCl(aq). Adding more of it will therefore lower the pH. 3. Name the strongest intermolecular force between two molecules of (CH3)2NH. Be specific. Due to the polar N-H bonds, two molecules of this compound will be attracted by H-bonds. 4. For the reaction MgCO3(s) = MgO(s) + CO2(g), which way will the equilibrium shift if pressure is increased? Why? The equilibrium will shift left so as to reduce the pressure. Note that there is only one gaseous species in the reaction. 5. Define the term “state function” and give three examples of one. A state function is one whose value is the same no matter what the rate of reaction and no matter what path is taken from reactants to products. Some examples are S, H, G, p, V, T. Part B. Answer all four questions (20 marks each). 1. For the reaction H2(g) + CO2(g) = CO(g) + H2O(g) at equilibrium at 25o C, the following partial pressures were measured: 2(g) 2(g) (g) 2 (g) H CO CO H O p 0.387 atm p 0.152atm p 0.180atm p 0.252atm = = = = (a) Calculate the equilibrium constant Kp 2 2 2 CO H O p H CO p p K p p (0.180)(0.252) 0.771 (0.387)(0.152) = = =

(ina vessela C.Calculate the partial pressure of e four gases v Pu.,atm Pco.,atm Pco,atm PH.o,atm nitial 0.5 0.5 0 Change Equilibrium 0.5-x 0.5-x At equilibrium,K PcoP:O =0.771 PH,Pco: (x(x) (0.5-x)0.5-x) =0.771 05-x=077=0.878 X X=0.878(0.5-X) x=0.439-0.878x 1.878x=0.439 x=0.234 Thus. P4,=Po,=0.5-x=0.5-0.234=0.266atm Pco PH:o =x=0.234atm Part C.Answer any three of the six questions.If you answer more than three,the best three will be used to calculate your mark(20 marks each). 1 Fuel cells for cars will likely use hydrogen as the fuel and oxygen as the oxidant.Using the following data: 2H+2e→Hg E0=0000V 02g+4Hem+4e→2H0 E°=1.229V (a)Write the balanced overall electrochemical reaction and calculate the standard cell potential O2g+4H(ea+4e→2H0d E=1.229V 2H2e→4Haa+4e E°=0.000V O2e+2H2g→2H2O0 E°=1.229V (b)Calculate the cell potential at 50C when P=3.00 atm and Po=1.30 atm E-E_RTIn(Q) nF 2
2 (b) 0.5 atm of H2(g) and 0.5 atm of CO2(g) are placed in a vessel at 25o C. Calculate the partial pressure of each of the four gases when equilibrium is attained. H2 p ,atm CO2 p ,atm CO p ,atm H O2 p ,atm Initial 0.5 0.5 0 0 Change -x -x +x +x Equilibrium 0.5 - x 0.5 - x x x At equilibrium, 2 2 2 CO H O p H CO p p K 0.771 p p = = 1/2 (x)(x) 0.771 (0.5 x)(0.5 x) x (0.771) 0.878 0.5 x x 0.878(0.5 x) x 0.439 0.878 x 1.878 x 0.439 x 0.234 = − − = = − = − = − = = Thus, 2 2 2 H CO CO H O p p 0.5 x 0.5 0.234 0.266atm p p x 0.234atm = = −= − = = == Part C. Answer any three of the six questions. If you answer more than three, the best three will be used to calculate your mark (20 marks each). 1. Fuel cells for cars will likely use hydrogen as the fuel and oxygen as the oxidant. Using the following data: 2 H+ (aq) + 2 e− → H2(g) Eo = 0.000 V O2(g) + 4 H+ (aq) + 4 e− → 2 H2O(l) Eo = 1.229 V (a) Write the balanced overall electrochemical reaction and calculate the standard cell potential. O2(g) + 4 H+ (aq) + 4 e- → 2 H2O(l) Eo = 1.229 V 2 H2(g) → 4 H+ (aq) + 4 e- Eo = 0.000 V _______________________________________________ O2(g) + 2 H2(g) → 2 H2O(l) Eo = 1.229 V (b) Calculate the cell potential at 50o C when H2(g) p 3. = 00 atm and O2(g) p 1. = 30 atm 0 RT E E ln(Q) nF = −

1 1 Q=- .Pi1.30W3.00=0.0855 E°=1.229V R=8.314 JK*mol' T=50℃=323K N=4 mol e" F=96487 C(mol e) Thus, E-RIm(Q)-129JC 8.314JK-'mol(323K) nF 4mole(96487C(mole(00855) =1.229JC--(-0.0173JC-) =1.246JC =1.246V 2.Using the following data,calculate the value of AHrof H2O →H0gl △H°=-241.8kJmo AH= -92 5.9 kJ mol 2Hg)+20g→H02g △H°=-1070.6 kJ mol 20g→02g △H=-498.3 kJ mol H00→H02xg △H=51.5 kJ mol We want AH°for the reaction H2e+O2gl→H,O2 H202g)→H2020 △H°=-51.5 kJ mol 2Hg,+20g→H02g △H=-1070.6kJmo h02g→0gl △H=(498.3)kJmo H,0g→2Hg+0g AH=-(-926 9)kI mol H2g+hO2e→H2Og △H°=-241.8 kJmol" H2e+O2e→H202D AH=-187.85 kJ mol 3 Calculate the pH and the concentrations of all species present(except water)in a 1.0 M solution of phosphorous acid,H;PO)For this acid,Ka=1.0 x 102and Ka2=2.6x 10.(The third proton is not acidic.) H3POxag+H2O-H3O'+H2PO3(Q) 3
3 2 2 2 2 O H 1 1 Q 0.0855 p p (1.30)(3.00) == = E0 = 1.229 V R = 8.314 J K-1mol-1 T = 50o C = 323 K N = 4 mol e- F = 96487 C (mol e- ) -1 Thus, 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 RT 8.314JK mol (323K) E E ln(Q) 1.229 J C ln(0.0855) nF 4 mole (96487 C(mole ) ) 1.229J C ( 0.0173J C ) 1.246J C 1.246V − − − − − − − − − =− = − = −− = = 2. Using the following data, calculate the value of ΔHo f of H2O2(l): H2(g) + ½ O2(g) → H2O(g) ΔHo = −241.8 kJ mol-1 2 H(g) + O(g) → H2O(g) ΔHo = −926.9 kJ mol-1 2 H(g) + 2O(g) → H2O2(g) ΔHo = −1070.6 kJ mol-1 2 O(g) → O2(g) ΔHo = −498.3 kJ mol-1 H2O2(l) → H2O2(g) ΔHo = 51.5 kJ mol-1 We want ΔHo for the reaction H2(g) + O2(g) → H2O2(l) H2O2(g) → H2O2(l) ΔHo = -51.5 kJ mol-1 2 H(g) + 2 O(g) → H2O2(g) ΔHo = -1070.6 kJ mol-1 ½ O2(g) → O(g) ΔHo = ½(498.3) kJ mol-1 H2O(g) → 2 H(g) + O(g) ΔHo = -(-926.9) kJ mol-1 H2(g) + ½ O2(g) → H2O(g) ΔHo = -241.8 kJ mol-1 __________________________________________________ H2(g) + O2(g) → H2O2(l) ΔHo = -187.85 kJ mol-1 3. Calculate the pH and the concentrations of all species present (except water) in a 1.0 M solution of phosphorous acid, H3PO3(aq). For this acid, Ka1 = 1.0 x 10-2 and Ka2 = 2.6 x 10-7. (The third proton is not acidic.) H3PO3(aq) + H2O(l) ⎯ H3O+ (aq) + H2PO3 - (aq)

[H,O'HPO=K. [H,POx] H3PO3ao)H3O(g)H2PO3() Initial 1.0 0 0 +x Equilibrium 1.0-x At equilibrium, (☒=K=0.01 10-x x2=0.01-0.01x x2+0.01x-0.01=0 x=-b±v6-4ac -0.01±√0.012-41-0.01) 2a 21① -0.01±0.20 =0.095or-0.105 thus,x=0.095 thus [HP03aal=1.0-x=0.905M H,0e=x=0.095M K 1.0x10-14 [oH小FH0a0095 =1.05x10-3M [HPO3e=x=0.095M pH=-log1olH30a=-log1o(0.095)=1.02 H2PO3ag+H2O0-H3O'(ag)+HPO3) [H,O'HPOK [H,PO3a】 but [H3O'(o]=[H2PO3(ag]=x thus,[HPO3(g]=Ka2=2.6 x 107M Titanium (Ti)metal crystallizes in a body-centred cubic(BCC)structur m.yo with an edge length of 331 pm Calculat e may em,or th e fact that the of the volume
4 3 (aq) 2 3 (aq) a1 3 3(aq) [H O ][H PO ] K [H PO ] + − = H3PO3(aq) H3O+ (aq) H2PO3 - (aq) Initial 1.0 0 0 Change -x +x +x Equilibrium 1.0 - x x x At equilibrium, a1 2 2 2 2 (x)(x) K 0.01 1.0 x x 0.01 0.01x x 0.01x 0.01 0 b b 4ac 0.01 0.01 4(1)( 0.01) x 2a 2(1) 0.01 0.20 2 0.095 or 0.105 thus, x 0.095 = = − = − + −= −± − −± − − = = − ± = = − = thus, [H3PO3(aq)] = 1.0 – x = 0.905 M [H3O+ (aq)] = x = 0.095 M 14 w 13 (aq) 3 (aq) K 1.0 10 [OH ] 1.05 10 M [H O ] 0.095 − − − + × = = =× [H2PO3 - (aq)] = x = 0.095 M pH = -log10[H3O+ (aq)] = -log10(0.095) = 1.02 H2PO3 - (aq) + H2O(l) ⎯ H3O+ (aq) + HPO3 -2 (aq) 2 3 (aq) 3 (aq) a 2 2 3 (aq) [H O ][HPO ] K [H PO ] + − − = but [H3O+ (aq)] = [H2PO3 - (aq)] = x thus, [HPO3 - (aq)] = Ka2 = 2.6 x 10-7 M 4. Titanium (Ti) metal crystallizes in a body-centred cubic (BCC) structure with an edge length of 331 pm. Calculate the radius of a titanium atom. You may use geometry to solve this problem, or the fact that the atoms in a BCC structure occupy 68% of the volume of the unit cell
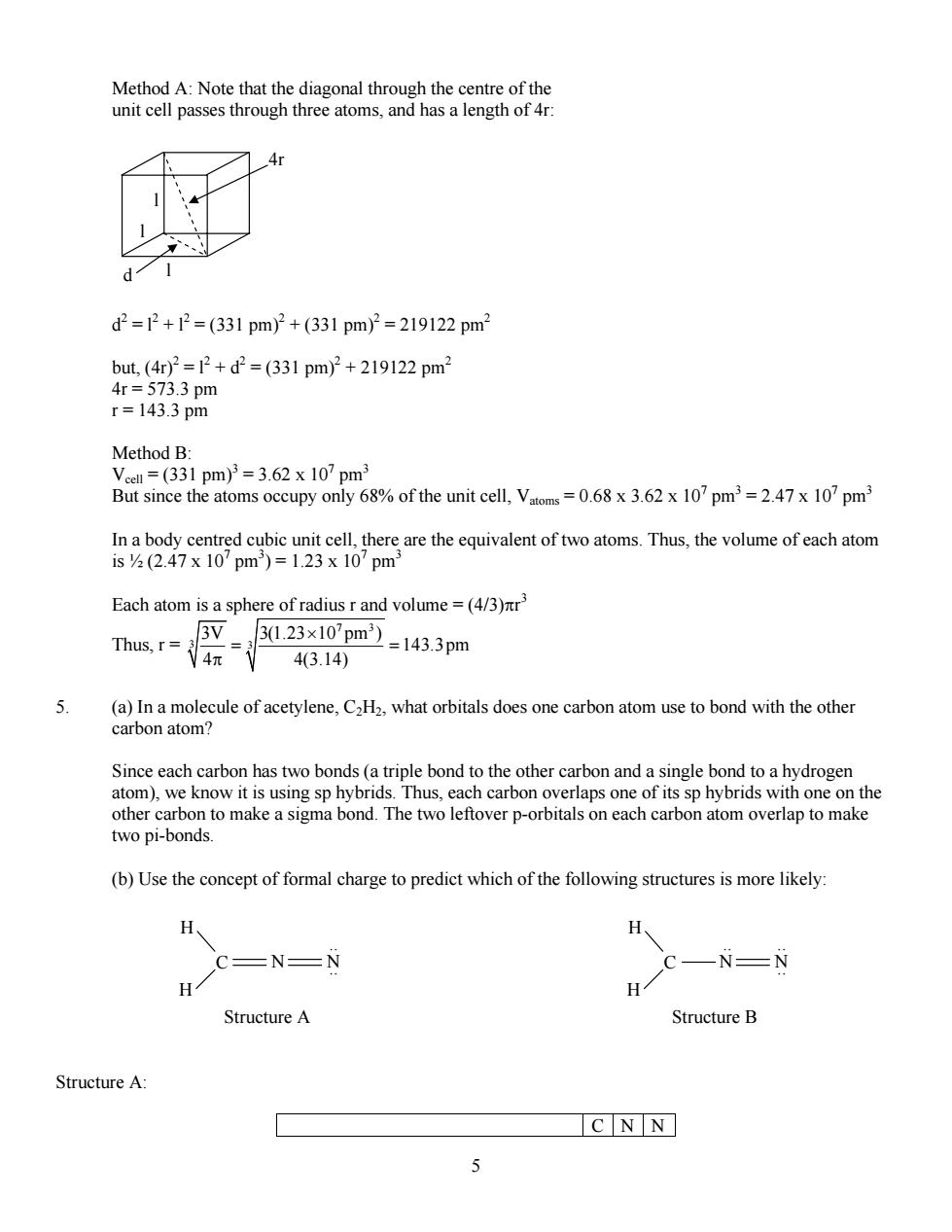
Method A:Note that the diagonal through the centre of th unit cell passes through three atoms,and has a length of 4 d2=2+2=(331pm)2+(331pm2=219122pm2 but(4r)2=2+d=(331pm)2+219122pm3 4r=573.3pm r=143.3pm Method B: 33 pm)=3.62 x107pm unit cell V10'pm71m In a body centred cubic unit cell,there are the equivalent of two atoms.Thus,the volume of each atom 1sy2(2.47X10Dm)=1.23X10'Dm Each atom is a sphere of radius r and volume=(4/3)nr' Thus,r= 3V 玩 3023×10pm-143.3pm 43.14) (a)In a molecule of acetylene,C2H2,what orbitals does one carbon atom use to bond with the other carbon atom? Since each carbon has two bonds(a triple bond to the other carbon and a single bond to a hydrogen atom),we know it is using sp hybrids.Thus,each carbon overlaps one of its sp hybrids with one on the other carbon to make a sigma bond.The two leftover p-orbitals on each carbon atom overlap to make two pi-bonds. (b)Use the concept of formal charge to predict which of the following structures is more likely: C=N=N -N-N H H StructureA Structure B Structure A C NN 5
5 Method A: Note that the diagonal through the centre of the unit cell passes through three atoms, and has a length of 4r: l l l d 4r d2 = l2 + l2 = (331 pm)2 + (331 pm)2 = 219122 pm2 but, (4r)2 = l2 + d2 = (331 pm)2 + 219122 pm2 4r = 573.3 pm r = 143.3 pm Method B: Vcell = (331 pm)3 = 3.62 x 107 pm3 But since the atoms occupy only 68% of the unit cell, Vatoms = 0.68 x 3.62 x 107 pm3 = 2.47 x 107 pm3 In a body centred cubic unit cell, there are the equivalent of two atoms. Thus, the volume of each atom is ½ (2.47 x 107 pm3 ) = 1.23 x 107 pm3 Each atom is a sphere of radius r and volume = (4/3)πr 3 Thus, r = 7 3 3 3 3V 3(1.23 10 pm ) 143.3pm 4 4(3.14) × = = π 5. (a) In a molecule of acetylene, C2H2, what orbitals does one carbon atom use to bond with the other carbon atom? Since each carbon has two bonds (a triple bond to the other carbon and a single bond to a hydrogen atom), we know it is using sp hybrids. Thus, each carbon overlaps one of its sp hybrids with one on the other carbon to make a sigma bond. The two leftover p-orbitals on each carbon atom overlap to make two pi-bonds. (b) Use the concept of formal charge to predict which of the following structures is more likely: C H H N N .. .. C H H N N.. .. .. Structure A Structure B Structure A: C N N

Valence Electrons Electrons assigned to atom in structure Formal Charge 01-1 Structure B: CNN Valence Electrons 455 Electrons assigned to atom in structure 3 56 Formal Charge 101 have the same formal charges,so we can not predict which structure is more 6
6 Valence Electrons 4 5 5 Electrons assigned to atom in structure 4 4 6 Formal Charge 0 1 -1 Structure B: C N N Valence Electrons 4 5 5 Electrons assigned to atom in structure 3 5 6 Formal Charge 1 0 -1 Both Structure A and Structure B have the same formal charges, so we can not predict which structure is more likely using formal charges