
Agency Problem and Legal Strategies Reporter:Jin Jie,Yang Wenjie and Zhang Na
Agency Problem and Legal Strategies Reporter: Jin Jie, Yang Wenjie and Zhang Na
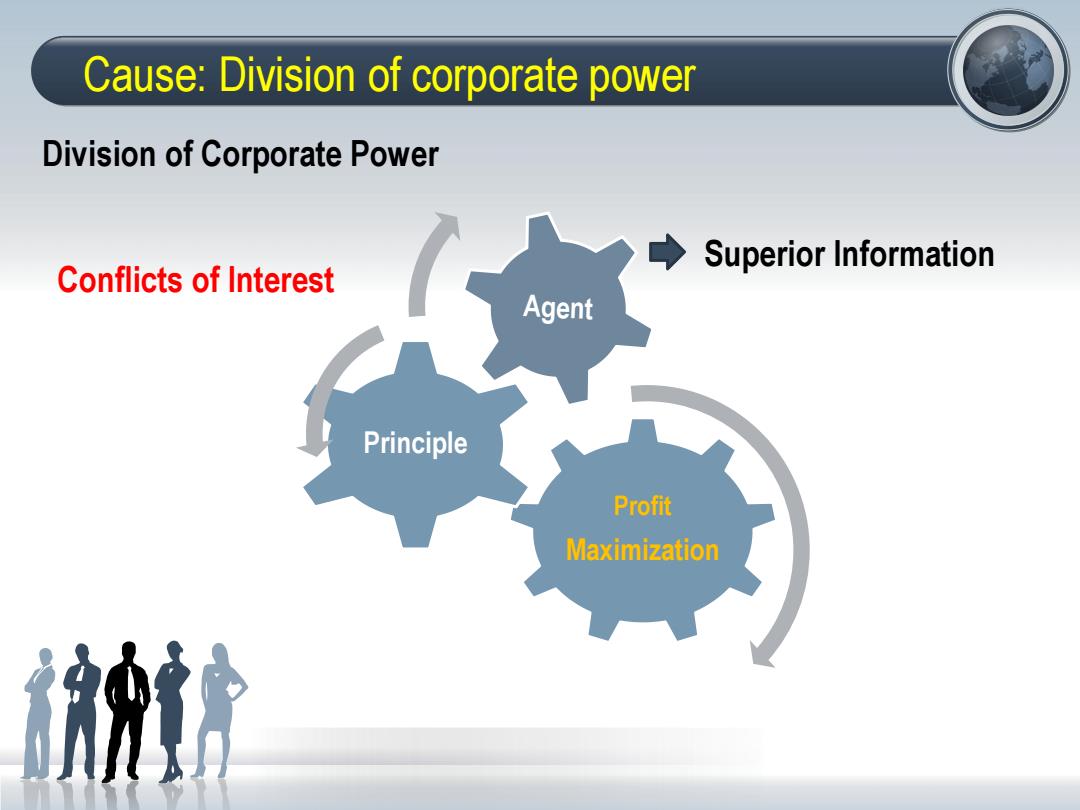
Cause:Division of corporate power Division of Corporate Power Superior Information Conflicts of Interest Principle Profit Maximization
Cause: Division of corporate power Profit Maximization Principle Agent Division of Corporate Power Superior Information Conflicts of Interest

Composition Residual Loss Agency cost Monitoring Cost of the Principal Bonding Cost of the Agent Theory of the Firm:Managerial Behavior,Agency Costs and Ownership Structure,Michael C.Jensen and William H.Meckling,Journal of Financial ms ceNo-
Composition Agency cost Theory of the Firm: Managerial Behavior, Agency Costs and Ownership Structure, Michael C. Jensen and William H. Meckling, Journal of Financial Economics, October, 1976, V.3, No.4, pp.305-360. Residual Loss Monitoring Cost of the Principal Bonding Cost of the Agent
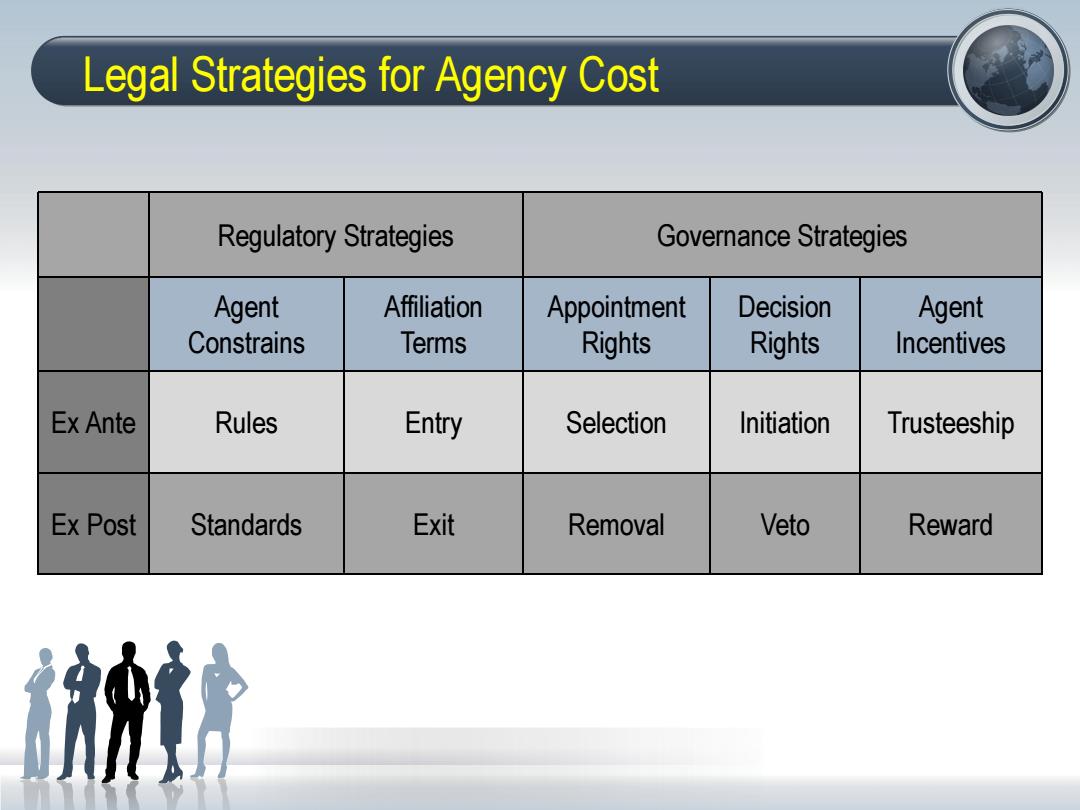
Legal Strategies for Agency Cost Regulatory Strategies Governance Strategies Agent Affiliation Appointment Decision Agent Constrains Terms Rights Rights Incentives Ex Ante Rules Entry Selection Initiation Trusteeship Ex Post Standards Exit Removal Veto Reward
Regulatory Strategies Governance Strategies Agent Constrains Affiliation Terms Appointment Rights Decision Rights Agent Incentives Ex Ante Rules Entry Selection Initiation Trusteeship Ex Post Standards Exit Removal Veto Reward Legal Strategies for Agency Cost

Regulatory vs.Governance Strategies Regulatory:directly constrain the actions of corporate actors. E.g.a standard of behavior such as a director's duty of loyalty and care. Governance:channel the distribution of power and payoffs within companies to reduce opportunism. E.g.the law may accord direct decision rights to a vulnerable corporate constituency,as when it requires shareholder approval of mergers
Regulatory vs. Governance Strategies Regulatory: directly constrain the actions of corporate actors. E.g. a standard of behavior such as a director’s duty of loyalty and care. Governance: channel the distribution of power and payoffs within companies to reduce opportunism. E.g. the law may accord direct decision rights to a vulnerable corporate constituency, as when it requires shareholder approval of mergers

Regulatory vs.Governance Strategies Regulatory:dictate substantive terms that govern the content of the principal-agent relationship,tending to constrain the agent's behavior directly. Governance:facilitate the principals'control over their agent's behavior. Regulatory:depends crucially on the ability of the principals to exercise the control rights accorded to them(coordination costs). Governance:depend on the ability of an external authority to determine whether or not the agent complied with particular prescription(a court or eregulatory body)
Regulatory vs. Governance Strategies Regulatory: dictate substantive terms that govern the content of the principal-agent relationship, tending to constrain the agent’s behavior directly. Governance: facilitate the principals’ control over their agent’s behavior. Regulatory: depends crucially on the ability of the principals to exercise the control rights accorded to them (coordination costs). Governance: depend on the ability of an external authority to determine whether or not the agent complied with particular prescription (a court or regulatory body)

Regulatory vs.Governance Strategies Regulatory:require effective disclosure mechanisms to ensure that information about the actions of agents can be 'verified'by the regulator. Governance:"softer"information may suffice
Regulatory vs. Governance Strategies Regulatory: require effective disclosure mechanisms to ensure that information about the actions of agents can be ‘verified’ by the regulator. Governance: “softer” information may suffice
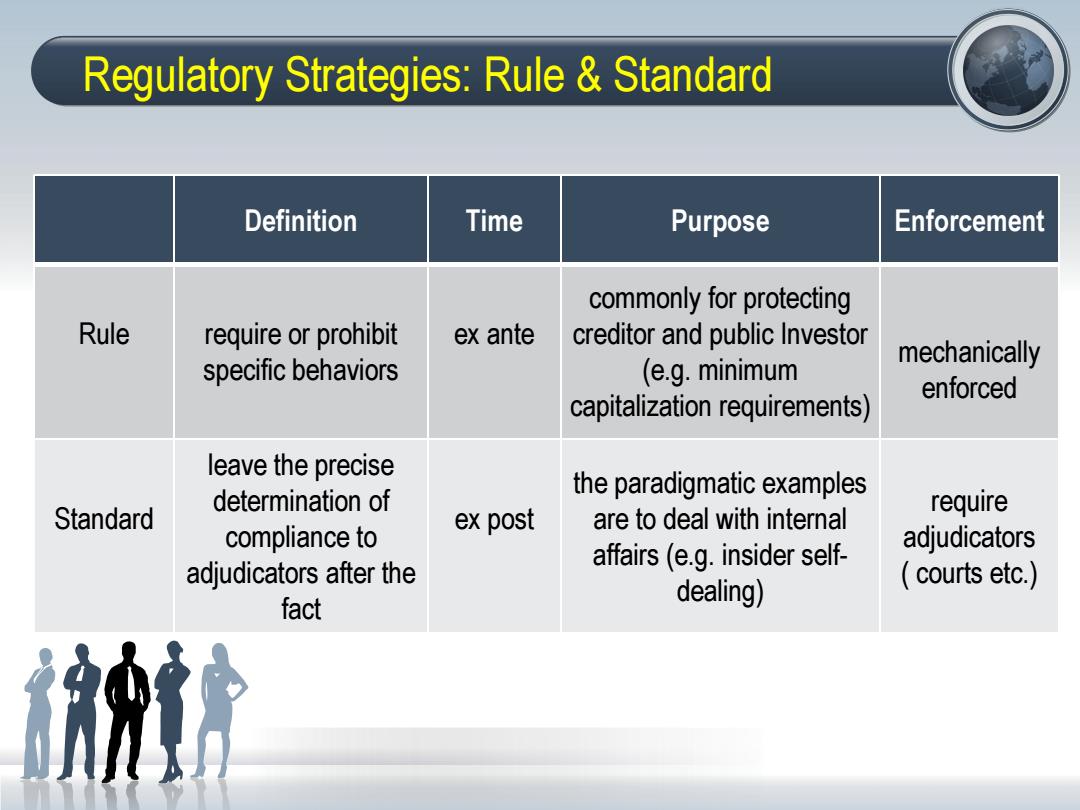
Regulatory Strategies:Rule Standard Definition Time Purpose Enforcement commonly for protecting Rule require or prohibit ex ante creditor and public Investor specific behaviors mechanically (e.g.minimum enforced capitalization requirements) leave the precise determination of the paradigmatic examples Standard require ex post are to deal with internal compliance to adjudicators adjudicators after the affairs(e.g.insider self- dealing) courts etc.) fact
Regulatory Strategies: Rule & Standard Definition Time Purpose Enforcement Rule require or prohibit specific behaviors ex ante commonly for protecting creditor and public Investor (e.g. minimum capitalization requirements) mechanically enforced Standard leave the precise determination of compliance to adjudicators after the fact ex post the paradigmatic examples are to deal with internal affairs (e.g. insider self- dealing) require adjudicators ( courts etc.)
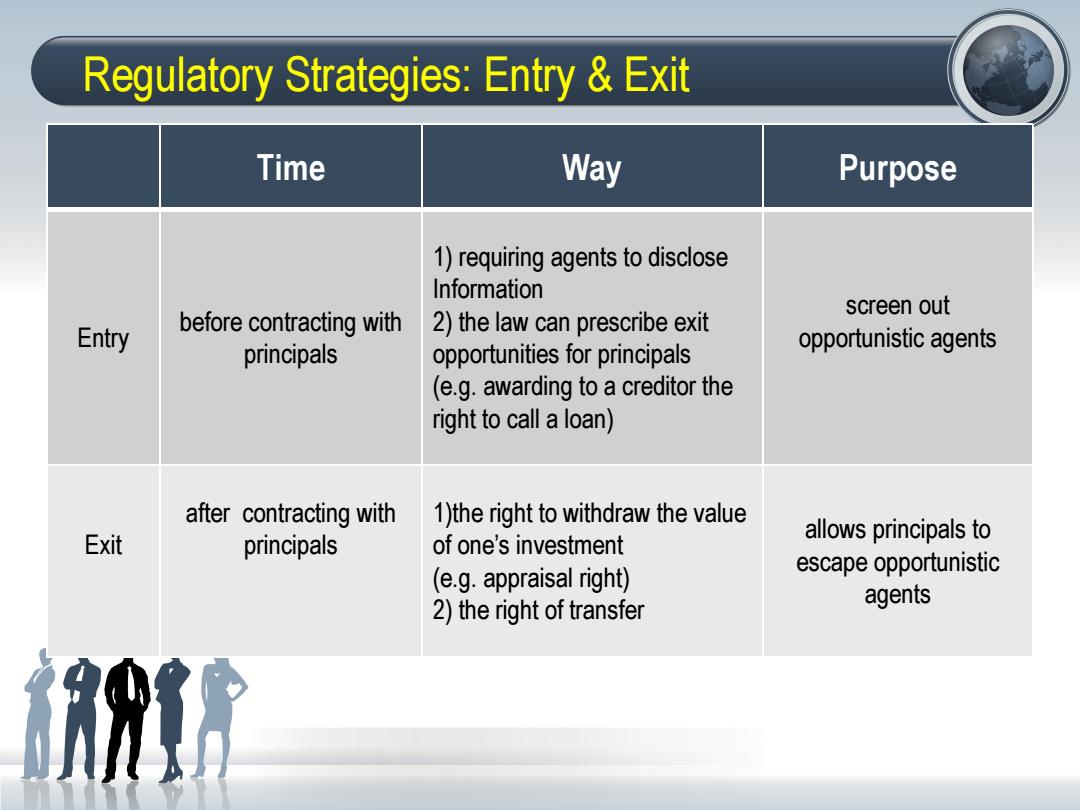
Regulatory Strategies:Entry Exit Time Way Purpose 1)requiring agents to disclose Information screen out Entry before contracting with 2)the law can prescribe exit principals opportunities for principals opportunistic agents (e.g.awarding to a creditor the right to call a loan) after contracting with 1)the right to withdraw the value Exit principals allows principals to of one's investment (e.g.appraisal right) escape opportunistic 2)the right of transfer agents
Regulatory Strategies: Entry & Exit Time Way Purpose Entry before contracting with principals 1) requiring agents to disclose Information 2) the law can prescribe exit opportunities for principals (e.g. awarding to a creditor the right to call a loan) screen out opportunistic agents Exit after contracting with principals 1)the right to withdraw the value of one’s investment (e.g. appraisal right) 2) the right of transfer allows principals to escape opportunistic agents
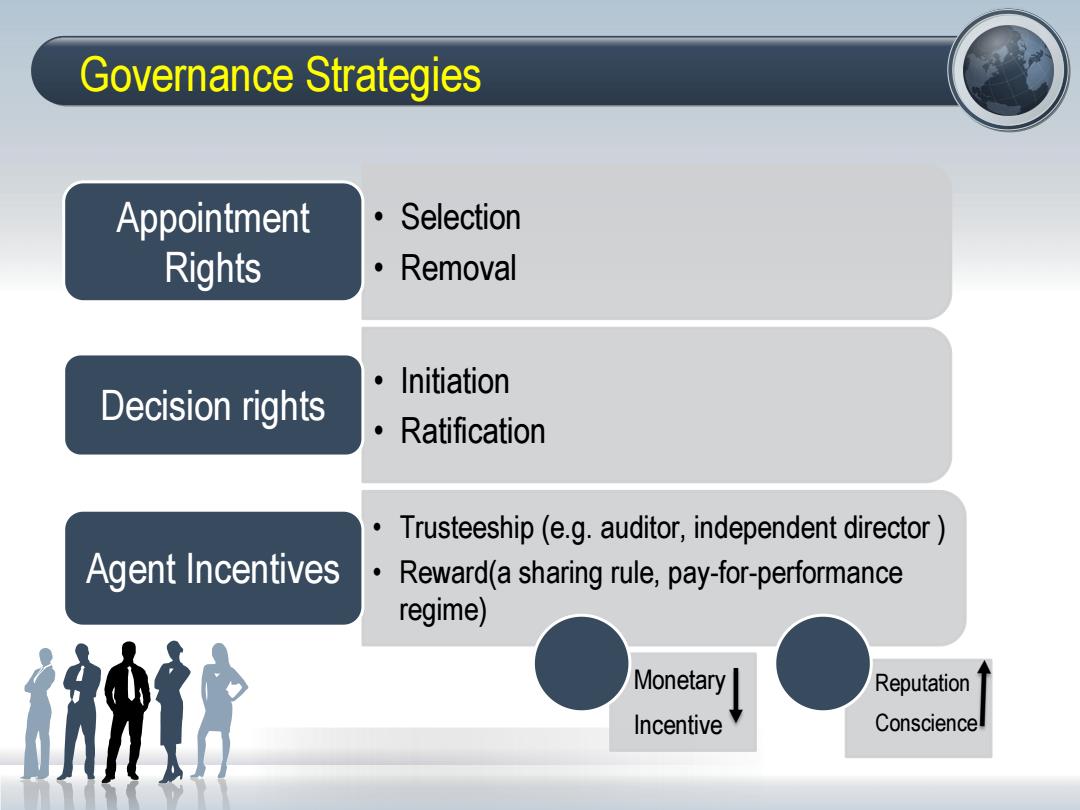
Governance Strategies Appointment ·Selection Rights ·Removal Initiation Decision rights Ratification Trusteeship(e.g.auditor,independent director Agent Incentives.Reward(a sharing rule,pay-for-performance regime) Monetary Reputation Incentive Consciencel
Governance Strategies • Selection • Removal Appointment Rights • Initiation • Ratification Decision rights • Trusteeship (e.g. auditor, independent director ) • Reward(a sharing rule, pay-for-performance regime) Agent Incentives Monetary Incentive Reputation Conscience