
ENFORCEMENT Part Two LIU Zhenzhen May30,2014
ENFORCEMENT Part Two LIU Zhenzhen May 30, 2014

Content Section 1 General Introduction Section 2 Outside Director Liablity -Section 3 Shareholder Derivative Suits -Section 4 Conclusion Reference: Outside Director Liability Across Countries (P140) Why Do Shareholder Derivative Suits Remain Rare in Continental Europe?(P150) Page·2
Page 2 Content Section 1 General Introduction Section 2 Outside Director Liablity Section 3 Shareholder Derivative Suits Section 4 Conclusion Reference: Outside Director Liability Across Countries (P140) Why Do Shareholder Derivative Suits Remain Rare in Continental Europe? (P150)

Section 1 General Introduction Corporate Law:Encourage investment and protect shareholder Agency:Shareholder v.s.Director -Enforcemet of Corporate Law:How to motivate the Director to act in the Shareholder's interest? Director:Legal Liabilty Shareholder:Shareholder Suits Agency Shareholder Director Principal Agent Page·3
Page 3 Section 1 General Introduction Corporate Law: Encourage investment and protect shareholder Agency: Shareholder v.s. Director Enforcemet of Corporate Law: How to motivate the Director to act in the Shareholder's interest? Director: Legal Liabilty Shareholder: Shareholder Suits Shareholder Principal Director Agent Agency

Section 2 Outside Director Liablity Director oInside Director D Directors who are also executives. Outside Director v.s.Independent Director Outside Director:Directors who are not excutives.(Non-Executive Director) Independent Director:Almost the same as Outsider Director,but not allowed to own shares of the company. Outside Director Liability oContent:Fiduciary Duty Consequence for Breach of Fiduciary Duty A lawsuit could oblige outside directors to pay damages or legal fees out of their own pocket. Aim:To make outside directors work hard and pay attention Page·4
Page 4 Section 2 Outside Director Liablity Director Inside Director Directors who are also executives. Outside Director v.s. Independent Director Outside Director: Directors who are not excutives.(Non-Executive Director) Independent Director: Almost the same as Outsider Director, but not allowed to own shares of the company. Outside Director Liability Content: Fiduciary Duty Consequence for Breach of Fiduciary Duty A lawsuit could oblige outside directors to pay damages or legal fees out of their own pocket. Aim: To make outside directors work hard and pay attention

Empirical Study on Outside Director Liability Scope of Research Country Feature U.K. The role of outside director is highly debated. 1.To explore how director liablities in a civil law country Germany 2.To assess the impact of formalizing the role of outside directors through a two-tier board structure Australia Common law jurisdiction Canada France Cicil law jurisdiction Japan South Korea Emerging market country Page5
Page 5 Empirical Study on Outside Director Liability Scope of Research Country Feature U.K. The role of outside director is highly debated. Germany 1. To explore how director liablities in a civil law country 2. To assess the impact of formalizing the role of outside directors through a two-tier board structure Australia Canada Common law jurisdiction France Japan Cicil law jurisdiction South Korea Emerging market country

Empirical Study on Outside Director Liability Findings In practice,the legal liability outside director faces rarely lead to personal payments. Suits could pose the risk of an out-of-pocket payment. o Shareholder Suits:Private Enforcement Public-minded Litigation:Public Enforcement D However,in most cases,D&O Insuranace is sufficient to cover legal expenses and damages. Practical Outcome Analysis o"Functional Convergence"on low (but non-zero)risk o Can the low liability risk motivate outside directors to be vigilant? D The reputational concern Public-minded litigation o When a governmental agency brings a civil lawsuit. A tiny risk of criminal prosecution for outside directors D Procedural Consideration:The "American Rule" Page·6
Page 6 Empirical Study on Outside Director Liability Findings In practice, the legal liability outside director faces rarely lead to personal payments. Suits could pose the risk of an out-of-pocket payment. Shareholder Suits: Private Enforcement Public-minded Litigation: Public Enforcement However, in most cases, D&O Insuranace is sufficient to cover legal expenses and damages. Practical Outcome & Analysis "Functional Convergence"on low (but non-zero) risk Can the low liability risk motivate outside directors to be vigilant? The reputational concern Public-minded litigation When a governmental agency brings a civil lawsuit. A tiny risk of criminal prosecution for outside directors Procedural Consideration: The "American Rule
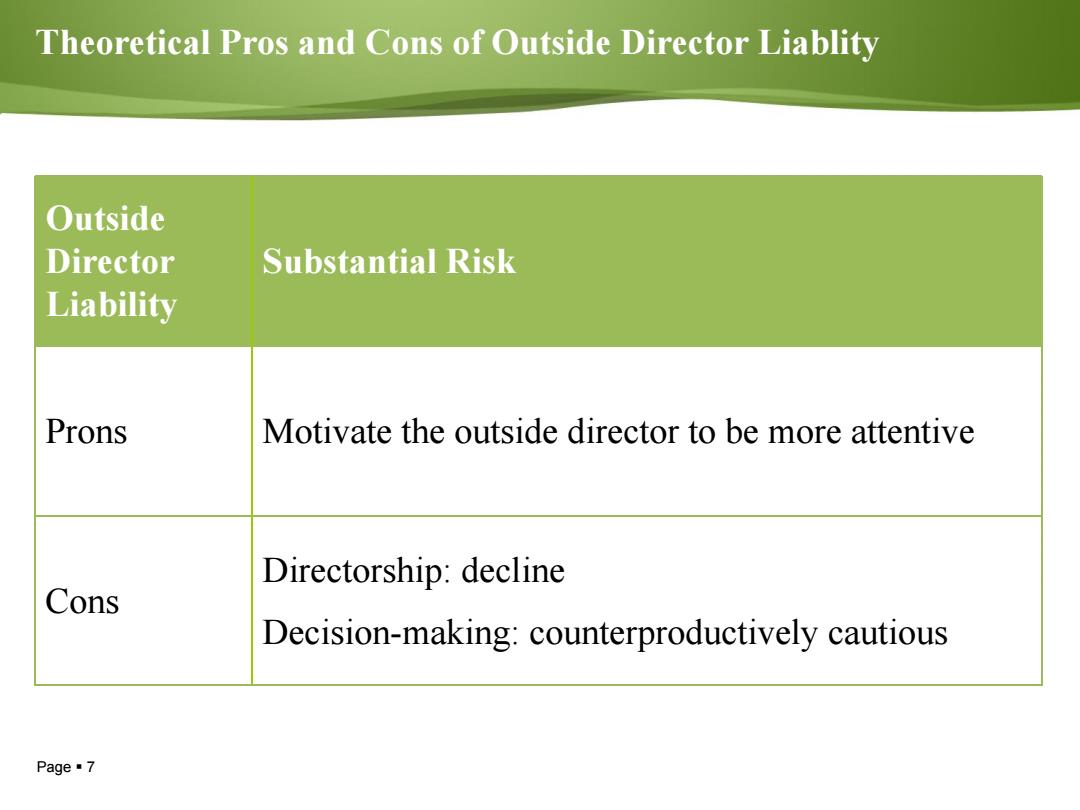
Theoretical Pros and Cons of Outside Director Liablity Outside Director Substantial Risk Liability Prons Motivate the outside director to be more attentive Directorship:decline Cons Decision-making:counterproductively cautious Page7
Page 7 Theoretical Pros and Cons of Outside Director Liablity Outside Director Liability Substantial Risk Prons Motivate the outside director to be more attentive Cons Directorship: decline Decision-making: counterproductively cautious

Section 3 Shareholder Suits:Private Enforcement -Shareholder Class Action A lawsuit brought for personal claims of all shareholders. Shareholder Derivative Suit A lawsuit brought by a shareholder on behalf of a corporation against a third party. Often,the third party is an insider of the corporation,such as an executive officer or director. Page8
Page 8 Section 3 Shareholder Suits: Private Enforcement Shareholder Class Action A lawsuit brought for personal claims of all shareholders. Shareholder Derivative Suit A lawsuit brought by a shareholder on behalf of a corporation against a third party. Often, the third party is an insider of the corporation, such as an executive officer or director

The Scarcity of Shareholder Derivative Suits in Continental Europe The small number of derivative suits in Continental Europe is often seen as a reason why corporate law is considered under-enforced in these jurisdictions. Scarcity of Derivative Suits Under-enforcement of Corporate Law But the author suggests that cThere is a significant degree ofenforcement through channels of corporate law,beyond enforcement derived from derivative suits. 3If a legal system discourages derivative suits,disgruntled shareholders will take the "Path of Least Resistance"and resort to other enforcement mechanisms. Page·9
Page 9 The Scarcity of Shareholder Derivative Suits in Continental Europe The small number of derivative suits in Continental Europe is often seen as a reason why corporate law is considered under-enforced in these jurisdictions. But the author suggests that There is a significant degree of enforcement through channels of corporate law, beyond enforcement derived from derivative suits. If a legal system discourages derivative suits, disgruntled shareholders will take the "Path of Least Resistance" and resort to other enforcement mechanisms. Scarcity of Derivative Suits Under-enforcement of Corporate Law ?

Explanations for the Absence of Derivative Suits Anna Karenina Principle Four Necessary Criteria 1.Minimum Share Ownership Requirements 2.Costs and the Allocation of Litigation Risk 3.Access to Information 4.Limitations regarding Potential Defendants Page·10
Page 10 Explanations for the Absence of Derivative Suits Four Necessary Criteria 1. Minimum Share Ownership Requirements 2. Costs and the Allocation of Litigation Risk 3. Access to Information 4. Limitations regarding Potential Defendants Anna Karenina Principle