
计算机问题求解一论题4-3 一群同态基本定理 2021年3月15日
计算机问题求解 – 论题4-3 - 群同态基本定理 2021年3月15日

问题1:我们为什么定义“同构”函数? iso-morphology Two groups (G,)and (H,o)are isomorphic if there exists a one-to-one and onto map GH such that the group operation is preserved;that is, (a·b)=(a)o(b) 同构其实可在 for all a and b in G.If G is isomorphic to H is called an isomorphism. 任何代数结构 (系统)上讨论
问题1:我们为什么定义“同构”函数 ? iso-morphology 同构其实可在 任何代数结构 (系统)上讨论

问题2:从这个定理中,你能解释我们为 什么研究“同构”吗? Theorem 9.6.Let o:G->H be an isomorphism of two groups.Then the following statements are true. 1.HG is an isomorphism. 2.G=H 3.If G is abelian,then H is abelian. 4.If G is cyclic,then H is cyclic. 5.If G has a subgroup of order n,then H has a subgroup of order n
问题2:从这个定理中,你能解释我们为 什么研究“同构”吗?

如何判断两个系统的同构? Theorem 9.7.All cyclic groups of infinite order are isomorphic to Z. PROOF.Let G be a cyclic group with infinite order and suppose that a is a generator of G.Define a map Z-G by o:n a".Then o(m+n)amtn a"a"o(m)o(n). 观察 To show that o is injective,suppose that m and n are two elements in Z, where m 4n.We can assume that m >n.We must show that am 4 a". 构造 Let us suppose the contrary;that is,am=a".In this case am-n=e,where m-n >0,which contradicts the fact that a has infinite order.Our map 证明(定义) is onto since any element in G can be written as an for some integer n and o(n)a". ▣
观察 构造 证明(定义) 如何判断两个系统的同构?

如何判断两个系统不同构? Example 9.5.Even though S3 and Z6 possess the same number of elements,we would suspect that they are not isomorphic,because Z6 is abelian and S3 is nonabelian.To demonstrate that this is indeed the case,suppose that Z6-S3 is an isomorphism.Let a,b e S3 be two elements such that ab ba.Since o is an isomorphism,there exist elements m and n in Z6 such that o(m)=a and o(n)=b. However, ab =o(m)o(n)=o(m+n)=o(n+m)=o(n)o(m)=ba, which contradicts the fact that a and b do not commute
如何判断两个系统不同构?

问题3.1:这个定理给我们什么感觉? The isomorphism of groups determines an equivalence rela- tion on the class of all groups. 如何去证明这个定理?
问题3.1:这个定理给我们什么感觉? 如何去证明这个定理?

几个有趣的同构结论 Theorem 9.7.All cyclic groups of infinite order are isomorphic to Z. Theorem 9.8.If G is a cyclic group of order n,then G is isomorphic to Zn. Corollary 9.9.If G is a group of order p,where p is a prime number,then G is isomorphic to Zp. Theorem 9.12 Cayley.Every group is isomorphic to a group of permutations
几个有趣的同构结论

Cayley,定理的证明 Theorem 9.12 Cayley.Every group is isomorphic to a group of permutations. ·从任意一个群G出发,构造一个置换群G’: ·由置换函数组成的群 G={g:9∈G ·由G出发,构造置换函数,置换函数的个数和群G相同 入g(a)=ga. ·构造群G到置换群G’的同构函数 ·证明这个函数的双射 0:g→入g ·证明这个函数是G到G’的同构
Cayley定理的证明 • 从任意一个群G出发,构造一个置换群G’: • 由置换函数组成的群 • 由G出发,构造置换函数,置换函数的个数和群G相同 • 构造群G到置换群G’的同构函数 • 证明这个函数的双射 • 证明这个函数是G到G’的同构
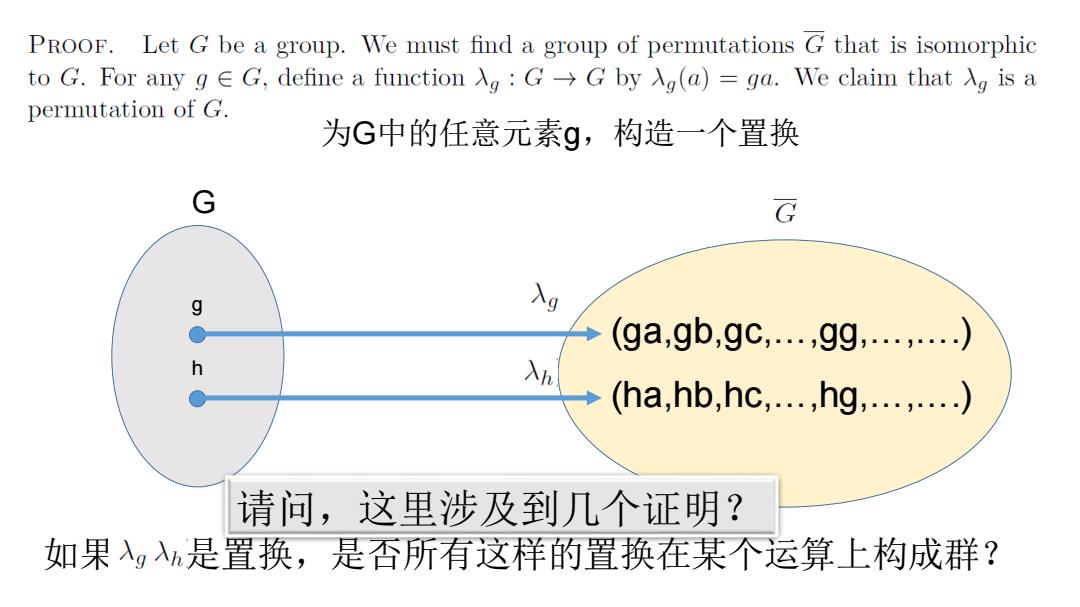
PROOF.Let G be a group.We must find a group of permutations G that is isomorphic toG.For any g∈G,define a functionλg:G→Gbyλg(a)=ga.W'e claim thatλgisa permutation of G. 为G中的任意元素g,构造一个置换 G G 入g (ga,gb,gc,…,gg,.….…) (ha,hb,hc,.,hg,.….) 请问,这里涉及到几个证明? 如果λg是置换,是否所有这样的置换在某个运算上构成群?
为G中的任意元素g,构造一个置换 G g (ga,gb,gc,…,gg,…,….) h (ha,hb,hc,…,hg,…,….) 如果 是置换,是否所有这样的置换在某个运算上构成群? 请问,这里涉及到几个证明?

2g是permutation? For any g∈G,define a function入g:G→Gby入g(a)=ga.We claim thatλgisa permutation of G.To show that Ag is one-to-one,suppose that Ag(a)=Ag(b).Then ga=入g(a)=λg(b)=gb. Hence,a =b.To show that A is onto,we must prove that for each a G,there is a b such that Ag(b)=a.Let b=g-a
𝜆𝑔 是permutation?