
Forages:An Introduction to Grassland Agriculture Chapter 1:Plant growth and development Instructor: Long Mingxiu F■RA AMA Copyright reseved by Long Miitg College of animal science,Northwest Agriculture Forestry University 西北农林科技大学动物科技学院草业科学系
__________________________________________________________________ College of animal science, Northwest Agriculture & Forestry University 西北农林科技大学动物科技学院草业科学系 Copyright reseved by Long Mingxiu Forages: An Introduction to Grassland Agriculture Chapter 1: Plant growth and development Instructor: Long Mingxiu

Overview of Chapter 1 On completion of this chapter you should learn: 1.The basic structure of plant 2.Growth and development 3.Physiology (factors that affect plant growth and development Light M20 Photophosphorylation ■RA C02 Calvin-Bensor Copyri cycle al science,Northwest Agriculture 8 Sugar 百北农林科技大学动物科技学院草业
__________________________________________________________________ College of animal science, Northwest Agriculture & Forestry University 西北农林科技大学动物科技学院草业科学系 Copyright reseved by Long Mingxiu On completion of this chapter you should learn: 1.The basic structure of plant 2.Growth and development 3.Physiology(factors that affect plant growth and development) Overview of Chapter 1

1.The basic structure of plant 1)Type of forage plants 2)Plant Structure and morphology F■RAG日 Copyright reseved by Long Mig College of animal science,Northwest Agriculture Forestry University 西北农林科技大学动物科技学院草业科学系
__________________________________________________________________ College of animal science, Northwest Agriculture & Forestry University 西北农林科技大学动物科技学院草业科学系 Copyright reseved by Long Mingxiu 1.The basic structure of plant • 1)Type of forage plants • 2)Plant Structure and morphology
1)Type of forage plants By cotyledon子叶:Dicots>双子叶onocots.单子叶 By family:Legumes,Grasses,sedge莎草科、 Cruciferae-十字花科、compositae菊科等 By branch:rhizome,bunchgrass,stolone 。 By leaves distribution on plant:top grass,bottom grass,rosette shape By living years:annual,biennial,perennial grass By water requirements:drought tolearance, mediate、wet endure ■RAG 吧right reseved by LongM College of animal science,Northwest Agriculture Forestry University 西北农林科技大学动物科技学院草业科学系
__________________________________________________________________ College of animal science, Northwest Agriculture & Forestry University 西北农林科技大学动物科技学院草业科学系 Copyright reseved by Long Mingxiu 1)Type of forage plants • By cotyledon子叶:Dicots双子叶 Monocots单子叶 • By family:Legumes ,Grasses ,sedge莎草科、 Cruciferae十字花科、compositae菊科等 • By branch:rhizome,bunchgrass,stolone • By leaves distribution on plant:top grass,bottom grass,rosette shape • By living years:annual,biennial,perennial grass • By water requirements:drought tolearance、 mediate、wet endure
1)Type of forage plants-continue By adaptable areas: Cool-season grass:A grass that grows best in spring and fall,blooms and sets seed in late spring or early summer,grows slowly or goes dormant in summer,greens up again in fall, and stays green into winter. Warm-season grass:A grass that does most of its growing in the hot summer,blooms and sets seed in the fall,and goes dormant when cold whether arrives. Copyright reseved by Long Miig College of animal science,Northwest Agriculture Forestry University 西北农林科技大学动物科技学院草业科学系
__________________________________________________________________ College of animal science, Northwest Agriculture & Forestry University 西北农林科技大学动物科技学院草业科学系 Copyright reseved by Long Mingxiu • By adaptable areas: Coolseason grass: A grass that grows best in spring and fall, blooms and sets seed in late spring or early summer, grows slowly or goes dormant in summer, greens up again in fall, and stays green into winter. • Warmseason grass: A grass that does most of its growing in the hot summer, blooms and sets seed in the fall, and goes dormant when cold whether arrives. 1)Type of forage plantscontinue

1)Type of forage plants-continue By morphology: Bunchgrass丛生:A grass that grows in a circular clump that gets larger each year.Because bunchgrasses do not spread and fill in thickly,they need to be seeded at a higher rate than sod-forming grasses for a thick stand of lawn. Sod-forming grass致密型:A grass that sends out stolons(stems that grow along the soil surface and root at the joints)or rhizomes (underground stems that root and send up new plants away from the original plant)and therefore tends to spread and fill in thickly. Copyright reseved by LongM影 College of animal science,Northwest Agriculture Forestry University 西北农林科技大学动物科技学院草业科学系
__________________________________________________________________ College of animal science, Northwest Agriculture & Forestry University 西北农林科技大学动物科技学院草业科学系 Copyright reseved by Long Mingxiu • By morphology: Bunchgrass丛生型: A grass that grows in a circular clump that gets larger each year. Because bunchgrasses do not spread and fill in thickly, they need to be seeded at a higher rate than sodforming grasses for a thick stand of lawn. • Sodforming grass致密型: A grass that sends out stolons (stems that grow along the soil surface and root at the joints) or rhizomes (underground stems that root and send up new plants away from the original plant) and therefore tends to spread and fill in thickly. 1)Type of forage plantscontinue
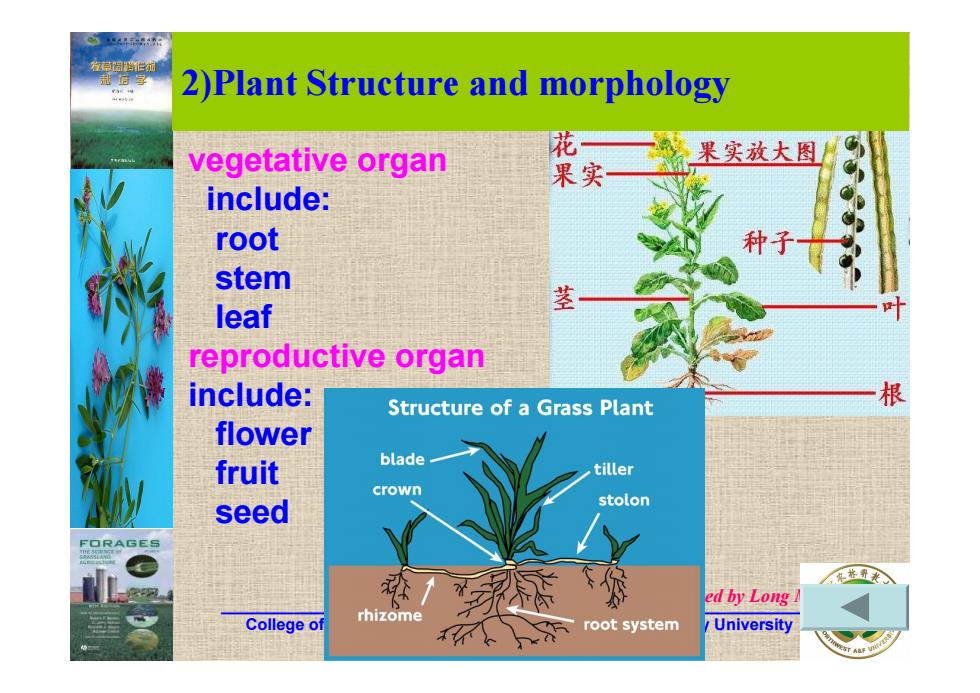
2)Plant Structure and morphology vegetative organ 花 果实放大图 果实 include: root 种子气 stem leaf reproductive organ include: Structure of a Grass Plant flower fruit blade tiller crown stolon seed ed by Long College o rhizome 不。 root system University
__________________________________________________________________ College of animal science, Northwest Agriculture & Forestry University 西北农林科技大学动物科技学院草业科学系 Copyright reseved by Long Mingxiu vegetative organ include: root stem leaf reproductive organ include: flower fruit seed 2)Plant Structure and morphology

2.Plant Growth and development ·1)What is growth2 2)How plants grow? A.seed structure B.Requirements for seed germination C.seed germination and seedling forming 3 Development A.concept B.Developmental stages C.overlaping and periodic rule of growth and development ■RA D.The special characters and phenomenon during plant growth Copyright reseved by Long Mi College of animal science,Northwest Agriculture&Forestry University 西北农林科技大学动物科技学院草业科学系
__________________________________________________________________ College of animal science, Northwest Agriculture & Forestry University 西北农林科技大学动物科技学院草业科学系 Copyright reseved by Long Mingxiu • 1)What is growth? • 2)How plants grow? A.seed structure B.Requirements for seed germination C.seed germination and seedling forming 3)Development A.concept B. Developmental stages C.overlaping and periodic rule of growth and development D. The special characters and phenomenon during plant growth 2.Plant Growth and development

2.Plant Growth and development 1)What is growth? 。 2)How plants grow? Starting Point-the seed Cell division Differentiation(分化)-tissues and organs Meristems(分裂组织)-shoot and root Repeating segments-the basis of plant form and function. Vegetative growth营养生长 ■RAE Reproductive growth生殖生长 Copyright reseved by Long Mid College of animal science,Northwest Agriculture Forestry University 西北农林科技大学动物科技学院草业科学系
__________________________________________________________________ College of animal science, Northwest Agriculture & Forestry University 西北农林科技大学动物科技学院草业科学系 Copyright reseved by Long Mingxiu • 1)What is growth? • 2)How plants grow? • Starting Point – the seed • Cell division • Differentiation(分化) – tissues and organs • Meristems(分裂组织) – shoot and root • Repeating segments – the basis of plant form and function. • Vegetative growth营养生长 • Reproductive growth生殖生长 2.Plant Growth and development

2.Plant Growth and development 种皮seed capsule保护层 胚根radicel A.seed structure) 胚一未来新植株的雏体胚轴hypocotyl (占种子重的2-3%) 胚芽embryo 子叶cotyledon 胚乳endosperm—store energy For grass,the endosperm in the caryopsis is relatively small,so there is little stored enery.Shallow planting is critical so seedlings can emerge and develop quickly before the reserves are used up. ■RA Copyright reseved by Long Mi College of animal science,Northwest Agriculture Forestry University 西北农林科技大学动物科技学院草业科学系
__________________________________________________________________ College of animal science, Northwest Agriculture & Forestry University 西北农林科技大学动物科技学院草业科学系 Copyright reseved by Long Mingxiu 种皮seed capsule——保护层 胚根radicel A.seed structure 胚——未来新植株的雏体 胚轴hypocotyl (占种子重的23%) 胚芽embryo 子叶cotyledon 胚乳endosperm——store energy For grass,the endosperm in the caryopsis颖 果 is relatively small,so there is little stored enery.Shallow planting is critical so seedlings can emerge and develop quickly before the reserves are used up. 2.Plant Growth and development